Integration of ZiYuan-3 Multispectral and Stereo Data for Modeling Aboveground Biomass of Larch Plantations in North China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
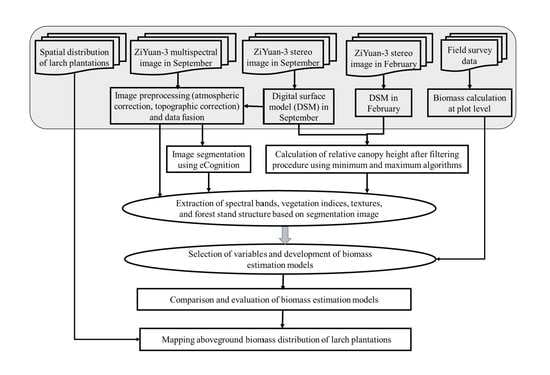
2.2. The Strategy of Forest Biomass Estimation using ZiYuan-3 Multispectral and Stereo Data
2.3. Data Preparation
2.4. Extraction of Potential Variables
2.4.1. Extraction of Spectral and Spatial Features
2.4.2. Extraction of Forest Canopy Features on the Basis of Bi-Temporal Digital Surface Model Data
2.5. Selection of Variables and Development of Biomass Estimation Models
2.6. Evaluation of Modeling Results and Application of the Developed Model for Prediction of Biomass Distribution
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Role of Relative Canopy Height in Reducing Data Saturation Problem
3.2. Analysis of Biomass Modeling Results
4. Discussion
4.1. The Role of Spectral and Spatial Features in Biomass Estimation
4.2. Potential Solution to Reduce the Data Saturation Problem in Optical Sensor Data
4.3. The Role of Forest Canopy Features in Improving Biomass Estimation
4.4. Implication of Using Multiple Data Sources in Biomass Estimation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, D. The potential and challenge of remote sensing–based biomass estimation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 1297–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafiseh, G.; Reza, S.; Ali, M. A review on biomass estimation methods using synthetic aperture radar data. Int. J. Geomat. Geosci. 2011, 1, 776–788. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C. Optical remote sensing of forest leaf area index and biomass. Prog. Phys. Geog. 2012, 37, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Sinha, P.; Taylor, S.; Alqurashi, A.F. Review of the use of remote sensing for biomass estimation to support renewable energy generation. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 097696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Chen, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, L.; Li, G.; Moran, E. A survey of remote sensing-based aboveground biomass estimation methods in forest ecosystems. Int. J. Digit Earth 2016, 9, 63–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.; Coops, N.; Wulder, M.; Wulder, M.; Thomas, H.; Piotr, T. Remote sensing technologies for enhancing forest inventories: A review. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 42, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Lu, D.; Wang, G.; Wu, C.; Huang, Y.; Yu, S. Examining spectral reflectance saturation in Landsat imagery and corresponding solutions to improve forest aboveground biomass estimation. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Lu, D.; Wang, G.; Liu, L.; Li, D.; Zhu, J.; Yu, S. Forest aboveground biomass estimation in Zhejiang Province using the integration of Landsat TM and ALOS PALSAR data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2016, 53, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Lu, D.; Chen, Q.; Keller, M.; Moran, E.; dos-Santos, M.; Bolfe, E.; Batistella, M. Examining effective use of data sources and modeling algorithms for improving biomass estimation in a moist tropical forest of the Brazilian Amazon. Int. J. Digit Earth 2017, 10, 996–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lu, D.; Li, G.; Wang, G.; Chen, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, D. Comparative analysis of modeling algorithms for forest aboveground biomass estimation in a subtropical region. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.; Boyd, D.; Cutler, M. Predictive relations of tropical forest biomass from Landsat TM data and their transferability between regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D. Aboveground biomass estimation using Landsat TM data in the Brazilian Amazon. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2509–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Mausel, P.; Brondízio, E.; Moran, E. Relationships between forest stand parameters and Landsat Thematic Mapper spectral responses in the Brazilian Amazon Basin. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 198, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Chen, Q.; Wang, G.; Moran, E.; Batistella, M.; Zhang, M.; Laurin, G.; Saah, D. Aboveground forest biomass estimation with Landsat and LiDAR data and uncertainty analysis of the estimates. J. For. Res-Jpn. 2012, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Batistella, M.; Moran, E. Satellite estimation of aboveground biomass and impacts of forest stand structure. Photogramm. Eng. Rem S. 2005, 71, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Lu, D.; Li, D. Exploring bamboo forest aboveground biomass estimation using Sentinel-2 data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, B.; Michael, A.; Joanne, C.; Geordie, H. Modeling stand height, volume, and biomass from very high spatial resolution satellite imagery and samples of airborne LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2308–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maack, J.; Kattenborn, T.; Fassnacht, F.E.; Enßle, F.; Hernández, J.; Corvalán, P.; Koch, B. Modeling forest biomass using Very-High-Resolution data—Combining textural, spectral and photogrammetric predictors derived from spaceborne stereo images. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 48, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.M.O.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Mesquita, P.; da Silva, J.R.M. Biomass estimation with high resolution satellite images: A case study of Quercus rotundifolia. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macedo, F.; Adélia, M.; Ana, C.; José, R.; Marques, D.; Paulo, A.; Ricardo, A. Above-ground biomass estimation for Quercus rotundifolia using vegetation indices derived from high spatial resolution satellite images. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, G.; Liu, Q. Modeling the stereoscopic features of mountainous forest landscapes for the extraction of forest heights from stereo imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Næsset, E.; Gobakken, T.; Bollandsås, O.; Gregoire, T.; Nelson, R.; Ståhl, G. Comparison of precision of biomass estimates in regional field sample surveys and airborne LiDAR-assisted surveys in Hedmark County, Norway. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mascaro, J.; Detto, M.; Asner, G.; Muller-Landau, H. Evaluating uncertainty in mapping forest carbon with airborne LiDAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3770–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefsky, M.; Cohen, W.; Harding, D.; Parker, G.; Acker, S.; Gower, S. Lidar remote sensing of above-ground biomass in three biomes. Global Ecol. Biogeogr. 2002, 11, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Vaglio, L.G.; Battles, J.; Saah, D. Integration of airborne lidar and vegetation types derived from aerial photography for mapping aboveground live biomass. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lu, D.; Keller, M.; Dos-Santos, M.; Bolfe, E.; Feng, Y.; Wang, C. Modeling and mapping agroforestry aboveground biomass in the Brazilian Amazon using airborne Lidar data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q. Lidar remote sensing of vegetation biomass. In Remote Sensing of Natural Resources; Wang, G., Weng, Q., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 399–420. [Google Scholar]
- Shean, D.; Alexandrov, O.; Moratto, Z.; Smith, B.; Joughin, I.; Porter, C.; Morin, P. An automated, open-source pipeline for mass production of digital elevation models (DEMs) from very-high-resolution commercial stereo satellite imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 116, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldbergs, G.; Maier, S.; Levick, S.; Andrew, E. Limitations of high resolution satellite stereo imagery for estimating canopy height in Australian tropical savannas. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2019, 75, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Dong, J.; Sun, G.; Zhang, J.; Pang, Y.; Tian, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, E. Synthesis of leaf-on and leaf-off unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) stereo imagery for the inventory of aboveground biomass of deciduous forests. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Onge, B.; Grandin, S. Estimating the height and basal area at individual tree and plot levels in Canadian Subarctic Lichen Woodlands using stereo WorldView-3 images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, H.; Wallerman, J.; Olsson, H.; Fransson, J. Estimating forest biomass and height using optical stereo satellite data and a DTM from laser scanning data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 39, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastaranta, M.; Markus, H.; Karjalainen, M.; Kankare, V.; Hyyppä, J.; Kaasalainen, S. TerraSAR-X stereo radargrammetry and airborne scanning LiDAR height metrics in imputation of forest aboveground biomass and stem volume. IEEE T Geosci. Remote 2014, 52, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Sun, G.; Ranson, K.J.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, W. Extraction of ground surface elevation from ZY-3 winter stereo imagery over deciduous forested areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Feng, Z.; Feng, Y.; Fan, J. Research on coniferous forest volume estimation model for Wangyedian experimental forest farm. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2013, 33, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Xie, M.; Gao, Y. Evaluation on the woodland resource value in Wangyedian trial forest farm. For. Invent. Plan. 2014, 29, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Ma, C. Struggle for sixty years, dream and flourishing industry—Record of development of Wangye Dian Experimental Forest Farm in Chifeng, the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. Land Green. 2015, 7, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lu, D.; Li, G.; Chen, E. Classification of land cover, forest, and tree species classes with ZiYuan-3 multispectral and stereo data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Sun, Y.J.; Ma, W. Biomass and carbon storage distribution of different density in Larix olgensis plantation. J. Fujian Coll. For. 2011, 3, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.L.; Yang, Z.Y. Estimating biomass and net primary production from forest inventory data: A case study of China’s Larix forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2002, 169, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, M.; Yan, Q.; Sun, O. Soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in forest ecosystems of Northeast China: A comparison between natural secondary forest and larch plantation. J. Plant Ecol-Uk 2010, 3, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, S.; Richards, J. Larches: Deciduous conifers in an evergreen world-in their harsh environments, these unique conifers support a net carbon gain similar to evergreens. Biosci. 1990, 40, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, T.; Yazaki, K.; Funada, R.; Maruyama, Y.; Mori, S.; Sasa, K. Forest health and vitality in northern Japan: A history of larch plantation. Res. Note Fac Forestry Univ. Joensuu. 2000, 92, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C. Biomass allometric equations for 10 co-occuring tree species in Chinese temperate forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 222, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Sun, G.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Z.; He, Y.; Huang, W. Retrieval of forest biomass from ALOS PALSAR data using a lookup table method. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I. Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 1973, 3, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Batistella, M. Exploring TM image texture and its relationships with biomass estimation in Rondônia, Brazilian Amazon. Acta Amazônica 2005, 35, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Chen, Q. Lidar Remote Sensing and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; p. 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Onge, B.; Hu, Y.; Vega, C. Mapping the height and above-ground biomass of a mixed forest using lidar and stereo IKONOS images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1277–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torresan, C.; Berton, A.; Carotenuto, F.; Di Gennaro, S.; Gioli, B.; Matese, A.; Miglietta, F.; Vagnoli, C.; Zaldei, A.; Wallace, L. Forestry applications of UAVs in Europe: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 2427–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Kenneth, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, G. Features of point clouds synthesized from multi-view ALOS/PRISM data and comparisons with LiDAR data in forested areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Ni, W.; Sun, G.; Huang, W.; Ranson, K.; Cook, B.; Guo, Z. Biomass retrieval from L-band polarimetric UAVSAR backscatter and PRISM stereo imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Datasets | Description | Date of Data Collection |
|---|---|---|
| Field survey data | A total of 24 sample plots were collected with an aboveground biomass (AGB) range of 51.83–175.59 Mg/ha, average AGB of 114.58 Mg/ha, and standard deviation of 41.36 Mg/ha. | September/October 2017 |
| ZiYuan-3 (ZY-3) data | ZY-3 data covered (1) four multispectral bands (three visible bands and one near-infrared band) with 5.8 m and (2) stereo imagery—nadir-view image with 2.1 m and backward and forward views with 3.5 m spatial resolution. After image preprocessing, the Gram–Schmidt tool was used to integrate multi-spectral and panchromatic data to produce a new dataset with a spatial resolution of 2 m. This fused image was used to produce a segmentation image using eCognition software [38]. | Two seasonal images: one ZY-3 image was acquired on 9 February 2015 with a sun elevation angle of 31.44° and azimuth angle of 163.06°; another ZY-3 image was acquired on 20 September 2017 with a sun elevation angle of 44.22° and azimuth angle of 148.18°. |
| Larch classification image | The larch classification result was developed from ZY-3 data using support vector machine (SVM)—user’s and producer’s accuracy of 79.7% and 94.8%. | Details were provided by Xie et al. [38]. |
| Digital surface model (DSM) data | The DSM data were extracted from ZY-3 stereo images in February and September, independently. This research directly used the results for calculation of relative canopy height (RCH) after post-processing of the bi-temporal DSM data. | Details were provided by Xie et al. [38]. |
| Vegetation Indices | Equations |
|---|---|
| Differenced vegetation index (DVI) | NIR − Red |
| Infrared percentage vegetation index (IPVI) | NIR/(NIR + Red) |
| Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | (NIR − Red)/(NIR + Red) |
| Normalized difference greenness index (NDGI) | (Green − Red)/(Green + Red) |
| Normalized difference water index (NDWI) | (Green − NIR)/(Green + NIR) |
| Ratio vegetation index (RVI) | NIR/Red |
| Re-normalized difference vegetation index (RDVI) | |
| Visible-band difference vegetation index (VDVI) | |
| Optimized soil adjusted vegetation index (OSAVI) | (NIR − Red)/(NIR + Red + 0.16) |
| Ratio of near-infrared (NIR) band to blue band | NIR/Blue |
| Data | Regression Models | R2 | AdjR2 | F-test | Beta | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral data | 263.855−0.555SBRed | 0.59 | 0.57 | 34.73 | −0.769 | ||
| Combination of spectral and stereo data | −13.475−0.487SBRed + 2.594RCH + 5.147StdRCH | 0.78 | 0.75 | 23.99 | −0.708 | 0.314 | 0.279 |
| Data | r | RMSE (Mg/ha) | RMSEr (%) | MAE (Mg/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral data | 0.616 | 33.89 | 29.57 | 30.68 |
| Combination of spectral and stereo data | 0.825 | 24.49 | 21.37 | 20.37 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, X.; Lu, D.; Chen, E. Integration of ZiYuan-3 Multispectral and Stereo Data for Modeling Aboveground Biomass of Larch Plantations in North China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2328. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192328
Li G, Xie Z, Jiang X, Lu D, Chen E. Integration of ZiYuan-3 Multispectral and Stereo Data for Modeling Aboveground Biomass of Larch Plantations in North China. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(19):2328. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192328
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guiying, Zhuli Xie, Xiandie Jiang, Dengsheng Lu, and Erxue Chen. 2019. "Integration of ZiYuan-3 Multispectral and Stereo Data for Modeling Aboveground Biomass of Larch Plantations in North China" Remote Sensing 11, no. 19: 2328. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192328
APA StyleLi, G., Xie, Z., Jiang, X., Lu, D., & Chen, E. (2019). Integration of ZiYuan-3 Multispectral and Stereo Data for Modeling Aboveground Biomass of Larch Plantations in North China. Remote Sensing, 11(19), 2328. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192328