Error Budget in the Validation of Radiometric Products Derived from OLCI around the China Sea from Open Ocean to Coastal Waters Compared with MODIS and VIIRS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Description of Atmospheric Correction
2.2. Error Budget
2.2.1. Total Error of the Satellite Product
2.2.2. Decomposition of the Total Error
2.2.3. Error of the Iterative Model
2.2.4. Error of the Aerosol LUTs and the Rayleigh-Corrected Radiance
3. Data and Method
3.1. In-Situ Data
3.2. Quality Control of the In Situ Data
3.2.1. Consistency of Multiple Measurements
3.2.2. Removal of the Surface-Reflected Radiance
3.2.3. Comparison with an IOP Model
3.3. Satellite-Derived Data
3.4. Match-Up Procedures
3.5. Statistical Method
4. Results
4.1. Variability of the In-Situ Data
4.2. Validation Results
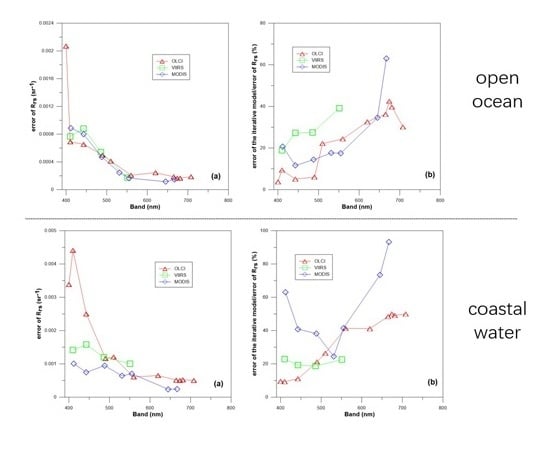
4.3. Difference between Open Ocean and Coastal Waters
5. Discussion
5.1. Influencing Factors in the Open Ocean
5.2. Influencing Factors in the Coastal Waters
6. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alvain, S.; Moulin, C.; Dandonneau, Y.; Loisel, H. Seasonal distribution and succession of dominant phytoplankton groups in the global ocean: A satellite view. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyendranath, S.; Aiken, J.; Alvain, S.; Barlow, R.; Bouman, H.; Bracher, A.; Brewin, R.; Bricaud, A.; Brown, C.; Ciotti, A. Phytoplankton functional types from Space. In Reports of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group (IOCCG); 15; International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group: Bedford, NS, Canada, 2014; pp. 1–156. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, J.H. Size distribution and settling velocities of suspended particles in a tidal embayment. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boss, E.; Pegau, W.S. Relationship of light scattering at an angle in the backward direction to the backscattering coefficient. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 5503–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buesseler, K.O.; Lamborg, C.H.; Boyd, P.W.; Lam, P.J.; Trull, T.W.; Bidigare, R.R.; Bishop, J.K.; Casciotti, K.L.; Dehairs, F.; Elskens, M. Revisiting carbon flux through the ocean’s twilight zone. Science 2007, 316, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quere, C.L.; Harrison, S.P.; Colin Prentice, I.; Buitenhuis, E.T.; Aumont, O.; Bopp, L.; Claustre, H.; Cotrim Da Cunha, L.; Geider, R.; Giraud, X.; et al. Ecosystem dynamics based on plankton functional types for global ocean biogeochemistry models. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 2016–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twardowski, M.S.; Boss, E.; Macdonald, J.B.; Pegau, W.S.; Barnard, A.H.; Zaneveld, J.R.V. A model for estimating bulk refractive index from the optical backscattering ratio and the implications for understanding particle composition in case I and case II waters. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2001, 106, 14129–14142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooker, S.; McClain, C. The calibration and validation of SeaWiFS data. Prog. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 427–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morel, A.; Huot, Y.; Gentili, B.; Werdell, P.J.; Hooker, S.B.; Franz, B.A. Examining the consistency of products derived from various ocean color sensors in open ocean (Case 1) waters in the perspective of a multi-sensor approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frouin, R.; Sei, A.; Hauss, B.; Pratt, P. Operational in-flight calibration of S-NPP VIIRS in the visible using Rayleigh scattering. In Proceedings of the SPIE 9218, Earth Observing Systems XIX, San Diego, CA, USA, 2 October 2014; Volume 921806. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M. Atmospheric correction for remotely-sensed ocean-colour products. In Reports of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group (IOCCG); 10; International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group: Bedford, NS, Canada, 2010; pp. 1–83. [Google Scholar]
- Jamet, C.; Loisel, H.; Kuchinke, C.P.; Ruddick, K.; Zibordi, G.; Feng, H. Comparison of three SeaWiFS atmospheric correction algorithms for turbid waters using AERONET-OC measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1955–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyens, C.; Jamet, C.; Schroeder, T. Evaluation of four atmospheric correction algorithms for MODIS-Aqua images over contrasted coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Mélin, F.; Voss, K.J.; Johnson, B.C.; Franz, B.A.; Kwiatkowska, E.; Huot, J.-P.; Wang, M.; Antoine, D. System vicarious calibration for ocean color climate change applications: Requirements for in-situ data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, T.; Hoepffner, N.; Stuart, V.; Brown, C. Why Ocean Colour? The Societal Benefits of Ocean-Colour Technology. In Reports of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group (IOCCG); 7; International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group: Bedford, NS, Canada, 2008; pp. 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- Greb, S.; Dekker, A.; Binding, C. Earth Observations in Support of Global Water Quality. In Reports of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group (IOCCG); 17; International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group: Bedford, NS, Canada, 2018; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Berruti, D.; Ferreira, B.; Femenias, M.H. The Global Monitoring for Environment and Security (GMES) Sentinel-3 mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 37–57. [Google Scholar]
- Malenovský, Z.; Rott, H.; Cihlar, J.; Schaepman, M.E.; García-Santos, G.; Fernandes, R.; Berger, M. Sentinels for science: Potential of Sentinel-1, -2, and -3 missions for scientific observations of ocean, cryosphere, and land. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Duan, H.; Cao, Z.; Xue, K.; Loiselle, S.; Yesou, H. Determination of the downwelling diffuse attenuation coefficient of lake water with the Sentinel-3A OLCI. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Mélin, F.; Berthon, J.-F. A regional assessment of OLCI data products. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mograne, M.A.; Jamet, C.; Loisel, H.; Vantrepotte, V.; Mériaux, X.; Cauvin, A. Evaluation of Five Atmospheric Correction Algorithms over French Optically-Complex Waters for the Sentinel-3A OLCI Ocean Color Sensor. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossn, J.I.; Ruddick, K.G.; Dogliotti, A.I. Atmospheric Correction of OLCI Imagery over Extremely Turbid Waters Based on the Red, NIR and 1016 nm Bands and a New Baseline Residual Technique. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Retrieval of water-leaving radiance and aerosol optical thickness over the oceans with SeaWiFS: A preliminary algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W.; Franz, B.A.; Werdell, P.J. Estimation of near-infrared water-leaving reflectance for satellite ocean color data processing. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 7521–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Fraser, R.S. An iterative radiative transfer code for ocean-atmosphere systems. J. Atmos. Sci. 1982, 39, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.; Munk, W. Measurement of the roughness of the sea surface from photographs of the sun’s glitter. Josa 1954, 44, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodhaine, B.A.; Wood, N.B.; Dutton, E.G.; Slusser, J.R. On Rayleigh optical depth calculations. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 1854–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepke, P. Effective reflectance of oceanic whitecaps. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 1816–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frouin, R.; Schwindling, M.; Deschamps, P.Y. Spectral reflectance of sea foam in the visible and near-infrared: In situ measurements and remote sensing implications. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1996, 101, 14361–14371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramska, M.; Petelski, T. Observations of oceanic whitecaps in the north polar waters of the Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, Z.; McClain, C.R.; Herman, J.R.; Franz, B.A.; Kwiatkowska, E.J.; Robinson, W.D.; Bucsela, E.J.; Tzortziou, M. Atmospheric correction for NO 2 absorption in retrieving water-leaving reflectances from the SeaWiFS and MODIS measurements. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 6504–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Gordon, H.R. Analysis of the influence of O2 A-band absorption on atmospheric correction of ocean-color imagery. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 2068–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Franz, B.A.; McClain, C.R.; Kwiatkowska, E.J.; Werdell, J.; Shettle, E.P.; Holben, B.N. New aerosol models for the retrieval of aerosol optical thickness and normalized water-leaving radiances from the SeaWiFS and MODIS sensors over coastal regions and open oceans. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 5545–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Berthon, J.-F.; Mélin, F.; D’Alimonte, D.; Kaitala, S. Validation of satellite ocean color primary products at optically complex coastal sites: Northern Adriatic Sea, Northern Baltic Proper and Gulf of Finland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2574–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Mélin, F.; Berthon, J.-F.; Holben, B.; Slutsker, I.; Giles, D.; D’Alimonte, D.; Vandemark, D.; Feng, H.; Schuster, G. AERONET-OC: A network for the validation of ocean color primary products. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1634–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, D.; Morel, A. A multiple scattering algorithm for atmospheric correction of remotely sensed ocean colour (MERIS instrument): Principle and implementation for atmospheres carrying various aerosols including absorbing ones. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1875–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.; Aiken, J.; Lavender, S. The atmospheric correction of water colour and the quantitative retrieval of suspended particulate matter in Case II waters: Application to MERIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1713–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, R.; Arnone, R.; Gould, R.; Martinolich, P.; Ransibrahmanakul, V. A partially coupled ocean-atmosphere model for retrieval of water-leaving radiance from SeaWiFS in coastal waters. NASA Technol. Memo 2003, 206892, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M. Remote sensing of the ocean contributions from ultraviolet to near-infrared using the shortwave infrared bands: Simulations. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavender, S.; Pinkerton, M.; Moore, G.; Aiken, J.; Blondeau-Patissier, D. Modification to the atmospheric correction of SeaWiFS ocean colour images over turbid waters. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.N.; Kuyatt, C.E. Guidelines for evaluating and expressing the uncertainty of NIST measurement results. In National Institute of Standards and Technology Technical Note 1297; Diane Publishing, US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.R. The study of uncertainties in physical measurements. In An Introduction to Error Analysis; University of Colorado: Boulder, CO, USA, 1982; Volume 73. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Gordon, H.R. Remote sensing of ocean color: Assessment of water-leaving radiance bidirectional effects on atmospheric diffuse transmittance. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 7887–7897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shettle, E.P.; Fenn, R.W. Models for the Aerosols of the Lower Atmosphere and the Effects of Humidity Variations on Their Optical Properties; Air Force Geophysics Lab Hanscom Afb Ma: Washington, DC, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Zibordi, G.; Mélin, F.; Hooker, S.B.; D’Alimonte, D.; Holben, B. An autonomous above-water system for the validation of ocean color radiance data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.L.; Morel, A.; Frouin, R.; Davis, C.; Arnone, R.; Carder, K.; Lee, Z.; Steward, R.; Hooker, S.; Mobley, C. Ocean Optics Protocols for Satellite Ocean Color Sensor Validation, Revision 4. Volume III: Radiometric Measurements and Data Analysis Protocols; Goddard Space Flight Space Center: Greenbelt, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ruddick, K.G.; De Cauwer, V.; Park, Y.-J.; Moore, G. Seaborne measurements of near infrared water-leaving reflectance: The similarity spectrum for turbid waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garaba, S.; Zielinski, O. Methods in reducing surface reflected glint for shipborne above-water remote sensing. J. Eur. Opt. Soc.-Rapid Publ. 2013, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdell, P.J.; McKinna, L.I.; Boss, E.; Ackleson, S.G.; Craig, S.E.; Gregg, W.W.; Lee, Z.; Maritorena, S.; Roesler, C.S.; Rousseaux, C.S. An overview of approaches and challenges for retrieving marine inherent optical properties from ocean color remote sensing. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 160, 186–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Mobley, C.; Arnone, R. Removal of surface-reflected light for the measurement of remote-sensing reflectance from an above-surface platform. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 26313–26324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilerson, A.; Carrizo, C.; Foster, R.; Harmel, T. Variability of the reflectance coefficient of skylight from the ocean surface and its implications to ocean color. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 9615–9633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.-E.; Park, Y.-J.; Ryu, J.-H.; Choi, J.-K.; Ahn, J.-H.; Min, J.-E.; Son, Y.-B.; Lee, S.-J.; Han, H.-J.; Ahn, Y.-H. Initial validation of GOCI water products against in-situ data collected around Korean peninsula for 2010–2011. Ocean Sci. J. 2012, 47, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Brown, O.B.; Evans, R.H.; Brown, J.W.; Smith, R.C.; Baker, K.S.; Clark, D.K. A semianalytic radiance model of ocean color. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1988, 93, 10909–10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z. Remote sensing of inherent optical properties: Fundamentals, tests of algorithms, and applications. In Reports of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group (IOCCG); 5; International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group: Bedford, NS, Canada, 2006; pp. 1–122. [Google Scholar]
- Garver, S.A.; Siegel, D.A. Inherent optical property inversion of ocean color spectra and its biogeochemical interpretation: 1. Time series from the Sargasso Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1997, 102, 18607–18625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritorena, S.; Siegel, D.A.; Peterson, A.R. Optimization of a semianalytical ocean color model for global-scale applications. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 2705–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Lin, G.; Chen, J.; Doxaran, D. On the modeling of hyperspectral remote-sensing reflectance of high-sediment-load waters in the visible to shortwave-infrared domain. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 1738–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werdell, P.J.; Bailey, S.W.; Franz, B.A.; Morel, A.; McClain, C.R. On-orbit vicarious calibration of ocean color sensors using an ocean surface reflectance model. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 5649–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, B.B.; Cannizzaro, J.P.; English, D.C.; Hu, C. Validation of VIIRS and MODIS reflectance data in coastal and oceanic waters: An assessment of methods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 220, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W.; Werdell, P.J. A multi-sensor approach for the on-orbit validation of ocean color satellite data products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélin, F.; Sclep, G.; Jackson, T.; Sathyendranath, S. Uncertainty estimates of remote sensing reflectance derived from comparison of ocean color satellite data sets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, G.; Cao, W.; Cui, T.; Wang, G.; Ling, J.; Sun, L.; Zhou, W.; Sun, Z.; Xu, Z. Assessment of SeaWiFS, MODIS, and MERIS ocean colour products in the South China Sea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 4252–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Qiu, Z.; Hu, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Zheng, L.; Peng, T.; He, Y. A hybrid method to estimate suspended particle sizes from satellite measurements over B ohai S ea and Y ellow S ea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 6742–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Lee, Z.; Shang, S. A system to measure the data quality of spectral remote-sensing reflectance of aquatic environments. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 8189–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Ahmad, Z.; Franz, B.A. The sensitivity of SeaWiFS ocean color retrievals to aerosol amount and type. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2016, 33, 1185–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Surface-roughness considerations for atmospheric correction of ocean color sensors. 1: The Rayleigh-scattering component. Appl. Opt. 1992, 31, 4247–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrizo, C.; Gilerson, A.; Foster, R.; Golovin, A.; El-Habashi, A. Characterization of radiance from the ocean surface by hyperspectral imaging. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 1750–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, D.; d’Ortenzio, F.; Hooker, S.B.; Bécu, G.; Gentili, B.; Tailliez, D.; Scott, A.J. Assessment of uncertainty in the ocean reflectance determined by three satellite ocean color sensors (MERIS, SeaWiFS and MODIS-A) at an offshore site in the Mediterranean Sea (BOUSSOLE project). J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Symbols | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Total measured radiance | |
| Radiance due to the Rayleigh scattering | |
| Contribution of the scattering by the aerosols and the scattering between the aerosols and the air molecules | |
| Rayleigh-corrected radiance | |
| Solar irradiance at the mean Earth-Sun distance | |
| Diffuse transmittance of the atmosphere from the surface to the sensor | |
| Remote-sensing reflectance | |
| Normalized water-leaving radiance | |
| Water reflectance | |
| , | Rayleigh, aerosol, and ozone optical thicknesses |
| Viewing direction | |
| , | Rayleigh and aerosol forward scattering probabilities |
| Aerosol single scattering albedo | |
| A | Error of A (any symbols can called A) |
| Period | Place | Number of Stations | Source of Rrs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2002.09 | BoS | 30 | ASD |
| 2017.08 | YS | 76 | SAS |
| 2018.03 | PRE | 30 | SAS |
| 2018.09 | ECS&SCS | 74 | SAS |
| Satellite | Product | n | Bias (sr−1) | RMSE (sr−1) | APD (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLCI | 13 | 0.001085 | 0.00300 | 43 | 0.00290 | |
| 13 | −0.000186 | 0.00252 | 30 | 0.00260 | ||
| 13 | 0.000120 | 0.00166 | 23 | 0.00172 | ||
| 13 | 0.000237 | 0.00107 | 18 | 0.00108 | ||
| 13 | 0.000061 | 0.00092 | 20 | 0.00096 | ||
| 13 | −0.000061 | 0.00052 | 21 | 0.00053 | ||
| 13 | −0.000241 | 0.00036 | 68 | 0.00031 | ||
| 13 | −0.000231 | 0.00030 | 58 | 0.00023 | ||
| 13 | −0.000206 | 0.00029 | 77 | 0.00024 | ||
| 13 | −0.000227 | 0.00030 | 66 | 0.00023 | ||
| 13 | −0.000177 | 0.00016 | 56 | 0.00018 | ||
| 13 | −0.000098 | 0.00012 | 79 | 0.00012 | ||
| MODIS | 15 | −0.000531 | 0.00149 | 39 | 0.00141 | |
| 15 | −0.000478 | 0.00127 | 30 | 0.00118 | ||
| 15 | −0.000662 | 0.00143 | 26 | 0.00127 | ||
| 15 | −0.000540 | 0.00122 | 19 | 0.00109 | ||
| 15 | −0.000708 | 0.00119 | 19 | 0.00095 | ||
| 15 | −0.000150 | 0.00041 | 48 | 0.00038 | ||
| 15 | −0.000213 | 0.00040 | 32 | 0.00034 | ||
| 15 | 0.000079 | 0.00032 | 40 | 0.00031 | ||
| VIIRS | 15 | −0.000481 | 0.00157 | 47 | 0.00155 | |
| 15 | −0.000495 | 0.00171 | 42 | 0.00169 | ||
| 15 | −0.000508 | 0.00151 | 30 | 0.00147 | ||
| 15 | −0.000549 | 0.00127 | 27 | 0.00118 | ||
| 15 | −0.000137 | 0.00033 | 36 | 0.00032 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Jamet, C.; Zhu, J.; Han, B.; Li, T.; Yang, A.; Guo, K.; Jia, D. Error Budget in the Validation of Radiometric Products Derived from OLCI around the China Sea from Open Ocean to Coastal Waters Compared with MODIS and VIIRS. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202400
Li J, Jamet C, Zhu J, Han B, Li T, Yang A, Guo K, Jia D. Error Budget in the Validation of Radiometric Products Derived from OLCI around the China Sea from Open Ocean to Coastal Waters Compared with MODIS and VIIRS. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(20):2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202400
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jun, Cédric Jamet, Jianhua Zhu, Bing Han, Tongji Li, Anan Yang, Kai Guo, and Di Jia. 2019. "Error Budget in the Validation of Radiometric Products Derived from OLCI around the China Sea from Open Ocean to Coastal Waters Compared with MODIS and VIIRS" Remote Sensing 11, no. 20: 2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202400
APA StyleLi, J., Jamet, C., Zhu, J., Han, B., Li, T., Yang, A., Guo, K., & Jia, D. (2019). Error Budget in the Validation of Radiometric Products Derived from OLCI around the China Sea from Open Ocean to Coastal Waters Compared with MODIS and VIIRS. Remote Sensing, 11(20), 2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202400