Quantifying Trends of Land Change in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during 2001–2015
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. LCLU Mapping
2.3. LCLUC Spatial Pattern Analysis
2.4. Environmental and Anthropogenic Forcing
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy of LCLU Mapping
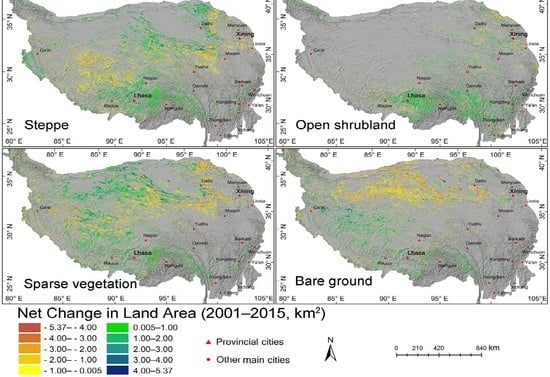
3.2. Patterns and Hotspots of Land-Cover Change in QTP during 2001–2015
4. Discussion
4.1. Economy Shift, Conservation Policy, and Agricultural Lands’ Change
4.2. Conservation, Climate Change, and Woodland Expansion into Grassland
4.3. Increased Precipitation/Warming and Water Surface Expansion/Glacier Retreat
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



References
- Qiu, J. The third pole. Nature 2008, 454, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, M.; Li, C.; Song, Z. Seasonal heating of the Tibetan Plateau and its effects on the evolution of the Asian summer monsoon. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 1992, 70, 319–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.X.; Liu, Y.M.; He, B.; Bao, Q.; Duan, A.M.; Jin, F.F. Thermal controls on the Asian summer monsoon. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funnell, D.; Parish, R. Mountain Environments and Communities; Routledge: London, UK, 2005; p. 432. [Google Scholar]
- Kutzbach, J.E.; Prell, W.L.; Ruddiman, W.F. Sensitivity of Eurasian climate to surface uplift of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geol. 1993, 101, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Hao, Z.; Tong, K. Discharge regime and simulation for the upstream of major rivers over Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 8500–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolch, T.; Kulkarni, A.; Kääb, A.; Huggel, C.; Paul, F.; Cogley, J.G.; Frey, H.; Kargel, J.S.; Fujita, K.; Scheel, M.; et al. The state and fate of Himalayan glaciers. Science 2012, 336, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 2010, 328, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yang, K. The cause of rapid lake expansion in the Tibetan Plateau: Climate wetting or warming? Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2017, 4, e1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, C. Biodiversity hotspots: A shortcut for a more complicated concept. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2015, 3, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B.; et al. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, H. Vegetation changes along the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau engineering corridor since 2000 induced by climate change and human activities. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Cui, M.; Chen, A.; Wang, X.; Ciais, P.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y. Altitude and temperature dependence of change in the spring vegetation green-up date from 1982 to 2006 in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Gong, T.L.; Li, J.Y. Decadal trend of climate in the Tibetan Plateau—Regional temperature and precipitation. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 3056–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, L.W.; Wesche, K.; Trachte, K.; Reudenbach, C.; Bendix, J. Climate variability rather than overstocking causes recent large scale cover changes of Tibetan pastures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, C.; Wu, L.; Xu, X.; Ou, Y. Wet-drought pattern and its relationship with vegetation change in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during 2001–2010. Arid Land Geogr. 2013, 36, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, J.S.; Haynes, M.A.; Kuemmerle, T.; Waller, D.M.; Radeloff, V.C. Regime shift on the roof of the world: Alpine meadows converting to shrublands in the southern Himalayas. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 158, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Tao, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C. The impact of climate change and anthropogenic activities on alpine grassland over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltridge, N.; Tao, J.; Unkovich, M.; Bonamano, A.; Gason, A.; Grover, S.; Wilkins, J.; Tashi, N.; Coventry, D. Agriculture in central Tibet: An assessment of climate, farming systems, and strategies to boost production. Crop Pasture Sci. 2009, 60, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddema, J.J.; Oleson, K.W.; Bonan, G.B.; Mearns, L.O.; Buja, L.E.; Meehl, G.A.; Washington, W.M. The importance of land-cover change in simulating future climates. Science 2005, 310, 1674–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Graf, H.-F. Recent land-cover changes on the Tibetan Plateau: A review. Clim. Chang. 2009, 94, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dietz, T.; Carpenter, S.R.; Folke, C.; Alberti, M.; Redman, C.L.; Schneider, S.H.; Ostrom, E.; Pell, A.N.; Lubchenco, J. Coupled human and natural systems. AMBIO J. Hum. Environ. 2007, 36, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Neumann, K.; Nol, L. Challenges in using land use and land-cover data for global change studies. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, Q.; Peng, C.; Wu, N.; Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, D.; Yang, G.; Tian, J.; et al. The impacts of climate change and human activities on biogeochemical cycles on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2940–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhao, D.; Wu, B. Analysis of land-cover changes in southwestern China since the 1990s. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 7858–7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gao, Q.; Wang, X.; Yu, M. Decadal trend in agricultural abandonment and woodland expansion in an agro-pastoral transition band in northern China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Yu, M. Discerning fragmentation dynamics of tropical forest and wetland during reforestation, urban sprawl, and policy shifts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Bai, W.; Zheng, D. Land cover change along the Qinghai-Tibet Highway and Railway from 1981 to 2001. J. Geogr. Sci. 2006, 16, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Dong, Z.; Hu, G.; Li, W.; Luo, W.; Tan, M. Land use and land-cover change and its driving forces in Maqu County, China in the past 25 years. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2016, 8, 432–440. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Yuan, Q.; Yan, C.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Li, A.; Ma, R.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Chang, C.; et al. Land cover changes of China from 2000 to 2010. Quat. Sci. 2014, 34, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Tan, K.; Nan, H.; Ciais, P.; Fang, J.; Wang, T.; Vuichard, N.; Zhu, B. Impacts of climate and CO2 changes on the vegetation growth and carbon balance of Qinghai–Tibetan grasslands over the past five decades. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2012, 98, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Q.; He, J.; Lu, Y.; Ji, L.; Xiao, J.; Luo, T. Carbon dynamics of terrestrial ecosystems on the Tibetan Plateau during the 20th century: An analysis with a process-based biogeochemical model. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Ju, J.; Ma, Q.; Turner, F.; Guo, Y. Spatiotemporal variations in volume of closed lakes on the Tibetan Plateau and their climatic responses from 1976 to 2013. Clim. Chang. 2017, 140, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gao, Q.; Wang, X.; Yu, M. Spatially differentiated trends in urbanization, agricultural land abandonment and reclamation, and woodland recovery in Northern China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, B.; Woodcock, C.E.; Hu, J.; Zhang, P.; Ozdogan, M.; Huang, D.; Yang, W.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Myneni, R.B. The impact of gridding artifacts on the local spatial properties of MODIS data: Implications for validation, compositing, and band-to-band registration across resolutions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dong, B.; Yin, Z.-Y.; Smith, R.S.; Guo, Q. Continental drift and plateau uplift control origination and evolution of Asian and Australian monsoons. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, D.R.; Maharjan, S.B.; Shrestha, A.B.; Shrestha, M.S.; Bajracharya, S.R.; Murthy, M.S.R. Climate and topographic controls on snow cover dynamics in the Hindu Kush Himalaya. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 3873–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, F.; Zheng, L.; Yang, L. Evaluation of grassland dynamics in the Northern-Tibet Plateau of China using remote sensing and climate data. Sensors 2007, 7, 3312–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Liu, Z. Probing into causes of geographical pattern of subalpine vegetation on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 1998, 4, 290–297. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, D.; Ding, Y.; Mu, M. Climate and Environmental Change in China: 1951–2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lehner, B.; Verdin, K.; Jarvis, A. New global hydrography derived from spaceborne elevation data. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2008, 89, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, P.; Eklundh, L. TIMESAT—A program for analyzing time-series of satellite sensor data. Comput. Geosci. 2004, 30, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.; Reuter, H.I.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E. Hole-Filled SRTM for the Globe Version 4. The CGIAR-CSI SRTM 90 m Database. 2008. Available online: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed on 20 October 2019).
- Zhang, X.; Sun, S.; Yong, S.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, R. Vegetation Map of the People’s Republic of China (1:1,000,000); Geology Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Etter, A.; McAlpine, C.; Phinn, S.; Pullar, D.; Possingham, H. Characterizing a tropical deforestation wave: A dynamic spatial analysis of a deforestation hotspot in the Colombian Amazon. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 1409–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, M.; Gao, Q. Continued reforestation and urban expansion in the new century of a tropical island in the Caribbean. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkel, M.; Carvalhais, N.; Verbesselt, J.; Mahecha, M.; Neigh, C.; Reichstein, M. Trend change detection in NDVI time series: Effects of inter-annual variability and methodology. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2113–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for International Earth Science Information Network (CIESIN). Gridded Population of the World, Version 4 (GPWv4): Population Density Adjusted to Match 2015 Revision UN WPP Country Totals; NASA Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC): Palisades, NY, USA, 2016.
- Zhang, J.; Wu, S.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Yang, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.H. Simulation of distribution of agricultural output value influenced by land use and topographical indices in Tibet. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2007, 23, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Tang, Y.; Luo, H.; Di, B.; Zhang, L. Local farmers’ perceptions of climate change and local adaptive strategies: A case study from the Middle Yarlung Zangbo River Valley, Tibet, China. Environ. Manag. 2013, 52, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-E.; Zeng, Y.; Zhong, L. Impact of climate change on tourism on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Research based on a literature review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Li, H.; Hua, X.; Peng, K.; Zhang, Y. Determinants of Engagement in Off-Farm Employment in the Sanjiangyuan Region of the Tibetan Plateau; BioOne: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Volume 37, pp. 464–473. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, R.; Wang, J. Research on the impact of transportation on tourism in Tibet and its developmental countermeasures. J. Tibet Univ. 2013, 1, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, J.S.; Kuemmerle, T.; Li, H.; Ren, G.; Zhu, J.; Radeloff, V.C. Using Landsat imagery to map forest change in southwest China in response to the national logging ban and ecotourism development. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, S.; Brown, C.; Jin, T.; Na, W. Agricultural development in a Tibetan township. Himalaya 2016, 35, 9–31. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Cheng, F.; Dong, S.; Zhao, H.; Hou, X.; Wu, X. Spatiotemporal dynamics of grassland aboveground biomass on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on validated MODIS NDVI. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, H.; Mi, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Jiang, L.; He, J.-S. Climate warming reduces the temporal stability of plant community biomass production. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yang, S.; Ma, S.; Zhou, J.; Chu, B.; Hua, R.; Hua, L. Overgrazing leads to soil cracking that later triggers the severe degradation of alpine meadows on the Tibetan Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Odorico, P.; Okin, G.S.; Bestelmeyer, B.T. A synthetic review of feedbacks and drivers of shrub encroachment in arid grasslands. Ecohydrology 2012, 5, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriotti, P.A.; Aguiar, M.R. Direct and indirect effects of grazing constrain shrub encroachment in semi-arid Patagonian steppes. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2012, 15, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, R.A.; Hackler, J.L. Sources and sinks of carbon from land-use change in China. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.S.; Manaswini, G.; Satish, K.V.; Singh, S.; Jha, C.S.; Dadhwal, V.K. Conservation priorities of forest ecosystems: Evaluation of deforestation and degradation hotspots using geospatial techniques. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, B.; Lavorel, S.; Sloan, S.; Tappeiner, U.; Geneletti, D. Characteristic trajectories of ecosystem services in mountains. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2017, 15, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Tam, C.; Chen, X. Ecological and socioeconomic effects of China’s policies for ecosystem services. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9477–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donchyts, G.; Baart, F.; Winsemius, H.; Gorelick, N.; Kwadijk, J.; van de Giesen, N. Earth’s surface water change over the past 30 years. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wu, W.; Wu, Y. Variations in China’s terrestrial water storage over the past decade using GRACE data. Geod. Geodyn. 2015, 6, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Wang, J.; Yang, K.; Wang, C.; Walter, B.A.; Crétaux, J.-F. Lake storage variation on the endorheic Tibetan Plateau and its attribution to climate change since the new millennium. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 064011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Song, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Heki, K.; Sun, W. The potential of GRACE gravimetry to detect the heavy rainfall-induced impoundment of a small reservoir in the upper Yellow River. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 6562–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, K. Glacier change, concentration, and elevation effects in the Karakoram Himalaya, Upper Indus Basin. Mt. Res. Dev. 2011, 31, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, A.F.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Shrestha, A.B.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Consistent increase in High Asia’s runoff due to increasing glacier melt and precipitation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, B. The spatial pattern of monthly air temperature of the Tibetan Plateau and its implications for the geo-ecology pattern of the Plateau. Geogr. Res. 2015, 34, 2084–2094. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Bosch, C.; Kang, S.; Andersson, A.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Q.; Cong, Z.; Chen, B.; Qin, D.; Gustafsson, Ö. Sources of black carbon to the Himalayan–Tibetan Plateau glaciers. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, A.D.; Noone, K.J. Soot in the Arctic snowpack: A cause for perturbations in radiative transfer. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1985, 19, 2045–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S. Temporal evolution of regional drought detected from GRACE TWSA and CCI SM in Yunnan Province, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, T.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Shang, H.; Zhu, L.; Shedayi, A.A.; Yu, H.; Cheng, G.; Liu, G.; et al. Linkages of the dynamics of glaciers and lakes with the climate elements over the Tibetan Plateau. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 185, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.C.; Smith, A.T. The pika and the watershed: The impact of small mammal poisoning on the ecohydrology of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ambio 2015, 44, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luthcke, S.B.; Rowlands, D.D.; Sabaka, T.J.; Loomis, B.D.; Horwath, M.; Arendt, A.A. Gravimetry measurements from space. In Remote Sensing of the Cryosphere; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 231–247. [Google Scholar]
- Moiwo, J.P.; Yang, Y.; Tao, F.; Lu, W.; Han, S. Water storage change in the Himalayas from the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) and an empirical climate model. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luthcke, S.B.; Sabaka, T.; Loomis, B.; Arendt, A.; McCarthy, J.; Camp, J. Antarctica, Greenland and Gulf of Alaska land-ice evolution from an iterated GRACE global mascon solution. J. Glaciol. 2013, 59, 613–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, Z.; Save, H.; Wiese, D.N.; Landerer, F.W.; Long, D.; Longuevergne, L.; Chen, J. Global evaluation of new GRACE mascon products for hydrologic applications. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 9412–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| AGRI | BARE | CLSH | DBLF | EBLF | ENLF | MIXF | MEDO | STEP | OPSH | SNOW | SPAS | URBN | WATR | SUM | UA (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGRI | 153 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 11 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 178 | 86.0 |
| BARE | 0 | 149 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 162 | 92.0 |
| CLSH | 4 | 0 | 92 | 4 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 17 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 131 | 70.2 |
| DBLF | 0 | 0 | 3 | 48 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 62 | 77.4 |
| EBLF | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 58 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 79 | 73.4 |
| ENLF | 0 | 0 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 195 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 222 | 87.8 |
| MIXF | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 58.3 |
| MEDO | 14 | 0 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 296 | 7 | 14 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 365 | 81.1 |
| STEP | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 47 | 5 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 64 | 73.4 |
| OPSH | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 43 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 65 | 66.2 |
| SNOW | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 100 |
| SPAS | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 37 | 2 | 1 | 57 | 64.9 |
| URBN | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 98 | 1 | 107 | 91.6 |
| WATR | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 100 |
| SUM | 177 | 159 | 140 | 63 | 64 | 224 | 31 | 330 | 67 | 80 | 30 | 54 | 111 | 53 | ||
| PA (%) | 86.4 | 93.7 | 65.7 | 76.2 | 90.6 | 87.1 | 22.6 | 89.7 | 70.1 | 53.8 | 96.7 | 68.5 | 88.3 | 94.3 | ||
| Average PA = 77.4%, average UA = 80.2%, OA = 82.2%, Kappa = 78.7% | ||||||||||||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Gao, Q.; Yu, M. Quantifying Trends of Land Change in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during 2001–2015. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202435
Wang C, Gao Q, Yu M. Quantifying Trends of Land Change in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during 2001–2015. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(20):2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202435
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chao, Qiong Gao, and Mei Yu. 2019. "Quantifying Trends of Land Change in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during 2001–2015" Remote Sensing 11, no. 20: 2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202435
APA StyleWang, C., Gao, Q., & Yu, M. (2019). Quantifying Trends of Land Change in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during 2001–2015. Remote Sensing, 11(20), 2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202435