Wetland Loss Identification and Evaluation Based on Landscape and Remote Sensing Indices in Xiong’an New Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
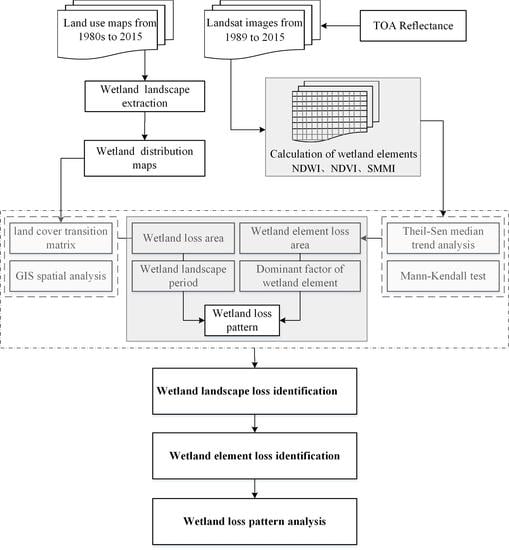
3. Methodology
3.1. The Analysis Method of Wetland Landscape Variation and Loss
3.1.1. Land Cover Transition Matrix
3.1.2. Identifying the Maximum Wetland Extent
3.2. The Analysis Method of Wetland Elements Loss
3.2.1. Calculation of Wetland Elements
3.2.2. Change Trend Analysis Method
3.3. The Pattern of Wetland Loss in the Landscape Integrated with Elements
4. Results
4.1. The Analysis of Wetland Landscape Variation and Loss
4.2. The Wetland Elements Loss in the Maximum Wetland Extent
4.3. The Pattern of Wetland Loss in A Landscape Integrated with Elements
5. Discussion
5.1. Contribution of the Wetland Loss Identification Method
5.2. Comparison of the Wetland Loss
5.3. Uncertainties and Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Wang, G.; Deng, W.; Hu, Y.; Hu, W.-W. Influence of hydrology process on wetland landscape pattern: A case study in the Yellow River Delta. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, F.; Johnson, V.C.; Bane, C.S.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of land cover and landscape change patterns in Ebinur Lake Wetland National Nature Reserve, China from 1972 to 2013. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 25, 619–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Hu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, M.; Guo, J.; Ren, B. Monitoring wetland changes both outside and inside reclamation areas for coastal management of the Northern Liaodong Bay, China. Wetlands 2017, 37, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermoso, V.; Clavero, M.; Green, A.J. Dams: Keep wetland damage in check. Nature 2019, 568, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sica, Y.V.; Quintana, R.D.; Radeloff, V.C.; Gavier-Pizarro, G.I. Wetland loss due to land use change in the Lower Paraná River Delta, Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Gong, H.; Wang, Y.; Khan, S.; Zhao, K. Driving forces for the marsh wetland degradation in the Honghe National Nature Reserve in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Environ. Model. Assess. 2009, 14, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Wu, B.; Zeng, Y.; Song, K.; Yi, K.; Luo, L. China’s wetlands loss to urban expansion. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2644–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Niu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, D.; Guo, J.; Liang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Huang, H.; et al. China’s wetland change (1990–2000) determined by remote sensing. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z. Mapping China’s wetlands and recent changes with remotely sensed data. In Remote Sensing of Wetlands; Tiner, R., Lang, M., Klemas, V., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 473–490. ISBN 978-1-4822-3735-1. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Tang, Z.; Li, J.; Lv, J.; Chen, Z.; Jia, K. Spatio-temporal change of lake water extent in wuhan urban agglomeration based on landsat images from 1987 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Jiang, W.; Jia, K.; Rao, P.; Lv, J. Analysis of the Dynamic Changes of the Baiyangdian Lake Surface Based on a Complex Water Extraction Method. Water 2018, 10, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowska-Zielinska, K.; Budzynska, M.; Tomaszewska, M.; Malinska, A.; Gatkowska, M.; Bartold, M.; Malek, I. Assessment of carbon flux and soil moisture in wetlands applying Sentinel-1 Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, B.R.; Ausseil, A.-G.E.; Gerbeaux, P. Wetland ecosystem services. In Ecosystem Services in New Zealand: Conditions and Trends; Manaaki Whenua Press: Lincoln, New Zealand, 2013; pp. 192–202. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Li, Y.; Gu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Xue, Y.; Hu, Q.; LaGrange, T.; Bishop, A.; Drahota, J.; Li, R. Assessing Nebraska playa wetland inundation status during 1985–2015 using Landsat data and Google Earth Engine. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Yan, Y.; Guo, H.; He, M.; Gu, Y.; Li, B. Monitoring rapid vegetation succession in estuarine wetland using time series MODIS-based indicators: An application in the Yangtze River Delta area. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petus, C.; Lewis, M.; White, D. Monitoring temporal dynamics of Great Artesian Basin wetland vegetation, Australia, using MODIS NDVI. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, W.; Cao, C.; Tian, R.; Liu, D.; Bao, D. Diagnosis of wetland ecosystem health in the Zoige Wetland, Sichuan of China. Wetlands 2018, 38, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-M.; Yeh, H.-C. Applying remote sensing techniques to monitor shifting wetland vegetation: A case study of Danshui River estuary mangrove communities, Taiwan. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, C.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Yu, J. Assessing the impacts of climate variability and human activities on streamflow in the water source area of Baiyangdian Lake. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Ke, L.; Pan, H.; Zhan, S.; Liu, K.; Ma, R. Long-term surface water changes and driving cause in Xiong’an, China: From dense Landsat time series images and synthetic analysis. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Shi, T.; Guan, H.; Fang, C.; Lin, Z. Prediction of ecological effects of potential population and impervious surface increases using a remote sensing based ecological index (RSEI). Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szantoi, Z.; Brink, A.; Buchanan, G.; Bastin, L.; Lupi, A.; Simonetti, D.; Mayaux, P.; Peedell, S.; Davy, J. A simple remote sensing based information system for monitoring sites of conservation importance. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2016, 2, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Mao, D.; Zhang, Y. A New vegetation index to detect periodically submerged mangrove forest using single-tide sentinel-2 imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, D.; Zhang, Y. Baiyangdian functional area division principle. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 1995, S1, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qi, S.; Na, X. Comparison of land use/land cover change and landscape patterns in Honghe National Nature Reserve and the surrounding Jiansanjiang Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 51, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Jiang, W.; Li, J.; Tang, Z. Spectral matching based on discrete particle swarm optimization: A new method for terrestrial water body extraction using multi-temporal Landsat 8 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Bauer, M.E. Comparison of impervious surface area and normalized difference vegetation index as indicators of surface urban heat island effects in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Im, J.; Lee, J.; Gong, H.; Ryu, Y. Characteristics of Landsat 8 OLI-derived NDVI by comparison with multiple satellite sensors and in-situ observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, W.; Yue, H.; Zhao, H. Dynamic soil moisture monitoring in shendong mining area using Temperature Vegetation Dryness Index. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering (RSETE), Nanjing, China, 24–26 June 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 5892–5895. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, M.G. A new measure of rank correlation. Biometrika 1938, 30, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yuan, L.; Wang, W.; Cao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, W. Spatio-temporal analysis of vegetation variation in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 51, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiwo, J.P.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Han, S.; Yang, Y. Impact of water resource exploitation on the hydrology and water storage in Baiyangdian Lake. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 3026–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| SNDVI | SNDWI | SSMMI | Z Value | Trend of the Wetland Element |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥0.005 | ≥0 | ≥0 | ≥1.96 | Significant degradation |
| ≥0.005 | ≥0 | ≥0 | −1.96–1.96 | Slight degradation |
| −0.005–0.005 | — | — | −1.96–1.96 | Stability |
| <−0.005 | <0 | <0 | −1.96–1.96 | Slight improvement |
| <−0.005 | <0 | <0 | <−1.96 | Significant improvement |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, J.; Jiang, W.; Wang, W.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. Wetland Loss Identification and Evaluation Based on Landscape and Remote Sensing Indices in Xiong’an New Area. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232834
Lv J, Jiang W, Wang W, Wu Z, Liu Y, Wang X, Li Z. Wetland Loss Identification and Evaluation Based on Landscape and Remote Sensing Indices in Xiong’an New Area. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(23):2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232834
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Jinxia, Weiguo Jiang, Wenjie Wang, Zhifeng Wu, Yinghui Liu, Xiaoya Wang, and Zhuo Li. 2019. "Wetland Loss Identification and Evaluation Based on Landscape and Remote Sensing Indices in Xiong’an New Area" Remote Sensing 11, no. 23: 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232834
APA StyleLv, J., Jiang, W., Wang, W., Wu, Z., Liu, Y., Wang, X., & Li, Z. (2019). Wetland Loss Identification and Evaluation Based on Landscape and Remote Sensing Indices in Xiong’an New Area. Remote Sensing, 11(23), 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232834