An Efficient Clustering Method for Hyperspectral Optimal Band Selection via Shared Nearest Neighbor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (a)
- Consider the similarity between each band and other bands by shared nearest neighbor [25]. Shared nearest neighbor can accurately reflect the local distribution characteristics of each band in space using the k-nearest neighborhood, which can better express the local density of the band to achieve band selection.
- (b)
- Take information entropy to be one of the evaluation indicators. When calculating the weight of each band, the information of each band is taken as one of the weight factors. It can retain useful information in a relatively complete way.
- (c)
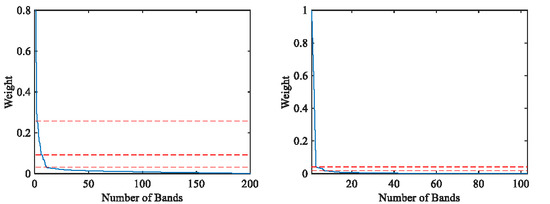
- Design an automatic method to determine the optimal band subset. Through the slope change of the weight curve, the maximum index of the significant critical point is found, which represents the optimal number of clusters to achieve band subset selection.
2. Methodology
2.1. Datasets Description
2.2. Proposed Method
2.2.1. Weight Computation
| Algorithm 1 Framework of SNNC |
|
2.2.2. Optimal Band Selection
2.2.3. Computational Complexity Analysis
2.3. Experimental Setup
3. Results
3.1. Parameter K Analysis
3.2. Performance Comparison
3.2.1. Classification Performance Comparison
3.2.2. Number of Recommended Bands
3.2.3. Processing Time Comparison
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hughes, G. On the mean accuracy of statistical pattern recognizers. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 1968, 14, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Nie, F.; Li, X. Detecting Coherent Groups in Crowd Scenes by Multiview Clustering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 54, 6516–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Qin, Z.; Nie, F.; Li, X. Spectral Embedded Adaptive Neighbors Clustering. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, PP, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wan, J.; Nie, F.; Liu, B.; Yan, C.; Li, X. Hierarchical Feature Selection for Random Projection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah-Hosseini, R.; Homayouni, S.; Safari, A. A Hybrid Kernel-Based Change Detection Method for Remotely Sensed Data in a Similarity Space. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12829–12858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reis, M.S.; Dutra, L.V.; Sant’Anna, S.J.S.; Escada, M.I.S. Examining Multi-Legend Change Detection in Amazon with Pixel and Region Based Methods. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, Y.; Mei, X.; Liu, C.; Ma, J. Hyperspectral Image Classification With Robust Sparse Representation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, Q.; Junyu, D.; Qizhi, X. Improvements in Sample Selection Methods for Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Liu, K.; Du, P.; Sheng, Y. Adaptive affinity propagation with spectral angle mapper for semi-supervised hyperspectral band selection. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 2656–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Du, Q.; Su, H.; Sheng, Y. An Efficient Method for Supervised Hyperspectral Band Selection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Valle, D.; Popescu, S.; Zhang, X.; Mallick, B. Hyperspectral remote sensing of plant biochemistry using Bayesian model averaging with variable and band selection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lin, J.; Yuan, Y. Salient Band Selection for Hyperspectral Image Classification via Manifold Ranking. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 27, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang C I, W.S. Constrained band selection for hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Gunn, S.R.; Damper, R.I.; Nelson, J.D.B. Band Selection for Hyperspectral Image Classification Using Mutual Information. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibarrola-Ulzurrun, E.; Marcello, J.; Gonzalo-Martin, C. Assessment of Component Selection Strategies in Hyperspectral Imagery. Entropy 2017, 19, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Dou, Y.; Zhao, L. A Geometry-Based Band Selection Approach for Hyperspectral Image Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4318–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Geng, X.; Ji, L. Exemplar Component Analysis: A Fast Band Selection Method for Hyperspectral Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Du, Q.; Du, P. Hyperspectral Imagery Visualization Using Band Selection. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2647–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Yang, H. Similarity-Based Unsupervised Band Selection for Hyperspectral Image Analysis. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Li, X. Optimal Clustering Framework for Hyperspectral Band Selection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5910–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, j.; Jiao, L.; Sun, T.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Multiple Kernel Learning Based on Discriminative Kernel Clustering for Hyperspectral Band Selection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 6516–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, Q. Dual-clustering-based hyperspectral band selection by contextual analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1431–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Laio, A. Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks. Science 2014, 344, 1492–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, S.; Tang, G.; Zhu, J.; Li, Q. A novel ranking-based clustering approach for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, R.A.; Patrick, E.A. Clustering Using a Similarity Measure Based on Shared Near Neighbors. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1973, C-22, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Tang, J.; Liang, D. Hyperspectral band selection via rank minimization. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2320–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Uso, A.; Pla, F.; Sotoca, J.M.; Garcia-Sevilla, P. Clustering-based hyperspectral band selection using information measures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 4158–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Data Set | Classifier (Measure) | UBS | E-FDPC | RMBS | OPBS | WaLuDi | SNNC | All Bands |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indian Pines | KNN(AOA) | 64.62 | 71.42 | 58.46 | 58.36 | 57.53 | 71.87 | 69.67 |
| KNN(kappa) | 59.27 | 67.10 | 52.08 | 51.94 | 51.02 | 67.68 | 65.13 | |
| SVM(AOA) | 75.92 | 78.68 | 69.96 | 72.99 | 71.10 | 79.54 | 83.39 | |
| SVM(kappa) | 72.32 | 75.64 | 65.43 | 69.16 | 66.97 | 76.64 | 81.06 | |
| Pavia University | KNN(AOA) | 86.29 | 85.50 | 84.11 | 84.31 | 83.53 | 87.27 | 86.83 |
| KNN(kappa) | 81.45 | 80.31 | 78.37 | 78.67 | 77.65 | 82.76 | 82.15 | |
| SVM(AOA) | 91.51 | 89.25 | 90.35 | 90.84 | 89.37 | 91.79 | 92.81 | |
| SVM(kappa) | 88.69 | 85.64 | 87.07 | 87.78 | 85.81 | 89.04 | 90.42 |
| Method | 11 Selected Bands | ACC | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBS | 15 | 36 | 58 | 82 | 105 | 119 | 136 | 145 | 152 | 162 | 196 | 0.529 |
| E-FDPC | 11 | 26 | 48 | 67 | 88 | 124 | 136 | 163 | 173 | 181 | 186 | 0.436 |
| RMBS | 1 | 2 | 5 | 28 | 34 | 77 | 79 | 103 | 105 | 106 | 144 | 0.440 |
| OPBS | 1 | 3 | 25 | 43 | 59 | 90 | 104 | 120 | 163 | 184 | 200 | 0.285 |
| WuLuDi | 1 | 3 | 5 | 23 | 27 | 35 | 57 | 85 | 104 | 172 | 199 | 0.479 |
| SNNC | 10 | 27 | 44 | 69 | 88 | 112 | 126 | 138 | 158 | 182 | 187 | 0.427 |
| Method | 7 Selected Band | ACC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBS | 7 | 30 | 51 | 73 | 86 | 97 | 101 | 0.475 |
| E-FDPC | 19 | 33 | 52 | 61 | 81 | 92 | 99 | 0.442 |
| RMBS | 1 | 2 | 5 | 28 | 34 | 77 | 79 | 0.597 |
| OPBS | 1 | 31 | 66 | 70 | 74 | 78 | 91 | 0.545 |
| WuLuDi | 2 | 40 | 68 | 69 | 71 | 74 | 89 | 0.638 |
| SNNC | 15 | 31 | 48 | 61 | 90 | 99 | 103 | 0.423 |
| Data Set | UBS | E-FDPC | RMBS | OPBS | WaLuDi | SNNC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indian Pines (11 bands) | 0.040 s | 0.005 s | 44.531 s | 0.013 s | 7.439 s | 0.333 s |
| Pavia University (7 bands) | 0.053 s | 0.015 s | 215.340 s | 0.033 s | 28.257 s | 1.184 s |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Li, X. An Efficient Clustering Method for Hyperspectral Optimal Band Selection via Shared Nearest Neighbor. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030350
Li Q, Wang Q, Li X. An Efficient Clustering Method for Hyperspectral Optimal Band Selection via Shared Nearest Neighbor. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(3):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030350
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qiang, Qi Wang, and Xuelong Li. 2019. "An Efficient Clustering Method for Hyperspectral Optimal Band Selection via Shared Nearest Neighbor" Remote Sensing 11, no. 3: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030350
APA StyleLi, Q., Wang, Q., & Li, X. (2019). An Efficient Clustering Method for Hyperspectral Optimal Band Selection via Shared Nearest Neighbor. Remote Sensing, 11(3), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030350