Bounding Surfaces in a Barchan Dune: Annual Cycles of Deposition? Seasonality or Erosion by Superimposed Bedforms?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Study Site
2. Methods
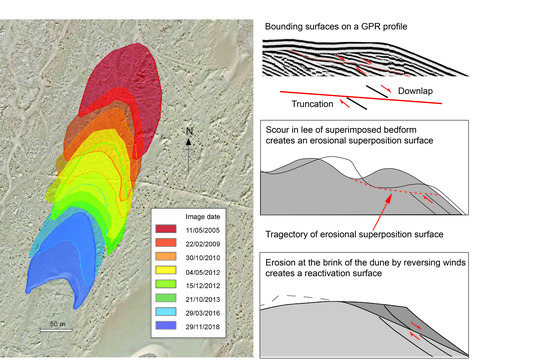
3. Results
3.1. Dune Migration
3.2. GPR Profiles
4. Discussion
4.1. Sand Flux
4.2. Dune Turnover Time and Superimposed Bedforms
4.3. Discussion of GPR Interpretation
4.4. Comparison with the Trench Sections Cut by McKee 1966
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McKee, E.D. A Study of Global Sand Seas; Geological Survey Professional Paper 1052; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1979; 429p.
- Wasson, R.J.; Hyde, R. Factors determining desert dune type. Nature 1983, 304, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R.A. The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes; Methuen & Co. LTD.: London, UK, 1941; 265p. [Google Scholar]
- Finkel, H.J. The Barchans of southern Peru. J. Geol. 1959, 67, 614–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.T.; Sharp, R.P. Barchan-dune movement in imperial valley, California. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1964, 75, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauermann, G.; Rognon, P.; Poliakov, A.; Herrmann, H.J. The shape of the barchan dunes of Southern Morocco. Geomorphology 2000, 36, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ould Ahmedou, D.; Ould Mahfoudh, A.; Dupont, P.; Ould El Moctar, A.; Valance, A.; Rasmussen, K.R. Barchan dune mobility in Mauritania related to dune and interdune sand fluxes. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, F02016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, O.; Parteli, E.J.R.; Herrmann, H.J. A continuous model for sand dunes: Review, new developments and application to barchan dune fields. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 35, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, S.; Avouac, J.-P.; Ayoub, F.; Ewing, R.; Vriend, N.; Heggy, E. Comparing dune migration measured from remote sensing with sand flux prediction based on weather data and model, a test case in Qatar. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 497, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbelrhiti, H.; Claudin, P.; Andreotti, B. Field evidence for surface-wave—Induced instability of sand dunes. Nature 2005, 437, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El belrhiti, H.; Douady, S. Equilibrium versus disequilibrium of barchan dunes. Geomorphology 2011, 125, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, E.D. Structures of dunes at White Sands National Monument, New Mexico (and a comparison with structures of dunes from other selected areas). Sedimentology 1966, 7, 3–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookfield, M.E. The origin of bounding surfaces in ancient aeolian sandstones. Sedimentology 1977, 24, 303–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocurek, G.A. Desert aeolian systems. In Sedimentary Environments: Processes, Facies and Stratigraphy; Reading, H.G., Ed.; Blackwell Science: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 125–153. [Google Scholar]
- Bristow, C.S.; Augustinus, P.C.; Wallis, I.C.; Jol, H.M.; Rhodes, E.J. Investigation of the age and migration of reversing dunes in Antarctica using GPR and OSL, with implications for GPR on Mars. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 289, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loope, D.B. Episodic deposition and preservation of eolian sands—A late Paleozoic example from southeastern Utah. Geology 1985, 13, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.A.; Archer, A.W. Spectral analysis of eolian foreset periodicities: Implications for Jurassic decadal-scale paleoclimatic oscillators. Paleoclimates 1999, 3, 239–255. [Google Scholar]
- Loope, D.B.; Rowe, C.M.; Joeckel, R.M. Annual monsoon rains recorded by Jurassic dunes. Nature 2001, 412, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, C.M.S.; Goldberg, K. Cyclic cross-bedding in the eolian dunes of the Sergi Formation (Upper Jurassic), Reconcavo Basin: Inferences about the wind regime. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2010, 296, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brothers, S.C.; Kocurek, G.; Brothers, T.C.; Buynevich, I.V. Stratigraphic architecture resulting from dune interactions: White Sands Dune Field, New Mexico. Sedimentology 2017, 64, 686–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, M.; Kocurek, G. Aeolian dune interactions preserved in the ancient rock record. Sediment. Geol. 2017, 358, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, C.S.; Pugh, J.; Goodall, T. Internal structure of aeolian dunes in Abu Dhabi determined using ground-penetrating radar. Sedimentology 1996, 43, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, C.S.; Bailey, S.D.; Lancaster, N. The sedimentary structure of linear sand dunes. Nature 2000, 406, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, C.S.; Lancaster, N.; Duller, G.A.T. Combining ground penetrating radar surveys and optical dating to determine dune migration in Namibia. J. Geol. Soc. 2005, 162, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, C.S.; Duller, G.A.T.; Lancaster, N. Age and dynamics of linear dunes in the Namib desert. Geology 2007, 35, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, C.S. Ground-Penetrating Radar in Dune Sands. In Ground Penetrating Radar: Theory and Applications; Jol, H.M., Ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 273–297. [Google Scholar]
- Guillemoteau, J.; Bano, M.; Dujardin, J.-R. Influence of grainsize, shape and compaction on georadar waves; examples of an aeolian dune. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 190, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardi, J.D.; Davis, D.M. Parabolic dune reactivation and migration at Napeague, NY, USA: Insights from aerial and GPR imagery. Geomorphology 2010, 114, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quian, R.; Liu, L. Internal structure of sand dunes in the Badain Jaran Desert revealed by GPR. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.D.; Ewing, R.C.; Bowling, R.; Weymer, B.A.; Barrineau, P.; Nittrouer, J.A.; Everett, M.E. Low-angle eolian deposits formed by protodune migration, insights into slipface development at White Sands Dune field, New Mexico. Aeolian Res. 2019, 36, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbelrhiti, H.; Andreotti, B.; Claudin, P. Barchan dune corridors: Field characterization and investigation of control parameters. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, F02S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jol, H.M.; Bristow, C.S. GPR in Sediments:advice on data collection, basic processing and interpretation, a good practice guide. In Ground Penetrating Radar in Sediments; Bristow, C.S., Jol, H.M., Eds.; Geological Society London Special Publication: London, UK, 2003; Volume 211, pp. 9–27. [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy, N. Ground-Penetrating Radar Data Processing, Modelling and Analysis. In Ground Penetrating Radar: Theory and Applications; Jol, H.M., Ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 141–176. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, J.M. An Introduction to Applied and Environmental Geophysics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997; 796p. [Google Scholar]
- Parteli, E.J.R.; Duran, O.; Bourke, M.C.; Tsoar, H.; Poschel, T.; Herrmann, H. Origins of barchan dune asymmetry: Insights from numerical simulations. Aeolian Res. 2014, 12, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bristow, C.S.; Mountney, N. Eolian landscapes: Eolian statigraphy. In Treatise on Geomorphology; Shroder, J., Lancaster, N., Eds.; Academic Press: Sand Diego, CA, USA, 2012; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, R.U.; Warren, A.; Goudie, A.S. Desert Geomorphology; UCL Press: London, UK, 1993; 526p. [Google Scholar]








| Date | Width Wd (m) | Width Wh (m) | Length Ld (m) | East Horn La (m) | West Horn Lb (m) | La/Lb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11/05/2005 | 122 | 103 | 94 | 78 | 43 | 1.8 |
| 25/02/2009 | 127 | 104 | 104 | 63 | 33 | 1.9 |
| 30/10/2010 | 129 | 110 | 104 | 57 | 36 | 1.6 |
| 04/05/2012 | 126 | 106 | 104 | 59 | 37 | 1.6 |
| 15/12/2012 | 116 | 97.5 | 103 | 49 | 26 | 1.9 |
| 21/10/2013 | 117 | 103 | 108 | 60 | 33 | 1.8 |
| 29/03/2016 | 106 | 98.7 | 94 | 56 | 46 | 1.2 |
| 29/11/2018 | 103 | 79 | 105 | 39 | 42 | 0.9 |
| Mean | 118.25 | 100.15 | 102 | 57.6 | 37 | |
| Standard deviation | 9.7 | 9.4 | 5.2 | 11.2 | 6.5 |
| Image Date from | Image Date to | Time Difference (years) | Distance Moved (m) | Annual Migration Rate (m/yr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11/05/2005 | 25/02/2009 | 3.6 | 85 | 23.6 |
| 25/02/2009 | 30/10/2010 | 1.68 | 32 | 19 |
| 30/10/2010 | 04/05/2012 | 1.58 | 33 | 20.1 |
| 04/05/2012 | 15/12/2012 | 0.88 | 13 | 22.4 |
| 15/12/2012 | 21/10/2013 | 0.84 | 12 | 14.3 |
| 21/10/2013 | 29/03/2016 | 2.4 | 53 | 22 |
| 29/03/2016 | 29/11/2018 | 2.7 | 58 | 21.5 |
| 11/05/2005 | 29/11/2018 | 13.55 | 290 | 21.4 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bristow, C.S. Bounding Surfaces in a Barchan Dune: Annual Cycles of Deposition? Seasonality or Erosion by Superimposed Bedforms? Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11080965
Bristow CS. Bounding Surfaces in a Barchan Dune: Annual Cycles of Deposition? Seasonality or Erosion by Superimposed Bedforms? Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(8):965. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11080965
Chicago/Turabian StyleBristow, Charles S. 2019. "Bounding Surfaces in a Barchan Dune: Annual Cycles of Deposition? Seasonality or Erosion by Superimposed Bedforms?" Remote Sensing 11, no. 8: 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11080965
APA StyleBristow, C. S. (2019). Bounding Surfaces in a Barchan Dune: Annual Cycles of Deposition? Seasonality or Erosion by Superimposed Bedforms? Remote Sensing, 11(8), 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11080965