Biomass Burning in Africa: An Investigation of Fire Radiative Power Missed by MODIS Using the 375 m VIIRS Active Fire Product
Abstract
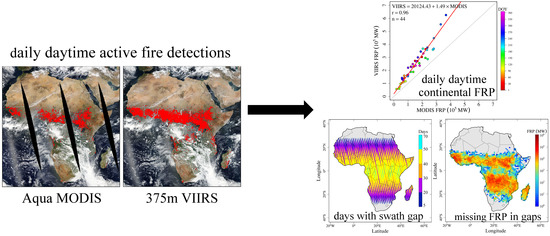
:1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. MODIS Sensing Geometry and Active Fire Data
2.2. VIIRS I-band Sensing Geometry and Active Fire Data
3. Methods
3.1. Correction of Inter-Scanline Repeat Fire Detections
3.2. Investigation of Missing MODIS FRP Due to Sampling Limitations
3.2.1. Extraction of Contemporaneous Fire Detections
3.2.2. Examination of Fire Detection Capability
3.2.3. Comparison of FRP on a Continental Scale and Various Grid Sizes
3.2.4. Adjustment of Grid-Level MODIS FRP
3.3. Investigation of Missing MODIS FRP inside Equatorial Swath Gaps
4. Results
4.1. Fire Detection Capability across Swath
4.2. Continental-Scale FRP
4.3. Grid-Level FRP
4.3.1. Missing MODIS FRP Due to Sampling Limitations
4.3.2. Underestimation of MODIS Grid FRP and Adjustment Models
4.4. Missing FRP inside MODIS Swath Gaps
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Calculation of the Cross-Meridian Width of a MODIS Swath Gap

References
- Crutzen, P.J.; Andreae, M.O. Biomass Burning in the Tropics: Impact on Atmospheric Chemistry and Biogeochemical Cycles. Science 1990, 250, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, D.M.J.S.; Balch, J.K.; Artaxo, P.; Bond, W.J.; Carlson, J.M.; Cochrane, M.A.; D’Antonio, C.M.; DeFries, R.S.; Doyle, J.C.; Harrison, S.P.; et al. Fire in the Earth System. Science 2009, 324, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Boschetti, L.; Roy, D.P.; Humber, M.L.; Justice, C.O. The Collection 6 MODIS burned area mapping algorithm and product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Randerson, J.T.; van der Werf, G.R. Analysis of daily, monthly, and annual burned area using the fourth-generation global fire emissions database (GFED4). J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2013, 118, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Werf, G.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Giglio, L.; van Leeuwen, T.T.; Chen, Y.; Rogers, B.M.; Mu, M.; van Marle, M.J.E.; Morton, D.C.; Collatz, G.J.; et al. Global fire emissions estimates during 1997–2016. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 697–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Randerson, J.T.; Chen, Y.; van der Werf, G.R.; Rogers, B.M.; Morton, D.C. Global burned area and biomass burning emissions from small fires. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2012, 117, G04012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roteta, E.; Bastarrika, A.; Padilla, M.; Storm, T.; Chuvieco, E. Development of a Sentinel-2 burned area algorithm: Generation of a small fire database for sub-Saharan Africa. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Justice, C.O.; Flynn, L.P.; Kendall, J.D.; Prins, E.M.; Giglio, L.; Ward, D.E.; Menzel, W.P.; Setzer, A.W. Potential global fire monitoring from EOS-MODIS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 32215–32238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, B.M.; Soja, A.J.; Goulden, M.L.; Randerson, J.T. Influence of tree species on continental differences in boreal fires and climate feedbacks. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.S.; Wooster, M.J. Remote classification of head and backfire types from MODIS fire radiative power and smoke plume observations. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2005, 14, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wooster, M.J.; Zhang, Y.H. Boreal forest fires burn less intensely in Russia than in North America. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L20505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freeborn, P.H.; Jolly, W.M.; Cochrane, M.A. Impacts of changing fire weather conditions on reconstructed trends in U.S. wildland fire activity from 1979 to 2014. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 2856–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paugam, R.; Wooster, M.; Freitas, S.; Val Martin, M. A review of approaches to estimate wildfire plume injection height within large-scale atmospheric chemical transport models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peterson, D.; Hyer, E.; Wang, J. Quantifying the potential for high-altitude smoke injection in the North American boreal forest using the standard MODIS fire products and subpixel-based methods. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 3401–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Kaufman, Y.J. A method to derive smoke emission rates from MODIS fire radiative energy measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2636–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, M.J.; Zhukov, B.; Oertel, D. Fire radiative energy for quantitative study of biomass burning: Derivation from the BIRD experimental satellite and comparison to MODIS fire products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 83–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeborn, P.H.; Wooster, M.J.; Hao, W.M.; Ryan, C.A.; Nordgren, B.L.; Baker, S.P.; Ichoku, C. Relationships between energy release, fuel mass loss, and trace gas and aerosol emissions during laboratory biomass fires. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D01301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremens, R.L.; Dickinson, M.B.; Bova, A.S. Radiant flux density, energy density and fuel consumption in mixed-oak forest surface fires. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2012, 21, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalov, I.B.; Berezin, E.V.; Ciais, P.; Broquet, G.; Beekmann, M.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Clerbaux, C.; Andreae, M.O.; Kaiser, J.W.; Schulze, E.D. Constraining CO2 emissions from open biomass burning by satellite observations of co-emitted species: A method and its application to wildfires in Siberia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 10383–10410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Kondragunta, S.; Roy, D.P. Investigation of the Fire Radiative Energy Biomass Combustion Coefficient: A Comparison of Polar and Geostationary Satellite Retrievals Over the Conterminous United States. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2018, 123, 722–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Cochrane, M.A. Investigating Smoke Aerosol Emission Coefficients using MODIS Active Fire and Aerosol Products—A Case Study in the CONUS and Indonesia. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2019, 124, 1413–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, B.; Wooster, M.J. A new top-down approach for directly estimating biomass burning emissions and fuel consumption rates and totals from geostationary satellite fire radiative power (FRP). Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaiser, J.W.; Heil, A.; Andreae, M.O.; Benedetti, A.; Chubarova, N.; Jones, L.; Morcrette, J.J.; Razinger, M.; Schultz, M.G.; Suttie, M.; et al. Biomass burning emissions estimated with a global fire assimilation system based on observed fire radiative power. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 527–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermote, E.; Ellicott, E.; Dubovik, O.; Lapyonok, T.; Chin, M.; Giglio, L.; Roberts, G.J. An approach to estimate global biomass burning emissions of organic and black carbon from MODIS fire radiative power. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D18205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Ellison, L. Global top-down smoke-aerosol emissions estimation using satellite fire radiative power measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6643–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Roy, D.P.; Kondragunta, S. Estimation of biomass-burning emissions by fusing the fire radiative power retrievals from polar-orbiting and geostationary satellites across the conterminous United States. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 211, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kondragunta, S.; Da Silva, A.; Lu, S.; Ding, H.; Li, F.; Zhu, Y. The Blended Global Biomass Burning Emissions Product from MODIS, VIIRS, and Geostaionary Satellites (GBBEPx) Version 3.1. Available online: http://www.ospo.noaa.gov/Products/land/gbbepx/docs/GBBEPx_ATBD.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Zhang, X.; Kondragunta, S.; Ram, J.; Schmidt, C.; Huang, H.-C. Near-real-time global biomass burning emissions product from geostationary satellite constellation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D14201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeborn, P.H.; Wooster, M.J.; Roberts, G. Addressing the spatiotemporal sampling design of MODIS to provide estimates of the fire radiative energy emitted from Africa. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Roy, D.P.; Boschetti, L.; Kremens, R. Exploiting the power law distribution properties of satellite fire radiative power retrievals: A method to estimate fire radiative energy and biomass burned from sparse satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D19303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Kondragunta, S.; Csiszar, I. Comparison of Fire Radiative Power Estimates From VIIRS and MODIS Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 4545–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, I.; Hüser, I.; Zhang, T.; Gehrke, B.; Kaiser, J.W. Correcting Swath-Dependent Bias of MODIS FRP Observations With Quantile Mapping. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pyne, S.J.; Andrews, P.L.; Laven, R.D. Introduction to Wildland Fire; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Bhattacharjee, P.S.; Tallapragada, V.; Lu, C.H.; Kondragunta, S.; da Silva, A.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.P.; Wei, S.W.; Darmenov, A.S.; et al. The implementation of NEMS GFS Aerosol Component (NGAC) Version 2.0 for global multispecies forecasting at NOAA/NCEP – Part 1: Model descriptions. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 2315–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Earl, N.; Simmonds, I.; Tapper, N. Weekly cycles of global fires—Associations with religion, wealth and culture, and insights into anthropogenic influences on global climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 9579–9589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolfe, R.E.; Nishihama, M.; Fleig, A.J.; Kuyper, J.A.; Roy, D.P.; Storey, J.C.; Patt, F.S. Achieving sub-pixel geolocation accuracy in support of MODIS land science. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Rogan, J.; Schneider, L.; Cochrane, M. Evaluating MODIS active fire products in subtropical Yucatán forest. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Loboda, T.; Roy, D.P.; Quayle, B.; Justice, C.O. An active-fire based burned area mapping algorithm for the MODIS sensor. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedinmyer, C.; Akagi, S.K.; Yokelson, R.J.; Emmons, L.K.; Al-Saadi, J.A.; Orlando, J.J.; Soja, A.J. The Fire INventory from NCAR (FINN): A high resolution global model to estimate the emissions from open burning. Geosci. Model Dev. 2011, 4, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroeder, W.; Oliva, P.; Giglio, L.; Csiszar, I.A. The New VIIRS 375 m active fire detection data product: Algorithm description and initial assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csiszar, I.; Schroeder, W.; Giglio, L.; Ellicott, E.; Vadrevu, K.P.; Justice, C.O.; Wind, B. Active fires from the Suomi NPP Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite: Product status and first evaluation results. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wooster, M.J.; Xu, W. Approaches for synergistically exploiting VIIRS I- and M-Band data in regional active fire detection and FRP assessment: A demonstration with respect to agricultural residue burning in Eastern China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vadrevu, K.; Lasko, K. Intercomparison of MODIS AQUA and VIIRS I-Band Fires and Emissions in an Agricultural Landscape—Implications for Air Pollution Research. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolfe, R.E.; Lin, G.; Nishihama, M.; Tewari, K.P.; Tilton, J.C.; Isaacman, A.R. Suomi NPP VIIRS prelaunch and on-orbit geometric calibration and characterization. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 11508–11521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolfe, R.E.; Roy, D.P.; Vermote, E. MODIS land data storage, gridding, and compositing methodology: Level 2 grid. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freeborn, P.H.; Wooster, M.J.; Roy, D.P.; Cochrane, M.A. Quantification of MODIS fire radiative power (FRP) measurement uncertainty for use in satellite-based active fire characterization and biomass burning estimation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1988–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Schroeder, W.; Hall, J.V.; Justice, C.O. MODIS Collection 6 Active Fire Product User’s Guide. Available online: http://modis-fire.umd.edu/files/MODIS_C6_Fire_User_Guide_B.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Giglio, L.; Schroeder, W.; Justice, C.O. The collection 6 MODIS active fire detection algorithm and fire products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, C.; Luccia, F.J.D.; Xiong, X.; Wolfe, R.; Weng, F. Early On-Orbit Performance of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite Onboard the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (S-NPP) Satellite. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1142–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroeder, W.; Giglio, L. NASA SPIS 375 m & 750 m Active Fire Detection Product User’s Guide Version 1.4. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/documents/427/VNP14_User_Guide_V1.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Roberts, G.; Wooster, M.J.; Lagoudakis, E. Annual and diurnal african biomass burning temporal dynamics. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 849–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, R.J. Use and misuse of the reduced major axis for line-fitting. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2009, 140, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Li, Z. Enhancement of a fire-detection algorithm by eliminating solar contamination effects and atmospheric path radiance: Application to MODIS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 6273–6293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.; Richter, D.; Strobl, C.; Schläpfer, D. Solar Influence on Fire Radiative Power Retrieved With the Bispectral Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4521–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, W.; Csiszar, I.; Morisette, J. Quantifying the impact of cloud obscuration on Remote Sens. of active fires in the Brazilian Amazon. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, C.O.; Giglio, L.; Korontzi, S.; Owens, J.; Morisette, J.T.; Roy, D.; Descloitres, J.; Alleaume, S.; Petitcolin, F.; Kaufman, Y. The MODIS fire products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibald, S.; Lehmann, C.E.R.; Gómez-Dans, J.L.; Bradstock, R.A. Defining pyromes and global syndromes of fire regimes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6442–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, J.; Trainer, M.; Murphy, D.; Brown, S.; Brewer, A.; Gao, R.S.; Fahey, D. Fire Influence on Regional to Global Environments and Air Quality (FIREX-AQ). Available online: https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/csd/projects/firex-aq/whitepaper.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2020).











| Grid Size (Degree) | Model Parameters | r2 | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β0 | β1 | β2 | |||
| 0.05 | 1.054 ± 0.02 ** | −0.045 ± 0.08 | −0.223 ± 0.07 ** | 0.93 | 0.026 |
| 0.10 | 1.133 ± 0.02 ** | 0.030 ± 0.08 | −0.265 ± 0.07 ** | 0.91 | 0.028 |
| 0.25 | 1.313 ± 0.02 ** | −0.006 ± 0.09 | 0.141 ± 0.07 ** | 0.74 | 0.030 |
| 0.50 | 1.401 ± 0.04 ** | 0.004 ± 0.16 | 0.074 ± 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.054 |
| 1.0 | 1.456 ± 0.05 ** | −0.085 ± 0.22 | 0.369 ± 0.18 ** | 0.72 | 0.070 |
| 2.5 | 1.564 ± 0.08 ** | −0.295 ± 0.35 * | 0.672 ± 0.29 ** | 0.68 | 0.113 |
| 5.0 | 1.690 ± 0.12 ** | −0.851 ± 0.48 ** | 1.219 ± 0.40 ** | 0.67 | 0.146 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Kondragunta, S. Biomass Burning in Africa: An Investigation of Fire Radiative Power Missed by MODIS Using the 375 m VIIRS Active Fire Product. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101561
Li F, Zhang X, Kondragunta S. Biomass Burning in Africa: An Investigation of Fire Radiative Power Missed by MODIS Using the 375 m VIIRS Active Fire Product. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(10):1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101561
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Fangjun, Xiaoyang Zhang, and Shobha Kondragunta. 2020. "Biomass Burning in Africa: An Investigation of Fire Radiative Power Missed by MODIS Using the 375 m VIIRS Active Fire Product" Remote Sensing 12, no. 10: 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101561
APA StyleLi, F., Zhang, X., & Kondragunta, S. (2020). Biomass Burning in Africa: An Investigation of Fire Radiative Power Missed by MODIS Using the 375 m VIIRS Active Fire Product. Remote Sensing, 12(10), 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101561