Shear-Wave Tomography Using Ocean Ambient Noise with Interference
Abstract
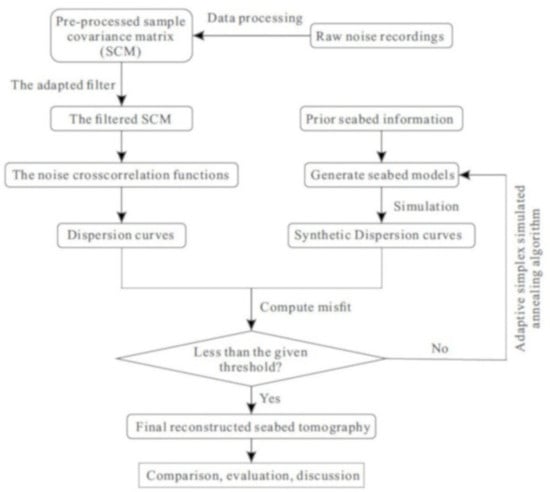
:1. Introduction
2. Array Geometry and Noise Analysis
2.1. Array Geometry
2.2. Noise Analysis
2.2.1. The ‘Natural Ambient Noise’
2.2.2. Event A
2.2.3. Event B
2.2.4. Events C
2.2.5. Discussion of the Events
2.2.6. Additional Insights on the Events
3. NCC Retrieval Using the Adapted Eigenvalue-Based Filter
3.1. An Overview of the Adapted Eigenvalue-Based Filter
3.2. The Result
3.2.1. Beamforming
3.2.2. The NCC Retrieval
4. Shear-Wave Tomography
4.1. The ASSA Inversion
4.2. Seabed Parameterizations
4.3. Tomography Result
5. Discussion
5.1. Depth Sensitivity
5.2. Tomography Resolution
5.3. Non-Uniqueness and Uncertainty
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PSI | Passive seismic interferometry |
| NCC | Noise crosscorrelations |
| 1D/2D/3D | 1/2/3 dimensional |
| PRMRA | Permanent reservoir monitoring receiver array |
| SCM | Sample covariance matrix |
| ASSA | Adaptive simplex simulated annealing algorithm |
Appendix A. The Strategies to Determine and K
Appendix A.1. The Determination of
Appendix A.2. The Determination of K
References
- Campillo, M.; Paul, A. Long-range correlations in the diffuse seismic coda. Science 2003, 299, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wapenaar, K. Retrieving the elastodynamic Green’s function of an arbitrary inhomogeneous medium by cross correlation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 254301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Draganov, D.; Wapenaar, K.; Thorbecke, J. Seismic interferometry: Reconstructing the earth’s reflection response. Geophysics 2006, 71, SI61–SI70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Ridder, S.; Biondi, B. Daily reservoir-scale subsurface monitoring using ambient seismic noise. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2969–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermann, A.; Froment, B.; Campillo, M.; Larose, E.; Planes, T.; Valette, B.; Chen, J.; Liu, Q. Seismic noise correlations to image structural and mechanical changes associated with the Mw 7.9 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 3155–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermann, A.; Kraft, T.; Larose, E.; Wiemer, S. Potential of ambient seismic noise techniques to monitor the St. Gallen geothermal site (Switzerland). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 4301–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aki, K. Space and time spectra of stationary stochastic waves, with special reference to microtremors. Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. 1957, 35, 415–456. [Google Scholar]
- Claerbout, J.F. Synthesis of a layered medium from its acoustic transmission response. Geophysics 1968, 33, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, R.L.; Lobkis, O.I. Ultrasonics without a source: Thermal fluctuation correlations at MHz frequencies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 134301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, R.L.; Lobkis, O.I. On the emergence of the Green’s function in the correlations of a diffuse field. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2001, 110, 3011–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derode, A.; Larose, E.; Tanter, M.; De Rosny, J.; Tourin, A.; Campillo, M.; Fink, M. Recovering the Green’s function from field-field correlations in an open scattering medium (L). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 113, 2973–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wapenaar, K. Synthesis of an inhomogeneous medium from its acoustic transmission response. Geophysics 2003, 68, 1756–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roux, P.; Sabra, K.G.; Kuperman, W.A.; Roux, A. Ambient noise cross correlation in free space: Theoretical approach. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 117, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rickett, J.; Claerbout, J. Acoustic daylight imaging via spectral factorization: Helioseismology and reservoir monitoring. Lead. Edge 1999, 18, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roux, P.; Fink, M. Green’s function estimation using secondary sources in a shallow water environment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 113, 1406–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehly, L.; Fry, B.; Campillo, M.; Shapiro, N.; Guilbert, J.; Boschi, L.; Giardini, D. Tomography of the Alpine region from observations of seismic ambient noise. Geophys. J. Int. 2009, 178, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pilz, M.; Parolai, S.; Bindi, D. Three-dimensional passive imaging of complex seismic fault systems: Evidence of surface traces of the Issyk-Ata fault (Kyrgyzstan). Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 194, 1955–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mordret, A.; Landès, M.; Shapiro, N.; Singh, S.; Roux, P. Ambient noise surface wave tomography to determine the shallow shear velocity structure at Valhall: Depth inversion with a Neighbourhood Algorithm. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 198, 1514–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galetti, E.; Curtis, A.; Baptie, B.; Jenkins, D.; Nicolson, H. Transdimensional Love-wave tomography of the British Isles and shear-velocity structure of the East Irish Sea Basin from ambient-noise interferometry. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 208, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, F.C.; Schmandt, B.; Farrell, J. Ambient noise tomography across Mount St. Helens using a dense seismic array. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 4492–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, R.L. Equipartition and retrieval of Green’s function. Earthq. Sci. 2010, 23, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.; Dong, H.; Ke, G.; Song, J. An adapted eigenvalue-based filter for ocean ambient noise processing. Geophysics 2019, 85, KS29–KS38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, V.C. On establishing the accuracy of noise tomography travel-time measurements in a realistic medium. Geophys. J. Int. 2009, 178, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, V.C. Understanding the amplitudes of noise correlation measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2011, 116, B09311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Froment, B.; Campillo, M.; Roux, P.; Gouedard, P.; Verdel, A.; Weaver, R.L. Estimation of the effect of nonisotropically distributed energy on the apparent arrival time in correlations. Geophysics 2010, 75, SA85–SA93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fichtner, A. Source and processing effects on noise correlations. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 197, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fichtner, A.; Stehly, L.; Ermert, L.; Boehm, C. Generalised interferometry-I: Theory for inter-station correlations. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 208, 603–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, B. Marine ambient seismic noise in the frequency range 1–10 Hz. Lead. Edge 2010, 29, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Choi, H. Response modification factors of chevron-braced frames. Eng. Struct. 2005, 27, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydoux, L.; de Rosny, J.; Shapiro, N.M. Pre-processing ambient noise cross-correlations with equalizing the covariance matrix eigenspectrum. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 210, 1432–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMechan, G.A.; Yedlin, M.J. Analysis of dispersive waves by wave field transformation. Geophysics 1981, 46, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosso, S.; Wilmut, M.; Lapinski, A.L. An adaptive-hybrid algorithm for geoacoustic inversion. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2001, 26, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M. DISPER80: A subroutine package for the calculation of seismic normal mode solutions. In Seismological Algorithms; Cinii: Tokyo, Japan, 1980; pp. 293–319. [Google Scholar]
- Castagna, J.P.; Batzle, M.L.; Eastwood, R.L. Relationships between compressional-wave and shear-wave velocities in clastic silicate rocks. Geophysics 1985, 50, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocher, T.M. Empirical Relations between Elastic Wavespeeds and Density in the Earth’s Crust. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2005, 95, 2081–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, E.; Hoeber, H.; Houbiers, M.; Lescoffit, S.P.; Ratcliffe, A.; Vinje, V. Time-lapse full-waveform inversion as a reservoir-monitoring tool—A North Sea case study. Lead. Edge 2016, 35, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Hansteen, F.; Curtis, A. Fully 3D Monte Carlo Ambient Noise Tomography over Grane Field. In Proceedings of the 81st EAGE Conference and Exhibition 2019, London, UK, 3–6 June 2019; Volume 2019, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]













| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| M | Number of models in the simplex | 11 |
| Initial temperature | ||
| Temperature decrease frequency | 10 | |
| Temperature reduction factor | 0.995 | |
| Convergence tolerance | 0.001 | |
| Standard deviation of data (km/s) | 0.1 |
| Parameter | Bound (km/s) | Parameter | Bound (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [0.1, 0.5] | [0.01, 0.10] | ||
| [0.2, 1.0] | [0.05, 0.80] | ||
| [0.3, 2.0] | [0.10, 0.80] | ||
| [0.3, 2.0] | [0.20, 0.80] | ||
| [0.3, 2.0] | semi-infinite | ||
| 0 | D | 0.125 | |
| 1.49 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, G.; Dong, H.; Ke, G.; Song, J. Shear-Wave Tomography Using Ocean Ambient Noise with Interference. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2969. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182969
Wu G, Dong H, Ke G, Song J. Shear-Wave Tomography Using Ocean Ambient Noise with Interference. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(18):2969. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182969
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Guoli, Hefeng Dong, Ganpan Ke, and Junqiang Song. 2020. "Shear-Wave Tomography Using Ocean Ambient Noise with Interference" Remote Sensing 12, no. 18: 2969. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182969
APA StyleWu, G., Dong, H., Ke, G., & Song, J. (2020). Shear-Wave Tomography Using Ocean Ambient Noise with Interference. Remote Sensing, 12(18), 2969. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182969