Updating of Land Cover Maps and Change Analysis Using GlobeLand30 Product: A Case Study in Shanghai Metropolitan Area, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sets
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sets
2.2.1. GlobeLand30
2.2.2. Landsat Imagery
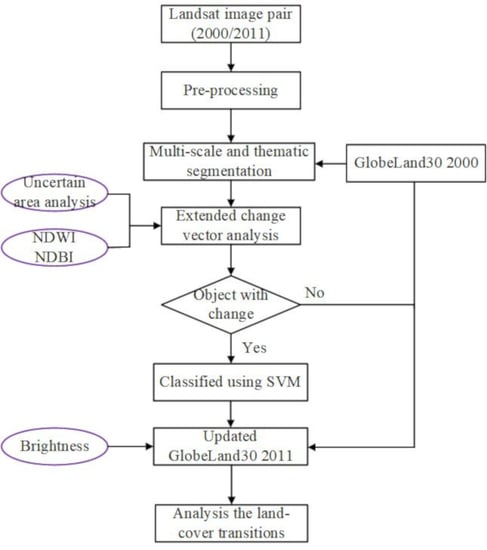
3. Method
3.1. Data Pre-Processing and Multiresolution Segmentation
3.2. Change Detection with Extended Change Vector Analysis
3.3. Updating of GlobeLand30 to 2011 by Transfer Learning
3.4. Accuracy Assessment
4. Results
4.1. Results of Change Detection and Method Comparison
4.2. Results of Land Cover Classification and Method Comparison
4.3. Results of Land Cover Changes Over the Past Decade
5. Discussion
5.1. The Influence of the Accuracy of the Base Map on Updating
5.2. Influence of ECVA on Updating
5.3. Influence of Object-Based Analysis on Updating
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, X.; Wen, D.W.; Li, J.Y.; Qin, R.J. Multi-level monitoring of subtle urban changes for the megacities of China using high-resolution multi-view satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 56, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Homer, C.; Fry, J. Updating the 2001 national land cover database land cover classification to 2006 by using Landsat imagery change detection methods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1133–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, M.C.; Loveland, T.R. A review of large area monitoring of land cover change using Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppin, P.; Jonckheere, I.; Nackaerts, K.; Muys, B. Digital change detection methods in ecosystem monitoring: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 10, 1565–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; Defries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S., III; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zell, E.; Huff, A.K.; Carpenter, A.T.; Friedl, L.A. A user-driven approach to determining critical earth observation priorities for societal benefit. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Qin, Y.Y.; Li, Z.B.; Mondini, A.C.; Casagli, N. Landslide mapping from multi-sensor data through improved change detection-based Markov random field. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Defries, R.S.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Sohlberg, R. Global land cover classification at 1 km spatial resolution using a classification tree approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1331–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, R.; Zhang, B.; Tong, Q.X. Land cover classification of the north china plain using MODIS_EVI time series. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulla-Menashe, D.; Friedl, M.A.; Krankina, O.N.; Baccini, A.; Woodcock, C.E.; Sibley, A.; Sun, G.; Kharuk, V.; Elsakov, V. Hierarchical mapping of northern Eurasian land cover using MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.S.; Yamaguchi, Y. An automated approach for updating land cover maps based on integrated change detection and classification methods. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 71, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.A.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.V.; Loveland, T.R.; Kommareddy, A.; et al. High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science 2013, 342, 851–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa, H.; Carrao, H.; Bação, F.; Caetano, M. Combining per-pixel and object-based classifications for mapping land cover over large areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Pei, F.; Wang, S. High-resolution multi-temporal mapping of global urban land using Landsat images based on the Google Earth Engine Platform. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveland, T.R.; Reed, B.C.; Brown, J.F.; Ohlen, D.O.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, L.; Merchant, J.W. Development of a GLC characteristics database and IGBP discover from 1 km AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1303–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; McIver, D.K.; Hodges, J.C.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Muchoney, D.; Strahler, A.H.; Woodcock, C.E.; Gopal, S.; Schneider, A.; Cooper, A.; et al. Global land cover mapping from MODIS: Algorithms and early results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Tan, B.; Schneider, A.; Ramankutty, N.; Sibley, A.; Huang, X. MODIS collection 5 global land cover: Algorithm refinements and characterization of new datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomé, E.; Belward, A.S. GLC2000: A new approach to GLC mapping from earth observation data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 1959–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontemps, S.; Defourney, P.; Bogaert, E.V.; Arino, O.; Kalogirou, V.; Perez, J.R. GlobCover2009 Products Description and Validation Report. 2010. Available online: http://due.esrin.esa.int/globcover/LandCover2009/GLOBCOVER2009_Validation_Report_2.2.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2019).
- Tateishi, R.; Uriyangqai, B.; Al-Bilbisi, H.; Ghar, M.A.; Tsend-Ayush, J.; Kobayashi, T.; Kasimu, A.; Hoan, N.T.; Shalaby, A.; Alsaaideh, B.; et al. Production of global land cover-GLCNMO. Int. J. Digit. Earth. 2011, 4, 22–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A.; Cao, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Han, G.; Peng, S.; Lu, M.; et al. Global land cover mapping at 30 m resolution: A POK-based operational approach. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 103, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogelmann, J.; Howard, S.M.; Yang, L.M.; Larson, C.R.; Wylie, B.K.; Van Driel, N. Completion of the 1990′s National Land Cover Data Set for the conterminous United States from Landsat Thematic Mapper data and ancillary data sources. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2001, 67, 650–662. [Google Scholar]
- Homer, C.; Dewitz, J.; Fry, J.; Coan, M.J.; Hossain, N.; Larson, C.; Herold, N.; McKerrow, A.J.; VanDriel, J.N.; Wickham, J. Completion of the 2001 National Land Cover Database for the conterminous United States. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2007, 73, 337–341. [Google Scholar]
- Homer, C.; Dewitz, J.; Yang, L.M.; Jin, S.M.; Danielson, P.; Xian, G.; Coulston, J.; Herold, N.; Wickham, J.; Megown, K. Completion of the 2011 national land cover database for the conterminous United States-representing a decade of land cover change information. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2015, 81, 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Gong, P. Improving 30 m global land-cover map FROM-GLC with time series MODIS and auxiliary data sets: A segmentation-based approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 5851–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, L.; Marconcini, M. Toward the automatic updating of land-cover maps by a domain-adaptation SVM classifier and a circular validation strategy. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 1108–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.J.; Zhou, W.Q.; Qian, Y.G.; Yan, J.L. A new approach for land cover classification and change analysis: Integrating backdating and an object-based method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.M.; Yang, L.M.; Danielson, P.; Homer, C.; Fry, J.; Xian, G. A comprehensive change detection method for updating the national land cover database to circa 2011. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.M.; Yang, L.M.; Zhu, Z.; Homer, C. A land cover change detection and classification protocol for updating Alaska NLCD 2001 to 2011. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 195, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.F.; Dong, Y.; Batunacun. An automatic approach for land-change detection and land updates based on integrated NDVI timing analysis and the CVAPS method with GEE support. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 146, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Du, P.J.; Samat, A.; Li, E.Z.; Wang, X.; Xia, J.S. Automatic updating of land cover maps in rapidly urbanizing regions by relational knowledge transferring from GlobeLand30. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demir, B.; Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L. Updating land-cover maps by classification of image time series: A novel change-detection-driven transfer learning approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, K.J.; Van den Bergh, F.; Roy, D.P.; Salmon, B.P.; Steenkamp, K.C.; MacAlister, B.; Swanepoel, D.; Jewitt, D. Rapid land cover map updates using change detection and robust random forest classifiers. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, T.J.; Luo, J.C.; Zhou, Y.N.; Wang, C.P.; Xi, J.B.; Fang, J.W. Geo-object-based land cover map update for high-spatial-resolution remote sensing images via change detection and label transfer. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ban, Y.F.; Gong, P.; Gini, C. Global land cover mapping using Earth observation satellite data: Recent progresses and challenges. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2011 Revision; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, J.; Furberg, D.; Ban, Y.F. Satellite monitoring of urbanization and environmental impacts-a comparison of Stockholm and Shanghai. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 38, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homer, C.; Huang, C.Q.; Yang, L.M.; Wylie, B.; Coan, M. Development of a 2001 national land-cover database for the United States. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2004, 70, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.Y.; Lo, C.P. Relative radiometric normalization performance for change detection from multi-date satellite images. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 967–980. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.Q.; Troy, A. An object-oriented approach for analyzing and characterizing urban landscape at the parcel level. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3119–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.Q.; Troy, A.; Grove, J.M. Object-based land cover classification and change analysis in the Baltimore metropolitan area using multitemporal high resolution remote sensing data. Sensors 2008, 8, 1613–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaschke, T. Object based image analysis for remote sensing. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benz, U.C.; Hofmann, P.; Willhauck, G.; Lingenfelder, I.; Heynen, M. Multi-resolution, object-oriented fuzzy analysis of remote sensing data for GIS-ready information. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2004, 58, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.L.; Landry, S.; Yu, Q. Object-based urban detailed land cover classification with high spatial resolution IKONOS imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 3285–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.Y.; Wei, A.; Shi, P.J.; Zhang, Q.F.; Zhao, Y.Y. Detecting land-use/land-cover change in rural–urban fringe areas using extended change-vector analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.C.; Gong, P.; Liang, L. A 30-year (1984–2013) record of annual urban dynamics of Beijing city derived from Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 166, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.F.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, D.G.; Yuan, M.; Feng, X.Z.; Kelly, M. Change detection of built-up land: A framework of combining pixel-based detection and object-based recognition. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desclée, B.; Bogaert, P.; Defourny, P. Forest change detection by statistical object-based method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.B.; Shi, W.Z.; Lu, P.; Yan, L.; Wang, Q.M.; Miao, Z.L. Landslide mapping from aerial photographs using change detection-based Markov Random Field. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Gong, P.; He, C.Y.; Pu, R.L.; Shi, P.J. Land-use/land-cover change detection using improved change-vector analysis. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L. A theoretical framework for unsupervised change detection based on change vector analysis in the polar domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 218–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.C.; Bruzzone, L.; Bovolo, F.; Du, P.J. Hierarchical unsupervised change detection in multitemporal hyperspectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 244–260. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X.H.; Pan, H.Y.; Liu, S.C.; Li, B.B.; Luo, X.; Xie, H.; Xu, X. A novel approach for hyperspectral change detection based on uncertain area analysis and improved transfer learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Ni, S. Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically mapping urban areas from TM imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcfeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yin, Z.; Zhong, H.; Xu, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, J. Monitoring urban expansion and land use/land cover changes of Shanghai metropolitan area during the transitional economy (1979–2009) in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 9, 1538–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhao, K.G.; Owers, R.P. Assessment of the image misregistration effects on object-based change detection. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 87, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.L.; Khorram, S. The effects of image misregistration on the accuracy of remotely sensed change detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1566–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Townshend, J.R.G.; Justice, C.O.; Gurney, C.; Mcmanus, J. The impact of misregistration on change detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]














| Land Cover Types | Area (Km2) | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Cultivated land | 4478.66 | 65.88 |
| Forest | 2.96 | 0.04 |
| Grass land | 18.78 | 0.28 |
| Wetland | 106.14 | 1.56 |
| Water bodies | 396.34 | 5.83 |
| Artificial surface | 1795.07 | 26.41 |
| Year | Path/Row | Data Used in GlobeLand30 | Data Used in This Study | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor | Data | Sensor | Date | ||
| 2000 | 118/38 | Landsat 7 | 2001/07/03 | Landsat 7 | 2001/07/03 |
| 118/39 | Landsat 7 | 2000/06/14 | Landsat 5 | 2000/05/21 | |
| 2011 | 118/38 | Landsat 7 | 2011/04/26 | Landsat 5 | 2011/05/20 |
| 118/39 | Landsat 7 | 2011/02/05 | Landsat 5 | 2011/05/20 | |
| Binary Change Detection Accuracy Assessment for ECVA_OB Method | ||||
| Classified Data | Reference Data | User’s acc. (%) | ||
| No Change | Change | Total | ||
| No change | 566 | 33 | 599 | 94.49 |
| Change | 134 | 267 | 401 | 66.58 |
| Total | 700 | 300 | 1000 | |
| Producer’s accuracy (%) | 80.86 | 89.00 | ||
| Overall accuracy (%) | 83.30 | |||
| Overall kappa statistics | 0.6373 | |||
| Binary Change Detection Accuracy Assessment for MCVA_PB Method | ||||
| Classified Data | Reference Data | User’s acc. (%) | ||
| No Change | Change | Total | ||
| No change | 611 | 109 | 720 | 84.86 |
| Change | 89 | 191 | 280 | 68.21 |
| Total | 700 | 300 | 1000 | |
| Producer’s accuracy (%) | 87.29 | 63.67 | ||
| Overall accuracy (%) | 80.20 | |||
| Overall kappa statistics | 0.5185 | |||
| Land Cover Type | Agreement (%) |
|---|---|
| Cultivated land | 83.22 |
| Grassland | 15.50 |
| Wetland | 62.20 |
| Water body | 52.26 |
| Artificial surface | 78.91 |
| Classified Data | Reference Data | User’s Accuracy (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated Land | Grassland | Wetland | Water Bodies | Artificial Surfaces | Total | ||
| Cultivated land | 406 | 8 | 2 | 12 | 98 | 526 | 77.19 |
| Grassland | 9 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 32 | 68.75 |
| Wetland | 4 | 0 | 27 | 1 | 0 | 32 | 84.38 |
| Water bodies | 0 | 0 | 2 | 88 | 3 | 93 | 94.62 |
| Artificial surfaces | 87 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 326 | 419 | 77.80 |
| Total | 506 | 30 | 32 | 106 | 428 | 1102 | |
| Producer’s accuracy (%) | 80.24 | 73.33 | 84.38 | 83.02 | 76.17 | ||
| Overall accuracy (%) | 78.86 | ||||||
| Kappa statistics | 0.6608 | ||||||
| Binary CD Method | Accuracy (%) | Classification Method | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCVA_OB | 79.40 | MCVA_OB+SVM | 78.13 |
| MCVA_PB | 80.20 | MCVA_PB+SVM | 75.95 |
| ECVA_PB | 81.80 | ECVA_PB+SVM | 75.86 |
| ECVA_OB | 83.30 | ECVA_OB+SVM | 78.86 |
| Classified Data | Reference Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated-Artificial | Cultivated-Water | Water-Cultivated | Water-Artificial | |
| No change | 44 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Cultivated–Artificial | 193 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Cultivated–Water | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Wetland–Artificial | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Water–Artificial | 0 | 0 | 21 | 8 |
| Water–Cultivated | 0 | 0 | 1 | 11 |
| Water–Grass | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Water–Wetland | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Total | 237 | 8 | 30 | 25 |
| Class accuracy (%) | 81.43 | 25 | 70 | 44 |
| Overall accuracy (%) | 75.67 | |||
| Change Class | Accuracy Acquired by Comparing GlobaLand30 2000 and Updated 2011 (%) | Accuracy Acquired by Comparing GlobeLand30 2000 and GlobeLand30 2010 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Cultivated–Artificial | 81.43 | 86.08 |
| Cultivated–Water | 25.00 | 25.00 |
| Water–Cultivated | 70.00 | 30.00 |
| Water–Artificial | 44.00 | 96.00 |
| Overall accuracy (%) | 75.67 | 79.67 |
| Classified Data | Reference Data | User’s Accuracy (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Change | Change | Total | ||
| No change | 570 | 76 | 646 | 88.23 |
| Change | 130 | 224 | 354 | 63.28 |
| Total | 700 | 300 | 1000 | |
| Producer’s accuracy (%) | 81.43 | 74.67 | ||
| Overall accuracy (%) | 79.40 | |||
| Overall kappa statistics | 0.5335 | |||
| Classified Data | Reference Data | User’s Accuracy (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Change | Change | Total | ||
| No change | 579 | 61 | 640 | 90.47 |
| Change | 121 | 239 | 360 | 66.39 |
| Total | 700 | 300 | 1000 | |
| Producer’s accuracy (%) | 82.71 | 79.67 | ||
| Overall accuracy (%) | 81.80 | |||
| Overall Kappa statistics | 0.5901 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, H.; Tong, X.; Xu, X.; Luo, X.; Jin, Y.; Xie, H.; Li, B. Updating of Land Cover Maps and Change Analysis Using GlobeLand30 Product: A Case Study in Shanghai Metropolitan Area, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193147
Pan H, Tong X, Xu X, Luo X, Jin Y, Xie H, Li B. Updating of Land Cover Maps and Change Analysis Using GlobeLand30 Product: A Case Study in Shanghai Metropolitan Area, China. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(19):3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193147
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Haiyan, Xiaohua Tong, Xiong Xu, Xin Luo, Yanmin Jin, Huan Xie, and Binbin Li. 2020. "Updating of Land Cover Maps and Change Analysis Using GlobeLand30 Product: A Case Study in Shanghai Metropolitan Area, China" Remote Sensing 12, no. 19: 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193147
APA StylePan, H., Tong, X., Xu, X., Luo, X., Jin, Y., Xie, H., & Li, B. (2020). Updating of Land Cover Maps and Change Analysis Using GlobeLand30 Product: A Case Study in Shanghai Metropolitan Area, China. Remote Sensing, 12(19), 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193147