Field-Validated Burn-Severity Mapping in North Patagonian Forests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- How do burn-severity estimators derived from satellite images relate to field-based measurements of fire impact in A. araucana vegetation types defined by stand structure and species composition?
- What are the classification thresholds that best discriminate severity classes across the range of A. araucana vegetation types?
- How well do fire-severity maps that are based on the different best performing spectral indices agree?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Remote Sensing Data
2.3. Field-Based Reference Burn Severity Data
2.4. Data Analyses
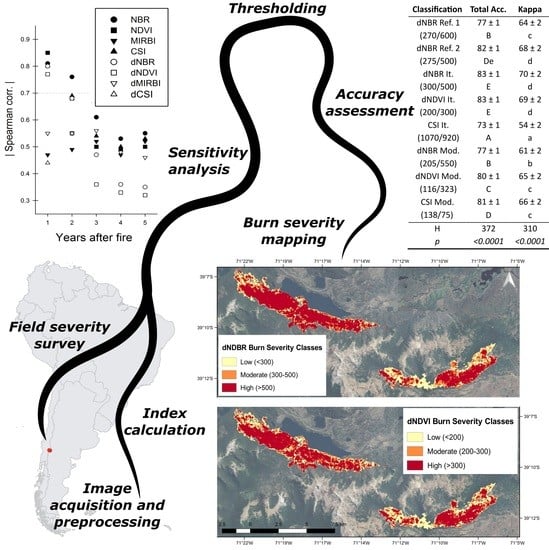
2.4.1. Sensitivity Analysis
2.4.2. Thresholding and Accuracy Assessment
2.5. Burn Severity Mapping
3. Results
3.1. Index Sensitivity
3.2. Thresholds and Accuracy of Selected Indices
3.3. Burn Severity Maps
4. Discussion
4.1. From Index Suitability to Index Selection
4.2. From Thresholding to Validated Classifications
4.3. Application: Burn Severity Mapping
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lentile, L.B.; Holden, Z.A.; Smith, A.M.S.; Falkowski, M.J.; Hudak, A.T. Remote sensing techniques to assess active fire characteristics and post fire effects. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2006, 194, 319–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smucker, K.M.; Hutto, R.L.; Steele, B.M. Changes in bird abundance after wildfire: Importance of fire severity and time since fire. Ecol. Appl. 2005, 15, 1535–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shenoy, A.; Johnstone, J.F.; Kasischke, E.S.; Kielland, K. Persistent effects of fire severity on early successional forests in interior Alaska. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 261, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, J.; Sanderman, J.; Miesel, J. Soil carbon pools and fluxes vary across a burn severity gradient three years after wildfire in Sierra Nevada mixed-conifer forest. Geoderma 2019, 333, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G.; Hargrove, W.; Gardner, R.H.; Romme, W.H. Effects of fire on landscape heterogeneity in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. J. Veg. Sci. 1994, 5, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, P.; Hardy, C.C.; Swetnam, T.W.; Rollins, M.G.; Long, D.G. Mapping fire regimes across time and space: Understanding coarse and fine-scale fire patterns. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2001, 10, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Santis, A.; Chuvieco, E. Burn severity estimation from remotely sensed data: Performance of simulation versus empirical models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Zhao, F. Remote sensing of fire effects: A review for recent advances in burned area and burn severity mapping. In Remote Sensing of Hydrometeorological Hazards; Petropoulos, G.P., Islam, T., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 261–283. [Google Scholar]
- White, J.D.; Ryan, K.C.; Key, C.H.; Running, S.W. Remote sensing of forest fire severity and vegetation recovery. Int. J. Wildland Fire 1996, 6, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rouse, W.J.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring vegetation systems in the Great Plains with ERTS. In NASA SP-251, Third ERTS-1 Symposium; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1974; pp. 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Key, C.H.; Benson, N.C. Landscape Assessment: Sampling and Analysis Methods; General Technical Report RMRS-GTR-164-CD; USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2006.
- Trigg, S.N.; Flasse, S. An evaluation of different bi-spectral spaces for discriminating burned shrub-savannah. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 2641–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.S.; Wooster, M.J.; Drake, N.A.; Dipotso, F.M.; Falkowski, M.J.; Hudak, A.T. Testing the potential of multi-spectral remote sensing for retrospectively estimating fire severity in African Savannahs. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 92–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, J.M.C. A comparative evaluation of NOAA/AVHRR vegetation indexes for burned surface detection and mapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epting, J.F.; Verbyla, D.L.; Sorbel, B. Evaluation of remotely sensed indices for assessing burn severity in interior Alaska using Landsat TM and ETM+. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veraverbeke, S.; Lhermitte, S.; Verstraeten, W.W.; Goossens, R. Evaluation of pre/post-fire differenced spectral indices for assessing burn severity in a Mediterranean environment with Landsat Thematic Mapper. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 3521–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-García, V.; Santamarta, M.; Fernández-Manso, A.; Quintano, C.; Marcos, E.; Calvo, L. Burn severity metrics in fire-prone pine ecosystems along a climatic gradient using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veraverbeke, S.; Lhermitte, S.; Verstraeten, W.W.; Goossens, R. A time-integrated MODIS burn severity assessment using the multi-temporal differenced normalized burn ratio (dNBRMT). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parks, S.A.; Dillon, G.K.; Miller, C. A new metric for quantifying burn severity: The Relativized Burn Ratio. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1827–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epting, J.F. Remote Sensing of Burn Severity and the Interactions between Burn Severity, Topography and Vegetation in Interior Alaska. Master’s Thesis, University of Alaska Fairbanks, Fairbanks, Alaska, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cocke, A.E.; Fulé, P.Z.; Crouse, J.E. Comparison of burn severity assessments using Differenced Normalized Burn Ratio and ground data. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2005, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soverel, N.O.; Perrakis, D.D.B.; Coops, N.C. Estimating burn severity from Landsat dNBR and RdNBR indices across western Canada. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1896–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; He, Y.; Tong, A. Evaluation of spectral indices for estimating burn severity in semiarid grasslands. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2016, 25, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammill, K.A.; Bradstock, R.A. Remote sensing of fire severity in the Blue Mountains: Influence of vegetation type and inferring fire intensity. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2006, 15, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, L.; Haest, B.; Veraverbeke, S.; Spanhove, T.; Borre, J.V.; Goossens, R. Burned area detection and burn severity assessment of a heathland fire in Belgium Using Airborne Imaging Spectroscopy (APEX). Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1803–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen Tran, B.; Tanase, M.A.; Bennett, L.T.; Aponte, C. Evaluation of spectral indices for assessing fire severity in Australian temperate forests. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitzberger, T.; Veblen, T.T. Fire-induced changes in northern Patagonian landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 1999, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermoz, M.; Kitzberger, T.; Veblen, T.T. Landscape influences on occurrence and spread of wildfires in Patagonian forests and shrublands. Ecology 2005, 86, 2705–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitzberger, T.; Aráoz, E.; Gowda, J.H.; Mermoz, M.; Morales, J.M. Decreases in fire spread probability with forest age promotes alternative community states, reduced resilience to climate variability and large fire regime shifts. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paritsis, J.; Holz, A.; Veblen, T.T.; Kitzberger, T. Habitat distribution modeling reveals vegetation flammability and land use as drivers of wildfire in SW Patagonia. Ecosphere 2013, 4, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiribelli, F.; Kitzberger, T.; Morales, J.M. Changes in vegetation structure and fuel charasteristics along post-fire succession promote alternative stable states and positive fire-vegetation feedbacks. J. Veg. Sci. 2018, 29, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veblen, T.T.; Kitzberger, T.; Raffaele, E.; Lorenz, D.C. Fire history and vegetation changes in northern Patagonia, Argentina. In Fire and Climatic Changes in Temperate Ecosystems of the Western Americas; Veblen, T.T., Baker, W., Montenegro, G., Swetnam, T.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 265–295. [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo, A.; González, M.E. Replacement patterns and species coexistence in an Andean Araucaria-Nothofagus forest. J. Veg. Sci. 2009, 20, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.E.; Veblen, T.T.; Sibold, J.S. Influence of fire severity on stand development of Araucaria araucana–Nothofagus pumilio stands in the Andean cordillera of south-central Chile. Austral Ecol. 2010, 35, 597–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundo, I.A.; Kitzberger, T.; Roig, F.A.; Villalba, R.; Barrera, M.D. Fire history in the Araucaria araucana forests of Argentina: Human and climate influences. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2013, 22, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holz, A.; Veblen, T.T. Variability in the Southern Annular Mode determines wildfire activity in Patagonia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veblen, T.T.; Holz, A.; Paritsis, J.; Raffaele, E.; Kitzberger, T.; Blackhall, M. Adapting to global environmental change in Patagonia: What role for disturbance ecology? Austral Ecol. 2011, 36, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.E.; Lara, A. Large fires in the Andean Araucaria forests: When a natural ecological process becomes a threat. Oryx 2015, 49, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burns, B.R. Fire-induced dynamics of Araucaria araucana-Nothofagus antarctica forest in the Southern Andes. J. Biogeogr. 1993, 20, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.E.; Szejner, M.; Muñoz, A.A.; Silva, J. Incendios catastróficos en bosques andinos de Araucaria-Nothofagus: Efecto de la severidad y respuesta de la vegetación. Bosque Nativ. 2009, 46, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Urrutia-Estrada, J.; Fuentes-Ramírez, A.; Hauenstein, E. Diferencias en la composición florística en bosques de Araucaria-Nothofagus afectados por distintas severidades de fuego. Gayana Botánica 2018, 75, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assal, T.J.; González, M.E.; Sibold, J. Burn severity controls on post-fire Araucaria-Nothofagus regeneration in the Andean Cordillera. J. Biogeogr. 2018, 45, 2483–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peñaloza Rubio, A.R. Zonificación de la Severidad de un Incendio Natural y su Descripción Topográfica Cuantitativa en el Parque Nacional Tolhuaca, IX Región, Chile. Bachelor’s Thesis, Facultad de Ciencias Forestales, Universidad Austral de Chile, Valdivia, Chile, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mermoz, M.; Müller, M.; Nuñez, C.; Pastore, H.; Ramilo, E. Evaluación ecológica del incendio “El Cristo” Área Futalaufquen-Parque Nacional Los Alerces Marzo-Abril de 2015; Administración de Parques Nacionales, Intendencia del Parque Nacional Los Alerces: Chubut, Argentina, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- De la Barrera, F.; Barraza, F.; Favier, P.; Ruiz, V.; Quense, J. Megafires in Chile 2017: Monitoring multiscale environmental impacts of burned ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 1526–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro Cerrillo, R.M.; Olave Ortiz, F.; Hayas, A.; Castillo, M. Metodología para la elaboración de un plan de restauración postincendio en Chile: La experiencia del Parque Nacional de Torres del Paine The experience of the Torres del Paine National Park. An. Inst. Patagon. 2015, 43, 53–73. [Google Scholar]
- De Fina, A.L. El clima de la región de los bosques andino-patagónicos argentinos. In La Región de Los Bosques Andino-Patagónicos. Sinopsis General. Colección Científica Del INTA N° 10; Dimitri, M.J., Ed.; INTA: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1972; pp. 35–58. [Google Scholar]
- Veblen, T.T.; Kitzberger, T.; Raffaele, E.; Mermoz, M.; González, M.E.; Sibold, J.S.; Holz, A. The historical range of variability of fires in the Andean Patagonian Nothofagus forest region. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2008, 17, 724–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorelli, L.A. Maderas y Bosques Argentinos; Editorial ACME: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Kitzberger, T.; Perry, G.L.W.; Paritsis, J.; Gowda, J.H.; Tepley, A.J.; Holz, A.; Veblen, T.T. Fire-vegetation feedbacks and alternative states: Common mechanisms of temperate forest vulnerability to fire in southern South America and New Zealand. N. Z. J. Bot. 2016, 54, 247–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- QGIS Development Team. QGIS Geographic Information System. Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project. 2018. Available online: http://qgis.osgeo.org (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Escuin, S.; Navarro, R.; Fernández, P. Fire severity assessment by using NBR (Normalized Burn Ratio) and NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) derived from LANDSAT TM/ETM images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1053–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stambaugh, M.C.; Hammer, L.D.; Godfrey, R. Performance of burn-severity metrics and classifications in oak woodlands and grasslands. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10501–10522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuvieco, E. Fundamentals of Satellite Remote Sensing: An Environmental Approach, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781498728072. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes-Ramírez, A.; Arroyo-Vargas, P.; Del Fierro, A.; Pérez, F. Post-fire response of Araucaria araucana (Molina) K. Koch: Assessment of vegetative resprouting, seed production and germination. Gayana Botánica 2019, 76, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaz-Delgado, R. Efecto de la recurrencia de los incendios sobre la resiliencia post- incendio de las comunidades vegetales de Cataluña a partir de imágenes de satélite. Ecosistemas 2003, 12, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Remer, L.A. Detection of forests using Mid-IR reflectance: An application for aerosol studies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veraverbeke, S.; Harris, S.; Hook, S. Evaluating spectral indices for burned area discrimination using MODIS/ASTER (MASTER) airborne simulator data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2702–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D.; Thode, A.E. Quantifying burn severity in a heterogeneous landscape with a relative version of the delta Normalized Burn Ratio (dNBR). Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Beaudoin, A.; Hébert, C.; Guindon, L.; Bauce, E. Assessing the potential of the differenced Normalized Burn Ratio (dNBR) for estimating burn severity in eastern Canadian boreal forests. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2017, 26, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbanov, E.; Vorobyev, O.; Leznin, S.; Polevshiova, Y.; Demisheva, E. Assessment of burn severity in Middle Povozhje with Landsat multitemporal data. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2017, 26, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cansler, C.A.; McKenzie, D. How robust are burn severity indices when applied in a new region? Evaluation of alternate field-based and remote-sensing methods. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 456–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chafer, C.J. A comparison of fire severity measures: An Australian example and implications for predicting major areas of soil erosion. Catena 2008, 74, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Key, C.H.; Ohlen, D.; Benson, N.C. Evaluate Sensitivities of Burn-Severity Mapping Algorithms for Different Ecosystems and Fire Histories in the United States; Final report to the Joint Fire Science Program; USGS, National Center of Earth Resources Observation and Science: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2006.
- Holden, Z.A.; Morgan, P.; Smith, A.M.S.; Vierling, L. Beyond Landsat: A comparison of four satellite sensors for detecting burn severity in ponderosa pine forests of the Gila Wilderness, NM, USA. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2010, 19, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Vogelmann, J.E.; Rollins, M.G.; Key, C.H.; Yang, L.; Huang, C.; Shi, H. Detecting post-fire burn severity and vegetation recovery using multitemporal remote sensing spectral indices and field-collected composite burn index data in a ponderosa pine forest. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 7905–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, S.A.; Holsinger, L.M.; Voss, M.A.; Loehman, R.A.; Robinson, N.P. Mean Composite Fire Severity Metrics Computed with Google Earth Engine Offer Improved Accuracy and Expanded Mapping Potential. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, J.L.; Sorbel, B. Assessing the differenced Normalized Burn Ratio’s ability to map burn severity in the boreal forest and tundra ecosystems of Alaska’s national parks. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2008, 17, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soverel, N.O.; Coops, N.C.; Perrakis, D.D.B.; Daniels, L.D.; Gergel, S.E. The transferability of a dNBR-derived model to predict burn severity across 10 wildland fires in western Canada. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2011, 20, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picotte, J.J.; Robertson, K.M. Validation of remote sensing of burn severity in south-eastern US ecosystems. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2011, 20, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.J.; Freeburn, J.T.; de Groot, W.J.; Pritchard, J.M.; Lynham, T.J.; Landry, R. Remote sensing of burn severity: Experience from western Canada boreal fires. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2008, 17, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.A.; Reynolds, J.H.; Koltun, J.M. Evaluating the ability of the differenced Normalized Burn Ratio (dNBR) to predict ecologically significant burn severity in Alaskan boreal forests. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2008, 17, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, N.H.F.; Kasischke, E.S.; Hall, R.J.; Murphy, K.A.; Verbyla, D.L.; Hoy, E.E.; Allen, J.L. Using Landsat data to assess fire and burn severity in the North American boreal forest region: An overview and summary of results. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2008, 17, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D.; Knapp, E.E.; Key, C.H.; Skinner, C.N.; Isbell, C.J.; Creasy, R.M.; Sherlock, J.W. Calibration and validation of the relative differenced Normalized Burn Ratio (RdNBR) to three measures of fire severity in the Sierra Nevada and Klamath Mountains, California, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhermitte, S.; Verbesselt, J.; Verstraeten, W.W.; Veraverbeke, S.; Coppin, P. Assessing intra-annual vegetation regrowth after fire using the pixel based regeneration index. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Wildfires | Field Survey | Landsat 8 OLI images | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Date | No. of Plots | Date | Path–Row | Pre-Fire | Post-Fire |
| Ñorquinco | 29/12/13 to 20/01/14 | 55 | 20/02/18 to 02/03/18 | 232–87 | 07/04/13 | 23/03/14; 26/03/15; 28/03/16; 15/03/17; 02/03/18 |
| Rucachoroy | 56 | |||||
| Strata | Severity Scale | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unburned | Low | Moderate | High | ||||
| 0 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | |
| Substrates | |||||||
| Litter | intact | charred | absent | absent | absent | absent | absent |
| Duff | intact | Intact | partially charred | charred | scarce | very scarce | absent |
| Light Fuels | intact | partially charred | charred/absent | absent | absent | absent | absent |
| Medium Fuels | intact | Intact | partially charred | partially charred | charred/absent | absent | absent |
| Heavy Fuels | intact | Intact | intact | intact | partially charred | charred | absent |
| Tall shrubs (1 to 6 m) | |||||||
| % altered foliage | 0% | 5% | 10% | 30% | 50% | 75% | 100% |
| % resprout | 100% | 95% | 90% | 60% | 30% | <10% | <1% |
| Intermediate trees (subcanopy) | |||||||
| % green foliage | 100% | 90% | 80% | 60% | 40% | <10% | 0% |
| % black foliage | 0% | 5% | 20% | 30% | 60% | >85% | 100% |
| % charred trunk height | 0% | 10% | 30% | 40% | 60% | 70% | >90% |
| Big trees (upper canopy) | |||||||
| % green foliage | 100% | 90% | 80% | 60% | 40% | <10% | 0% |
| % black foliage | 0% | 5% | 20% | 30% | 60% | >85% | 100% |
| % charred trunk height | 0% | 10% | 30% | 40% | 60% | 70% | >90% |
| mCBI | %DT | NBR | NDVI | CSI | dNBR | dNDVI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mCBI | 1 | 0.87 * | −0.81 * | −0.85 * | −0.80 * | 0.80 * | 0.77 * |
| %DT | 0.87 * | 1 | −0.77 * | −0.83 * | −0.78 * | 0.77 * | 0.77 * |
| Plots | NBRpost | NDVIpost | CSIpost | dNBR | dNDVI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 111 | 0.95 | 1.06 | 0.90 | 1.10 | 0.93 | |
| Canopy | Regen. | ||||||
| Low | R | 30 | 0.92 | 1.04 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 1.03 |
| Tall | R | 25 | 1.00 | 1.21 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 1.03 |
| Tall | S | 18 | 1.00 | 0.73 | 0.80 | 1.12 | 0.89 |
| Tall | RS | 27 | 1.58 | 1.64 | 1.40 | 1.56 | 1.05 |
| Two tiered | R | 11 | 0.43 | 0.23 | 0.29 | 0.58 | 0.40 |
| Overall | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 1.03 | 0.88 | ||
| Low | Moderate | High | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification | Total Acc. | Kappa | UE | PE | UE | PE | UE | PE |
| dNBR Ref. 1 (270/600) | 77 ± 1 | 64 ± 2 | 15 ± 2 | 11 ± 2 | 55 ± 2 | 21 ± 2 | 1 ± 1 | 27 ± 2 |
| B | c | B | c | bc | f | d | a | |
| dNBR Ref. 2 (275/500) | 82 ± 1 | 68 ± 2 | 15 ±2 | 11 ±2 | 46 ± 2 | 49 ± 2 | 11 ±1 | 11 ± 1 |
| De | d | B | c | d | c | c | e | |
| dNBR It. (300/500) | 83 ± 1 | 70 ± 2 | 17 ± 2 | 7 ± 2 | 41 ± 2 | 49 ± 2 | 11 ± 1 | 11 ± 1 |
| E | d | Ab | d | e | c | c | e | |
| dNDVI It. (200/300) | 83 ± 1 | 69 ± 2 | 20±2 | 3 ±2 | 33 ±2 | 59 ±2 | 13 ±1 | 9 ± 1 |
| E | d | A | e | f | b | b | ef | |
| CSI It. (1070/920) | 73 ± 1 | 54 ± 2 | 12 ± 2 | 39 ± 2 | 64 ± 2 | 44 ± 2 | 11 ± 1 | 16 ± 1 |
| A | a | C | a | a | d | c | c | |
| dNBR Mod. (205/550) | 77 ± 1 | 61 ± 2 | 6 ± 2 | 26 ± 2 | 58 ±2 | 33 ± 2 | 11 ± 1 | 19 ± 2 |
| B | b | D | b | b | e | c | b | |
| dNDVI Mod. (116/323) | 80 ± 1 | 65 ± 2 | 6 ± 2 | 28 ± 2 | 52 ± 2 | 32 ± 2 | 11 ± 1 | 14 ± 2 |
| C | c | D | b | c | e | bc | d | |
| CSI Mod. (138/75) | 81 ± 1 | 66 ± 2 | 17 ± 2 | 7 ± 2 | 43 ± 2 | 67 ± 2 | 15 ± 2 | 8 ± 1 |
| D | c | B | d | de | a | a | f | |
| H | 372 | 310 | 310 | 267 | 353 | 249 | 575 | 539 |
| p | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| dNBR It. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Moderate | High | Total (ha) | Agreement | ||
| dNDVI It. | Low | 658 | 183 | 18 | 859 | 77% |
| Moderate | 47 | 288 | 267 | 603 | 48% | |
| High | 0 | 136 | 1703 | 1839 | 93% | |
| Total (ha) | 706 | 608 | 1988 | 3302 | ||
| Agreement | 93% | 47% | 86% | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franco, M.G.; Mundo, I.A.; Veblen, T.T. Field-Validated Burn-Severity Mapping in North Patagonian Forests. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020214
Franco MG, Mundo IA, Veblen TT. Field-Validated Burn-Severity Mapping in North Patagonian Forests. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(2):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020214
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranco, María Guadalupe, Ignacio A. Mundo, and Thomas T. Veblen. 2020. "Field-Validated Burn-Severity Mapping in North Patagonian Forests" Remote Sensing 12, no. 2: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020214
APA StyleFranco, M. G., Mundo, I. A., & Veblen, T. T. (2020). Field-Validated Burn-Severity Mapping in North Patagonian Forests. Remote Sensing, 12(2), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020214