Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of PM2.5, PM10, and AOD over Canal Head Taocha Station, Henan Province
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Areas and Methods
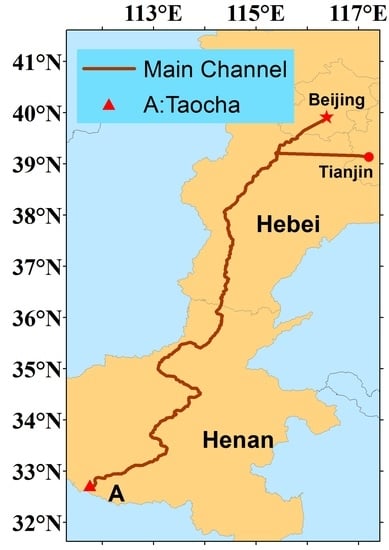
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overall Characteristics of PM10, PM2.5, and Meteorological Parameters at TC Station
3.2. Seasonal Characteristics of PM10 and PM2.5 and Meteorological Parameters at TC Station
3.3. Daily Variation Characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 and Meteorological Parameters at TC Station
3.4. Remote Sensing Analysis of CALIPSO AOD
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Boucher, O. A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelieveld, J.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandolfi, M.; Cusack, M.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. Variability of aerosol optical properties in the western mediterranean basin. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8189–8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulmala, M.; Kontkanen, J.; Junninen, H.; Lehtipalo, K.; Manninen, H.E.; Nieminen, T.; Petaja, T.; Sipila, M.; Schobesberger, S.; Rantala, P. Direct observations of atmospheric aerosol nucleation. Science 2013, 339, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, S.; Hansen, J.; Nazarenko, L.; Luo, Y. Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in china and india. Science 2002, 297, 2250–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramanathan, V.; Crutzen, P.J.; Kiehl, J.T. Aerosols, climate, and the hydrological cycle. Science 2005, 294, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Obregón, M.A.; Costa, M.J.; Silva, A.M.; Serrano, A. Spatial and temporal variation of aerosol and water vapour effects on solar radiation in the mediterranean basin during the last two decades. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stachlewska, I.S.; Zawadzka, O.; Engelmann, R. Effect of heat wave conditions on aerosol optical properties derived from satellite and ground-based remote sensing over poland. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evgenieva, T.; Wiman, B.L.; Kolev, N.I.; Savov, P.B.; Donev, E.H.; Ivanov, D.I.; Kolev, I.N. Three-point observation in the troposphere over sofia-plana mountain, bulgaria. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 9343–9363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edenhofer, O.; Seyboth, K. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Encyclopedia of Energy, Natural Resource, and Environmental Economics. Earth Syst. Environ. Sci. 2013, 1, 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfi, M.; Ripoll, A.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A. Climatology of aerosol optical properties and black carbon mass absorption cross section at a remote high-altitude site in the western mediterranean basin. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6443–6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergin, M.H.; Cass, G.R.; Xu, J.; Fang, C.; Zeng, L.M.; Yu, T.; Salmon, L.G.; Kiang, C.S.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.H. Aerosol radiative, physical, and chemical properties in beijing during june 1999. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 17969–17980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Cao, F. Fine particulate matter (pm2.5) in china at a city level. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Chan, C.K. Source apportionment of pm2.5 in urban area of hong kong. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 138, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, M.P.; Yue, Z.W.; Buzcu, B. Source apportionment of fine particulate matter in houston, tx, using organic molecular markers. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2117–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappos, A.D.; Bruckmann, P.; Eikmann, T.; Englert, N.; Heinrich, U.; Hoeppe, P.; Koch, E.; Krause, G.H.M.; Kreyling, W.G.; Rauchfuss, K. Health effects of particles in ambient air. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2004, 207, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Götschi, T.; Heinrich, J.; Sunyer, J.; Künzli, N. Long-term effects of ambient air pollution on lung function: A review. Epidemiology 2008, 19, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Englert, N. Fine particles and human health--a review of epidemiological studies. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 149, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, S.; Gong, W.; Jin, Y. Characteristics of aerosol within the nocturnal residual layer and its effects on surface pm2.5 over china. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 241, 117841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope Iii, C.A.; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, F.W.S.; Tam, W.; Wong, T.W.; Lai, C.K.W.; Wong, G.W.K.; Leung, T.F.; Ng, S.S.S.; Hui, D.S.C. Effects of air pollution on asthma hospitalization rates in different age groups in hong kong. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 37, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.T. Associations between daily mortalities from respiratory and cardiovascular diseases and air pollution in hong kong, china. Occup. Environ. Med. 2002, 59, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mysliwiec, M.J.; Kleeman, M.J. Source apportionment of secondary airborne particulate matter in a polluted atmosphere. Environ. Ence Technol. 2002, 36, 5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, J.; Pathak, B.; Patadia, F.; Bhuyan, P.K.; Gogoi, M.M.; Babu, S.S. Satellite-retrieved direct radiative forcing of aerosols over north-east india and adjoining areas: Climatology and impact assessment. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Dickinson, R.E.; Su, L.; Zhou, C.; Wang, K. PM 2.5 pollution in china and how it has been exacerbated by terrain and meteorological conditions. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, F.; Peng, R.D.; Bell, M.L.; Pham, L.; McDermott, A.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M. Fine particulate air pollution and hospital admission for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. JAMA J. Am. Med Assoc. 2006, 295, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Jing, X.; Wei, M.; Pu, W. Seasonal and diurnal variations of ambient pm_(2.5) concentration in urban and rural environments in beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2893–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Primbs, T.; Tao, S.; Simonich, S.L.M. Atmospheric particulate matter pollution during the 2008 beijing olympics. Environ. Ence Technol. 2009, 43, 5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E. Evaluation of modis aerosol retrieval algorithms over the beijing-tianjin-hebei region during low to very high pollution events. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 7941–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.; Estelles, V.; Cuevasagulló, E. Column aerosol optical properties and aerosol radiative forcing during a serious haze-fog month over north china plain in 2013 based on ground-based sunphotometer measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2125–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.J.; Ma, N.; Größ, J.; Kecorius, S.; Lu, K.D.; Shang, D.J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.S.; Zeng, L.M.; Hu, M.; et al. Thermodynamic properties of nanoparticles during new particle formation events in the atmosphere of north china plain. Atmos. Res. 2017, 188, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, L.; Lin, A.; Ming, Z.; Bilal, M.; Tao, M. Aerosol optical properties and associated direct radiative forcing over the yangtze river basin during 2001–2015. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, K.; Zou, J.; Guo, J.; Lu, M.; Bilal, M.; Zhang, K.; Ma, F.; Zhang, Y. Estimating pm1 concentrations from modis over yangtze river delta of china during 2014–2017. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 195, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Hu, B.; Shi, Y. Spatial-temporal characteristics of aerosol loading over the yangtze river basin during 2001–2015. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 38, 2138–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Wiedensohler, A.; Eichler, H.; Su, H.; Gnauk, T.; Brüggemann, E.; Herrmann, H.; Heintzenberg, J.; Slanina, J.; Tuch, T. Aerosol optical properties and related chemical apportionment at xinken in pearl river delta of china. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6351–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Engelmann, R.; Althausen, D.; Wandinger, U.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; He, Q. High aerosol load over the pearl river delta, china, observed with raman lidar and sun photometer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.P.; Zhang, H.P.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.F. Influence of the south-north water diversion project and the mitigation projects on the water quality of han river. Ence Total Environ. 2008, 406, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Liu, H.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Multi-time-scale climatic variations over eastern china and implications for the south-north water diversion project. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 600–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Q. Dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the danjiangkou reservoir, china. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Ji, X.; Yang, H.; Yao, X.; Chan, C.K.; Cadle, S.H.; Chan, T.; Mulawa, P.A. Concentration and chemical composition of pm 2.5 in shanghai for a 1-year period. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Yao, X. Air pollution in mega cities in china. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wong, H.; Yin, Q.; Wang, J. Estimation of daily pm2.5 concentration and its relationship with meteorological conditions in beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 48, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Tao, R. Variations in pm10, pm2.5 and pm1.0 in an urban area of the sichuan basin and their relation to meteorological factors. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charlson, R.J.; Schwartz, S.E.; Hales, J.M.; Cess, R.D.; Coakley, J.A.; Hansen, J.E.; Hofmann, D.J. Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Ence 1992, 255, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.; Nazeer, M.; Shi, Y.; Wang, L.; Kumar, K.; Ho, H.; Mazhar, U.; Bleiweiss, M.; Qiu, Z. Characteristics of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) over urban, suburban, and rural areas of hong kong. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Sun, J.Y.; Zhang, X.C.; Che, H.Z.; Li, Y. Spatial and temporal variations of the concentrations of pm10, pm2.5 and pm1 in china. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2015, 15, 3585–13598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhu, Z. Aerosol optical properties of a haze episode in wuhan based on ground-based and satellite observations. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 699–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winker, D.M.; Tackett, J.L.; Getzewich, B.J.; Liu, Z.; Vaughan, M.A.; Rogers, R.R. The global 3-d distribution of tropospheric aerosols as characterized by caliop. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 3345–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Su, B.; Bilal, M.; Atique, L.; Usman, M.; Qiu, Z.; Ali, M.; Han, G. An investigation of vertically distributed aerosol optical properties over pakistan using calipso satellite data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Hourly | Counts | Mean | SD | Percentiles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| base | 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | |||
| T (℃) | 16,115 | 16.19 | 10.10 | 2.10 | 7.80 | 16.50 | 24.90 | 29.10 |
| RH (%) | 16,115 | 57.95 | 26.47 | 19.70 | 39.10 | 56.20 | 82.00 | 94.40 |
| W (m/s) | 16,115 | 1.30 | 1.19 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.90 | 1.80 | 2.90 |
| V(°) | 16,115 | 164.42 | 103.33 | 0 | 103 | 147 | 201 | 332 |
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) | 16,115 | 50.91 | 22.00 | 34.00 | 40.00 | 47.00 | 54.00 | 56.00 |
| PM10 (μg/m3) | 16,115 | 57.18 | 25.02 | 38.00 | 45.00 | 52.00 | 61.00 | 63.00 |
| Month | T (℃) | RH (%) | W (m/s) | V (°) | PM2.5(μg/m3) | PM10(μg/m3) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | Std | |
| Jan | 3.06 | 3.18 | 79.55 | 16.47 | 1.28 | 0.92 | 179.53 | 104.00 | 53.16 | 23.04 | 59.71 | 26.2 |
| Feb | 3.70 | 4.02 | 80.77 | 15.59 | 1.32 | 1.02 | 171.71 | 103.65 | 53.35 | 24.05 | 59.94 | 27.35 |
| Mar | 12.53 | 4.83 | 72.86 | 20.56 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 135.61 | 93.94 | 51.76 | 21.14 | 58.16 | 24.04 |
| Apr | 16.12 | 4.85 | 62.44 | 19.92 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 127.62 | 93.05 | 50.5 | 19 | 56.74 | 21.61 |
| May | 22.10 | 4.49 | 42.28 | 16.81 | 1.28 | 1.23 | 168.99 | 105.30 | 48.63 | 17.42 | 54.64 | 19.84 |
| Jun | 26.23 | 3.80 | 33.59 | 13.94 | 1.67 | 1.37 | 194.66 | 101.77 | 48.5 | 21.08 | 54.42 | 23.98 |
| Jul | 27.96 | 3.67 | 31.05 | 13.55 | 1.85 | 1.44 | 193.27 | 103.32 | 49.62 | 23.35 | 55.68 | 26.54 |
| Aug | 28.09 | 3.15 | 30.77 | 13.54 | 1.83 | 1.46 | 191.31 | 107.31 | 48.7 | 24.33 | 54.61 | 27.63 |
| Sep | 23.83 | 4.24 | 37.98 | 14.85 | 1.44 | 1.21 | 187.89 | 104.65 | 48.5 | 18.91 | 54.46 | 21.54 |
| Oct | 17.33 | 3.47 | 58.09 | 17.58 | 0.81 | 0.87 | 126.94 | 96.40 | 48.53 | 13.34 | 54.57 | 15.19 |
| Nov | 11.24 | 3.61 | 78.10 | 17.64 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 127.99 | 88.18 | 53.4 | 23.73 | 59.97 | 27 |
| Dec | 4.47 | 4.50 | 82.85 | 14.58 | 1.25 | 1.03 | 156.83 | 97.13 | 54.58 | 25.94 | 61.33 | 29.51 |
| Month | T(℃) | RH(%) | W(m/s) | V(°) | PM2.5(μg/m3) | PM10(μg/m3) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | std | Mean | Std | |
| 0 | 14.87 | 9.38 | 60.03 | 26.17 | 1.40 | 1.35 | 166.96 | 108.72 | 48.97 | 19.28 | 54.96 | 21.94 |
| 1 | 14.54 | 9.29 | 60.11 | 26.97 | 1.41 | 1.28 | 173.90 | 105.97 | 50.58 | 21.60 | 56.78 | 24.57 |
| 2 | 14.17 | 9.24 | 60.76 | 26.41 | 1.31 | 1.29 | 167.30 | 107.52 | 49.90 | 18.96 | 56.03 | 21.55 |
| 3 | 13.85 | 9.16 | 61.64 | 25.93 | 1.38 | 1.20 | 169.21 | 96.34 | 52.26 | 22.11 | 58.71 | 25.15 |
| 4 | 13.62 | 9.08 | 61.61 | 26.59 | 1.33 | 1.25 | 168.51 | 103.29 | 50.16 | 18.10 | 56.36 | 20.61 |
| 5 | 13.40 | 9.02 | 61.87 | 27.00 | 1.25 | 1.24 | 155.18 | 103.73 | 50.74 | 20.98 | 56.99 | 23.85 |
| 6 | 13.26 | 9.04 | 63.40 | 27.04 | 1.22 | 1.14 | 161.01 | 102.15 | 51.24 | 23.14 | 57.50 | 26.33 |
| 7 | 13.53 | 9.32 | 62.07 | 27.36 | 1.35 | 1.23 | 175.19 | 99.17 | 50.16 | 20.30 | 56.31 | 23.11 |
| 8 | 14.16 | 9.74 | 62.12 | 26.17 | 1.37 | 1.30 | 167.34 | 109.68 | 49.33 | 19.67 | 55.37 | 22.37 |
| 9 | 15.20 | 9.90 | 59.13 | 26.74 | 1.35 | 1.23 | 166.26 | 101.93 | 50.70 | 22.71 | 56.96 | 25.80 |
| 10 | 16.28 | 10.09 | 58.60 | 26.15 | 1.19 | 1.12 | 152.95 | 104.31 | 49.35 | 20.70 | 55.36 | 23.54 |
| 11 | 17.28 | 10.24 | 56.59 | 25.52 | 1.13 | 1.07 | 158.13 | 108.30 | 48.52 | 17.75 | 54.47 | 20.20 |
| 12 | 18.16 | 10.40 | 54.70 | 24.22 | 1.30 | 1.21 | 159.00 | 108.62 | 51.52 | 24.28 | 57.90 | 27.59 |
| 13 | 18.93 | 10.56 | 53.59 | 25.96 | 1.33 | 1.15 | 178.29 | 109.09 | 50.69 | 22.05 | 56.99 | 25.07 |
| 14 | 19.38 | 10.74 | 53.26 | 25.87 | 1.31 | 1.20 | 165.53 | 100.22 | 51.71 | 23.59 | 58.12 | 26.82 |
| 15 | 19.72 | 10.78 | 50.24 | 26.78 | 1.45 | 1.26 | 171.79 | 97.62 | 52.30 | 24.80 | 58.77 | 28.18 |
| 16 | 19.61 | 10.78 | 52.15 | 27.74 | 1.31 | 1.20 | 156.92 | 97.95 | 53.85 | 24.53 | 60.50 | 27.90 |
| 17 | 19.09 | 10.72 | 53.74 | 26.61 | 1.35 | 1.26 | 158.18 | 103.72 | 54.50 | 27.71 | 61.30 | 31.49 |
| 18 | 18.30 | 10.58 | 56.07 | 26.12 | 1.27 | 1.14 | 162.96 | 104.87 | 51.06 | 23.87 | 57.33 | 27.14 |
| 19 | 17.32 | 10.28 | 56.29 | 25.62 | 1.21 | 1.08 | 161.98 | 102.91 | 52.33 | 22.54 | 58.78 | 25.64 |
| 20 | 16.62 | 9.89 | 57.23 | 26.37 | 1.27 | 1.18 | 157.64 | 101.25 | 52.94 | 25.83 | 59.46 | 29.38 |
| 21 | 16.17 | 9.69 | 58.69 | 25.48 | 1.16 | 1.08 | 158.36 | 101.56 | 49.77 | 19.56 | 55.85 | 22.26 |
| 22 | 15.74 | 9.52 | 58.17 | 25.29 | 1.27 | 1.17 | 170.41 | 102.33 | 49.07 | 19.56 | 55.06 | 22.25 |
| 23 | 15.26 | 9.45 | 60.20 | 26.82 | 1.41 | 1.25 | 170.28 | 97.77 | 53.09 | 25.43 | 59.65 | 28.91 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Wu, D.; Su, B.; Bilal, M.; Li, Y.; Li, B.L. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of PM2.5, PM10, and AOD over Canal Head Taocha Station, Henan Province. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3432. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203432
Zhang M, Wu D, Su B, Bilal M, Li Y, Li BL. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of PM2.5, PM10, and AOD over Canal Head Taocha Station, Henan Province. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(20):3432. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203432
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Miao, Dongyu Wu, Bo Su, Muhammad Bilal, Yuying Li, and B. Larry Li. 2020. "Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of PM2.5, PM10, and AOD over Canal Head Taocha Station, Henan Province" Remote Sensing 12, no. 20: 3432. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203432
APA StyleZhang, M., Wu, D., Su, B., Bilal, M., Li, Y., & Li, B. L. (2020). Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of PM2.5, PM10, and AOD over Canal Head Taocha Station, Henan Province. Remote Sensing, 12(20), 3432. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203432