Solar Brightening/Dimming over China’s Mainland: Effects of Atmospheric Aerosols, Anthropogenic Emissions, and Meteorological Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Place and Data
2.1.1. Place
2.1.2. Data
2.2. Methodology
3. Results
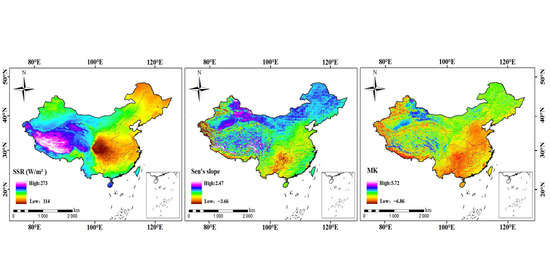
3.1. Trends of Surface Solar Radiation (SSR) over China
3.2. Factor Analysis of the Long-Term Variability of SSR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wild, M. Global dimming and brightening: A review. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D00D16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilbao, J.; Román, R.; Miguel, A. Turbidity coefficients from normal direct solar irradiance in Central Spain. Atmos. Res. 2014, 143, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E.; Bleiweiss, M.P.; Dubois, D. A Simplified high resolution MODIS Aerosol Retrieval Algorithm (SARA) for use over mixed surfaces. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Wang, L.; Lin, A.; Zhang, M.; Xia, X.; Hu, B.; Niu, Z. Comparison of deterministic and data-driven models for solar radiation estimation in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Zou, L.; Feng, L.; Wei, J.; Qin, W.; Niu, Z. Prediction of diffuse solar radiation based on multiple variables in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 103, 151–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacovides, C.P.; Tymvios, F.S.; Assimakopoulos, V.D.; Kaltsounides, N.A. Comparative study of various correlations in estimating hourly diffuse fraction of global solar radiation. Renew. Energy 2006, 31, 2492–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambezidis, H.D.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Kharol, S.K.; Moorthy, K.K.; Satheesh, S.K.; Kalapureddy, M.C.R.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Sharma, A.R.; Wild, M. Multi-decadal variation of the net downward shortwave radiation over south Asia: The solar dimming effect. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, M.; Gilgen, H.; Roesch, A.; Ohmura, A.; Long, C.N.; Dutton, E.G.; Forgan, B.; Kallis, A.; Russak, V.; Tsvetkov, A. From dimming to brightening: Decadal changes in solar radiation at Earth’s surface. Science 2005, 308, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinker, R.T.; Zhang, B.; Dutton, E.G. Do satellites detect trends in surface solar radiation? Science 2005, 308, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanhill, G. Global dimming: A new aspect of climate change. Weather 2005, 60, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanhill, G.; Cohen, S. Global dimming: A review of the evidence for a widespread and significant reduction in global radiation with discussion of its probable causes and possible agricultural consequences. Agric. Meteorol. 2001, 107, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanhill, G. Solar Irradiance, air pollution and temperature changes in the Arctic. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1995, 352, 247–258. [Google Scholar]
- Gilgen, H.; Roesch, A.; Wild, M.; Ohmura, A. Decadal changes in shortwave irradiance at the surface in the period from 1960 to 2000 estimated from Global Energy Balance Archive Data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D00D08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohmura, A. Observed long-term variations of solar irradiance at the Earth’s surface. In Solar Variability and Planetary Climates; Calisesi, Y., Bonnet, R.M., Gray, L., Langen, J., Lockwood, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Kaiser, D.P.; Leung, L.R.; Xu, M. More frequent cloud-free sky and less surface solar radiation in China from 1955 to 2000. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.C.; Dickinson, R.E.; Wild, M.; Liang, S. Atmospheric impacts on climatic variability of surface incident solar radiation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 9581–9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhou, C.; Wild, M. A Revisit of Global Dimming and Brightening Based on the Sunshine Duration. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 4281–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Xia, X.A. Long-term trends in solar radiation and the associated climatic factors over China for 1961–2000. Ann. Geophys. 2005, 23, 2425–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che, H.Z.; Shi, G.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Arimoto, R.; Zhao, J.Q.; Xu, L.; Wang, B.; Chen, Z.H. Analysis of 40 years of solar radiation data from China, 1961–2000. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wild, M. A new look at solar dimming and brightening in China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Cheng, C.C.K.; He, J. Solar radiation trend across China in recent decades: A revisit with quality-controlled data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, F.; Wang, K.C. Determining Factors of Monthly to Decadal Variability in Surface Solar Radiation in China: Evidences From Current Reanalyses. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 9161–9182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinker, R.T.; Laszlo, I. Modeling surface solar Irradiance for satellite spplications on a global scale. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 1992, 31, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Rossow, W.B.; Lacis, A.A.; Oinas, V.; Mishchenko, M.I. Calculation of radiative fluxes from the surface to top of atmosphere based on ISCCP and other global data sets: Refinements of the radiative transfer model and the input data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Fu, C. Assessment of GEWEX/SRB version 3.0 monthly global radiationdataset over China. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2011, 112, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liang, S.; Zhou, G.; Wu, H.; Zhao, X. Generating global land surface satellite incident shortwave radiation and photosynthetically active radiation products from multiple satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Qin, J.; Yang, K.; Liu, S.; Lu, N.; Niu, X. Retrieving high-resolution surface solar radiation with cloud parameters derived by combining MODIS and MTSAT data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2543–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelaro, R.; McCarty, W.; Suarez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R.; et al. The Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.; Günther, G.; Li, D.; Stein, O.; Wu, X.; Griessbach, S.; Heng, Y.; Konopka, P.; Müller, R.; Vogel, B.; et al. From ERA-Interim to ERA5: The considerable impact of ECMWF’s next-generation reanalysis on Lagrangian transport simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3097–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; Niu, X. A 16-year dataset (2000–2015) of high-resolution (3 h, 10 km) global surface solar radiation. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramanathan, V.; Crutzen, P.J.; Kiehl, J.T.; Rosenfeld, D. Aerosols, climate, and the hydrological cycle. Science 2001, 294, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, X.A.; Wang, P.C.; Chen, H.B.; Liang, F. Analysis of downwelling surface solar radiation in China from National Centers for Environmental Prediction reanalysis, satellite estimates, and surface observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Dickinson, R.E.; Liang, S. Clear sky visibility has decreased over land globally from 1973 to 2007. Science 2009, 323, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Yang, K.; Huang, J.; Tang, W.; Qin, J.; Niu, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, D.; Lu, N.; Fu, R. Impacts of wind stilling on solar radiation variability in China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Niu, X.L.; Lin, C.G.; Jing, X.W. A revisit to decadal change of aerosol optical depth and its impact on global radiation over China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 150, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liepert, B.G. Recent changes in solar radiation under cloudy conditions in Germany. Int. J. Clim. 1997, 17, 1581–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, X.L.; Wild, M. Causes of dimming and brightening in China inferred from homogenized daily clear-sky and all-sky in situ surface solar radiation records (1958–2016). J. Clim. 2019, 32, 5901–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherhead, E.C.; Reinsel, G.C.; Tiao, G.C.; Meng, X.-L.; Choi, D.; Cheang, W.-K.; Keller, T.; DeLuisi, J.; Wuebbles, D.J.; Kerr, J.B.; et al. Factors affecting the detection of trends: Statistical considerations and applications to environmental data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 17149–17161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. A new measure of rank correlation. Biometrika 1938, 30, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, C. Variability of the solar “constant” on time scales of minutes to years. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1987, 92, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, D.; Herber, A.; Thomason, L.W.; Leiterer, U. Vertical distribution of the spectral aerosol optical depth in the Arctic from 1993 to 1996. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 1857–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohvril, H.; Teral, H.; Neiman, L.; Kannel, M.; Uustare, M.; Tee, M.; Russak, V.; Okulov, O.; Jõeveer, A.; Kallis, A.; et al. Global dimming and brightening versus atmospheric column transparency, Europe, 1906–2007. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Yan, F.; Chin, M.; Diehl, T.; Mahowald, N.; Schultz, M.; Wild, M.; Wu, Y.; Yu, C. Anthropogenic and natural contributions to regional trends in aerosol optical depth, 1980–2006. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, M.; Huang, B. Spatio-temporal variation and impact factors analysis of satellite-based aerosol optical depth over China from 2002 to 2015. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 129, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmann, B. On the role of climate forcing by volcanic sulphate and volcanic ash. Adv. Meteorol. 2014, 2014, 340123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, M. Enlightening global dimming and brightening. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Yang, Y.H. China’s dimming and brightening: Evidence, causes and hydrological implications. Ann. Geophys. 2014, 32, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Ding, B.H.; Qin, J.; Tang, W.J.; Lu, N.; Lin, C.G. Can aerosol loading explain the solar dimming over the Tibetan Plateau? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L20710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saikawa, E.; Naik, V.; Horowitz, L.W.; Liu, J.F.; Mauzerall, D.L. Present and potential future contributions of sulfate, black and organic carbon aerosols from China to global air quality, premature mortality and, radiative forcing. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2814–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Gelencsér, A. Black carbon or brown carbon? The nature of light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3131–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, Y.C.; Simpson, R.W.; McTainsh, G.H.; Vowles, P.D.; Cohen, D.D.; Bailey, G.M. Source apportionment of visibility degradation problems in Brisbane (Australia) using the multiple linear regression techniques. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 3237–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evan, A.T.; Heidinger, A.K.; Vimont, D.J. Arguments against a physical long-term trend in global ISCCP cloud amounts. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Wild, M.; Folini, D.; Fraedrich, K.; Ren, G.; Kang, S. Decadal variation of surface solar radiation in the Tibetan Plateau from observations, reanalysis and model simulations. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 2073–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Min, M. Development of a 50-year daily surface solar radiation dataset over China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Wang, W.; Leung, L.R.; Kaiser, D.P. Variability of solar radiation under cloud-free skies in China: The role of aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Pinker, R.T.; Ma, Y.; Koike, T.; Wonsick, M.M.; Cox, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Stackhouse, P. Evaluation of satellite estimates of downward shortwave radiation over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Koike, T.; Stackhouse, P.; Mikovitz, C.; Cox, S.J. An assessment of satellite surface radiation products for highlands with Tibet instrumental data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Name | Description | Data Collection | Data Source | Temporal Scale | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSR | Global solar radiation | A high-resolution global surface solar radiation | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center (http://data.tpdc.ac.cn) | 1984–2016 | 10 km, 3 h |
| AODANA | Aerosol optical depth (AOD) analysis | instM_2d_gas_Nx | |||
| TAUTOT | In cloud optical thickness of all clouds | tavgM_2d_rad_Nx | |||
| TQV | Total precipitable water vapor | instM_2d_int_Nx | 0.5° × 0.625° (latitude × longitude) | ||
| PS | Surface pressure | instM_2d_asm_Nx | MERRA-2 (http://disc.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/mdisc/) | 1984–2016 | monthly-mean |
| SO2EMAN | SO2 anthropogenic emissions | tavgM_2d_adg_Nx | |||
| SO4EMAN | SO4 anthropogenic emissions | tavgM_2d_adg_Nx | |||
| OCEMAN | Organic carbon anthropogenic emissions | tavgM_2d_adg_Nx | |||
| BCEMAN | Black carbon anthropogenic emissions | tavgM_2d_adg_Nx |
| NEC | NWC | IM | TP | NC | LP | MYP | SBS | SC | YPS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSR (Wm−2) | −0.1551 | −0.1597 | −0.1040 | −0.2494 | −0.4491 | −0.3399 | −0.7141 | −0.6367 | −0.8218 | −0.5790 |
| AOD | 0.0025 | 0.0007 | 0.0004 | 0.0006 | 0.0094 | 0.0049 | 0.0122 | 0.0093 | 0.0093 | 0.0026 |
| TAUTOT | −0.0111 | 0.0409 | 0.0238 | 0.0702 | −0.0388 | 0.0207 | −0.0490 | 0.0040 | 0.0237 | 0.0393 |
| PS (hpa) | 0.3139 | 2.9727 | 3.2313 | 3.2221 | 0.5048 | 2.4038 | −1.4629 | 0.7171 | −0.9542 | 0.8912 |
| TQV (kg m−3) | 0.0200 | 0.0365 | 0.0265 | 0.0255 | 0.0240 | 0.0338 | 0.0443 | 0.0395 | 0.0598 | 0.0214 |
| BC (10−12 kg m−2s−1) | 0.0509 | 0.0045 | 0.0141 | 0.0038 | 0.1851 | 0.0996 | 0.1266 | 0.1421 | 0.0639 | 0.0428 |
| OC (10−12 kg m−2s−1) | 0.0466 | 0.0024 | 0.0097 | 0.0057 | 0.1551 | 0.0709 | 0.1297 | 0.1421 | 0.0717 | 0.0454 |
| SO4 (10−12 kg m−2s−1) | 0.1011 | 0.0074 | 0.0723 | 0.0076 | 0.4443 | 0.1557 | 0.3448 | 0.2094 | 0.2421 | 0.0735 |
| SO2 (10−12 kg m−2s−1) | 0.0218 | 0.0016 | 0.0156 | 0.0016 | 0.0958 | 0.0336 | 0.0743 | 0.0451 | 0.0522 | 0.0158 |
| Author(s) | Data Source(s) | Period | Trend Slope |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liang et al. [18] | 42 (stations) | 1961–2000 | −0.52 Wm−2 yr−1 |
| Che et al. [19] | 64 (stations) | 1961–2000 | −0.45 Wm−2 yr−1 |
| Tang et al. [21] | 459 (stations) | 1961–2000 | −0.23 Wm−2 yr−1 |
Yang et al. [37] | 95 (stations) | 1958–1999 1958–2016 | −0.74 ± 0.04 Wm−2 yr−1 −0.49 ± 0.03 Wm−2 yr−1 |
| Feng et al. [22] | 2400 (stations) MERRA-2 (reanalysis) | 1980–2014 1980–2014 | −0.72 Wm−2 yr−1 −0.87 Wm−2 yr−1 |
| Wu et al. [25] | GEWEX-SRB (satellite retrievals date) | 1984–1994 1994–2004 | −0.21 Wm−2 yr−1 −0.50 Wm−2 yr−1 |
| Present research | Table 1 | 1984–2016 | −0.371 Wm−2 yr−1 |
| Author(s) | Data Source(s) | Period | Trend Slope |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tang et al. [22] | 38 (stations) | 1961–1978 1979–2006 | 0.17 ± 0.19 Wm−2 yr−1 −0.22 ± 0.12 Wm−2 yr−1 |
| You et al. [56] | 10 (stations) NCEP/NCAR ECHAM5-HAM | 1960–2009 1960–2009 1960–2009 | −0.10 Wm−2 yr−1 0.11 Wm−2 yr−1 −0.054 Wm−2 yr−1 |
| Tang et al. [57] | 96 (stations) | 1961–1978 1978–2010 | 0.035 Wm−2 yr−1 −0.22 Wm−2 yr−1 |
| Present research | Table 1 | 1984–2016 | −0.25 Wm−2 yr−1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, H.; Qin, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X. Solar Brightening/Dimming over China’s Mainland: Effects of Atmospheric Aerosols, Anthropogenic Emissions, and Meteorological Conditions. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010088
Fang H, Qin W, Wang L, Zhang M, Yang X. Solar Brightening/Dimming over China’s Mainland: Effects of Atmospheric Aerosols, Anthropogenic Emissions, and Meteorological Conditions. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(1):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010088
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Hejin, Wenmin Qin, Lunche Wang, Ming Zhang, and Xuefang Yang. 2021. "Solar Brightening/Dimming over China’s Mainland: Effects of Atmospheric Aerosols, Anthropogenic Emissions, and Meteorological Conditions" Remote Sensing 13, no. 1: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010088
APA StyleFang, H., Qin, W., Wang, L., Zhang, M., & Yang, X. (2021). Solar Brightening/Dimming over China’s Mainland: Effects of Atmospheric Aerosols, Anthropogenic Emissions, and Meteorological Conditions. Remote Sensing, 13(1), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010088