Using GRACE Data to Study the Impact of Snow and Rainfall on Terrestrial Water Storage in Northeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. GRACE Data
2.2. GlobSnow Snow Water Equivalent Products
2.3. Average Monthly Data of ERA5-Land
2.4. SOI
2.5. Fitting Method
2.6. Methods for Separating Interannual and Seasonal Signals
3. Results
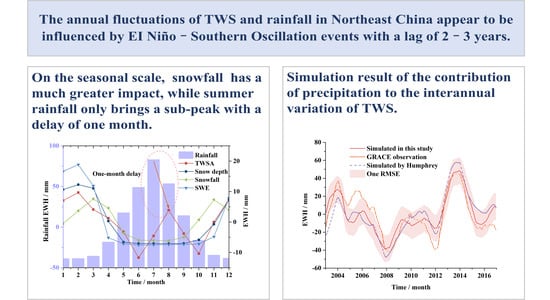
3.1. Impact of Rainfall and Snowfall on Seasonal Changes in TWSA in Northeast China
3.2. Impact of ENSO on Rainfall and TWSA in Northeast China
3.3. Simulation of the Interannual Contribution of Rainfall to TWS in Northeast China
4. Discussion
4.1. Challenge of Investigating Snow Cover Mass Change Using GRACE Data
4.2. Uncertainties in ENSO Impact on Rainfall and TWS in Northeast China
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, N.; Yoon, J.; Mariotti, A.; Swenson, S. Variability of Basin-Scale Terrestrial Water Storage from a PER Water Budget Method: The Amazon and the Mississippi. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 248–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J.S. Remote sensing of terrestrial water storage, soil moisture and surface waters. Geophys. Monogr. 2004, 150, 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, X.; Wu, J.J.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, H. Variations in water storage in China over recent decades from GRACE observations and GLDAS. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Rodell, M.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D.; Dam, T.M. Assimilation of GRACE terrestrial water storage into a land surface model: Evaluation and potential value for drought monitoring in western and central Europe. J. Hydrol. 2012, 446–447, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, R.; Schwintzer, P.; Flechtner, F.; Reigber, C.; Guentner, A.; Doell, P.; Ramillien, G.; Cazenave, A.; Petrovic, S.; Jochmann, H. GRACE observations of changes in continental water storage. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2006, 50, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M.; et al. The Global Land Data Assimilation System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Li, T.; Zheng, W.; Hu, L.; Han, S.C.; Tangdamrongsub, N.; Šprlák, M.; Huang, Z. Improving regional groundwater storage estimates from grace and global hydrological models over Tasmania, Australia. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 1809–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramillien, G.; Frappart, F.; Cazenave, A.; Güntnerb, A. Time variations of land water storage from an inversion of 2 years of GRACE geoids. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 235, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, W.; Hu, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Han, S.C. Statistical Downscaling of GRACE-Derived Groundwater Storage Using ET Data in the North China Plain. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 5973–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Famiglietti, J.S. The potential for satellite-based monitoring of groundwater storage changes using GRACE: The High Plains aquifer, Central US. J. Hydrol. 2002, 263, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, H.; Ma, J.; Zheng, W.; Zeng, J. Comparison of soil moisture in gldas model simulations and in situ observations over the tibetan plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2658–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wahr, J.; Molenaar, M.; Bryan, F. Time variability of the Earth’s gravity field: Hydrological and oceanic effects and their possible detection using GRACE. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1998, 103, 30205–30229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapley, B.D.; Bettadpur, S.; Watkins, M.; Reigber, C. The gravity recovery and climate experiment: Mission overview and early results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L09607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.K. Satellite in low orbit (CHAMP, GRACE, GOCE) and high precision earth gravity field. The latest progress of satellite gravity geodesy and its great influence on geoscience. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2002, 22, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, K.; Heki, K. Coseismic gravity changes of the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake from satellite gravimetry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L00G12. [Google Scholar]
- Heki, K.; Matsuo, K. Coseismic gravity changes of the 2010 earthquake in central Chile from satellite gravimetry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L24306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zemp, M.; Huss, M.; Thibert, E.; Eckert, N.; McNabb, R.; Huber, J.; Barandun, M.; Machguth, H.; Nussbaumer, S.; Gärtner-Roer, I. Global glacier mass changes and their contributions to sea-level rise from 1961 to 2016. Nature 2019, 568, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rignot, E.; Mouginot, J.; Scheuchl, B.; van den Broeke, M.; van Wessem, M.J.; Morlighem, M. Four decades of Antarctic ice sheet mass balance from 1979–2017. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Ni, S.; Tang, L.; Hu, X. Long-term and inter-annual mass changes of Patagonia ice field from GRACE. Geod. Geodyn. 2019, 10, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Heki, K.; Qian, A. Acceleration in the global mean sea level rise: 2005–2015. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 11905–11913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, L.; Tang, H.; Yi, S.; Sun, W. The trend and seasonal change of sediment in the East China Sea detected by GRACE. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditmar, P. Conversion of time-varying stokes coefficients into mass anomalies at the earth’s surface considering the earth’s oblateness. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghobadi-Far, K.; Šprlák, M.; Han, S.C. Determination of Ellipsoidal Surface Mass Change from GRACE Time-Variable Gravity Data. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 219, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Zhong, M.; Lemoine, J.; Richard, B.; Hsu, H.T.; Xia, J. Evaluation of groundwater depletion in North China using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data and ground-based measurements. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Velicogna, I.; Famiglietti, J.S. Satellite-based estimates of groundwater depletion in India. Nature 2009, 460, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.L.; Wilson, C.R.; Tapley, B.D. The 2009 exceptional Amazon flood and interannual terrestrial water storage change observed by GRACE. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W12526. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; E, D.-C.; Chao, D.-B.; Wang, H. Seasonal and inter-annual change in land water storage from GRACE. Chin. J. Geophys. 2009, 52, 2987–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forootan, E.; Schumacher, M.; Mehrnegar, N.; Bezděk, A.; Shum, C.K. An Iterative ICA-based Reconstruction Method to Produce Consistent Time-Variable Total Water Storage Fields using GRACE and Swarm Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1639. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Shum, C.; Zhong, M.; Pan, Y. Groundwater Storage Changes in China from Satellite Gravity: An Overview. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, W.; Wang, C.Q.; Mu, D.P.; Zhong, M.; Zhong, Y.L.; Xu, H.Z. Groundwater storage variations in the North China Plain from GRACE with spatial constraints. Chin. J. Geophys. 2017, 60, 1630–1642. [Google Scholar]
- Tangdamrongsub, N.; Han, S.C.; Jasinski, M.F.; Šprlák, M. Quantifying Water Storage Change and Land Subsidence Induced by Reservoir Impoundment Using GRACE, Landsat, and GPS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhong, M.; Feng, W.; Zhong, Y.L.; Xu, H.Z. Effects of two strong ENSO events on terrestrial water storage anomalies in China from GRRACE during 2005–2017. Chin. J. Geophys. 2020, 63, 141–154. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Chao, B.F.; Chen, J.; Wilson, C.R. Terrestrial water storage anomalies of Yangtze River Basin droughts observed by GRACE and connections with ENSO. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2015, 126, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Chen, J.; Wilson, C.R.; Li, J.; Hu, X.; Fu, R. Global Terrestrial Water Storage Changes and Connections to ENSO Events. Surv. Geophys. 2018, 39, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.L.; Zhong, M.; Feng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wu, D. Groundwater Depletion in the West Liaohe River Basin, China and Its Implications Revealed by GRACE and In Situ Measurements. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 493. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V.V.; DiGirolamo, N.E.; Bayr, K.J. MODIS snow-cover products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, J.; Walker, J.; Houser, P. Factors affecting remotely sensed snow water equivalent uncertainty. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Yang, Z.L.; Niu, G.Y.; Dickinson, R.E. Enhancing the estimation of continental-scale snow water equivalent by assimilating modis snow cover with the ensemble kalman filter. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D08120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nolin, A.W. Recent advances in remote sensing of seasonal snow. J. Glaciol. 2010, 56, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, F.; Russell, H.A.J. Estimating snow mass and peak river flows for the Mackenzie River basin using grace satellite observations. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frappart, F.; Ramillien, G.; Biancamaria, S.; Mognard, N.; Cazenave, A. Evolution of high-latitude snow mass derived from the grace gravimetry mission (2002–2004). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, G.Y.; Seo, K.W.; Yang, Z.L.; Wilson, C.; Su, H.; Chen, J.; Rodell, M. Retrieving snow mass from grace terrestrial water storage change with a land surface model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L15704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forman, B.A.; Reichle, R.H.; Rodell, M. Assimilation of terrestrial water storage from grace in a snow-dominated basin. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W01507. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.J.; Mi, D.S. Distribution of snow cover in China. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 1983, 5, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.H.; Wang, Z.L.; Cui, Y. Snow cover of China during the last 40 years: Spatial distribution and international variation. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2009, 31, 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.T.; Li, X.; Xu, X.C.; He, Z.Q. Spatial-temporal variations analysis of snow cover in China from 1992–2010. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 2641–2654. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.M.; Li, D.L.; Cheng, G.Y. GIS-based spatializing method for estimating snow cover depth in Northeast China and its nabes. Arid Zone Res. 2012, 29, 927–933. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Pan, Y.; Gong, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, C. Comparing Groundwater Storage Changes in Two Main Grain Producing Areas in China: Implications for Sustainable Agricultural Water Resources Management. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Ries, J.C.; Tapley, B.D. Variations of the earth’s figure axis from satellite laser ranging and GRACE. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2011, 116, B01409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landerer, F. Monthly Estimates of Degree-1 (Geocenter) Gravity Coefficients, Generated from GRACE (04-2002-06/2017) and GRACE-FO (06/2018 Onward) RL06 Solutions, GRACE Technical Note 13, the GRACE Project, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. 2019. Available online: https://podaac-tools.jpl.nasa.gov/drive/files/allData/grace/docs/TN-13_GEOC_CSR_RL06.txt (accessed on 1 November 2020).
- Sun, Y.; Riva, R.; Ditmar, P. Optimizing estimates of annual variations and trends in geocenter motion and J2 from a combination of GRACE data and geophysical models. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 8352–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geruo, A.; Wahr, J.; Zhong, S. Computations of the viscoelastic response of a 3-D compressible Earth to surface loading: An application to Glacial Isostatic Adjustment in Antarctica and Canada. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 192, 557–572. [Google Scholar]
- Kusche, J.; Schmidt, R.; Petrovic, S.; Rietbroek, R. Decorrelated GRACE time-variable gravity solutions by GFZ, and their validation using a hydrological model. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farrell, W.E. Deformation of the Earth by surface loads. Rev. Geophys. 1972, 10, 761–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Globsnow. Available online: www.globsnow.info (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Chen, X.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Zhao, K.; Zheng, X.; Jiang, T. Based on Snow Cover Survey Data of Accuracy Veri-fication and Analysis of Passive Microwave Snow Cover Remote Sensing Products in Northeast China. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2019, 34, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar]
- ERA5-European Environment Agency. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/external/era-interim-1 (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Muñoz Sabater, J. ERA5-Land Monthly Averaged Data from 1981 to Present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). 2019. Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/reanalysis-era5-land-monthly-means?tab=overview (accessed on 10 November 2020). [CrossRef]
- Climate Glossary-Southern Oscillation Index (SOI). Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/glossary/soi.shtml (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Chang, L.; Sun, W. Greening Trends of Southern China Confirmed by GRACE. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.B.; Wei, F.Y.; Liu, G.L.; Zhao, C.S.; Yu, X.X.; Zheng, C.Q.; Ning, Y.X.; Qian, J.G.; Shi, J.J. Celiang Pingcha, 1st ed.; China University of Mining and Technology Press: Xuzhou, China, 2008; pp. 7–132. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 1992, 1, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, A.; England, M.H.; Cai, W. Impact of Indo-Pacific Feedback Interactions on ENSO Dynamics Diagnosed Using Ensemble Climate Simulations. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 7743–7763. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.T.; Wu, R. Respective impacts of the East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO on winter rainfall in China. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D02107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, D.; Wu, Y. Yangtze floods and droughts (China) and teleconnections with ENSO activities (1470–2003). Quat. Int. 2006, 144, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, A.G.; Ge, J.P.; Pang, D.Q. Asynchronous Response of Droughts to ENSO in China. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2006, 28, 535–542. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, S.; Song, C.Q.; Heki, K.; Kang, S.; Chang, L. Satellite-observed monthly glacier and snow mass changes in southeast Tibet: Implication for substantial meltwater contribution to the Brahmaputra. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 2267–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, V.; Gudmundsson, L. GRACE-REC: A reconstruction of climate-driven water storage changes over the last century. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1153–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klees, R.; Zapreeva, E.A.; Winsemius, H.C.; Savenije, H.H.G. The bias in GRACE estimates of continental water storage variations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1227–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longuevergne, L.; Scanlon, B.R.; Wilson, C.R. GRACE Hydrological estimates for small basins: Evaluating processing approaches on the High Plains Aquifer, USA. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W11517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Li, Q.; Sun, P. Terrestrial Water Storage in China: Spatiotemporal Pattern and Driving Factors. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]












| Data Style | Annual Amplitude/mm | σ/mm | Annual Phase/Month | σ/Month |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWSA | 6.64 | 2.16 | 0.94 (January) | 0.44 |
| Rainfall | 56.64 | 2.17 | 6.51 (June–July) | 0.05 |
| Snowfall | 5.81 | 0.64 | 0.79 (January) | 0.15 |
| Snow depth | 10.33 | 0.60 | 1.11 (January) | 0.08 |
| SWE | 12.40 | 0.65 | 1.08 (January) | 0.07 |
| Number | n/Month | a | RMSE/mm | ME/mm | Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14 | 0.3 | 15.54 | 13.06 | 0.81 |
| 2 | 14 | 0.4 | 14.82 | 12.52 | 0.81 |
| 3 | 15 | 0.3 | 15.16 | 12.66 | 0.82 |
| 4 | 15 | 0.4 | 14.59 | 12.44 | 0.82 |
| 5 | 16 | 0.3 | 14.86 | 12.35 | 0.82 |
| 6 | 16 | 0.4 | 14.50 | 12.37 | 0.82 |
| 7 | 17 | 0.3 | 14.67 | 12.14 | 0.82 |
| 8 | 17 | 0.4 | 15.53 | 12.34 | 0.82 |
| 9 | 18 | 0.3 | 14.57 | 12.04 | 0.82 |
| 10 | 18 | 0.4 | 14.72 | 12.32 | 0.82 |
Publisher′s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, A.; Yi, S.; Chang, L.; Sun, G.; Liu, X. Using GRACE Data to Study the Impact of Snow and Rainfall on Terrestrial Water Storage in Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4166. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244166
Qian A, Yi S, Chang L, Sun G, Liu X. Using GRACE Data to Study the Impact of Snow and Rainfall on Terrestrial Water Storage in Northeast China. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(24):4166. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244166
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, An, Shuang Yi, Le Chang, Guangtong Sun, and Xiaoyang Liu. 2020. "Using GRACE Data to Study the Impact of Snow and Rainfall on Terrestrial Water Storage in Northeast China" Remote Sensing 12, no. 24: 4166. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244166
APA StyleQian, A., Yi, S., Chang, L., Sun, G., & Liu, X. (2020). Using GRACE Data to Study the Impact of Snow and Rainfall on Terrestrial Water Storage in Northeast China. Remote Sensing, 12(24), 4166. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244166