Evaluation of the Radar QPE and Rain Gauge Data Merging Methods in Northern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
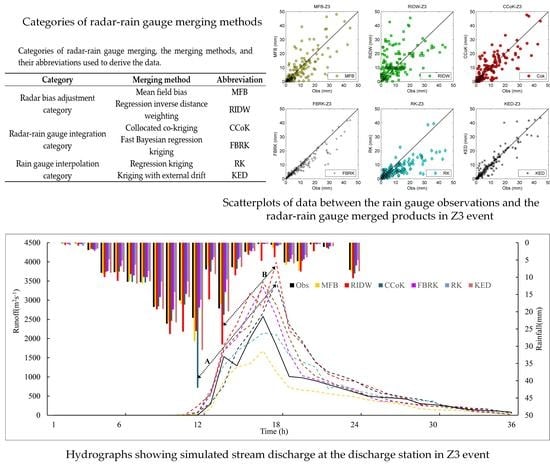
2.1. Radar-Rain Gauge Merging Methods
2.1.1. Radar Bias Adjustment Category
2.1.2. Radar-Rain Gauge Integration Category
2.1.3. Rain Gauge Interpolation Category Using the Spatial Association of Radar as an Addition
2.2. Meteorological Evaluation
2.2.1. Leave-One-Out Cross Validation (LOOCV)
2.2.2. Hybrid Hydrological Model (Hybrid-Hebei Model)
3. Study Area and Data
3.1. Study Area and Events
3.2. Weather Radar and Data
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Evaluation of Radar-Rain Gauge Merging Methods
4.2. Hydrological Model Performance Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Varlas, G.; Anagnostou, M.; Spyrou, C.; Papadopoulos, A.; Kalogiros, J.; Mentzafou, A.; Michaelides, S.; Baltas, E.; Karymbalis, E.; Katsafados, P. A multi-platform hydrometeorological analysis of the flash flood event of 15 November 2017 in Attica, Greece. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvadore, E.; Bronders, J.; Batelaan, O. Hydrological modelling of urbanized catchments: A review and future directions. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, S.; Fowler, H.; Evans, J.; Alexander, L.; Berg, P.; Johnson, F.; Kendon, E.; Lenderink, G.; Roberts, N. Future changes to the intensity and frequency of short-duration extreme rainfall. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 522–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, P.; Fatichi, S.; Gaál, L.; Szolgay, J.; Burlando, P. Storm type effects on super Clausius–Clapeyron scaling of intense rainstorm properties with air temperature. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1753–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobligeois, F.; Andréassian, V.; Perrin, C.; Tabary, P.; Loumagne, C. When does higher spatial resolution rainfall information improve streamflow simulation? An evaluation using 3620 flood events. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 575–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Borga, M.; Vivoni, E.R.; Papadopoulos, A. Sensitivity of a mountain basin flash flood to initial wetness condition and rainfall variability. J. Hydrol. 2011, 402, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Beek, C.; Leijnse, H.; Stricker, J.; Uijlenhoet, R.; Russchenberg, H. Performance of high-resolution X-band radar for rainfall measurement in The Netherlands. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berne, A.; Krajewski, W.F. Radar for hydrology: Unfulfilled promise or unrecognized potential? Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Refsgaard, J.C.; Sonnenborg, T.O.; Vejen, F.; Jensen, K.H. Statistical analysis of the impact of radar rainfall uncertainties on water resources modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W09526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-Y.; Vivekanandan, J.; Ikeda, K.; Lin, P.-L. Quantitative precipitation estimation of the epic 2013 Colorado flood event: Polarization radar-based variational scheme. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2016, 55, 1477–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, J.L.; Binns, A.D. A review of gauge-radar merging methods for quantitative precipitation estimation in hydrology. Can. Water Resour. J. 2016, 41, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, H.; Yin, J. Utilization of a C-band polarimetric radar for severe rainfall event analysis in complex terrain over eastern China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, J.W. Integration of radar and raingage data for improved rainfall measurement. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 1970, 9, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arsenault, R.; Brissette, F. Determining the optimal spatial distribution of weather station networks for hydrological modeling purposes using RCM datasets: An experimental approach. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárdossy, A.; Das, T. Influence of rainfall observation network on model calibration and application. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habib, E.; Haile, A.T.; Tian, Y.; Joyce, R.J. Evaluation of the high-resolution CMORPH satellite rainfall product using dense rain gauge observations and radar-based estimates. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1784–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudenhoofdt, E.; Delobbe, L. Generation and verification of rainfall estimates from 10-yr volumetric weather radar measurements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1223–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-P.; Ochoa-Rodríguez, S.; Onof, C.; Willems, P. Singularity-sensitive gauge-based radar rainfall adjustment methods for urban hydrological applications. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4001–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jewell, S.A.; Gaussiat, N. An assessment of kriging-based rain-gauge–radar merging techniques. Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 2015, 141, 2300–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, J.L. Evaluation of Gauge-Radar Merging Methods for Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in Hydrology: A Case Study in the Upper Thames River Basin. Master’s Thesis, The University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.P.; Ochoa-Rodríguez, S.; Simões, N.E.; Onof, C.; Maksimović, C. Radar-raingauge data combination techniques: A revision and analysis of their suitability for urban hydrology. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todini, E. A Bayesian technique for conditioning radar precipitation estimates to rain-gauge measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2001, 5, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation; Oxford University Press on Demand: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, S.; Pegram, G. Combining radar and rain gauge rainfall estimates using conditional merging. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2005, 6, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarini, G.; Mandapaka, P.V.; Krajewski, W.F.; Moore, R.J. Rainfall and sampling uncertainties: A rain gauge perspective. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuurmans, J.; Bierkens, M.; Pebesma, E.; Uijlenhoet, R. Automatic prediction of high-resolution daily rainfall fields for multiple extents: The potential of operational radar. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 1204–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Engel, B.A. NEXRAD quantitative precipitation estimations for hydrologic simulation using a hybrid hydrologic model. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, S.J.; Moore, R.J. Hydrological modelling using raingauge-and radar-based estimators of areal rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2008, 358, 159–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, P.; Mieleitner, J. Analyzing input and structural uncertainty of nonlinear dynamic models with stochastic, time-dependent parameters. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W10402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anagnostou, M.; Nikolopoulos, E.; Kalogiros, J.; Anagnostou, E.; Marra, F.; Mair, E.; Bertoldi, G.; Tappeiner, U.; Borga, M. Advancing precipitation estimation and streamflow simulations in complex terrain with X-band dual-polarization radar observations. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rico-Ramirez, M.; Liguori, S.; Schellart, A. Quantifying radar-rainfall uncertainties in urban drainage flow modelling. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nanding, N.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A.; Han, D. Comparison of different radar-raingauge rainfall merging techniques. J. Hydroinform. 2015, 17, 422–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Rodriguez, S.; Wang, L.P.; Willems, P.; Onof, C. A review of radar-rain gauge data merging methods and their potential for urban hydrological applications. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 6356–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borup, M.; Grum, M.; Linde, J.J.; Mikkelsen, P.S. Dynamic gauge adjustment of high-resolution X-band radar data for convective rain storms: Model-based evaluation against measured combined sewer overflow. J. Hydrol. 2016, 539, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, S.; Jones, D.; Moore, R. Static and dynamic calibration of radar data for hydrological use. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2000, 4, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Baeck, M.L.; Meierdiercks, K.L.; Miller, A.J.; Krajewski, W.F. Radar rainfall estimation for flash flood forecasting in small urban watersheds. Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 2087–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitzmiller, D.; Miller, D.; Fulton, R.; Ding, F. Radar and multisensor precipitation estimation techniques in National Weather Service hydrologic operations. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.J.; Krajewski, W.F.; Bowles, D.S. Stochastic interpolation of rainfall data from rain gages and radar using cokriging: 1. Design of experiments. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiles, J.-P.; Delfiner, P. Geostatistics: Modeling Spatial Uncertainty; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 497. [Google Scholar]
- Velasco-Forero, C.A.; Sempere-Torres, D.; Cassiraga, E.F.; Gómez-Hernández, J.J. A non-parametric automatic blending methodology to estimate rainfall fields from rain gauge and radar data. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 986–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmaryan, L.; Journel, A. Two Markov models and their application. Math. Geol. 1999, 31, 965–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Ng, T.L. Fast Bayesian Regression Kriging Method for Real-Time Merging of Radar, Rain Gauge, and Crowdsourced Rainfall Data. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 3194–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecinati, F.; Wani, O.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A. Comparing Approaches to Deal with Non-Gaussianity of Rainfall Data in Kriging-Based Radar-Gauge Rainfall Merging. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 8999–9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdin, R.; Frei, C.; Künsch, H.R. Data transformation and uncertainty in geostatistical combination of radar and rain gauges. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1332–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberlandt, U. Geostatistical interpolation of hourly precipitation from rain gauges and radar for a large-scale extreme rainfall event. J. Hydrol. 2007, 332, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadoux, A.M.-C.; Brus, D.J.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A.; Heuvelink, G.B. Sampling design optimisation for rainfall prediction using a non-stationary geostatistical model. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 107, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Liu, J.; Yan, D.; Ding, L.; Li, C. Ensemble flood forecasting based on a coupled atmospheric-hydrological modeling system with data assimilation. Atmos. Res. 2019, 224, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Hong, Z.; Pan, Y.; Yu, J.; Maguire, L. China’s 1 km Merged Gauge, Radar and Satellite Experimental Precipitation Dataset. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, L.; Liu, L.; Gu, S. An algorithm of identifying convective and echo in mixed precipitation and its application in estimating rainfall intensity. Plateau Meteorol. 2007, 26, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Langston, C.; Howard, K. Brightband identification based on vertical profiles of reflectivity from the WSR-88D. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1859–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, B.; Buytaert, W.; Zulkafli, Z.; Lavado, W.; Willems, B.; Robles, L.A.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, J.P. High-resolution satellite-gauge merged precipitation climatologies of the Tropical Andes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 1190–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foehn, A.; Hernández, J.G.; Schaefli, B.; De Cesare, G. Spatial interpolation of precipitation from multiple rain gauge networks and weather radar data for operational applications in Alpine catchments. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 1092–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heistermann, M.; Kneis, D. Benchmarking quantitative precipitation estimation by conceptual rainfall-runoff modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W06514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goudenhoofdt, E.; Delobbe, L. Evaluation of radar-gauge merging methods for quantitative precipitation estimates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erdin, R. Geostatistical Methods for Hourly Radar-Gauge Combination: An Explorative, Systematic Application at Meteoswiss; MeteoSchweiz: Zürich, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- García-Pintado, J.; Barberá, G.G.; Erena, M.; Castillo, V.M. Rainfall estimation by rain gauge-radar combination: A concurrent multiplicative-additive approach. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W01415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Rodriguez, S.; Wang, L.; Bailey, A.; Schellart, A.; Willems, P.; Onof, C. Evaluation of radar-rain gauge merging methods for urban hydrological applications: Relative performance and impact of gauge density. In Proceedings of the UrbanRain15 Proceedings “Rainfall in Urban and Natural Systems”, Pontresina, Switzerland, 1–5 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Berndt, C.; Rabiei, E.; Haberlandt, U. Geostatistical merging of rain gauge and radar data for high temporal resolutions and various station density scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavetski, D.; Kuczera, G.; Franks, S.W. Bayesian analysis of input uncertainty in hydrological modeling: 1. Theory. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.; Cornelissen, T.; Fang, Z.; Bogena, H.; Diekkrüger, B.; Kollet, S.; Stisen, S. Inter-comparison of three distributed hydrological models with respect to seasonal variability of soil moisture patterns at a small forested catchment. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huuskonen, A.; Saltikoff, E.; Holleman, I. The operational weather radar network in Europe. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Category | Merging Method | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| Radar bias adjustment category | Mean field bias | MFB |
| Regression inverse distance weighting | RIDW | |
| Radar-rain gauge integration category | Collocated co-kriging | CCoK |
| Fast Bayesian regression kriging | FBRK | |
| Rain gauge interpolation category | Regression kriging | RK |
| Kriging with external drift | KED |
| Catchment | Event ID | Date | Start Time | Duration | Rain Gauges | Accumulated Rainfall (mm) | Peak Flow (m3s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zijingguan | Z1 | 22/05/2007 | 00:00 | 17 h | 11 | 39.52 | 6.8 |
| Z2 | 10/08/2008 | 00:00 | 10 h | 45.53 | 2.5 | ||
| Z3 | 21/07/2012 | 04:00 | 14 h | 155.43 | 2580.0 | ||
| Z4 | 19/07/2016 | 05:00 | 19 h | 74.29 | 53.4 | ||
| Fuping | F1 | 29/07/2007 | 20:00 | 24 h | 8 | 63.38 | 29.7 |
| F2 | 30/07/2012 | 08:00 | 24 h | 50.48 | 70.7 | ||
| F3 | 01/09/2012 | 08:00 | 18 h | 40.30 | 13.7 | ||
| F4 | 25/07/2016 | 00:00 | 11 h | 10.8 | 2020 |
| Radar Name | Name of Radar Site | Frequency (GHz) | Beam Width (°) | Antenna Diameter (m) | Pulse Width (μs) | Antenna Gain (db) | Peak Power (kw) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shijiazhuang | SA | 2.7~3.0 | 1 | 11.8 * | 1.57 | ≥44 | 650 |
| Basin | Indicator | OR | MFB | RIDW | CCoK | FBRK | RK | KED |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zijingguan | BIAS | −2.84 | −1.69 | 1.61 | 0.58 | 0.24 | −0.71 | 0.34 |
| RMSE | 4.84 | 4.49 | 3.28 | 3.3 | 1.31 | 2.92 | 1.41 | |
| MRTE | 1.86 | 1.22 | 1.03 | 0.55 | 0.21 | 0.78 | 0.22 | |
| Fuping | BIAS | −1.08 | −0.36 | 0.33 | 0.20 | −0.08 | −0.28 | −0.11 |
| RMSE | 3.78 | 2.14 | 1.64 | 2.22 | 1.18 | 2.72 | 1.21 | |
| MRTE | 1.63 | 0.98 | 0.49 | 0.57 | 0.19 | 0.73 | 0.22 |
| Event | Indicator | OR | MFB | RIDW | CCoK | FBRK | RK | KED |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | BIAS | −0.84 | −0.49 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.07 | −0.16 | −0.10 |
| RMSE | 2.33 | 1.05 | 1.08 | 0.87 | 0.41 | 1.05 | 0.53 | |
| MRTE | 0.73 | 0.34 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.06 | |
| Z2 | BIAS | −1.195 | −0.78 | 0.61 | −0.14 | −0.06 | −0.31 | 0.09 |
| RMSE | 5.69 | 2.26 | 2.15 | 1.86 | 0.85 | 1.97 | 1.07 | |
| MRTE | 1.87 | 0.67 | 0.52 | 0.34 | 0.09 | 0.40 | 0.14 | |
| Z3 | BIAS | −4.40 | −2.36 | 2.34 | 1.17 | 0.54 | −1.01 | 0.76 |
| RMSE | 9.11 | 7.97 | 5.35 | 6.17 | 2.96 | 5.78 | 3.23 | |
| MRTE | 2.69 | 1.90 | 1.27 | 1.53 | 0.50 | 1.34 | 0.69 | |
| Z4 | BIAS | −2.68 | −1.01 | 0.71 | −0.33 | −0.16 | −0.66 | 0.21 |
| RMSE | 6.61 | 4.12 | 3.12 | 1.31 | 0.97 | 2.10 | 0.99 | |
| MRTE | 2.12 | 1.68 | 1.11 | 0.66 | 0.20 | 0.87 | 0.31 |
| Event | Indicator | OR | MFB | RIDW | CCoK | FBRK | RK | KED |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | BIAS | −1.87 | −0.93 | 0.41 | 0.76 | −0.23 | −0.68 | −0.31 |
| RMSE | 5.43 | 3.33 | 2.35 | 2.12 | 1.42 | 2.67 | 1.66 | |
| MRTE | 3.27 | 1.40 | 1.06 | 0.73 | 0.19 | 1.28 | 0.43 | |
| F2 | BIAS | −0.93 | −0.53 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.08 | −0.24 | 0.09 |
| RMSE | 2.79 | 1.89 | 1.36 | 1.84 | 0.61 | 1.45 | 0.96 | |
| MRTE | 1.55 | 0.62 | 0.33 | 0.45 | 0.11 | 0.34 | 0.20 | |
| F3 | BIAS | −0.95 | −0.53 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.03 | −0.26 | 0.07 |
| RMSE | 2.71 | 1.32 | 0.89 | 1.01 | 0.51 | 0.92 | 0.65 | |
| MRTE | 0.71 | 0.47 | 0.18 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.12 | |
| F4 | BIAS | −0.59 | −0.25 | 0.17 | 0.24 | −0.04 | 0.28 | 0.05 |
| RMSE | 4.18 | 2.02 | 1.68 | 1.87 | 0.43 | 1.78 | 0.64 | |
| MRTE | 0.88 | 0.36 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 0.26 | 0.11 |
| Event | Indicator | MFB | RIDW | CCoK | FBRK | RK | KED |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | NSE | 0.37 | 0.44 | 0.51 | 0.57 | 0.46 | 0.60 |
| RE | −0.47 | 0.57 | 0.24 | 0.21 | −0.38 | 0.26 | |
| Z2 | NSE | 0.47 | 0.41 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 0.46 | 0.61 |
| RE | −0.38 | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.28 | −0.29 | 0.24 | |
| Z3 | NSE | 0.36 | 0.52 | 0.42 | 0.53 | 0.41 | 0.49 |
| RE | −0.52 | 0.54 | 0.35 | 0.28 | −0.16 | 0.41 | |
| Z4 | NSE | 0.26 | 0.37 | 0.41 | 0.52 | 0.38 | 0.50 |
| RE | −0.68 | 0.61 | 0.55 | 0.38 | −0.69 | 0.28 | |
| F1 | NSE | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.48 | 0.58 | 0.42 | 0.55 |
| RE | −0.47 | 0.68 | 0.56 | 0.42 | −0.48 | 0.38 | |
| F2 | NSE | 0.41 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.61 | 0.49 | 0.62 |
| RE | −0.55 | 0.95 | 0.77 | 0.55 | −0.48 | 0.48 | |
| F3 | NSE | 0.36 | 0.42 | 0.46 | 0.54 | 0.40 | 0.51 |
| RE | −0.49 | 0.78 | 0.63 | 0.37 | −0.33 | 0.65 | |
| F4 | NSE | 0.21 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.53 | 0.35 | 0.55 |
| RE | −0.68 | 0.44 | 0.36 | 0.68 | −0.57 | 0.48 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, Q.; Liu, J.; Tian, J.; Jiao, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, W.; Yu, F. Evaluation of the Radar QPE and Rain Gauge Data Merging Methods in Northern China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030363
Qiu Q, Liu J, Tian J, Jiao Y, Li C, Wang W, Yu F. Evaluation of the Radar QPE and Rain Gauge Data Merging Methods in Northern China. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(3):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030363
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Qingtai, Jia Liu, Jiyang Tian, Yufei Jiao, Chuanzhe Li, Wei Wang, and Fuliang Yu. 2020. "Evaluation of the Radar QPE and Rain Gauge Data Merging Methods in Northern China" Remote Sensing 12, no. 3: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030363
APA StyleQiu, Q., Liu, J., Tian, J., Jiao, Y., Li, C., Wang, W., & Yu, F. (2020). Evaluation of the Radar QPE and Rain Gauge Data Merging Methods in Northern China. Remote Sensing, 12(3), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030363