Ecological Risk Assessment and Impact Factor Analysis of Alpine Wetland Ecosystem Based on LUCC and Boosted Regression Tree on the Zoige Plateau, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
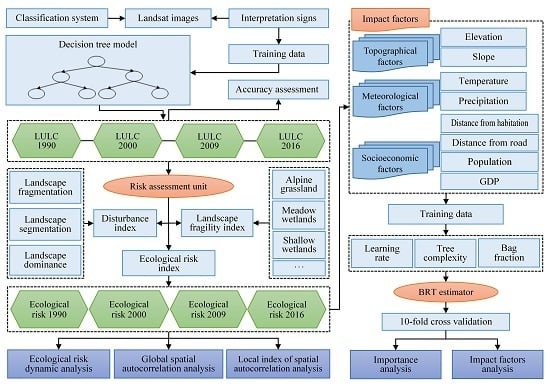
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Field Data
2.2.2. Remote Sensing Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Classification and Accuracy Assessment Methods
2.3.2. LULC Dynamic Degree Model
2.3.3. Construction of the Land Use/Cover ERA Model
2.3.4. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis Methods
2.3.5. Boosted Regression Tree (BRT) Model
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-temporal Patterns in LUCC
3.1.1. Classification Results and Accuracy
3.1.2. LULC Dynamics Change in 1990–2016
3.2. Analysis of Landscape Ecological Risk
3.2.1. Spatio-temporal Characteristics of Landscape Ecological Risk
3.2.2. Global Spatial Autocorrelation of Ecological Risk Index (ERI)
3.2.3. Local Spatial Autocorrelation of ERI
3.3. Analysis of the Impact Factors for ERI
4. Discussion
4.1. Mechanisms of Influence on the Ecological Risk
4.2. Innovative Strategies in the Present Study
4.3. The Improvement of Classification and ERA in Future Study
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Alpine grassland, alpine wetlands and shallow marshes are the main LULC types on the Zoige Plateau. From 1990 to 2016, the areas of alpine grassland and meadow wetlands showed a gradual increasing trend and the shallow marsh area continuously decreased. From 1990 to 2016, the LULC of the study area experienced remarkable changes, in particular, the changes in deep marshes, aeolian sediments and construction land were the most intense, while the change in alpine grassland was slow.
- (2)
- From 1990 to 2016, the ecological risk on the Zoige Plateau increased, in particular, regions with higher and moderate ecological risks covered large areas. The ecological risk of the study area showed remarkable spatio-temporal variations, significant spatial correlation and a high degree of spatial clustering.
- (3)
- The topography, climate and human activities have certain influences on the stability of the alpine wetland ecosystem of the Zoige Plateau. The elevation has the largest influence on the ecological risk of the area, primarily because human activities are the most intense in low-elevation parts of the plateau, disturbing the ecosystems to the greatest extent and causing high ecological risk. Furthermore, warming and drying climate conditions caused decreased surface runoff, the drying of marshes, shrinkage of lakes and the desertification of grasslands, resulting in the deterioration of ecological stability. Economic development has led to an increase in the demand for livestock products, and the resulting increase in the number of livestock has caused overgrazing of pastures and has adversely affected the ecosystem.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, G.L.; Zhang, L.C.; Zhang, Q.; Musyimi, Z.; Jiang, Q.H. Spatio–temporal dynamics of wetland landscape patterns based on remote sensing in Yellow River Delta, China. Wetlands 2014, 34, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.M.; Zhao, W.; Li, A.N.; Bian, J.H.; Zhang, Z.J. Subpixel inundation mapping using landsat-8 OLI and UAV data for a wetland region on the Zoige Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.F.; Liu, H.Y. Advance in wetland classification and wetland landscape classification researches. Wetl. Sci. 2014, 1, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.W.; Li, S.N.; Wei, W.; Song, X.J. Research progress on alpine wetland changes and driving forces in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during the last three decades. Chin. J. Ecol. 2019, 38, 856–862. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, L.S.; Zhang, H.F. Recent changes in wetlands on the Tibetan Plateau: A review. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 879–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cadavid Restrepo, A.M.; Yang, Y.R.; Hamm, N.A.S.; Gray, D.J.; Barnes, T.S.; Williams, G.M.; Soares Magalhaes, R.J.; McManus, D.P.; Guo, D.H.; Clements, A.C.A. Land cover change during a period of extensive landscape restoration in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.L.; Wang, P.; Huang, H.S. Ecological risk assessment of land use change in the Poyang Lake eco-economic zone, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2013, 10, 328–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Liang, X.Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, J.N. The dynamic changes to ecological risk in the Loess Hilly-gully region and its terrain gradient analysis: A case study of Mizhi County, Shaanxi Province, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 8584–8592. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, T. Integration of ecosystem services into ecological risk assessment for implementation in ecosystem based river management: A case study of the Yellow River, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2013, 19, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekmohammadi, B.; Blouchi, L.R. Ecological risk assessment of wetland ecosystems using multi criteria decision making and geographic information system. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 41, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.P.; Zhang, Z.D.; Wan, L.W.; Yang, C.X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.E.; Chen, Y. Landscape pattern optimization in Ningjiang River Basin based on landscape ecological risk assessment. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 1420–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q.W.; Zhang, X.W.; Ma, H.K.; Wu, J.S. Review of landscape ecological risk and an assessment framework based on ecological services: ESRISK. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 843–855. [Google Scholar]
- Piggott, J.J.; Townsend, C.R.; Matthaei, C.D. Re-conceptualizing synergism and antagonism among multiple stressors. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, S.S.; Graham, N.A.J.; Connolly, S.R. Evidence for multiple stressor interactions and effects on coral reefs. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.T.; Pan, J.F.; Pu, X.M.; Wang, B.; Pan, J.J. Current status of coastal wetlands in China: Degradation, restoration, and future management. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 164, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, W.G. Twenty years before and hence; Ecological risk assessment at multiple scales with multiple stressors and multiple endpoints. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2003, 9, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Shi, X.L.; Li, J.L.; Wang, L.L.; Liu, R.P. Land use change and ecological risk assessment in Hang Zhou city. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 38, 274–281. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Su, W.C.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.M.; Deng, J.X. Regional ecological risk assessment of land use in the flooding zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir area based on relative risk model. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2012, 32, 248–256. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.G.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Land use ecological risk evaluation in Three Gorges Reservoir area based on normal cloud model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, K.; Kuai, X.; Chen, Y.; Qi, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Risk assessment of land ecology on a regional scale: Application of the relative risk model to the mining city of Deye, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2017, 23, 550–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolo, R.E.; Van Dam, R.A.; Bayliss, P. Regional ecological risk assessment for Australia’s Tropical Rivers: Application of the relative risk model. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2012, 18, 16–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Yang, X.C.; Jin, Y.X.; Xu, B.; Zhou, Q.B. Remote sensing and evaluation of the wetland ecological degradation process of the Zoige Plateau Wetland in China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.G.; Lv, J.X.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.H. Marsh wetland degradation risk assessment and change analysis: A case study in the Zoige Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Jin, Y.X.; Mao, X.F. Ecological risk assessment of cities on the Tibetan Plateau based on land use/land cover changes – Case study of Delingha City. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.T.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C.Z.; Wang, X.R.; Zheng, D.F. Landscape ecological risk assessment of Xi river Basin based on land-use change. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 5952–5960. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, W.B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhuang, D.F. Impacts of road network expansion on landscape ecological risk in a megacity, China: A case study of Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Yushanjiang, A.; Wang, D.F. Ecological risk assessment due to land use/cover changes (LUCC) in Jinghe County, Xinjiang, China from 1990 to 2014 based on landscape patterns and spatial statistics. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, D. Boosted trees for ecological modeling and prediction. Ecology 2007, 88, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Main, A.R.; Michel, N.L.; Headley, J.V.; Peru, K.M.; Morrissey, C.A. Ecological and landscape drivers of neonicotinoid insecticide detections and concentrations in Canada’s prairie wetlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8367–8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Du, Z.C.; Zhang, D.M.; Yu, S.C.; Hao, Y.T. Boosted regression tree model-based assessment of the impacts of meteorological drivers of hand, foot and mouth disease in Guangdong, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisa, S.V.; Walter, V.; Morgan, P.; Catherine, L.; José, P.G.; Diamantina, M.G.; Philippe, L.; Alejandro, L.C.; Niko, S.; Marie-Pierre, H.; et al. Malaria risk assessment and mapping using satellite imagery and boosted regression trees in the Peruvian Amazon. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15173. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, L.L.; Chen, Z.K.; Zou, Y.C.; Lu, X.G.; Guo, J.W.; Tang, X.G. Effect of Zoige alpine wetland degradation on the density and fractions of soil organic carbon. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 51, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.H.; Wang, J.J.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Hua, O.; Wei, D. Landscape pattern evolution processes of alpine wetlands and their driving factors in the Zoige Plateau of China. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 10, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Xu, B.; Jin, Y.X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.B.; Guo, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, X.C. Advances in studies of wetlands in Zoige Plateau. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2016, 32, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.X.; Wang, Y.B. Changes in alpine wetland ecosystems of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from 1967 to 2004. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 180, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, Z.B.; Hu, G.Y.; Yan, C.Z.; Wang, W.L.; Lu, J.F. Aeolian desertification and its causes in the Zoige Plateau of China’s Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 59, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Li, K.; Yang, Y. Evaluation index system of swamp degradation in Zoige Plateau of Sichuan. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 1826–1836. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, P.; Chanda, A.; Ghosh, A.; Ghosh, S.; Das, S.; Ghosh, T.; Hazra, S. Threats to coastal communities of Mahanadi delta due to imminent consequences of erosion-present and near future. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Meng, B.P.; Liang, T.G.; Feng, Q.S.; Gao, J.L. Modeling alpine grassland cover based on MODIS data and support vector machine regression in the headwater region of the Huanghe River, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 218, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tri, A.; Anoj, S.; Dong, L. Evaluation of water indices for surface water extraction in a Landsat 8 scene of Nepal. Sensors 2018, 18, 2580. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Yu, T.; Zhang, W.H. Validation of GaoFen-1 Satellite Geometric Products Based on Reference Data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2019, 47, 1331–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.F.; Lehmkuhl, F.; Falk, D. Quantifying land degradation in the Zoige Basin, NE Tibetan Plateau using satellite remote sensing data. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.Y.; Gao, G.Y.; Shen, Q.; Wang, X.F.; Ma, Y.; Lü, Y.; Fu, B. Spatio-temporal characteristics and driving forces of landscape structure changes in the middle reach of the Heihe River Basin from 1990 to 2015. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yushanjiang, A.; Jing, Y.Q. Assessing and predicting changes of the ecosystem service values based on land use/cover change in Ebinur Lake Wetland National Nature Reserve, Xinjiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.S.; Li, B.J.; Juana, P.M. Monitoring Land-Use/Land-Cover Changes at a Provincial Large Scale Using an Object-Oriented Technique and Medium-Resolution Remote-Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.J.; Liu, K.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.H.; Li, J.; He, Z. Identifying Mangrove Species Using Field Close-Range Snapshot Hyperspectral Imaging and Machine-Learning Techniques. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Q.Y.; Guo, J.Y.; Yan, J.F.; Wang, H. Land use and landscape pattern changes of Weihai, China based on object-oriented svm classification from landsat MSS/TM/OLI images. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.Y.; Cheng, W.M.; Wang, N.; Liu, Q.Y.; Ma, T.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhou, C.H. Spatio-temporal distribution and transformation of cropland in geomorphologic regions of China during 1990–2015. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.P.; Yu, K.Q.; Feng, Y.J. Ecological risk assessment of rural-urban ecotone based on landscape pattern: A case study in Daiyue District of Tai’an City, Shandong Province of East China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 705–712. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.; Li, X.Y.; Li, Z.G.; Chen, W.; He, X.Y.; Qi, S. Assessment of ecological risk of coastal economic developing zone in Jinzhou Bay based on landscape pattern. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 3441–3450. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.B.; Shi, P.J.; Luo, J. Landscape ecological risk assessment of the Shiyang river Basin. Commun. Comput. Inf. 2013, 399, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Zhao, Y.H.; Liu, J.C.; Han, L.; Ao, Y.; Yin, S. Landscape ecological risk assessment in Qinling Mountain. Geol. J. 2018, 53, 342–351. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, S.; Yang, Z.P.; Fang, H.; Shi, T.G.; Dong, L. Assessing landscape ecological risk for a world natural heritage site: A case study of Bayanbulak in China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 269–283. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Hou, X.Y.; Wu, Y.J.; Cheng, F.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Dong, S.K. Research progress on landscape ecological networks. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 3947–3956. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.L.; Kung, C.C.; Zhao, Y.L. Spatial disparities of regional forest land change based on ESDA and GIS at the county level in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei area. Front. Earth Sci. 2012, 6, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Leathwick, J.R.; Hastie, T. A working guide to boosted regression trees. J. Anim. Ecol. 2008, 77, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leticia, V.; Lucía, A.; Alejandra, R.H.; Ana, G.; Karina, M.; Eduardo, B.; Gastón, A. Relationship between astringency and phenolic composition of commercial Uruguayan Tannat wines: Application of boosted regression trees. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.L.; Wang, X.J.; Zhu, X.P.; Jia, H.T.; Han, D.L. Landscape pattern changes in alpine wetland of Bayanbulak Swan Lake during 1996–2015. J. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 1897–1911. [Google Scholar]
- Ghulam, A.; Ghulam, O.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Freeman, K.; Porton, I.; Maimaitiyiming, M. Remote sensing based spatial statistics to document tropical rainforest transition pathways. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6257–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, H.J.; Ouyang, H.; Cui, B.S.; Wang, Q.G.; Chen, H. Changes in landscape pattern of alpine wetlands on the Zoige Plateau in the past four decades. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.K.; Lv, X.G. Comparison between the Marsh Wetland Landscape Patterns in the Zoige Plateau for two periods. Wetl. Sci. 2010, 8, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, P.F.; Wu, N.; Luo, P.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, M.H. Analysis of dynamics and driving factors of wetland landscape in Zoige, eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Mt. Sci 2009, 6, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Li, G.P. Zoige climate change and its impact on wetland degradation. Plateau Meteorol. 2007, 26, 422–428. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y.; He, Y.X.; Ju, P.J.; Zhu, Q.A.; Liu, J.L.; Chen, H. Application of analytic hierarchy process in wetland degradation research. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2019, 25, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, K.P.; Li, G.Q.; Wang, J.; Lv, T.; Kong, X.X. Influence of human activities to the wetland landscape pattern in Zoige Plateau. Yellow River 2016, 38, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, S.J.; Sun, J.H. The peatland area change in past 20 years in the Zoige Basin, eastern Tibetan Plateau. Front. Earth Sci. 2011, 5, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Lu, Q.F.; Song, K.C.; Qin, G.H.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; Li, H. Remotely sensing the ecological influences of ditches in Zoige Peatland, eastern Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 5186–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, R.; Mountrakis, G.; Stehman, S.V. A meta-analysis of remote sensing research on supervised pixel-based land-cover image classification processes: General guidelines for practitioners and future research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, G.Y.; Dong, Z.B.; Wei, Z.H.; Lu, J.F. Land use and land cover change monitoring in the Zoige Wetland by remote sensing. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2009, 7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Land Use/Cover Types | Training Data | Validation Data | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Samples | UAV Samples | GF-1/Google Earth Images Samples | GF-1/Google Earth Images Samples | |
| Alpine grassland | 101 | 30 | 19 | 460 |
| Meadow wetlands | 52 | 11 | 37 | 205 |
| Shallow marshes | 6 | 7 | 87 | 200 |
| Deep marshes | 16 | 6 | 28 | 70 |
| River and lake | 14 | 5 | 11 | 50 |
| Aeolian sediments | 11 | 5 | 34 | 80 |
| Construction land | 22 | 6 | 2 | 50 |
| Gravel land | 2 | 0 | 28 | 32 |
| Total | 224 | 70 | 246 | 1147 |
| V0 | V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | V6 | V7 | V8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V0 | 1 | ||||||||
| V1 | −0.318 | 1 | |||||||
| V2 | −0.222 | 0.456 | 1 | ||||||
| V3 | 0.260 | −0.378 | −0.177 | 1 | |||||
| V4 | −0.020 | 0.323 | 0.147 | 0.009 | 1 | ||||
| V5 | −0.026 | 0.150 | 0.038 | −0.099 | 0.041 | 1 | |||
| V6 | −0.059 | 0.102 | 0.027 | −0.141 | 0.013 | 0.094 | 1 | ||
| V7 | 0 | 0.001 | 0 | −0.020 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0 | 1 | |
| V8 | 0 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.001 | 0 | 0.010 | −0.018 | 0.042 | 1 |
| Learning Rate | tc1 | tc5 | tc10 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Data Correlation | CV Correlation | Training Data Correlation | CV Correlation | Training Data Correlation | CV Correlation | |
| lr0.05 | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.95 | 0.85 | 0.97 | 0.85 |
| lr0.01 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.93 | 0.84 |
| lr0.005 | 0.71 | 0.68 | 0.85 | 0.79 | 0.90 | 0.82 |
| lr0.001 | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.78 | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.78 |
| Land Use/Cover Types | 1990 | 2000 | 2009 | 2016 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UA (%) | PA (%) | UA (%) | PA (%) | UA (%) | PA (%) | UA (%) | PA (%) | |
| Alpine grassland | 85.65 | 93.81 | 84.13 | 93.81 | 89.35 | 92.36 | 93.26 | 93.46 |
| Meadow wetlands | 95.61 | 88.69 | 93.17 | 88.69 | 93.17 | 84.51 | 95.12 | 87.84 |
| Shallow marshes | 96.00 | 91.43 | 94.00 | 91.43 | 94.00 | 89.10 | 91.50 | 90.59 |
| Deep marshes | 97.14 | 97.14 | 97.14 | 97.14 | 90.00 | 98.44 | 87.14 | 98.39 |
| River and lake | 82.00 | 85.42 | 68.00 | 85.12 | 92.00 | 85.19 | 82.00 | 77.36 |
| Aeolian sediments | 67.50 | 62.79 | 76.25 | 62.07 | 80.00 | 73.56 | 71.25 | 86.36 |
| Construction land | 92.00 | 90.20 | 92.00 | 90.20 | 88.00 | 97.78 | 88.00 | 93.62 |
| Gravel land | 85.29 | 67.44 | 82.35 | 66.67 | 44.12 | 88.24 | 82.35 | 73.69 |
| OA (%) | 88.83 | 87.45 | 89.10 | 90.50 | ||||
| Kappa coefficient | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.88 | ||||
| Land Use/Cover Types | 1990–2000 | 2000–2009 | 2009–2016 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change Area (km2) | Dynamic Degree (%) | Change Area (km2) | Dynamic Degree (%) | Change Area (km2) | Dynamic Degree (%) | |
| Alpine grassland | 2005.10 | 1.34 | 1604.22 | 1.10 | −1675.58 | 1.47 |
| Meadow wetlands | 2262.12 | 11.77 | 1862.43 | 9.88 | 1475.09 | 10.29 |
| Shallow marshes | −2114.99 | 6.41 | −897.65 | 3.55 | −1309.74 | 7.30 |
| Deep marshes | −206.52 | 8.58 | 133.35 | 16.85 | −128.71 | 21.67 |
| River and lake | −167.10 | 6.27 | 107.78 | 7.06 | 168.19 | 11.12 |
| Aeolian sediments | −316.48 | 8.64 | −361.6 | 16.81 | 437.66 | 18.74 |
| Construction land | 45.83 | 8.54 | 115.23 | 20.90 | 138.40 | 15.10 |
| Gravel land | −604.69 | 6.08 | −305.28 | 7.92 | 442.00 | 16.63 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, M.; Ge, J.; Gao, J.; Meng, B.; Li, Y.; Yin, J.; Liu, J.; Feng, Q.; Liang, T. Ecological Risk Assessment and Impact Factor Analysis of Alpine Wetland Ecosystem Based on LUCC and Boosted Regression Tree on the Zoige Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030368
Hou M, Ge J, Gao J, Meng B, Li Y, Yin J, Liu J, Feng Q, Liang T. Ecological Risk Assessment and Impact Factor Analysis of Alpine Wetland Ecosystem Based on LUCC and Boosted Regression Tree on the Zoige Plateau, China. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(3):368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030368
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Mengjing, Jing Ge, Jinlong Gao, Baoping Meng, Yuanchun Li, Jianpeng Yin, Jie Liu, Qisheng Feng, and Tiangang Liang. 2020. "Ecological Risk Assessment and Impact Factor Analysis of Alpine Wetland Ecosystem Based on LUCC and Boosted Regression Tree on the Zoige Plateau, China" Remote Sensing 12, no. 3: 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030368
APA StyleHou, M., Ge, J., Gao, J., Meng, B., Li, Y., Yin, J., Liu, J., Feng, Q., & Liang, T. (2020). Ecological Risk Assessment and Impact Factor Analysis of Alpine Wetland Ecosystem Based on LUCC and Boosted Regression Tree on the Zoige Plateau, China. Remote Sensing, 12(3), 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030368