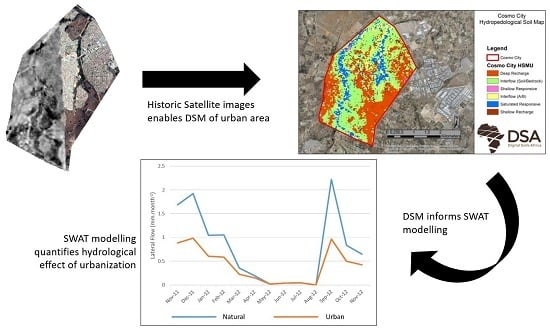
Combining Historical Remote Sensing, Digital Soil Mapping and Hydrological Modelling to Produce Solutions for Infrastructure Damage in Cosmo City, South Africa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. General Survey
2.2.2. Digital Soil Mapping
2.2.3. Hydrological Modelling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Digital Soil Mapping
3.2. Modelling Results
3.2.1. Kampala Crescent
3.2.2. Cosmo City
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN-DESA), Population Division. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, C.J.; Roy, A.; Feminella, J.W.; Cottingham, P.; Groffman, P.M.; Morgan, R.P., II. The urban stream syndrome: Current knowledge and the search for a cure. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 706–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.M.; Witza, E.; Blanca, V.; Souliea, C.; Penalver-Navarroa, M.; Dervieux, A. A case study of land cover change (1950–2003) and runoff in a Mediterraean catchment. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dams, J.; Dujardin, J.; Reggers, R.; Bashir, I.; Canters, F.; Batelaan, O. Mapping impervious surface change from remote sensing for hydrological modeling. J. Hydrol. 2013, 485, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toll, D.G.; Abedin, Z.; Buma, J.; Cui, Y.; Osman, A.S.; Phoon, K.K. The Impact of Changes in the Water Table and Soil Moisture on Structural Stability of Buildings and Foundation Systems: Systematic Review CEE10-005 (SR90); Technical Report; Collaboration for Environmental Evidence. 2012. Available online: http://dro.dur.ac.uk/18298/ (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Dippenaar, M.A.; Van Rooy, J.L. Vadose Zone Characterization for Hydrogeological and Geotechnical Application. In IAEG/AEG Annual Meeting Proceedings; Shakoor, A., Cato, K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrane, S.J. Impacts of urbanisation on hydrological and water quality dynamics, and urban water management: A review. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 2295–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.S. Hydropedology: Bridging disciplines, scales, and data. Vadose Zone J. 2003, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ticehurst, J.L.; Cresswell, H.P.; Mckenzie, N.J.; Glover, M.R. Interpreting soil and topographic properties to conceptualize hillslope hydrology. Geoderma 2007, 137, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tol, J.J.; Le Roux, P.A.L.; Hensley, M. Soil indicators of hillslope hydrology in Bedford catchment. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 2010, 27, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Tol, J.J.; Le Roux, P.A.L.; Hensley, M.; Lorentz, S.A. Soil as indicator of hillslope hydrological behaviour in the Weatherley Catchment, Eastern Cape, South Africa. Water SA 2010, 36, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lilly, A.; Boorman, D.B.; Hollis, J.M. The development of a hydrological classification of UK soils and the inherent scale changes. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1998, 50, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; McSweeney, K.; Lowery, B. Identification of the spatial distribution of soils using a 255 process-based terrain characterization. Geoderma 2001, 103, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tol, J.J.; van Zijl, G.M.; Riddell, E.S.; Fundisi, D. Application of hydropedological insights in hydrological modelling of the Stevenson Hamilton Research Supersite, Kruger National Park, South Africa. Water SA 2015, 41, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Zijl, G.M.; Le Roux, P.A.L. Creating a hydrological soil map for the Stevenson Hamilton Supersite, Kruger National Park. Water SA 2014, 40, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McBratney, A.B.; Mendoça Santos, M.L.; Minasny, B. On digital soil mapping. Geoderma 2003, 117, 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahiny, A.S.; Clarke, K.C. Simulating hydrologic impacts of urban growth using SLEUTH, multi criteria evaluation and runoff modelling. J. Environ. Inform. 2013, 22, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohana-Levi, N.; Givati, A.; Alfasi, N.; Peeters, A.; Karnieli, A. Predicting the effects of urbanization on runoff after frequent rainfall events. J. Land Use Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chormanski, J.; Van de Voorde, T.; De Roeck, T.; Batelaan, O.; Canters, F. Improving Distributed Runoff Prediction in Urbanized Catchments with Remote Sensing based Estimates of Impervious Surface Cover. Sensors 2008, 8, 910–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Council for Geoscience. Geological Data 1:250 000; Council for Geoscience: Pretoria, South Africa, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Land Type Survey Staff. Land Types of South Africa: Digital Map (1:250 000 Scale) and Soil Inventory Datasets; ARC-Institute for Soil, Climate and Water: Pretoria, South Africa, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mucina, L.; Rutherford, M.C. (Eds.) The Vegetation of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland; Strelitzia 19; South African National Biodiversity Institute: Pretoria, South Africa, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, R.E. South African Atlas of Climatology and Agrohydrology; WRC Report 1489/1/06; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Classification Working Group. Soil Classification: A Taxonomic System for South Africa; Department of Agricultural Development: Pretoria, South Africa, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015 International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- USGS (United States Geological Survey) Landsat images. Available online: http://landsat.usgs.gov (accessed on 23 November 2018).
- Conrad, O.; Bechtel, B.; Bock, M.; Dietrich, H.; Fischer, E.; Gerlitz, L.; Wehberg, J.; Wichmann, V.; Boehner, J. System for Automated Geoscientific Analyses (SAGA) v. 2.1.4.Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1991–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Zijl, G.M.; Van Tol, J.J.; Tinnefeld, M.; Le Roux, P.A.L. A hillslope based digital soil mapping approach, for hydropedological assessments. Geoderma 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zijl, G.M.; Bouwer, D. Soil Observation Dataset from the Halfway House Granites; University of the Free State dataset; University of the Free State: Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Van Tol, J.J.; Lorentz, S.A. Hydropedological interpretation of soil distribution patterns to characterise groundwater/surface-water interactions. Vadose Zone J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kempen, B.; Brus, D.J.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Stoorvogel, J.J. Updating the 1: 50 000 Dutch soil map using legacy soil data: A multinomial logistic regression approach. Geoderma 2009, 151, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zijl, G.M.; Bouwer, D.; van Tol, J.J.; Le Roux, P.A.L. Functional digital soil mapping: A case study from Namarroi, Mozambique. Geoderma 2014, 219–220, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimůnek, J.; Van Genuchten, M.T.; Šejna, M. The HYDRUS Software Package for Simulating Two- and Three-Dimensional Movement of Water, Heat, and Multiple Solutes in Variably-Saturated Media; Technical Manual, Version 1.0; PC Progress: Prague, Czech Republic, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Schaap, M.G.; Leij, F.J.; van Genuchten, M.T. ROSETTA: A computer program for estimating soil hydraulic parameters with hierarchical pedotransfer functions. J. Hydrol. 2001, 251, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoterraimage. 2013–2014 South African National Land-Cover Dataset; Report Created for Department of Environmental Sciences; DEA/CARDNO SCPF002: Implementation of Land Use Maps for South Africa; Department of Environmental Affairs: Pretoria, South Africa, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Pan, H.L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Kistler, R.; Woollen, J.; Behringer, D.; et al. The NCEP Climate Forecast System Reanalysis. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2010, 91, 1015–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Zijl, G.M.; Le Roux, P.A.L.; Smith, H.J.C. Rapid soil mapping under restrictive conditions in Tete, Mozambique. In Digital Soil Assessments and Beyond; Minasny, B., Malone, B.P., McBratney, A.B., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 335–339. [Google Scholar]
- MacMillan, R.A.; Moon, D.E.; Coupé, R.A.; Phillips, N. Predictive ecosystem mapping (PEM) for 8.2 million ha of forestland, British Columbia, Canada. In Digital Soil Mapping; Bridging Research, Environmental Application and Operation; Boettinger, J.L., Howell, D.W., Moore, A.C., Hartemink, A.E., Kienast Brown, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, A.-X.; Yang, L.; Li, B.; Qin, C.; English, E.; Burt, J.E.; Zhou, C. Purposive sampling for digital soil mapping for areas with limited data. In Digital Soil Mapping with Limited Data; Hartemink, A.E., McBratney, A.B., Mendonça-Santos, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]











| Hydropedological Soil Form | Soil Forms (SCWG 1991) | Reference Groups (IUSS 2015) | Defining Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deep Recharge | Clovelly, Constantia, Griffin, Hutton, Shortlands | Acrisols, Nitisols | Soil profiles showing no signs of wetness in the profile |
| Shallow Recharge | Mispah, Glenrosa, Mayo | Leptosols | Shallow soils with chromic colors in the topsoil |
| Interflow (A/B) | Constantia, Kroonstad, Longlands, Sterkspruit, Wasbank | Stagnosols, Planosols, Plinthosols | Signs of wetness between top and subsoil |
| Interflow (Soil/Bedrock) | Avalon, Bainsvlei, Bloemdal, Dresden, Fernwood, Glencoe, Pinedene, Tukulu, Westleigh | Acrisols, Stagnosols, Arenosols, Plinthosols, | Signs of wetness at soil bedrock interface |
| Saturated Responsive | Katspruit, Rensburg | Gleysols | Gleyed subsoil |
| Shallow Responsive | Mispah, Glenrosa | Leptosols | Shallow soil with bleached colors in the topsoil |
| Hydraulic Properties | Van Genuchten Parameters | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizon | Db | FC | DUL | Θs | Ks | Sand | Silt | Clay | Θr | Θs | Alpha | n | Ks | lambda |
| g·cm−3 | mm·mm−1 | mm·mm−1 | mm·mm−1 | mm·h−1 | % | % | % | |||||||
| Orthic A | 1.39 | 0.2 | 0.22 | 0.477 | 237.2 | 67.6 | 11 | 22 | 0.1 | 0.44 | 0.00315 | 1.4802 | 237 | 0.5 |
| Red Apedal | 1.42 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.464 | 73.9 | 56.6 | 15 | 29 | 0.1 | 0.43 | 0.00294 | 1.4273 | 73.9 | 0.5 |
| Soft Plinthic | 1.55 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.416 | 2 | 39.7 | 14 | 46 | 0.1 | 0.42 | 0.00216 | 1.2054 | 4.1 | 0.5 |
| Gleyic | 1.55 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.416 | 1 | 27.6 | 20 | 53 | 0.1 | 0.41 | 0.00231 | 1.2042 | 1.2 | 0.5 |
| Lithic | 1.26 | 0.09 | 0.28 | 0.526 | 65.7 | 55.4 | 14 | 31 | 0.1 | 0.49 | 0.00271 | 1.3588 | 65.7 | 0.5 |
| Saprolite/Bed rock | 0.1 | 0.26 | 0.00258 | 1.1497 | 0.1 | 0.5 | ||||||||
| Soil Association | Hydrological Groups | Layer | Depth | Bulk Density | Wilting Point | Ks | Carbon | Clay | Silt | Sand |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm | g·cm−3 | mm·mm−1 | mm·h−1 | % | ||||||
| Interflow (A/B) | C | 1 | 300 | 1.4 | 0.06 | 237 | 1.87 | 21.6 | 11.1 | 67.6 |
| 2 | 600 | 1.4 | 0.09 | 73.9 | 0.6 | 29.1 | 14.7 | 56.6 | ||
| 3 | 1200 | 1.5 | 0.08 | 2 | 0.5 | 46.2 | 14.2 | 39.7 | ||
| Interflow (Soil/bedrock) | C | 1 | 300 | 1.4 | 0.06 | 237 | 1.87 | 21.6 | 11.1 | 67.6 |
| 2 | 1200 | 1.4 | 0.09 | 73.9 | 0.6 | 29.1 | 14.7 | 56.6 | ||
| 3 | 1500 | 1.5 | 0.08 | 2 | 0.5 | 46.2 | 14.2 | 39.7 | ||
| Recharge (deep) | A | 1 | 300 | 1.4 | 0.06 | 237 | 1.87 | 21.6 | 11.1 | 67.6 |
| 2 | 1200 | 1.6 | 0.07 | 284 | 0.6 | 29.7 | 13.2 | 57.2 | ||
| 3 | 1500 | 1.5 | 0.09 | 73.9 | 0.6 | 29.1 | 14.7 | 56.6 | ||
| Recharge (shallow) | A | 1 | 300 | 1.4 | 0.06 | 237 | 1.87 | 21.6 | 11.1 | 67.6 |
| Responsive (wet) | D | 1 | 300 | 1.4 | 0.06 | 237 | 1.87 | 21.6 | 11.1 | 67.6 |
| 2 | 1000 | 1.5 | 0.09 | 1 | 1.87 | 52.8 | 19.6 | 27.6 | ||
| Responsive (shallow) | C | 1 | 300 | 1.4 | 0.06 | 237 | 1.87 | 21.6 | 11.1 | 67.6 |
| Users Accuracy | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep Recharge | Shallow Recharge | Interflow (Soil/Bedrock) | Interflow (A/B) | Saturated Responsive | Total | Correct | % Accuracy | ||
| Producer’s Accuracy | Deep Recharge | 3 | 3 | 3 | 100 | ||||
| Shallow Recharge | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 33 | |||
| Interflow (Soil/Bedrock) | 8 | 8 | 8 | 100 | |||||
| Interflow (A/B) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | |||||
| Saturated Responsive | 2 | 2 | 2 | 100 | |||||
| Total | 4 | 1 | 9 | 1 | 2 | 17 | |||
| Correct | 3 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 2 | 15 | |||
| % Accuracy | 75 | 100 | 89 | 100 | 100 | 88 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van Zijl, G.; van Tol, J.; Bouwer, D.; Lorentz, S.; le Roux, P. Combining Historical Remote Sensing, Digital Soil Mapping and Hydrological Modelling to Produce Solutions for Infrastructure Damage in Cosmo City, South Africa. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030433
van Zijl G, van Tol J, Bouwer D, Lorentz S, le Roux P. Combining Historical Remote Sensing, Digital Soil Mapping and Hydrological Modelling to Produce Solutions for Infrastructure Damage in Cosmo City, South Africa. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(3):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030433
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan Zijl, George, Johan van Tol, Darren Bouwer, Simon Lorentz, and Pieter le Roux. 2020. "Combining Historical Remote Sensing, Digital Soil Mapping and Hydrological Modelling to Produce Solutions for Infrastructure Damage in Cosmo City, South Africa" Remote Sensing 12, no. 3: 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030433
APA Stylevan Zijl, G., van Tol, J., Bouwer, D., Lorentz, S., & le Roux, P. (2020). Combining Historical Remote Sensing, Digital Soil Mapping and Hydrological Modelling to Produce Solutions for Infrastructure Damage in Cosmo City, South Africa. Remote Sensing, 12(3), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030433