Fusion of Five Satellite-Derived Products Using Extremely Randomized Trees to Estimate Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux over Europe
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. Satellite-Derived Terrestrial LE Products
2.1.1. Revised Remote Sensing-Based Penman (RS-PM)- LE Product
2.1.2. Shuttleworth–Wallace Dual-Source (SW)-Based LE Product
2.1.3. Priestley-Taylor of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (PT-JPL)-Based LE Product
2.1.4. Modified Satellite-Based Priestley–Taylor (MS-PT)-Based LE Product
2.1.5. Semi-Empirical Penman Algorithm (SEMI-PM)-Based LE Product
2.2. Eddy Covariance Data
3. Methods
3.1. Extremely Randomized Trees
3.2. Other Machine Learning Fusion Methods
3.2.1. Gradient Boosting Regression Tree
3.2.2. Random Forests
3.2.3. Gaussian Process Regression
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
3.4. Experimental Setup
4. Results
4.1. Evaluation of Satellite-Derived Terrestrial LE Products
4.2. Fusion of Five Satellite-Derived Terrestrial LE Products Using Extremely Randomized Trees
4.2.1. Model Development Using 39 Training Flux Tower Sites
4.2.2. Model Evaluation against 37 Validation Flux Tower Sites
4.2.3. Implementation of Fusing Five LE Products Using Extremely Randomized Trees
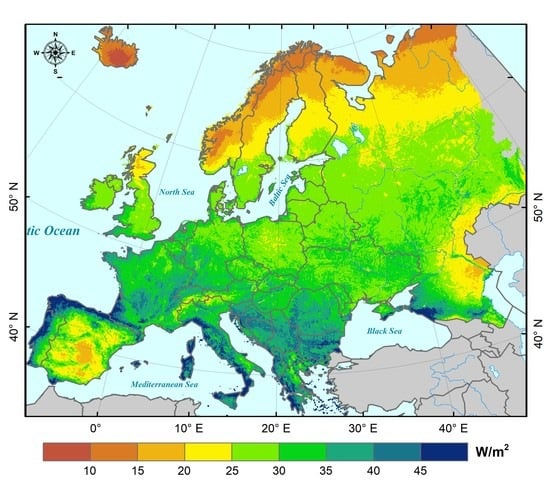
4.3. Mapping of Terrestrial LE Products over Europe
5. Discussion
5.1. The Performance of the Extremely Randomized Trees Fusion Method
5.2. Spatial Discrepancy with Global LE Products
5.3. Uncertainties of the Merged LE Estimates
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Betts, A. Land-Surface-Atmosphere Coupling in Observations and Models. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2009, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Fisher, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Estimation of high-resolution terrestrial evapotranspiration from Landsat data using a simple Taylor skill fusion method. J. Hydrol. 2017, 553, 508–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, G. Ecological Climatology: Concepts and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, C.; Prigent, C.; Mueller, B.; Seneviratne, S.I.; McCabe, M.F.; Wood, E.F.; Rossow, W.B.; Balsamo, G.; Betts, A.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; et al. Global intercomparison of 12 land surface heat flux estimates. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C.; Martens, B.; Miralles, D.G.; Fisher, J.; Beck, H.E.; Fernández-Prieto, D. Exploring the merging of the global land evaporation WACMOS-ET products based on local tower measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 4513–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monteith, J.L. Evaporation and environment. In Symposia of the Society for Experimental Biology; Cambridge University Press (CUP): Cambridge, UK, 1965; pp. 205–234. [Google Scholar]
- Priestley, C.; Taylor, R. On the assessment of surface heat flux and evaporation using large-scale parameters. Mon. Weather Rev. 1972, 100, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Heinsch, F.A.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Development of a global evapotranspiration algorithm based on MODIS and global meteorology data. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, D.G.; Holmes, T.R.H.; De Jeu, R.A.M.; Gash, J.H.; Meesters, A.G.C.A.; Dolman, H. Global land-surface evaporation estimated from satellite-based observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Hong, Y.; Feng, F. Bayesian multi-model estimation of global terrestrial latent heat flux from eddy covariance, meteorological and satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 4521–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Ryu, Y. Multi-scale evaluation of global gross primary productivity and evapotranspiration products derived from Breathing Earth System Simulator (BESS). Remote. Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 528–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Jia, Z.; Zhu, M. Measurements of evapotranspiration from eddy-covariance systems and large aperture scintillometers in the Hai River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 487, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shao, Q.; Liu, J. The performances of modis-gpp and -et products in china and their sensitivity to input data (fpar/lai). Remote. Sens. 2014, 7, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhoff, A.; Paz, A.R.; Aragão, L.E.O.C.; Mu, Q.; Malhi, Y.; Collischonn, W.; Rocha, H.R.; Running, S.W. Assessment of the MODIS global evapotranspiration algorithm using eddy covariance measurements and hydrological modelling in the Rio Grande basin. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1658–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Jia, L.; Menenti, M. Comparison of MOD16 and LSA-SAF MSG evapotranspiration products over Europe for 2011. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 510–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A, R.; N, M.; R, M. Validation of global evapotranspiration product (mod16) using flux tower data in the african savanna, south africa. Remote. Sens. 2014, 6, 942–945. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Jia, L. Monitoring of Evapotranspiration in a Semi-Arid Inland River Basin by Combining Microwave and Optical Remote Sensing Observations. Remote. Sens. 2015, 7, 3056–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Peters-Lidard, C.; Tian, Y.; Houser, P.; Geiger, J.; Olden, S.; Lighty, L.; Eastman, J.; Doty, B.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; et al. Land information system: An interoperable framework for high resolution land surface modeling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2006, 21, 1402–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.-J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M.; et al. The Global Land Data Assimilation System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Z.B. A surface energy balance system (sebs) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes from point to continental scale. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL). 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.W.; Rosenberg, N.J. A resistance model to predict evapotranspiration and its application to a sugar beet field1. Agron. J. 1973, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerink, G.; Su, Z.; Menenti, M. S-SEBI: A simple remote sensing algorithm to estimate the surface energy balance. Phys. Chem. Earth, Part B: Hydrol. Oceans Atmosphere 2000, 25, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C. A Two-Source Time-Integrated Model for Estimating Surface Fluxes Using Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing. Remote. Sens. Environ. 1997, 60, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Shi, P.; Dou, W. Estimation of daily evapotranspiration using a two-layer remote sensing model. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2005, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M. A two-source approach for estimating turbulent fluxes using multiple angle thermal infrared observations. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 1495–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M. Evaluation of soil and vegetation heat flux predictions using a simple two-source model with radiometric temperatures for partial canopy cover. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 94, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.M.; Kustas, W.P.; Humes, K.S. A two-source approach for estimating soil and vegetation energy fluxes in observations of directional radiometric surface temperature. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 77, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Yu, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Lin, Y.; Fisher, J.; McVicar, T.R.; Cheng, J.; Jia, K.; et al. A simple temperature domain two-source model for estimating agricultural field surface energy fluxes from Landsat images. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 5211–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.; Tu, K.P.; Baldocchi, D.D. Global estimates of the land–atmosphere water flux based on monthly AVHRR and ISLSCP-II data, validated at 16 FLUXNET sites. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Cheng, J.; Liu, S.; Fisher, J.; Zhang, X.; Jia, K.; Zhao, X.; Qin, Q.; Zhao, B.; et al. MODIS-driven estimation of terrestrial latent heat flux in China based on a modified Priestley–Taylor algorithm. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 171, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, K.; Jia, K.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, B.; Fisher, J.; Mu, Q.; et al. A satellite-based hybrid algorithm to determine the Priestley–Taylor parameter for global terrestrial latent heat flux estimation across multiple biomes. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2015, 165, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Dickinson, R.E. A review of global terrestrial evapotranspiration: Observation, modeling, climatology, and climatic variability. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Z.; Fisher, J.; Mu, Q.; et al. Improving global terrestrial evapotranspiration estimation using support vector machine by integrating three process-based algorithms. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 242, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, R.; Wan, Z.; Bi, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tang, B.; Yan, G.; Zhang, X. A Review of Current Methodologies for Regional Evapotranspiration Estimation from Remotely Sensed Data. Sensors 2009, 9, 3801–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Chen, X. MODIS-Based Estimation of Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux over North America Using Three Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote. Sens. 2017, 9, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bodesheim, P.; Jung, M.; Gans, F.; Mahecha, M.; Reichstein, M. Upscaled diurnal cycles of land–atmosphere fluxes: A new global half-hourly data product. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 1327–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, T.; Guo, Z.; Liu, S.; He, X.; Meng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xia, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; et al. Evaluating Different Machine Learning Methods for Upscaling Evapotranspiration from Flux Towers to the Regional Scale. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 8674–8690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, B.; Hirschi, M.; Jimenez, C.; Ciais, P.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; Dolman, A.J.; Fisher, J.B.; Jung, M.; Ludwig, F.; Maignan, F.; et al. Benchmark products for land evapotranspiration: Landflux-eval multi-dataset synthesis. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 3707–3720. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, F.; Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Jia, K.; Pinter, K.; Mccaughey, J.H. An empirical orthogonal function-based algorithm for estimating terrestrial latent heat flux from eddy covariance, meteorological and satellite observations. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, F. Combining Datasets of Satellite-Retrieved Products. Part I: Methodology and Water Budget Closure. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1677–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Ding, Z.; Han, T.; Ma, J.; Huang, C.; He, J.; Ma, T. Multi-model ensemble prediction of terrestrial evapotranspiration across north China using Bayesian model averaging. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 2861–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.T.; Uddiny, M.A. Human activity recognition from wearable sensors using extremely randomized trees. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Information Communication Technology (ICEEICT), Savar, Dhaka, 21–23 May 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurts, P.; Louppe, G. Learning to rank with extremely randomized trees. In Proceedings of the JMLR: Workshop and Conference Proceedings, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 11–13 April 2011; Volume 14, pp. 49–61. Available online: http://proceedings.mlr.press/v14/geurts11a/geurts11a.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Shuttleworth, W.J.; Wallace, J. Evaporation from sparse crops-an energy combination theory. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1985, 111, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Dickinson, R.E.; Wild, M.; Liang, S. Evidence for decadal variation in global terrestrial evapotranspiration between 1982 and 2002: 1. Model development. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foken, T. THE ENERGY BALANCE CLOSURE PROBLEM: AN OVERVIEW. Ecol. Appl. 2008, 18, 1351–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twine, T.; Kustas, W.; Norman, J.; Cook, D.; Houser, P.; Meyers, T.; Prueger, J.; Starks, P.; Wesely, M. Correcting eddy-covariance flux underestimates over a grassland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 103, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geurts, P.; Ernst, D.; Wehenkel, L. Extremely randomized trees. Mach. Learn. 2006, 63, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, D.; Li, D.; Chen, X.; Xin, N. A mobile recommendation system based on logistic regression and gradient boosting decision trees. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.; Zhang, T. Learning nonlinear functions using regularized greedy forest. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hou, N.; Zhang, W.; Jia, K.; Yao, Y. Estimation of surface downward shortwave radiation over China from AVHRR data based on four machine learning methods. Sol. Energy 2019, 177, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hesterberg, T. Bootstrap. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 497–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, C.E.; Williams, C.K.I. Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pasolli, L.; Melgani, F.; Blanzieri, E. Gaussian Process Regression for Estimating Chlorophyll Concentration in Subsurface Waters From Remote Sensing Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, J.M.; Chen, J.; Gough, C.M.; Martin, T.A.; Dragoni, D. Evaluating spatial and temporal patterns of MODIS GPP over the conterminous U.S. against flux measurements and a process model. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugster, W.; Rouse, W.R.; Sr, R.A.P.; McFadden, J.P.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Kittel, T.; Chapin, F.S.; Liston, G.E.; Vidale, P.L.; Vaganov, E.; et al. Land-atmosphere energy exchange in Arctic tundra and boreal forest: Available data and feedbacks to climate. Glob. Chang. Boil. 2000, 6, 84–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienecker, M.M.; Suarez, M.J.; Gelaro, R.; Todling, R.; Bacmeister, J. Merra: Nasa’s modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 3624–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Running, S.W.; Nemani, R.R. Sensitivity of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) terrestrial primary production to the accuracy of meteorological reanalyses. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2006, 111, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finnigan, J.J.; Clement, R.; Malhi, Y.; Leuning, R.; Cleugh, H. A Re-Evaluation of Long-Term Flux Measurement Techniques Part I: Averaging and Coordinate Rotation. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2003, 107, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.; Wan, S.; Su, B.; Katul, G.G.; Monson, R.; Luo, Y. Gap-filling missing data in eddy covariance measurements using multiple imputation (MI) for annual estimations. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 121, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalma, J.D.; McVicar, T.R.; McCabe, M.F. Estimating Land Surface Evaporation: A Review of Methods Using Remotely Sensed Surface Temperature Data. Surv. Geophys. 2008, 29, 421–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




















| ID | LE Product Algorithms | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Forcing Inputs | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Revised remote sensing-based Penman LE product (RS-PM) | 0.05 degrees | Daily | Rn, Ta, Tmin, RH, FPAR, LAI | Mu et al. (2011) |
| 2 | Shuttleworth–Wallace dual-source-based LE product (SW) | 0.05 degrees | Daily | Rn, Ta, RH, WS, LAI | Shuttleworth and Wallace (1985) |
| 3 | Priestley–Taylor of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory-based LE product (PT-JPL) | 0.05 degrees | Daily | Rn, Ta, Tmax, RH, FPAR, NDVI, LAI | Fisher et al. (2008) |
| 4 | Modified satellite-based Priestley–Taylor LE product (MS-PT) | 0.05 degrees | Daily | Rn, Ta, Tmax, Tmin, NDVI | Yao et al. (2013) |
| 5 | Semi-empirical Penman-based LE product (SEMI-PM) | 0.05 degrees | Daily | Rs, Ta, RH, WS, NDVI | Wang et al. (2010a) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, K.; Yao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Bei, X.; Guo, X. Fusion of Five Satellite-Derived Products Using Extremely Randomized Trees to Estimate Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux over Europe. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040687
Shang K, Yao Y, Li Y, Yang J, Jia K, Zhang X, Chen X, Bei X, Guo X. Fusion of Five Satellite-Derived Products Using Extremely Randomized Trees to Estimate Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux over Europe. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(4):687. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040687
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Ke, Yunjun Yao, Yufu Li, Junming Yang, Kun Jia, Xiaotong Zhang, Xiaowei Chen, Xiangyi Bei, and Xiaozheng Guo. 2020. "Fusion of Five Satellite-Derived Products Using Extremely Randomized Trees to Estimate Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux over Europe" Remote Sensing 12, no. 4: 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040687
APA StyleShang, K., Yao, Y., Li, Y., Yang, J., Jia, K., Zhang, X., Chen, X., Bei, X., & Guo, X. (2020). Fusion of Five Satellite-Derived Products Using Extremely Randomized Trees to Estimate Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux over Europe. Remote Sensing, 12(4), 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040687