A Combined IR-GPS Satellite Analysis for Potential Applications in Detecting and Predicting Lightning Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Instrumentations and Methods
2.1. LINET
- 2D location of the flash through a time of arrival algorithm (TOA)
- Exploitation of the time delay at the sensor nearest to the lightning
- Time relaxation of the travel path of the radio-wave
2.2. SEVIRI
2.3. GPS
3. Results and Discussion
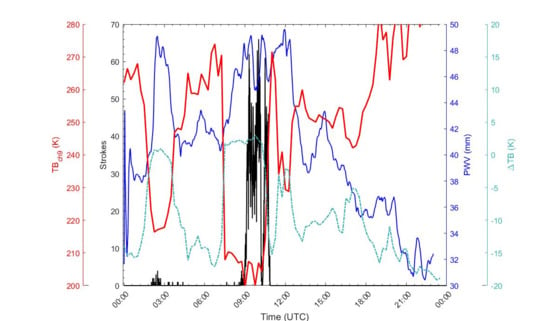
3.1. Naples, 5th September 2015
- ICs are easier to be triggered than CGs, especially at the beginning of the cell’s lightning activity, because the path to be ionized is generally shorter.
- The presence of a LINET station in Naples certainly guarantees an optimum ability of detecting IC lightning strokes in the area of the considered event.
3.2. Pineto, 2nd September 2018
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willis, P.T.; Hallett, J.; Black, R.A.; Hendricks, W. An aircraft study of rapid precipitation development and electrification in a growing convective cloud. Atmos. Res. 1994, 33, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T. Riming Electrification as a Charge Generation Mechanism in Thunderstorms. J. Atmos. Sci. 1978, 35, 1536–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaratne, E.R.; Saunders, C.P.R.; Hallett, J. Laboratory studies of the charging of soft-hail during ice crystal interactions. Q. J. Royal Met. Soc. 1983, 109, 609–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R.E.; Aubagnac, J.-P. The lightning activity of a hailstorm as a function of changes in its microphysical characteristics inferred from polarimetric radar observations. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 16799–16813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saunders, C.P.R.; Keith, W.D.; Mitzeva, R.P. The effect of liquid water on thunderstorm charging. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueras i Ventura, J.; Pineda, N.; Besic, N.; Grazioli, J.; Hering, A.; van der Velde, O.A.; Romero, D.; Sunjerga, A.; Mostajabi, A.; Azadifar, M.; et al. Polarimetric radar characteristics of lightning initiation and propagating channels. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 2881–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figueras i Ventura, J.; Pineda, N.; Besic, N.; Grazioli, J.; Hering, A.; van der Velde, O.A.; Romero, D.; Sunjerga, A.; Mostajabi, A.; Azadifar, M.; et al. Analysis of the lightning production of convective cells. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 5573–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, C.; Asfur, M. Lightning and Climate: The Water Vapor Connection; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Herring, T.A.; Rocken, C.; Anthes, R.A.; Ware, R.H. GPS meteorology: Remote sensing of atmospheric water vapor using the global positioning system. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 15787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Bevis, M.; Fang, P.; Bock, Y.; Chiswell, S.; Businger, S.; Rocken, C.; Solheim, F.; van Hove, T.; Ware, R.H.; et al. GPS Meteorology: Direct Estimation of the Absolute Value of Precipitable Water. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1996, 35, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Businger, S.; Chiswell, S.; Bevis, M.; Duan, J.; Anthes, R.A.; Rocken, C.; Ware, R.H.; Exner, M.; van Hove, T.; Solheim, F. The Promise of GPS in Atmospheric Monitoring. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soci. 1996, 77, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sapucci, L.F.; Machado, L.A.T.; Menezes de Souza, E.; Campos, T.B. GPS-PWV jumps before intense rain events. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2016, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shoji, Y. Retrieval of Water Vapor Inhomogeneity Using the Japanese Nationwide GPS Array and its Potential for Prediction of Convective Precipitation. J. Meteorol. Soci. Japan 2013, 91, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Realini, E.; Sato, K.; Tsuda, T.; Susilo; Manik, T. An observation campaign of precipitable water vapor with multiple GPS receivers in western Java, Indonesia. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2014, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mascitelli, A.; Federico, S.; Fortunato, M.; Avolio, E.; Torcasio, R.C.; Realini, E.; Mazzoni, A.; Transerici, C.; Crespi, M.; Dietrich, S. Data assimilation of GPS-ZTD into the RAMS model through 3D-Var: Preliminary results at the regional scale. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 30, 055801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, H.Y.; Inoue, T. Characteristics of the Water-Vapor Field over the Kanto District Associated with Summer Thunderstorm Activities. SOLA 2007, 3, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farnell, C.; Rigo, T.; Pineda, N. Lightning jump as a nowcast predictor: Application to severe weather events in Catalonia. Atmos. Res. 2017, 183, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, E.; Schultz, C.; Carey, L.; Cecil, D.; Bateman, M. Automated storm tracking and the lightning jump algorithm using GOES-R Geostationary Lightning Mapper (GLM) proxy data. J. Oper. Meteor. 2016, 4, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnell, C.; Rigo, T.; Pineda, N. Exploring radar and lightning variables associated with the Lightning Jump. Can we predict the size of the hail? Atmos. Res. 2018, 202, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, H.-D.; Schmidt, K.; Oettinger, P.; Wirz, M. Lightning detection with 3-D discrimination of intracloud and cloud-to-ground discharges: LIGHTNING DETECTION WITH 3-D MODE. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, H.-D.; Schmidt, K.; Fuchs, B.; Oettinger, W.P.; Holler, H. Cloud Lightning: Detection and Utilization for Total Lightning Measured in the VLF/LF Regime. J. Lightning Res. 2007, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, J. The SEVIRI Instrument; ESA/ESTEC: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 13–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sampietro, D.; Caldera, S.; Capponi, M.; Realini, E. Geoguard—An Innovative Technology Based on Low-Cost GNSS Receivers to Monitor Surface Deformations; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mascitelli, A.; Coletta, V.; Bombi, P.; de Cinti, B.; Federico, S.; Matteucci, G.; Mazzoni, A.; Muzzini, V.G.; Petenko, I.; Dietrich, S. Tree Motion: Following the wind-induced swaying of arboreous individual using a GNSS receiver. Ital. J. Agrometeorol. 2019, 3, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Colosimo, G. VADASE: Variometric Approach for Displacement Analysis Stand-Alone Engine; La Sapienza Univ.: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fratarcangeli, F.; Savastano, G.; D’Achille, M.; Mazzoni, A.; Crespi, M.; Riguzzi, F.; Devoti, R.; Pietrantonio, G. VADASE Reliability and Accuracy of Real-Time Displacement Estimation: Application to the Central Italy 2016 Earthquakes. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campanelli, M.; Mascitelli, A.; Sanò, P.; Diémoz, H.; Estellés, V.; Federico, S.; Iannarelli, A.M.; Fratarcangeli, F.; Mazzoni, A.; Realini, E.; et al. Precipitable water vapour content from ESR/SKYNET sun–sky radiometers: Validation against GNSS/GPS and AERONET over three different sites in Europe. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capponi, M.; Sampietro, D.; Sansò, F. Very Improved KINematic Gravimetry: A New Approach to Aerogravimetry; La Sapienza Univ.: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Klejer, F. Troposphere Modeling and Ffiltering for Precise GPS Leveling; Publications on Geodesy; Nederlandse Commissie voor Geodesie: Delft, The Netherlands, 2004; ISBN 978-90-6132-284-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann-Wellenhof, B.; Lichtenegger, H.; Collins, J. Global Positioning System: Theory and Practice; Springer: Wien, Austria, 1992; ISBN 978-3-211-82364-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takasu, T.; Yasuda, A. Development of the low-cost RTK-GPS receiver with an open source program package RTKLIB. In Proceedings of the International Convention Center Jeju Korea, Jeju, Korea, 10 December 2009; pp. 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; de Rosnay, P.; Bell, B.; Schepers, D.; Simmons, A.; Soci, C.; Abdalla, S.; Alonso-Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bechtold, P.; et al. Operational Global Reanalysis: Progress, Future Directions and Synergies with NWP; ERA Report Series; ECMWF: Berkshire, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Berberan-Santos, M.N.; Bodunov, E.N.; Pogliani, L. On the barometric formula. Am. J. Phys. 1997, 65, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Feng, Y. GPS water vapor estimation using interpolated surface meteorological data from Australian automatic weather stations. J. Global Position. Syst. 2003, 2, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, A.C.; Porcù, F.; Baldini, L.; Petracca, M.; Casella, D.; Dietrich, S.; Mugnai, A.; Sanò, P.; Vulpiani, G.; Panegrossi, G. Observational analysis of an exceptionally intense hailstorm over the Mediterranean area: Role of the GPM Core Observatory. Atmos. Res. 2017, 192, 72–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Channel Number | Name | λcen (µm) | λmin (µm) | λmax (µm) | Main Gas Absorber | Main Gas Absorber |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIS 0.6 | 0.635 | 0.56 | 0.71 | Window | Cloud detection |
| 2 | VIS 0.8 | 0.81 | 0.74 | 0.88 | Window | Cloud detection |
| 3 | NIR 1.6 | 1.64 | 1.50 | 1.78 | Window | |
| 4 | IR 3.9 | 3.90 | 3.48 | 4.36 | Window | |
| 5 | WV 6.2 | 6.25 | 5.35 | 7.15 | Water Vapor | |
| 6 | WV7.3 | 7.35 | 6.85 | 7.85 | Water Vapor | |
| 7 | IR 8.7 | 8.70 | 8.30 | 9.10 | Window | |
| 8 | IR 9.7 | 9.66 | 9.38 | 9.94 | Ozone | |
| 9 | IR 10.8 | 10.80 | 9.80 | 11.80 | Window | |
| 10 | IR 12.0 | 12.0 | 11.0 | 13.0 | Window | |
| 11 | IR 13.4 | 13.40 | 12.40 | 14.40 | Carbon dioxide | |
| 12 | HRV | Broad channel (about 0.4–1.1) | Window/Water Vapor | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Adderio, L.P.; Pazienza, L.; Mascitelli, A.; Tiberia, A.; Dietrich, S. A Combined IR-GPS Satellite Analysis for Potential Applications in Detecting and Predicting Lightning Activity. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12061031
D’Adderio LP, Pazienza L, Mascitelli A, Tiberia A, Dietrich S. A Combined IR-GPS Satellite Analysis for Potential Applications in Detecting and Predicting Lightning Activity. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(6):1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12061031
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Adderio, Leo Pio, Luigi Pazienza, Alessandra Mascitelli, Alessandra Tiberia, and Stefano Dietrich. 2020. "A Combined IR-GPS Satellite Analysis for Potential Applications in Detecting and Predicting Lightning Activity" Remote Sensing 12, no. 6: 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12061031
APA StyleD’Adderio, L. P., Pazienza, L., Mascitelli, A., Tiberia, A., & Dietrich, S. (2020). A Combined IR-GPS Satellite Analysis for Potential Applications in Detecting and Predicting Lightning Activity. Remote Sensing, 12(6), 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12061031