Detecting Change in Forest Structure with Simulated GEDI Lidar Waveforms: A Case Study of the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid (HWA; Adelges tsugae) Infestation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Structural Signals of the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid Infestation
1.2. Lidar Remote Sensing for Monitoring Forest Health
1.3. Study Design
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview
2.2. Simulated GEDI Data
2.3. Airborne Lidar Scanner (ALS) Data
2.4. Metrics
2.5. Field Data
2.6. Comparing ALS with the GEDI Simulator
2.7. Selecting and Evaluating Waveform Disturbance Metrics
2.8. Simulating the Impact of GEDI’s Noise
2.9. Simulating GEDI’s Noise and Spatial Coverage
3. Results
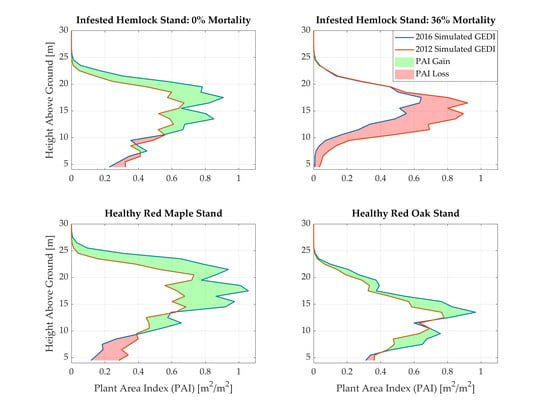
3.1. Simulation Results
3.2. Variable Selection
3.3. Waveform Change Metrics
3.4. Simulating GEDI’s Noise
3.5. Simulating GEDI’s Noise and Spatial Coverage
4. Discussion
4.1. Overview
4.2. Structural Impacts of Hemlock Woolly Adelgid
4.3. Comparing ALS Datasets with the GEDI Simulator
4.4. Toward Change Detection and Disturbance Monitoring with GEDI
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Evaluating Potential Sensor Bias
References
- Oliver, C.D. Forest Development in North America Following Major Disturbances. For. Ecol. Manag. 1980, 3, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwig, D.A.; Foster, D.R. Forest Response to the Introduced Hemlock Woolly Adelgid in Southern New England, USA. J. Torrey Bot. Soc. 1998, 125, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwig, D.A.; Barker Plotkin, A.A.; Davidson, E.A.; Lux, H.; Savage, K.E.; Ellison, A.M. Foundation species loss affects vegetation structure more than ecosystem function in a northeastern USA forest. PeerJ. 2013, 1, e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, B.L.; Skinner, M.; Gouli, S.; Ashikaga, T.; Teillon, H.B. Low lethal temperature for hemlock woolly adelgid (Homoptera: Adelgidae). Environ. Entomol. 1999, 28, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, M.S.; Cheah, C.A.S.-J. Important Mortality Factors in the Life Cycle of Hemlock Woolly Adelgid, Adelges tsugae Annand (Homoptera: Adelgidae) in the Northeastern United States. In Proceedings of the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid Symposium, East Brunswick, NJ, USA, 5–7 February 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, B.L.; Skinner, M.; Gouli, S.; Ashikaga, T.; Teillon, H.B. Survival of Hemlock Woolly Adelgid (Homoptera: Adelgidae) at Low Temperatures. For. Sci. 1998, 44, 414–420. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, M.; Parker, B.L.; Gouli, S.; Ashikaga, T. Regional Responses of Hemlock Woolly Adelgid (Homoptera: Adelgidae) to Low Temperatures. Environ. Entomol. 2003, 32, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, A.; Elkinton, J.; Hayhoe, K.; Buonaccorsi, J. Role of winter temperature and climate change on the survival and future range expansion of the hemlock woolly adelgid (Adelges tsugae) in eastern North America. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2008, 13, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukes, J.S.; Pontius, J.; Orwig, D.; Garnas, J.R.; Rodgers, V.L.; Brazee, N.; Cooke, B.; Theoharides, K.A.; Stange, E.E.; Harrington, R.; et al. Responses of insect pests, pathogens, and invasive plant species to climate change in the forests of northeastern North America: What can we predict? Can. J. For. Res. 2009, 39, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotter, R.T.; Shields, K.S. Variation in Winter Survival of the Invasive Hemlock Woolly Adelgid (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) Across the Eastern United States. Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elkinton, J.S.; Lombardo, J.A.; Roehrig, A.D.; McAvoy, T.J.; Mayfield, A.; Whitmore, M. Induction of cold hardiness in an invasive herbivore: The case of hemlock woolly adelgid (Hemiptera: Adelgidae). Environ. Entomol. 2017, 46, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubayah, R.O.; Blair, J.B.; Goetz, S.J.; Fatoyinbo, L.; Hansen, M.C.; Healey, S.P.; Hofton, M.; Hurtt, G.; Kellner, J.R.; Luthcke, S.; et al. The Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation: High-resolution laser ranging of the Earth’s forests and topography. Sci. Remote Sens. 2020, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domec, J.-C.; Rivera, L.N.; King, J.S.; Peszlen, I.; Hain, F.; Smith, B.; Frampton, J. Hemlock woolly adelgid (Adelges tsugae) infestation affects water and carbon relations of eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis) and Carolina hemlock (Tsuga caroliniana). New Phytol. 2013, 199, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, M.C.; Preisser, E.L.; Porter, A.; Elkinton, J.; Ellison, A.M. Modeling range dynamics in heterogeneous landscapes: Invasion of the hemlock woolly adelgid in eastern North America. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellison, A.; Orwig, D.; Fitzpatrick, M.; Preisser, E. The Past, Present, and Future of the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid (Adelges tsugae) and Its Ecological Interactions with Eastern Hemlock (Tsuga canadensis) Forests. Insects 2018, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pekel, J.F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, E.L.J. Atlas of the United States Trees, 1st ed.; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Carey, J.H. Tsuga canadensis. In Fire Effects Information System; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory: Missoula, MT, USA, 1993; Available online: https://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/plants/tree/tsucan/all.html (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Kellner, J.R.; Clark, D.B.; Hubbell, S.P. Pervasive canopy dynamics produce short-term stability in a tropical rain forest landscape. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calders, K.; Schenkels, T.; Bartholomeus, H.; Armston, J.; Verbesselt, J.; Herold, M. Monitoring spring phenology with high temporal resolution terrestrial LiDAR measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 203, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, S.; Næsset, E.; Hanssen, K.H.; Christiansen, E. Mapping defoliation during a severe insect attack on Scots pine using airborne laser scanning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Dennison, P.E.; Zhao, F.; Shendryk, I.; Rickert, A.; Hanavan, R.P.; Cook, B.D.; Serbin, S.P. Mapping canopy defoliation by herbivorous insects at the individual tree level using bi-temporal airborne imaging spectroscopy and LiDAR measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Dubayah, R. Light-driven growth in Amazon evergreen forests explained by seasonal variations of vertical canopy structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Nelson, R.F.; Næsset, E.; Ørka, H.O.; Coops, N.C.; Hilker, T.; Bater, C.W.; Gobakken, T. Lidar sampling for large-area forest characterization: A review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weishampel, J.F.; Drake, J.B.; Cooper, A.; Blair, J.B.; Hofton, M. Forest canopy recovery from the 1938 hurricane and subsequent salvage damage measured with airborne LiDAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, D.; Lefsky, M.; Parker, G.; Blair, J. Laser altimeter canopy height profiles: Methods and validation for closed-canopy, broadleaf forests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.B.; Dubayah, R.O.; Clark, D.B.; Knox, R.G.; Blair, J.B.; Hofton, M.A.; Chazdon, R.L.; Weishampel, J.F.; Prince, S.D. Estimation of tropical forest structural characteristics using large-footprint lidar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marselis, S.M.; Tang, H.; Armston, J.D.; Calders, K.; Labrière, N.; Dubayah, R. Distinguishing vegetation types with airborne waveform lidar data in a tropical forest-savanna mosaic: A case study in Lopé National Park, Gabon. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubayah, R.O.; Sheldon, S.L.; Clark, D.B.; Hofton, M.A.; Blair, J.B.; Hurtt, G.C.; Chazdon, R.L. Estimation of tropical forest height and biomass dynamics using lidar remote sensing at La Selva, Costa Rica. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Sun, G.; Dubayah, R.; Cook, B.; Montesano, P.; Ni, W.; Zhang, Z. Mapping biomass change after forest disturbance: Applying LiDAR footprint-derived models at key map scales. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, P.L.; Healey, S.P.; Ståhl, G.; Saarela, S.; Holm, S.; Andersen, H.-E.; Dubayah, R.O.; Duncanson, L.; Hancock, S.; Armston, J.; et al. Statistical properties of hybrid estimators proposed for GEDI-NASA’s global ecosystem dynamics investigation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 065007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, S.; Armston, J.; Hofton, M.; Sun, X.; Tang, H.; Duncanson, L.I.; Kellner, J.R.; Dubayah, R. The GEDI simulator: A large-footprint waveform lidar simulator for calibration and validation of spaceborne missions. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 294–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, B.J.; Hofton, M.A. Modeling laser altimeter return waveforms over complex vegetation using high-resolution elevation data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 2509–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwig, D.; Foster, D.; Ellison, A. Harvard Forest CTFS-ForestGEO Mapped Forest Plot since 2014. 2015. Available online: https://harvardforest1.fas.harvard.edu/exist/apps/datasets/showData.html?id=hf253 (accessed on 9 September 2019).
- Cook, B.; Corp, L.; Nelson, R.; Middleton, E.; Morton, D.; McCorkel, J.; Masek, J.; Ranson, K.; Ly, V.; Montesano, P. NASA Goddard’s LiDAR, Hyperspectral and Thermal (G-LiHT) Airborne Imager. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4045–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kampe, T.; Johnson, B.R.; Kuester, M.; Keller, M. NEON: The first continental-scale ecological observatory with airborne remote sensing of vegetation canopy biochemistry and structure. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2010, 4, 043510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, S.; Anderson, K.; Disney, M.; Gaston, K.J. Measurement of fine-spatial-resolution 3D vegetation structure with airborne waveform lidar: Calibration and validation with voxelised terrestrial lidar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 188, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blair, J.B.; Rabine, D.L.; Hofton, M.A. The Laser Vegetation Imaging Sensor: A medium-altitude, digitisation-only, airborne laser altimeter for mapping vegetation and topography. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1999, 54, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofton, M.A.; Minster, J.B.; Blair, J.B. Decomposition of laser altimeter waveforms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Armston, J. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) for GEDI L2B Footprint Canopy Cover and Vertical Profile Metrics; Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2019; Available online: https://gedi.umd.edu/data/documents/ (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Chen, J.M.; Rich, P.M.; Gower, S.T.; Norman, J.M.; Plummer, S. Leaf area index of boreal forests: Theory, techniques, and measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 29429–29443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni-Meister, W.; Jupp, D.L.; Dubayah, R. Modeling Lidar Waveforms in Heterogeneous and Discrete Canopies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1943–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armston, J.; Disney, M.; Lewis, P.; Scarth, P.; Phinn, S.; Lucas, R.; Bunting, P.; Goodwin, N. Direct retrieval of canopy gap probability using airborne waveform lidar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Dubayah, R.; Swatantran, A.; Hofton, M.; Sheldon, S.; Clark, D.B.; Blair, B. Retrieval of vertical LAI profiles over tropical rain forests using waveform lidar at La Selva, Costa Rica. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Brolly, M.; Zhao, F.; Strahler, A.H.; Schaaf, C.; Ganguly, S.; Zhang, G.; Dubayah, R. Deriving and validating Leaf Area Index (LAI) at multiple spatial scales through lidar remote sensing: A case study in Sierra National Forest, CA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofton, M.; Blair, B.; Story, S.; Yi, D. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) for GEDI Transmit and Receive Waveform Processing for L1 and L2 Products; Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2019; Available online: https://gedi.umd.edu/data/documents/ (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Anderson-Teixeira, K.J.; Davies, S.J.; Bennett, A.C.; Gonzalez-Akre, E.B.; Muller-Landau, H.C.; Joseph Wright, S.; Abu Salim, K.; Almeyda Zambrano, A.M.; Alonso, A.; Baltzer, J.L.; et al. CTFS-ForestGEO: A worldwide network monitoring forests in an era of global change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 528–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orwig, D.A.A.; Boucher, P.; Paynter, I.; Saenz, E.; Li, Z.; Schaaf, C. The potential to characterize ecological data with terrestrial laser scanning in Harvard Forest, MA. Interface Focus 2018, 8, 20170044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2009, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwig, D.A.; Foster, D.R.; Mausel, D.L. Landscape patterns of hemlock decline in New England due to the introduced hemlock woolly adelgid. J. Biogeogr. 2002, 29, 1475–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]












| G-LiHT | NEON | |
|---|---|---|
| Instrument | Riegl VQ-480 | Optech ALTM Gemini |
| Beam divergence (mrad) | 0.3 | 0.8 |
| Altitude (m) | ~300 | ~1000 |
| Wavelength (nm) | 1550 | 1064 |
| Pulse repetition frequency (PRF; kHz) | 300 | 100 |
| Max number of returns per pulse | 8 | 4 |
| Max scan angle used (degrees) | 36 | 18 |
| Point density (points/m2) | 29.6 | 6.8 |
| Acquisition date | June 2012 | August 2016 |
| Variable | Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| ΒRH10 | −0.23 ± 0.08 | 0.002 |
| ΒPAI11-12m | −0.29 ± 0.08 | <0.001 |
| Intercept | −1.89 ± 0.08 | <0.001 |
| R2 | 0.6 | N/A |
| RMSE | 0.08 | N/A |
| Species | Median | Mean | N | p-Value from Hemlock |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemlock | −0.072 | −0.064 ± 0.012 | 186 | N/A |
| Red Oak | 0.001 | 0.020 ± 0.013 | 138 | < 0.001 |
| Red Maple | 0.003 | 0.041 ± 0.017 | 82 | < 0.001 |
| White Pine | −0.020 | 0.001 ± 0.025 | 40 | 0.15 |
| Red Pine | 0.051 | 0.057 ± 0.031 | 25 | < 0.001 |
| Species | Median | Mean | N | p-Value from Hemlock |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemlock | −0.085 | −1.563 ± 0.263 | 186 | N/A |
| Red Oak | 3.610 | 4.200 ± 0.305 | 138 | < 0.001 |
| Red Maple | 0.995 | 2.166 ± 0.396 | 82 | < 0.001 |
| White Pine | 2.070 | 2.507 ± 0.567 | 40 | < 0.001 |
| Red Pine | 1.760 | 1.695 ± 0.717 | 25 | < 0.001 |
| Day-Coverage Noise | Night-Power Noise | Noiseless | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-LiHT 2012 | NEON 2016 | G-LiHT 2012 | NEON 2016 | ||
| F-statistic | 0.43 | 1.47 | 6.79 | 5.39 | 15.22 |
| p-value | 0.65 | 0.250 | 0.002 | 0.007 | <0.001 |
| η2 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.22 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boucher, P.B.; Hancock, S.; Orwig, D.A.; Duncanson, L.; Armston, J.; Tang, H.; Krause, K.; Cook, B.; Paynter, I.; Li, Z.; et al. Detecting Change in Forest Structure with Simulated GEDI Lidar Waveforms: A Case Study of the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid (HWA; Adelges tsugae) Infestation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12081304
Boucher PB, Hancock S, Orwig DA, Duncanson L, Armston J, Tang H, Krause K, Cook B, Paynter I, Li Z, et al. Detecting Change in Forest Structure with Simulated GEDI Lidar Waveforms: A Case Study of the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid (HWA; Adelges tsugae) Infestation. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(8):1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12081304
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoucher, Peter Brehm, Steven Hancock, David A Orwig, Laura Duncanson, John Armston, Hao Tang, Keith Krause, Bruce Cook, Ian Paynter, Zhan Li, and et al. 2020. "Detecting Change in Forest Structure with Simulated GEDI Lidar Waveforms: A Case Study of the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid (HWA; Adelges tsugae) Infestation" Remote Sensing 12, no. 8: 1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12081304
APA StyleBoucher, P. B., Hancock, S., Orwig, D. A., Duncanson, L., Armston, J., Tang, H., Krause, K., Cook, B., Paynter, I., Li, Z., Elmes, A., & Schaaf, C. (2020). Detecting Change in Forest Structure with Simulated GEDI Lidar Waveforms: A Case Study of the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid (HWA; Adelges tsugae) Infestation. Remote Sensing, 12(8), 1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12081304