A Multi-Branch Feature Fusion Strategy Based on an Attention Mechanism for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
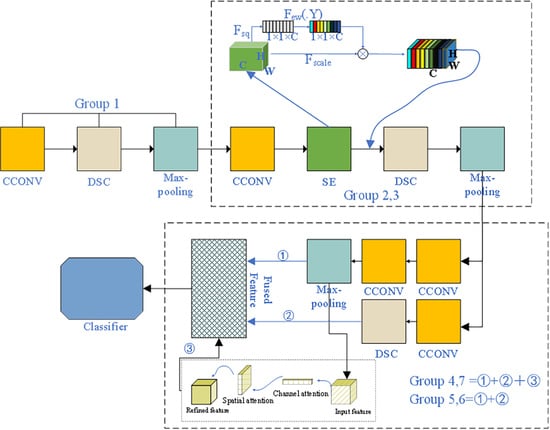
2.1. The Structure of the Proposed Method
| Algorithm 1 Framework of the proposed AMB-CNN model |
| Input: is a feature map with size , the number of convolution kernels is |
| 1: Learn shallow features |
| 2: For in range Group 4 |
| 3: Extract the feature of target image |
| 4: Introducing dynamic features and activating channel weights |
| 5: Eliminate data offset ( represents the result after the normalization of the hidden layer, and represents the weight parameter and represents the input of any hidden layer activation function in the network) |
| 6: Mapping features to a high-dimensional, non-linear space end |
| 7: Learn deep features |
| 8: For in range (Group4:Group9) |
| 9: Through multi convolution cooperative feature exploration, are obtained ( represents the features of the second branch extracted from the fourth to seventh group) |
| 10: Generative attention characteristics ( is the global average pooling operations in spatial dimension, is the global max pooling operations in spatial dimension. is the global average pooling operations in channel dimension, is the global max pooling operations in channel dimension.) |
| 11: Fusion of multi segment features end |
| 12: classifier |
| 13: send to the classifier |
| Output: the predicted category labels |
2.2. Feature Extraction and Attention Module
2.3. Some Strategies of Building Lightweight Model
2.4. The Strategy of Nonlinear Feature Enhancement
2.5. Dataset Settings
2.5.1. UC Merced Land-Use Dataset (UCM21)
2.5.2. AID30 Dataset
2.5.3. RSSCN7 Dataset
2.5.4. NWPU45 Dataset
3. Experiment and Analysis
3.1. Setting of the Experiments
3.1.1. Data Preprocessing
3.1.2. Parameter Settings
3.2. The Performance of the Proposed Model
3.3. Comparison with Advanced Methods
4. Discussion
4.1. Model Analysis
4.2. Visual Dimension Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, X.; Yuan, Y.; Lu, X. A Deep Scene Representation for Aerial Scene Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4799–4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Fang, J.; Lu, X.; Feng, Y. Remote sensing image scene classification using rearranged local features. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 1779–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Q.; Lv, H.; Huang, C.; Li, Y. An Inversion-Based Fusion Method for Inland Water Remote Monitoring. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 5599–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yuan, Y.; Lu, X. Attribute-Cooperated Convolutional Neural Network for Remote Sensing Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 8358–8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Xia, J.; Du, P.; Lin, C.; Samat, A. Integrating multilayer features of convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5653–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Ma, J. Learning Source-Invariant Deep Hashing Convolutional Neural Networks for Cross-Source Remote Sensing Image Retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6521–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aude, O. Chapter 41—Gist of the Scene. In Neurobiology of Attention; Laurent, I., Geraint, R., John, K.T., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Gamage, P.T.; Azad, M.K.; Taebi, A.; Sandler, R.H.; Mansy, H.A. Clustering Seismocardiographic Events using Unsupervised Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Signal Processing in Medicine and Biology Symposium (SPMB), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1 December 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Risojevic, V.; Babic, Z. Unsupervised Quaternion Feature Learning for Remote Sensing Image Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Xiong, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Tao, D. Stacked Convolutional Denoising Auto-Encoders for Feature Representation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 47, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2012, 60, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ding, L. Scene classification based on two-stage deep feature fusion. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaib, S.; Liu, H.; Gu, Y.; Yao, H. Deep Feature Fusion for VHR Remote Sensing Scene Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4775–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Yang, C.; Yao, X.; Guo, L.; Han, J. When deep learning meets metric learning: Remote sensing image scene classification via learning discriminative CNNs. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2811–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Mu, X.; Yang, Z.; Yi, Z. A novel two-stage scene classification model based on feature variable significance in high-resolution remote sensing. Geocarto Int. 2019, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2017, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv Prepr. 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Tang, P.; Zhao, L. Remote sensing image scene classification using CNN-CapsNet. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xiong, B.; Kuang, G. Attention Receptive Pyramid Network for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 2738–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ma, S.; Pan, H. FDTA: Fully Convolutional Scene Text Detection with Text Attention. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 155441–155449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, B.; Zheng, X. Sound Active Attention Framework for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 1985–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Haffari, G.; Norouzi, M. Sequence to Sequence Mixture Model for Diverse Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 22nd Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–1 November 2018; pp. 583–592. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Feng, M.; dos Santos, C.N.; Yu, M.; Xiang, B.; Zhou, B.; Bengio, Y. A structured self-attentive sentence embedding. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2017, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Chanussot, J.; Li, X. Scene Classification With Recurrent Attention of VHR Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Chen, W.; Han, W.; Li, X.; Wang, L. Channel-Attention-Based DenseNet Network for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 4121–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Guo, H.; Xu, Q.; Lu, J.; Zhao, C.; Lin, Y. Hierarchical Attention and Bilinear Fusion for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 6372–6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhichri, H.; Alswayed, A.S.; Bazi, Y.; Ammour, N.; Alajlan, N.A. Classification of Remote Sensing Images Using EfficientNet-B3 CNN Model With Attention. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 14078–14094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; He, F.; Yang, Y.; Hu, F. Semi-supervised representation learning for remote sensing image classification based on generative adversarial networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 54135–54144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lin, W.; Tang, P. Multiple resolution block feature for remote-sensing scene classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 6884–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yao, R.; Liu, B.; Zheng, Y. Siamese convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Ma, D.; Yao, R.; Liu, B.; Zheng, Y. Remote sensing scene classification based on rotation-invariant feature learning and joint decision making. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2019, 2019, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Ji, W.; Li, X.; Zheng, X. Bidirectional adaptive feature fusion for remote sensing scene classification. Neurocomputing 2019, 328, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Qin, Q. Scene Classification Based on Multiscale Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 7109–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, R.; Fang, L.; Lu, T.; He, N. Self-Attention-Based Deep Feature Fusion for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.D.; Meng, J.; Xie, W.Y.; Shao, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Weighted spatial pyramid matching collaborative representation for remote-sensing-image scene classification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, N.; Fang, L.; Li, S.; Plaza, J.; Plaza, A. Skip-connected covariance network for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 31, 1461–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, N.; Fang, L.; Li, S.; Plaza, A.; Plaza, J. Remote sensing scene classification using multilayer stacked covariance pooling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6899–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, S.; Zheng, X.; Lu, X. Remote sensing scene classification by gated bidirectional network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Sun, H.; Zheng, X. A Feature Aggregation Convolutional Neural Network for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7894–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietal, B. Aggregated deep fisher feature for VHR remote sensing scene classification. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 3508–3523. [Google Scholar]
- Boualleg, Y.; Farah, M.; Farah, I.R. Remote Sensing Scene Classification Using Convolutional Features and Deep Forest Classifier. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1944–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; He, N.; Fang, L.; Plaza, A. Scale-free convolutional neural network for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6916–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, N.; Ye, Q. Positional Context Aggregation Network for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, L. Branch Feature Fusion Convolution Network for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5194–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, D.; Wang, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, C.; Zhou, Y. Deep Discriminative Representation Learning with Attention Map for Scene Classification. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.-S.; Hu, J.; Hu, F.; Shi, B.; Bai, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X. AID: A Benchmark Data Set for Performance Evaluation of Aerial Scene Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3965–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


















| DATA SET | MobileNet | AMB-CNN | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA(%) | KAPPA(%) | AP(%) | F1 | OA(%) | KAPPA(%) | AP(%) | F1 | |
| 80/20 UC | 97.62 | 97.50 | 97.71 | 97.61 | 99.52 | 99.50 | 99.55 | 99.52 |
| 20/80 AID | 87.21 | 86.76 | 87.43 | 87.18 | 93.27 | 93.04 | 93.05 | 92.99 |
| 50/50 AID | 92.12 | 91.84 | 92.24 | 92.11 | 95.44 | 95.38 | 95.50 | 95.42 |
| 10/90 NWPU | 82.66 | 82.27 | 82.74 | 82.60 | 88.99 | 88.74 | 89.04 | 88.95 |
| 20/80 NWPU | 87.85 | 87.57 | 87.89 | 87.81 | 92.42 | 92.25 | 92.50 | 92.43 |
| 50/50 RSSCN | 91.50 | 90.08 | 91.51 | 91.47 | 95.14 | 94.33 | 95.18 | 95.15 |
| The Network Model | OA(%) | Number of Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Semi-supervised representation learning method [33] | 94.05 ± 1.2 | 210 M |
| Multiple resolution BlockFeature method [34] | 94.19 ± 1.5 | - |
| Siamese CNN [35] | 94.29 | - |
| Siamese ResNet50 with R.D method [36] | 94.76 | - |
| Bidirectional adaptive feature fusion method [37] | 95.48 | 130 M |
| Multiscale CNN [38] | 96.66 ± 0.90 | 60 M |
| VGG_VD16 with SAFF method [39] | 97.02 ± 0.78 | 15 M |
| Variable-weighted multi-fusion method [20] | 97.79 | - |
| ResNet+WSPM-CRC method [40] | 97.95 | 23 M |
| Skip-Connected CNN [41] | 98.04 ± 0.23 | 6 M |
| VGG16 with MSCP [42] | 98.36 ± 0.58 | - |
| Gated bidirectiona+global feature method [43] | 98.57 ± 0.48 | 138 M |
| Feature aggregation CNN [44] | 98.81 ± 0.24 | 130 M |
| Aggregated deep fisher feature method [45] | 98.81 ± 0.51 | 23 M |
| Discriminative CNN [19] | 98.93 ± 0.10 | 130 M |
| VGG16-DF method [46] | 98.97 | 130 M |
| Scale-free CNN [47] | 99.05 ± 0.27 | 130 M |
| Inceptionv3+CapsNet method [23] | 99.05 ± 0.24 | 22 M |
| Positional context aggregation method [48] | 99.21 ± 0.18 | 28 M |
| LCNN-BFF method [49] | 99.29 ± 0.24 | 6.2 M |
| DDRL-AM method [50] | 99.05 ± 0.08 | - |
| HABFNet [31] | 99.29 ± 0.35 | 6.2 M |
| EfficientNetB3-Attn-2 [32] | 99.21 ± 0.22 | - |
| The proposed AMB-CNN | 99.52 ± 0.11 | 5.6 M |
| The Network Model | OA(%) | Number of Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| VGG16+SVM method [51] | 87.18 | 130 M |
| Variable-weighted multi-fusion method [20] | 89.1 | - |
| TSDFF method [17] | 92.37 ± 0.72 | - |
| ResNet+SPM-CRC method [40] | 93.86 | 23 M |
| ResNet+WSPM-CRC method [40] | 93.9 | 23 M |
| LCNN-BFF method [49] | 94.64 ± 0.21 | 6.2 M |
| Aggregated deep Fisher feature method [45] | 95.21 ± 0.50 | 23 M |
| The proposed AMB-CNN | 95.14 ± 0.24 | 5.6 M |
| The Network Model | OA(20/80)(%) | OA(50/50)(%) | Number of Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bidirectional adaptive feature fusion method [37] | - | 93.56 | 130 M |
| VGG16+CapsNet [23] | 91.63 ± 0.19 | 94.74 ± 0.17 | 130 M |
| Feature aggregation CNN [44] | - | 95.45 ± 0.11 | 130 M |
| Discriminative +VGG16 [19] | 90.82 ± 0.16 | 96.89 ± 0.10 | 130 M |
| VGG16 with MSCP [42] | 91.52 ± 0.21 | 94.42 ± 0.17 | - |
| Fine-tuning method [51] | 86.59 ± 0.29 | 89.64 ± 0.36 | 130 M |
| Gated bidirectiona method [43] | 90.16 ± 0.24 | 93.72 ± 0.34 | 18 M |
| Gated bidirectiona+global feature method [43] | 92.20 ± 0.23 | 95.48 ± 0.12 | 138 M |
| VGG_VD16 with SAFF method [39] | 90.25 ± 0.29 | 93.83 ± 0.28 | 15 M |
| TSDFF method [17] | - | 91.8 | - |
| Discriminative+AlexNet [19] | 85.62 ± 0.10 | 94.47 ± 0.12 | 60 M |
| AlexNet with MSCP [42] | 88.99 ± 0.38 | 92.36 ± 0.21 | - |
| Skip-connected CNN [41] | 91.10 ± 0.15 | 93.30 ± 0.13 | 6 M |
| LCNN-BFF method [49] | 91.66 ± 0.48 | 94.64 ± 0.16 | 6.2 M |
| DDRL-AM method [50] | 92.36 ± 0.10 | 96.25 ± 0.05 | - |
| The proposed AMB-CNN | 93.27 ± 0.22 | 95.54 ± 0.13 | 5.6 M |
| The Network Model | OA(10/90)(%) | OA(20/80)(%) | Number of Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| VGG16+CapsNet [23] | 85.05 ± 0.13 | 89.18 ± 0.14 | 130 M |
| Discriminative with AlexNet [19] | 85.56 ± 0.20 | 87.24 ± 0.12 | 130 M |
| Discriminative with VGG16 [19] | 89.22 ± 0.50 | 91.89 ± 0.22 | 130 M |
| R.D method [36] | - | 91.03 | - |
| AlexNet with MSCP [42] | 81.70 ± 0.23 | 85.58 ± 0.16 | - |
| VGG16 with MSCP [42] | 85.33 ± 0.17 | 88.93 ± 0.14 | - |
| VGG_VD16 with the SAFF method [39] | 84.38 ± 0.19 | 87.86 ± 0.14 | 15 M |
| Fine-tuning method [51] | 87.15 ± 0.45 | 90.36 ± 0.18 | 130 M |
| Skip-connected CNN [41] | 84.33 ± 0.19 | 87.30 ± 0.23 | 6 M |
| LCNN-BFF method [49] | 86.53 ± 0.15 | 91.73 ± 0.17 | 6.2 M |
| The proposed AMB-CNN | 88.99 ± 0.14 | 92.42 ± 0.14 | 5.6 M |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L. A Multi-Branch Feature Fusion Strategy Based on an Attention Mechanism for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13101950
Shi C, Zhao X, Wang L. A Multi-Branch Feature Fusion Strategy Based on an Attention Mechanism for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(10):1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13101950
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Cuiping, Xin Zhao, and Liguo Wang. 2021. "A Multi-Branch Feature Fusion Strategy Based on an Attention Mechanism for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification" Remote Sensing 13, no. 10: 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13101950
APA StyleShi, C., Zhao, X., & Wang, L. (2021). A Multi-Branch Feature Fusion Strategy Based on an Attention Mechanism for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification. Remote Sensing, 13(10), 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13101950