A Study on the Range Equation Modeling for Multichannel Medium-Earth-Orbit SAR-GMTI Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
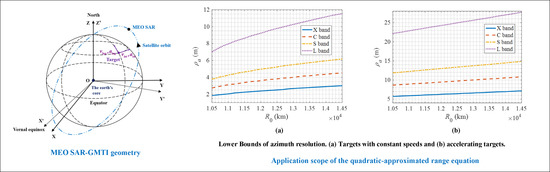
2. MEO SAR-GMTI Geometry
3. Range Equation Modeling
3.1. Derivation of the Quadratic-Approximated Range Equation for the Reference Channel
3.2. Derivation of the Quadratic-Approximated Range Equation for the nth Channel
4. Investigation on the Accuracy of the Quadratic-Approximated Range Equation
- (1)
- The phase error is strongly sensitive to the azimuth resolution and the wavelength. It is approximately proportional to the square of the wavelength and inversely proportional to the cube of the azimuth resolution.
- (2)
- The phase error is proportional to the distance between the target and the MEO SAR and is inversely proportional to the speed of the MEO SAR. In addition, the phase error depends on the target’s along-track acceleration, while the dependency between the phase error and the target’s radial acceleration and along-track velocity can be ignored.
- (3)
- Different from LEO SAR, the dependency between the phase error and the target’s radial velocity can be neglected. Moreover, in the case of MEO SAR, the phase error depends also on the projection of the satellite’s acceleration onto the direction of its velocity vector and the projection of the satellite’s jerk onto the radial direction.
5. Numerical Results
5.1. Phase Error
5.2. Influence of the Phase Error on the GMTI Performance
5.3. Quadratic-Approximated Range Equation’s Scope of Application
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SAR | synthetic aperture radar |
| GMTI | ground moving target indication |
| RCM | range cell migration |
| ATI | along-track interferometric |
| LEO | low-Earth-orbit |
| MEO | medium-Earth-orbit |
| ECI | Earth-centered inertial |
| ECR | Earth-centered rotating |
| SNR | signal-to-noise ratio |
References
- Moreira, A.; Prats-iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.P.; Papathanassiou, K. A Tutorial on Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE Mag. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Y.; Tang, S.Y.; Guo, P.; So, H.C.; Zhang, L.R. 2-D Spatially Variant Motion Error Compensation for High-Resolution Airborne SAR Based on Range-Doppler Expansion Approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.Y.; Guo, P.; Zhang, L.R.; So, H.C. Focusing Hypersonic Vehicle-Borne SAR Data Using Radius/Angle Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Zhang, J.C.; Jin, Y.H.; Yu, H.W.; Liang, B.G.; Yang, D.G. Real-Time Processing of Spaceborne SAR Data with Nonlinear Trajectory Based on Variable PRF. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Bai, X.R.; Gong, C.; Zhou, F. Hybrid Inference Network for Few-Shot SAR Automatic Target Recognition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.K.; Liu, B.C.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.M.; Nie, L.S.; Zeng, L.N.; Bi, G.A. An accurate imaging and doppler chirp rate estimation algorithm for airborne CSSAR-GMTI systems. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 170077–170086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, S.V.; Krieger, G. Multi-Channel SAR for ground Moving Target Indication. Elsevier Acad. Press Libr. Signal Process. 2014, 2, 911–986. [Google Scholar]
- Dragoševic, M.V.; Henschel, M.D.; Livingstone, C.E. An Approach to Ship Motion Estimation With Dual-Receive Antenna SAR. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 26–30 May 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.P.; Liao, G.S.; Zhu, S.Q.; Yang, D.; Du, W.T. Efficient Compressed Sensing Method for Moving Targets Imaging by Exploiting the Geometry Information of the Defocused Results. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, D.; Dominguez, E.M.; Small, D.; Schaepman, M.E.; Meier, E. Moving-Target Tracking in Single-Channel Wide-Beam SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 50, 4735–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bacci, A.; Martorella, M.; Gray, D.A.; Berizzi, F. Space-Doppler Adaptive Processing for Radar Imaging of Moving Targets Masked by Ground Clutter. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2015, 9, 712–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Tan, X.; Chen, Z.; Dong, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L. Refocusing of Ground Moving Targets with Doppler Ambiguity Using Keystone Transform and Modified Second-Order Keystone Transform for Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sens. 2021, 2, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti-Maori, D.; Sikaneta, I.; Gierull, C.H. Optimum SAR/GMTI Processing and Its Application to the Radar Satellite RADARSAT-2 For Traffic Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3868–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S. Moving Target Indication Via RADARSAT-2 Multichannel Synthetic Aperture Radar Processing. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2010, 2010, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rousseau, L.P.; Gierull, C.H.; Chouinard, J.Y. First Results from an Experimental SCANSAR-GMTI Mode on RADARSAT-2. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 5068–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastina, D.; Turin, F. Exploitation of the COSMO-SkyMed SAR System for GMTI Applications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 966–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, S.V.; Krieger, G. Dual-Platform Large Along-Track Baseline GMTI. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 3, 1554–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budillon, A.; Gierull, C.H.; Pascazio, V.; Schirinzi, G. Along Track Interferometric SAR systems for Ground Moving Target Indication: Achievements, Potentials and Outlook. IEEE Mag. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 8, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.J. Imaging Algorithm for Medium-Earth-Orbit SAR. Ph.D. Thesis, Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Matar, J.; López-Dekker, P.; Krieger, G. Potentials and Limitations of MEO SAR. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2016: 11th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 6–9 June 2016; pp. 1035–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, M.; Xing, M.D.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.C. Two-dimensional Spectrum For MEO SAR Processing Using a Modified Advanced Hyperbolic Range Equation. Electron. Lett. 2011, 47, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.J.; Qiu, X.; Hu, D.; Ding, C. Focusing of Medium-Earth-Orbit SAR with Advanced Nonlinear Chirp Scaling Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.J.; Qiu, X.; Hu, D.; Han, B.; Ding, C. Medium-Earth-orbit SAR Focusing Using Range Doppler Algorithm with Integrated Two-Step Azimuth Perturbation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.B.; Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Yang, W.; Han, Y. Higher Order Nonlinear Chirp Scaling Algorithm for Medium Earth Orbit Synthetic Aperture Radar. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 096084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.L.; Xing, M.D.; Sun, G.C.; Gao, Y.X.; Liu, W.K.; Guo, L.; Lan, Y. Focusing of Medium-Earth-Orbit SAR Using an ASE-Velocity Model Based on MOCO Principle. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3963–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.K.; Sun, G.C.; Xia, X.G.; Chen, J.L.; Guo, L.; Xing, M.D. A Modified CSA Based on Joint Time-Doppler Resampling For MEO SAR Stripmap Mode. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3573–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithm and Implementation; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.F.; Bao, Z.; Wang, H.Y.; Liao, G.S. Performance Improvement for Constellation SAR Using Signal Processing Techniques. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2006, 42, 436–452. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Li, Z.F.; Liao, G.S. System Error Analysis and Calibration Methods for Multichannel SAR. PIER 2011, 112, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.K.; Nie, L.S. Study on the Range Equation Modeling of MEO SAR-GMTI systems. In Proceedings of the 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Xiamen, China, 26–29 November 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.K.; Wang, F.; Zeng, L.N.; Chen, H.M. A Study on the Cubic Range Model for MEO SAR Ground Moving Target Imaging. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing, Xi’an, China, 21–24 August 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X. Introduce to the Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar; National Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.K.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, B.C.; Zhang, S.X.; Nie, L.S.; Bi, G.A. A New Motion Parameter Estimation and Relocation Scheme for Airborne Three-Channel CSSAR-GMTI Systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4107–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrara, W.G.; Goodman, R.S.; Majewski, R.M. Spotlight Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing Algorithms; Artech House: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Gierull, C.H.; Cerutti-Maori, D.; Ender, J. Ground Moving Target Indication with Tandem Satellite Constellations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, J.; Gierull, C.H.; Cerutti-Maori, D. Improved Space-Based Moving Target Indication via Alternate Transmission and Receiver Switching. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3960–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Height of the orbit | 10,000 km |
| Radius of the Earth | 6371 km |
| Right ascension of ascending node | 0 |
| Argument of perigee | 0 |
| Orbit inclination | 90° |
| Eccentricity | 0 |
| Greenwich hour angle at ta = 0 | 0 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| λ | 0.056 m |
| d | 4 m |
| ρa | 10 m |
| δlat | 10° |
| δlng | 30° |
| Ta | 6.26 s |
| PRF | 500 Hz |
| R0 | 1.12 × 104 km |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Huo, T.; Nie, L. A Study on the Range Equation Modeling for Multichannel Medium-Earth-Orbit SAR-GMTI Systems. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142734
Li Y, Wang T, Huo T, Nie L. A Study on the Range Equation Modeling for Multichannel Medium-Earth-Orbit SAR-GMTI Systems. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(14):2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142734
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yongkang, Tong Wang, Tianyu Huo, and Laisen Nie. 2021. "A Study on the Range Equation Modeling for Multichannel Medium-Earth-Orbit SAR-GMTI Systems" Remote Sensing 13, no. 14: 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142734
APA StyleLi, Y., Wang, T., Huo, T., & Nie, L. (2021). A Study on the Range Equation Modeling for Multichannel Medium-Earth-Orbit SAR-GMTI Systems. Remote Sensing, 13(14), 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142734