Study on Urban Spatial Pattern Based on DMSP/OLS and NPP/VIIRS in Democratic People’s Republic of Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Study Area
2.1.2. Remote-Sensing Data
2.1.3. Other Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Data Preprocessing
2.2.2. DMSP/OLS Correction
- (1)
- Determining the invariant target area. Hegang City in Heilongjiang Province in China is selected as the constant target area, and the global radiometric calibration image (F162006) obtained by the F16 satellite sensor from 28 November 2005 to 24 December 2006 is used as the reference image.
- (2)
- Mutual correction and saturation correction. The defects of the DMSP/OLS data mean that mutual correction and saturation correction are required. The key is to calculate the parameter value and estimate the correlation coefficient of the regression correction model of each expected correction image and reference image. The specific operational steps are as follows: mask the Hegang area in the F162006 reference image, extract the DN values of all pixels of each expected correction image, and list them into the same gray matrix. Exponential, linear, logarithmic, quadratic polynomial, and idempotent regression analyses are performed between the image to be corrected and the reference image, giving five groups of correlation coefficients R2 (Table 1). In this paper, the power regression model (1) is used to correct the NSL data:where DN is the original DN value of the DMSP/OLS data, DNcor is DN after intercalibration, and a and b are coefficients as listed in Table 1.
- (3)
- Continuous correction. Because of the problem of abnormal wave DN value of simultaneous interpreting images from different sensors and images acquired by different sensors in different years, continuity correction is needed [32]. To make full use of the information from multiple satellites in the same year, Equation (2) is used to correct the NSL data in the same year, and Equation (3) is used to make cross-year correction:where is the DN value of the ith lit pixel from the intra-annual composition in the nth year, and and are the DN values of the ith lit pixel from two inter-calibrated NSL data in the nth year (n = 1994, 1997, …, 2007):
2.2.3. DMSP/OLS and NPP/VIIRS Mutual Correction
2.2.4. Extraction of Urban Built-Up Areas
2.2.5. Urbanization Dynamic Expansion Index
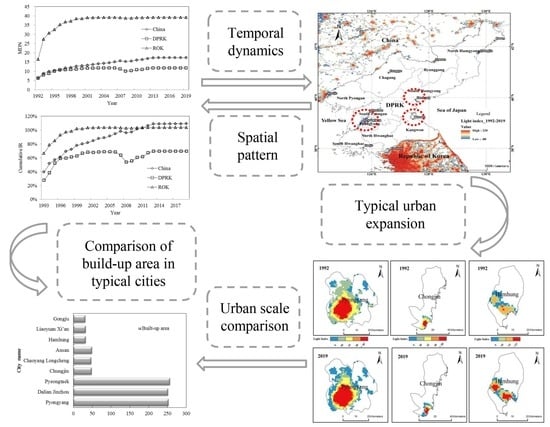
3. Results
3.1. Night-Light Brightness Changes in DPRK, China, and ROK
3.2. Analysis of Urban Spatial Pattern and Change
4. Discussion
4.1. Selection and Spatial Pattern of Typical Cities in DPRK
4.2. Dynamic Expansion of Typical Cities in DPRK
4.3. Comparison of Typical Cities in DPRK, China, and ROK
4.4. Robustness of Main Results
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hao, Q.H. Effectiveness and constraints of UN sanctions on DPRK. Contemp. Int. Relat. 2017, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S. The development and prospect of China–DPRK economic and trade relations under UN sanctions. J. Northeast Asian Stud. 2021, 1, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q. Opportunities and challenges for DPRK to participate in Belt and Road construction. Chin. Foreign Invest. 2021, 6, 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.C.; Zhang, P.Y.; Wang, D.Y. North Korean urbanization process and spatial pattern. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Puertas, O.L.; Henríquez, C.; Francisco, J.M. Assessing spatial dynamics of urban growth using an integrated land use model. Application in Santiago Metropolitan Area, 2010–2045. Land Use Policy 2014, 38, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.C.; Adler, S. North Korean planning: Urban changes and regional balance. Cities 2002, 19, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Yan, H.W.; Zhou, L.; Dang, X.W. Using SVM classify Landsat image to analyze the spatial and temporal characteristics of main urban expansion analysis in Democratic People’s Republic of Korea. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2020, 32, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.S.; Li, Z.Q. China–North Korea–South Korea Economic Cooperation Framework. Dongjiang J. 2019, 36, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y. Construction of Northeast Asia community of destiny from the perspective of Asian security concept. Northeast Asia Forum 2021, 30, 95–110,128. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.S. Obligation-based cooperation: Role theory and Sino-US East Asian security interaction. J. Int. Secur. Stud. 2021, 39, 57–79,158,159. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, K.; Yamakawa, S. Estimation of flood damage to rice production in North Korea in 1995. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Z.N. Food shortage in North Korea and its solution. Contemp. Int. Relat. 2013, 1, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, B. Comparative study on changes of croplands between North Korea and South Korea during 1990–2015. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 920–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.; Cha, Y. Interdecadal variation in Korean spring drought in the early 1990s. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2017, 78, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W. The changes of geo-strategic status of Korean Peninsular vs. the unity of Japan and Korea. J. Yanbian Univ. 2010, 43, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, W.Z.; Xu, J.H. Remote sensing research on spatial pattern of urban old city transformation based on linear spectral analysis: A case study of Shanghai central city in 1997–2000. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 8, 966–974. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.H.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.Y.; Liao, M.S.; Qiu, J.Z. Detection and analysis of urban land use changes through multi-temporal impervious surface mapping. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 14, 593–606. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.L.; Wang, C.X.; Gong, W.K.; Chen, Z.Q.; Shi, K.F.; Wu, B.; Hong, Y.C.; Li, Q.X.; Wu, J.P. Nighttime light remote sensing and urban studies: Data, methods, applications, and prospects. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 25, 342–364. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.S.; Li, R.J.; Li, J.M. Study on urban spatiotemporal expansion pattern of three first-class urban agglomerations in China derived from integrated DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2020, 22, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, N.; Kyba, C.C.; Zhang, Q.; de Miguel, A.S.; Román, M.O.; Li, X.; Portnov, B.A.; Molthan, A.L.; Jechow, A.; Miller, S.D.; et al. Remote sensing of night lights: A review and an outlook for the future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.L.; Li, T.; Yue, Q.; Wang, Z. Spatiotemporal variations in energy consumption and their influencing factors in China based on the integration of the DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS nighttime light datasets. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, S.D.; Straka, W.; Mills, S.P.; Elvidge, C.D.; Lee, T.F.; Solbrig, J.; Walther, A.; Heidinger, A.K.; Weiss, S.C. Illuminating the capabilities of the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (NPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) day/night band. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6717–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Lawrence, W.T.; Stutzer, D.C.; Elvidge, C.D. A technique for using composite DMSP/OLS “City Lights” satellite data to map urban area. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.F.; He, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Huang, Q.X.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y. Mapping urban dynamics (1992–2018) in Southeast Asia using consistent nighttime light data from DMSP and VIIRS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.L.; Yang, Y.P. Mapping urban areas with integration of DMSP/OLS nighttime light and MODIS data using machine learning techniques. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12419–12439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Nordhaus, W.D. VIIRS nighttime lights in the estimation of cross-sectional and time-series GDP. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Yang, K. Automated extraction of built-up areas by fusing VIIRS nighttime lights and Landsat-8 data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Román, M.O.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Kalb, V.; Miller, S.D.; Molthan, A.; Schultz, L.; Bell, J.; Stokes, E.C.; Pandey, B.; et al. NASA’s Black Marble nighttime lights product suite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.E.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.W.; Erwin, E.H.; Zhizhin, M. A fifteen year record of global natural gas flaring derived from satellite data. Energies 2019, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.Y.; Wu, Z.F.; Kuang, Y.Q.; Huang, N.S. Correction of DMSP/OLS night-time light images and its application in China. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2015, 17, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, F.C.; Baugh, K.E.; Ghosh, T.; Zhizhin, M.; Elvidge, C.D. DMSP-OLS radiance calibrated nighttime lights time series with intercalibration. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1855–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.L.; Li, C. Potential of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light imagery for modeling the regional economy of China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3057–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.Q.; Hu, Y.J.; Huang, C.; Shi, K.F.; Wu, J.P. Estimating house vacancy rate in metropolitan areas using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2188–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.F.; Huang, Y.X.; Hu, Y.J.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.Q.; Chen, L.J.; Wu, J.P. Evaluating the ability of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data to estimate the gross domestic product and the electric power consumption of China at multiple scales: A comparison with DMSP-OLS data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C. Why VIIRS data are superior to DMSP for mapping nighttime lights. Proc. Asia-Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.Y. The urbanization model and process in Bohai Sea surrounding area in the 1990s by using DMSP/OLS. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2005, 60, 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, L. Application of compound night light index derived from DMSP/OLS data to urbranization analysis in China in the 1990s. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2003, 58, 893–902. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Lang, Q.; Yang, H.; Shi, K.; Ge, W. Identification of polycentric cities in China based on NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhuo, L.; Shi, P.J.; Toshiaki, I. The study on urbanization process in China based on DMSP/OLS data: Development of a light index for urbanization level estimation. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 7, 168–175. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.Q.; Song, W.; Liu, H.X.; Wu, Q.S.; Shi, K.F.; Wu, J.P. A new approach for detecting urban centers and their spatial structure with nighttime light remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6309–6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C.D. Spatial analysis of global urban extent from DMSP-OLS night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sensor | Year | a | b | R2 | Sensor | Year | a | b | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F10 | 1992 | 1.713 | 0.962 | 0.490 | F15 | 2001 | 0.655 | 1.284 | 0.883 |
| F10 | 1993 | 0.834 | 1.321 | 0.818 | F15 | 2002 | 0.901 | 1.132 | 0.780 |
| F10 | 1994 | 0.944 | 1.259 | 0.790 | F15 | 2003 | 1.400 | 1.064 | 0.834 |
| F12 | 1994 | 0.915 | 1.253 | 0.767 | F15 | 2004 | 1.201 | 1.060 | 0.807 |
| F12 | 1995 | 0.894 | 1.226 | 0.787 | F15 | 2005 | 1.093 | 1.107 | 0.898 |
| F12 | 1996 | 1.139 | 1.148 | 0.782 | F15 | 2006 | 1.453 | 0.978 | 0.717 |
| F12 | 1997 | 0.895 | 1.224 | 0.750 | F15 | 2007 | 2.149 | 0.865 | 0.575 |
| F12 | 1998 | 0.780 | 1.223 | 0.804 | F16 | 2004 | 0.895 | 1.085 | 0.737 |
| F12 | 1999 | 1.002 | 1.174 | 0.812 | F16 | 2005 | 1.502 | 0.968 | 0.668 |
| F14 | 1997 | 1.648 | 1.117 | 0.738 | F16 | 2006 | 1.171 | 1.039 | 0.714 |
| F14 | 1998 | 1.167 | 1.198 | 0.826 | F16 | 2007 | 1.129 | 1.034 | 0.731 |
| F14 | 1999 | 1.455 | 1.148 | 0.781 | F16 | 2008 | 0.892 | 1.078 | 0.753 |
| F14 | 2000 | 1.654 | 0.985 | 0.644 | F16 | 2009 | 0.545 | 1.167 | 0.739 |
| F14 | 2001 | 1.520 | 1.007 | 0.687 | F18 | 2010 | 0.475 | 1.130 | 0.538 |
| F14 | 2002 | 1.516 | 0.990 | 0.721 | F18 | 2011 | 0.542 | 1.153 | 0.721 |
| F14 | 2003 | 1.616 | 0.966 | 0.717 | F18 | 2012 | 0.722 | 1.033 | 0.547 |
| F15 | 2000 | 0.837 | 1.190 | 0.812 | F18 | 2013 | 0.503 | 1.090 | 0.531 |
| Region | Light Area after Extraction [km2] | Relative Error [%] | Region | Light Area after Extraction [km2] | Relative Error [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROK | 1474 | 0.95 | Shandong | 2328 | 0.43 |
| DPRK | 518 | −13.13 | Henan | 1361 | 0.22 |
| Taiwan | 538 | 9.11 | Hubei | 853 | −1.41 |
| Hong Kong | 277 | 53.43 | Hunan | 907 | −0.99 |
| Macao | 2 | 0.00 | Guangdong | 4015 | −0.67 |
| Beijing | 1486 | 1.28 | Guangxi | 666 | −0.30 |
| Tianjin | 594 | −0.34 | Hainan | 383 | 1.04 |
| Hebei | 2667 | 2.06 | Chongqing | 324 | 0.93 |
| Shanxi | 833 | 2.16 | Sichuan | 1176 | 0.51 |
| Inner Mongolia | 664 | −0.45 | Guizhou | 155 | 3.87 |
| Liaoning | 2258 | −1.86 | Yunnan | 580 | 1.21 |
| Jilin | 1676 | −3.28 | Tibet | 76 | 7.89 |
| Heilongjiang | 3331 | −1.08 | Shaanxi | 372 | 0.27 |
| Shanghai | 785 | −3.57 | Gansu | 285 | 0.35 |
| Jiangsu | 1472 | −1.49 | Qinghai | 176 | 0.57 |
| Zhejiang | 1365 | 0.00 | Ningxia | 42 | 4.76 |
| Anhui | 758 | 1.85 | Xinjiang | 491 | 1.63 |
| Fujian | 1787 | 3.75 | Jiangxi | 657 | 1.22 |
| Year | City | Built-Up Area | Administrative Area | Minimum | Maximum | Average | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | Pyongyang | 231 | 1160.67 | 12 | 80 | 30.61 | 7071.00 |
| Chungjin | 61 | 1512.68 | 12 | 66 | 25.57 | 1560.00 | |
| Hamhung | 21 | 545.77 | 12 | 17 | 13.67 | 287.00 | |
| 2019 | Pyongyang | 252 | 1160.67 | 12 | 158 | 40.75 | 10,269.00 |
| Chungjin | 48 | 1512.68 | 12 | 101 | 33.90 | 1627.00 | |
| Hamhung | 32 | 545.77 | 12 | 18 | 14.81 | 474.00 |
| Province | County | Built-Up Area | Minimum | Maximum | Average | Sum | Light per Capita |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyongyang | Pyongyang | 252 | 12 | 158 | 40.75 | 10,269.00 | 33.55 |
| Liaoning | Dalian Jinzhou | 251 | 43 | 190 | 91.83 | 23,050.00 | 259.57 |
| Gyeonggi | Pyeongtaek | 256 | 86 | 186 | 129.00 | 33,024.00 | 757.43 |
| North Hamgyeong | Chungjin | 48 | 12 | 101 | 33.90 | 1627.00 | 25.42 |
| Liaoning | Chaoyang Longcheng | 47 | 40 | 146 | 64.30 | 3022.00 | 136.13 |
| Gyeonggi | Ansan | 49 | 139 | 194 | 167.53 | 8209.00 | 114.01 |
| South Hamgyeong | Hamhung | 32 | 12 | 18 | 14.81 | 474.00 | 8.57 |
| Jilin | Liaoyuan Xi’an | 32 | 41 | 131 | 73.13 | 2340.00 | 171.68 |
| Chungcheongnam | Gongju | 31 | 89 | 162 | 118.61 | 3677.00 | 260.78 |
| City | 1990 (GHSL) | 1992 | 2000 (GHSL) | 2015 (GHSL) | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyongyang | 248 | 231 | 263 | 274 | 252 |
| Chungjin | 64 | 61 | 69 | 57 | 48 |
| Hamhung | 26 | 21 | 31 | 34 | 32 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, C. Study on Urban Spatial Pattern Based on DMSP/OLS and NPP/VIIRS in Democratic People’s Republic of Korea. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4879. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234879
Jiang L, Liu Y, Wu S, Yang C. Study on Urban Spatial Pattern Based on DMSP/OLS and NPP/VIIRS in Democratic People’s Republic of Korea. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(23):4879. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234879
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Luguang, Ye Liu, Si Wu, and Cheng Yang. 2021. "Study on Urban Spatial Pattern Based on DMSP/OLS and NPP/VIIRS in Democratic People’s Republic of Korea" Remote Sensing 13, no. 23: 4879. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234879
APA StyleJiang, L., Liu, Y., Wu, S., & Yang, C. (2021). Study on Urban Spatial Pattern Based on DMSP/OLS and NPP/VIIRS in Democratic People’s Republic of Korea. Remote Sensing, 13(23), 4879. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234879