Remote Sensing of Lake Water Clarity: Performance and Transferability of Both Historical Algorithms and Machine Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
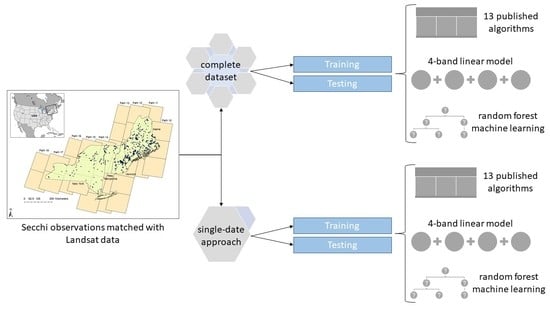
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Observations of Secchi Depth
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Implementation of Algorithms
| Name | Source | Predicted Variable (m) | Formula | Samples | Images | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allee and Johnson | [34] | Secchi Depth | Red − mean (Red) | 30 | 10 | 0.74 |
| Baban | [94] | Secchi Depth | Blue | 14 | 1 | 0.68 |
| Chipman et al. | [95] | ln (Secchi Depth) | Blue/Red | 15,615 | 17 | 0.85 |
| Dekker and Peters 1 | [26,96] | ln (Secchi Depth) | ln (Red) | 15 | 1 | 0.86 |
| Dekker and Peters 2 | [26,97] | Secchi Depth | Red | 15 | 1 | 0.81 |
| Dominguez Gomez et al. | [92] | Secchi Depth | (Green)x | 16 | 5 | 0.9 |
| Giardino et al. | [35] | Secchi Depth | Blue/Green | 4 | 1 | 0.85 |
| Kloiber et al. | [30,31,40,98,99] | ln (Secchi Depth) | Blue/Red + Blue | 374 | 13 | 0.93 |
| Lathrop and Lillesand | [38,56] | ln (Secchi Depth) | Green | 9 | 1 | 0.98 |
| Lavery et al. | [100] | Secchi Depth | Red + Blue/Red | 18–25 | 4 | 0.81 |
| Mancino et al. | [101] | Secchi Depth | Red/Green + Blue/Green + Blue | 60 | 1 | 0.82 |
| Wu et al. | [41,102] | ln (Secchi Depth) | Blue + Red | 25 | 5 | 0.83 |
| Yip et al. | [14] | Secchi Depth | Infrared + Green + Blue | 120 | 136 | 0.6 |
2.5. Algorithm Assessment
3. Results
| Training Data | Test Data | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model Name | MAE (m) | RMSE (m) | Pseudo-R2 | MAE (m) | RMSE (m) | Pseudo-R2 | Bias (m) |
| Allee and Johnson | 1.79 | 2.26 | 0.05 | 1.79 | 2.31 | −0.16 | 0.85 |
| Baban | 1.83 | 2.31 | 0.01 | 1.80 | 2.32 | −0.18 | 0.9 |
| Chipman et al. | 1.82 | 3.83 | 0.09 | 2.04 | 3.73 | −0.33 | 1.28 |
| Dekker and Peters | 1.82 | 2.32 | 0.08 | 1.99 | 2.56 | −0.33 | 1.35 |
| Dekker and Peters 2 | 1.80 | 2.26 | 0.05 | 1.79 | 2.31 | −0.16 | 0.85 |
| Dominguez Gomez et al. | 1.81 | 2.27 | 0.04 | 1.79 | 2.31 | −0.17 | 0.86 |
| Giardino et al. | 1.72 | 2.16 | 0.13 | 1.75 | 2.25 | −0.11 | 0.75 |
| Kloiber et al. | 1.82 | 3.60 | 0.10 | 2.04 | 3.58 | −0.34 | 1.27 |
| Lathrop and Lillesand | 1.82 | 2.32 | 0.09 | 1.98 | 2.54 | −0.31 | 1.32 |
| Lavery et al. | 1.75 | 2.21 | 0.09 | 1.77 | 2.30 | −0.16 | 0.83 |
| Mancino et al. | 1.71 | 2.14 | 0.15 | 1.75 | 2.25 | −0.11 | 0.74 |
| Wu et al. | 1.75 | 2.24 | 0.16 | 1.92 | 2.48 | −0.27 | 1.25 |
| Yip et al. | 1.64 | 2.07 | 0.20 | 1.67 | 2.17 | −0.03 | 0.65 |
| 4-Band | 1.63 | 2.06 | 0.21 | 1.67 | 2.17 | −0.04 | 0.65 |
| Random Forest | 1.37 | 1.81 | 0.39 | 1.60 | 2.08 | 0.05 | 0.61 |
4. Discussion
Algorithm Comparison
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doherty, E.; Murphy, G.; Hynes, S.; Buckley, C. Valuing Ecosystem Services across Water Bodies: Results from a Discrete Choice Experiment. Ecosyst. Serv. 2014, 7, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, H.; Hamilton, D.P.; Doole, G.J. Evaluating Services and Damage Costs of Degradation of a Major Lake Ecosystem. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 22, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, K.C.; Winslow, L.A.; Read, J.S.; Hansen, G.J.A. Climate-Induced Warming of Lakes Can Be Either Amplified or Suppressed by Trends in Water Clarity. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2016, 1, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, K.M.J.; Poor, P.J.; Taylor, L.O. Estimating the Demand for Protecting Freshwater Lakes from Eutrophication. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1999, 81, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, J.P.; Halstead, J.M.; Boyle, K.M.J.; Huang, J.-C. An Hedonic Analysis of the Effects of Lake Water Clarity on New Hampshire Lakefront Properties. Agric. Resour. Econ. Rev. 2002, 31, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poor, P.J.; Pessagno, K.L.; Paul, R.W. Exploring the Hedonic Value of Ambient Water Quality: A Local Watershed-Based Study. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 60, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, P.J.; Milon, J.W.; Scrogin, D.O. The Spatial Extent of Water Quality Benefits in Urban Housing Markets. Land Econ. 2011, 87, 628–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Available online: https://www.millenniumassessment.org/en/index.html (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Bruhn, L.C.; Soranno, P.A. Long Term (1974–2001) Volunteer Monitoring of Water Clarity Trends in Michigan Lakes and Their Relation to Ecoregion and Land Use/Cover. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2005, 21, 10–23. [Google Scholar]
- Gunn, J.M.; Snucins, E.; Yan, N.D.; Arts, M.T. Use of Water Clarity to Monitor the Effects of Climate Change and Other Stressors on Oligotrophic Lakes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2001, 67, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, E.K.; Patil, V.P.; Oliver, S.K.; Hetherington, A.L.; Brentrup, J.A.; Zwart, J.A.; Winters, K.M.; Corman, J.R.; Nodine, E.R.; Woolway, R.I.; et al. The Importance of Lake-Specific Characteristics for Water Quality across the Continental United States. Ecol. Appl. 2015, 25, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soranno, P.A.; Bacon, L.C.; Beauchene, M.; Bednar, K.E.; Bissell, E.G.; Boudreau, C.K.; Boyer, M.G.; Bremigan, M.T.; Carpenter, S.R.; Carr, J.W.; et al. LAGOS-NE: A Multi-Scaled Geospatial and Temporal Database of Lake Ecological Context and Water Quality for Thousands of US Lakes. GigaScience 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stephens, D.L.B.; Carlson, R.E.; Horsburgh, C.A.; Hoyer, M.V.; Bachmann, R.W.; Canfield, D.E., Jr. Regional Distribution of Secchi Disk Transparency in Waters of the United States. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2015, 31, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, H.D.; Johansson, J.; Hudson, J.J. A 29-Year Assessment of the Water Clarity and Chlorophyll-a Concentration of a Large Reservoir: Investigating Spatial and Temporal Changes Using Landsat Imagery. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, E.K.; Carr, L.; Cicco, L.D.; Dugan, H.A.; Hanson, P.C.; Hart, J.A.; Kreft, J.; Read, J.S.; Winslow, L.A. Water Quality Data for National-Scale Aquatic Research: The Water Quality Portal. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lottig, N.R.; Wagner, T.; Norton Henry, E.; Spence Cheruvelil, K.; Webster, K.E.; Downing, J.A.; Stow, C.A.; Heffernan, J.; Soranno, P.; Angilletta, M.; et al. Long-Term Citizen-Collected Data Reveal Geographical Patterns and Temporal Trends in Lake Water Clarity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preisendorfer Secchi Disk Science: Visual Optics of Natural Waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1986, 31, 909–926. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvato, L.; Coordinator, S.D.-I.P. The 2015 Secchi Dip-in Report. 22. Available online: https://z0ku333mvy924cayk1kta4r1-wpengine.netdna-ssl.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/Final-2015-Secchi-Dip-In-Report.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Williamson, C.E.; Neale, P.J. Ultraviolet Light. In Encyclopedia of Inland Waters; Likens, G.E., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 705–714. ISBN 978-0-12-370626-3. [Google Scholar]
- Brezonik, P.; Menken, K.D.; Bauer, M. Landsat-Based Remote Sensing of Lake Water Quality Characteristics, Including Chlorophyll and Colored Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM). Lake Reserv. Manag. 2005, 21, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambou, V.W.; Taylor, W.D.; Hern, S.C.; Williams, L.R. Comparisons of Trophic State Measurements. Water Res. 1983, 17, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, O.T. The Effect of Non-Algal Turbidity on the Relationship of Secchi Depth to Chlorophyll a. Hydrobiologia 1986, 140, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, U.; Adrian, R.; De Senerpont Domis, L.; Elser, J.J.; Gaedke, U.; Ibelings, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Lürling, M.; Molinero, J.C.; Mooij, W.M.; et al. Beyond the Plankton Ecology Group (PEG) Model: Mechanisms Driving Plankton Succession. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathrop, R.G. Landsat Thematic Mapper Monitoring of Turbid Inland Water Quality. Photogramm. Eng. 1992, 58, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.; Skaggs, R.; Warwick, R. Reconnaissance Analysis of Lake Condition In east-Central Minnesota. Available online: https://conservancy.umn.edu/bitstream/handle/11299/205799/L1036.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Dekker, A.G.; Peters, S.W.M. The Use of the Thematic Mapper for the Analysis of Eutrophic Lakes: A Case Study in the Netherlands. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillesand, T.M. Use of Landsat Data to Predict the Trophic State of Minnesota Lakes. Photogramm. Eng. 1983, 49, 219–229. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, J.C.; Cooper, C.M.; Schiebe, F.R. The Relationship of MSS and TM Digital Data with Suspended Sediments, Chlorophyll, and Temperature in Moon Lake, Mississippi. Remote. Sens. Environ. 1990, 33, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.M.; Forsythe, R.D.; Vaughan, G.E.; Olmsted, L.L. Assessing Water Quality in Catawba River Reservoirs Using Landsat Thematic Mapper Satellite Data. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1998, 14, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloiber, S.M.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Application of Landsat Imagery to Regional-Scale Assessments of Lake Clarity. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4330–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloiber, S.M.; Brezonik, P.L.; Olmanson, L.G.; Bauer, M.E. A Procedure for Regional Lake Water Clarity Assessment Using Landsat Multispectral Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathrop, R.G.; Lillesand, T.M.; Yandell, B. Testing the Utility of Simple Multi-Date Thematic Mapper Calibration Algorithms for Monitoring Turbid Inland Waters. Remote Sens. 1991, 12, 2045–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukata, R.P.; Jerome, J.H.; Kondratyev, K.Y.; Pozdnyakov, D.V. Optical Properties and Remote Sensing of Inland and Coastal Waters, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; ISBN 978-0-203-74495-6. [Google Scholar]
- Allee, R.J.; Johnson, J.E. Use of Satellite Imagery to Estimate Surface Chlorophyll a and Secchi Disc Depth of Bull Shoals Reservoir, Arkansas, USA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Pepe, M.; Brivio, P.A.; Ghezzi, P.; Zilioli, E. Detecting Chlorophyll, Secchi Disk Depth and Surface Temperature in a Sub-Alpine Lake Using Landsat Imagery. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 268, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, V.Y.; Carmona, F.; Rivas, R.; Lagomarsino, L.; Diovisalvi, N.; Zagarese, H.E. Development of an Empirical Model for Chlorophyll-a and Secchi Disk Depth Estimation for a Pampean Shallow Lake (Argentina). Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2018, 21, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.C.; Schiebe, F.R. Monitoring Suspended Sediments with Remote Sensing Techniques. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. Hydrol. Appl. Space Technol. 1986, 160, 233–243. [Google Scholar]
- Harrington, J.A.; Schiebe, F.R.; Nix, J.F. Remote Sensing of Lake Chicot, Arkansas: Monitoring Suspended Sediments, Turbidity, and Secchi Depth with Landsat MSS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 39, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiebe, F.R.; Ritchie, J.C. Suspended Sediment Monitored by Satellite. In Proceedings of the Fourth Federal Interagency Sedimentation Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24–27 March 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Bauer, M.E.; Brezonik, P.L. A 20-Year Landsat Water Clarity Census of Minnesota’s 10,000 Lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4086–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, I.M.; Loftin, C.S.; Sader, S.A. Combining Lake and Watershed Characteristics with Landsat TM Data for Remote Estimation of Regional Lake Clarity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, E.S.; Cardille, J.A.; Koll-Egyed, T.; Fortin, M.-J. Landsat 8 Lake Water Clarity Empirical Algorithms: Large-Scale Calibration and Validation Using Government and Citizen Science Data from across Canada. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michie, D.; Spiegelhalter, D.J.; Taylor, C. Others Machine Learning. Neural Stat. Classif. 1994, 13, 1–298. [Google Scholar]
- Pahlevan, N.; Smith, B.; Schalles, J.; Binding, C.; Cao, Z.; Ma, R.; Alikas, K.; Kangro, K.; Gurlin, D.; Hà, N.; et al. Seamless Retrievals of Chlorophyll-a from Sentinel-2 (MSI) and Sentinel-3 (OLCI) in Inland and Coastal Waters: A Machine-Learning Approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Sarkar, S.; Franz, B.A.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; He, J. Sentinel-2 MultiSpectral Instrument (MSI) Data Processing for Aquatic Science Applications: Demonstrations and Validations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najah Ahmed, A.; Binti Othman, F.; Abdulmohsin Afan, H.; Khaleel Ibrahim, R.; Ming Fai, C.; Shabbir Hossain, M.; Ehteram, M.; Elshafie, A. Machine Learning Methods for Better Water Quality Prediction. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; He, Z.; Su, J.; Xi, B.; Zhu, C. Using Artificial Neural Network Models for Eutrophication Prediction. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuhn, C.; de Matos Valerio, A.; Ward, N.; Loken, L.; Sawakuchi, H.O.; Kampel, M.; Richey, J.; Stadler, P.; Crawford, J.; Striegl, R.; et al. Performance of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 Surface Reflectance Products for River Remote Sensing Retrievals of Chlorophyll-a and Turbidity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gege, P. WASI-2D: A Software Tool for Regionally Optimized Analysis of Imaging Spectrometer Data from Deep and Shallow Waters. Comput. Geosci. 2014, 62, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dekker, A.G.; Malthus, T.J.; Seyhan, E. Quantitative Modeling of Inland Water Quality for High-Resolution MSS Systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1991, 29, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R.A. Deriving Inherent Optical Properties from Water Color: A Multiband Quasi-Analytical Algorithm for Optically Deep Waters. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 5755–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Qi, L.; Yan, J.; Lin, G. A Semi-Analytical Scheme to Estimate Secchi-Disk Depth from Landsat-8 Measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.; Alcântara, E.; Watanabe, F.; Imai, N. Retrieval of Secchi Disk Depth from a Reservoir Using a Semi-Analytical Scheme. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kvålseth, T.O. Cautionary Note about R 2. Am. Stat. 1985, 39, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathrop, R.G.; Lillesand, T.M. Use of Thematic Mapper Data to Assess Water Quality in Green Bay and Central Lake Michigan. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1986, 52, 671–680. [Google Scholar]
- Peckham, S.D.; Lillesand, T.M. Detection of Spatial and Temporal Trends in Wisconsin Lake Water Clarity Using Landsat-Derived Estimates of Secchi Depth. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2006, 22, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, S.; Soranno, P.; Cheruvelil, K.S.; Batzli, S.A. Regional Assessment of Lake Water Clarity Using Satellite Remote Sensing. J. Limnol. 2003, 62, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Needelman, M.S.; Kealy, M.J. Recreational Swimming Benefits Of New Hampshire Lake Water Quality Policies: An Application of a Repeated Discrete Choice Model. Agric. Resour. Econ. Rev. 1995, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Homer, C.; Dewitz, J.; Yang, L.; Jin, S.; Danielson, P.; Xian, G.; Coulston, J.; Herold, N.; Wickham, J.; Megown, K. Completion of the 2011 National Land Cover Database for the Conterminous United States—Representing a Decade of Land Cover Change Information. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2015, 81, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services Volunteer Lake Assessment Program. Available online: https://www.des.nh.gov/organization/divisions/water/wmb/vlap/ (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- National Water Quality Monitoring Council. Available online: https://www.waterqualitydata.us/ (accessed on 24 September 2020).
- Maine Department of Environmental Protection. Available online: https://www.maine.gov/dep/ (accessed on 24 September 2020).
- Lake Champlain Basin Program. Available online: https://www.lcbp.org/water-environment/ (accessed on 24 September 2020).
- NYS Deptartment of Environmental Conservation. Available online: https://www.dec.ny.gov/25.html (accessed on 24 September 2020).
- Vermont Department of Environmental Conservation. Available online: https://dec.vermont.gov/ (accessed on 24 September 2020).
- Ross, M.R.V.; Topp, S.N.; Appling, A.P.; Yang, X.; Kuhn, C.; Butman, D.; Simard, M.; Pavelsky, T.M. AquaSat: A Data Set to Enable Remote Sensing of Water Quality for Inland Waters. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 10012–10025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Claverie, M.; Franch, B. Preliminary Analysis of the Performance of the Landsat 8/OLI Land Surface Reflectance Product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masek, J.G.; Vermote, E.F.; Saleous, N.E.; Wolfe, R.; Hall, F.G.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Gao, F.; Kutler, J.; Lim, T.-K. A Landsat Surface Reflectance Dataset for North America, 1990–2000. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Geological Survey. Landsat 4-7 Collection 1 (C1) Surface Reflectance (LEDAPS) Product Guide; EROS Data Center: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2020; p. 39.
- US Geological Survey. Landsat 8 Collection 1 (C1) Land Surface Reflectance Code (LaSRC) Product Guide; EROS Data Center: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2020; p. 38.
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Turbid Wakes Associated with Offshore Wind Turbines Observed with Landsat 8. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinmetz, F.; Deschamps, P.-Y.; Ramon, D. Atmospheric Correction in Presence of Sun Glint: Application to MERIS. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 9783–9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doerffer, R.; Schiller, H. The MERIS Case 2 Water Algorithm. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Weathers, K.C.; Norouzi, H.; Steele, B. Assessing the Effectiveness of Landsat 8 Chlorophyll a Retrieval Algorithms for Regional Freshwater Monitoring. Ecol. Appl. 2018, 28, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preliminary Assessment of the Value of Landsat 7 ETM+ Data Following Scan Line Corrector Malfunction 2003. Available online: https://prd-wret.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/assets/palladium/production/s3fs-public/atoms/files/SLC_off_Scientific_Usability.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Pulliainen, J.T.; Koponen, S.S.; Hallikainen, M.T. Water Quality Retrievals from Combined Landsat TM Data and ERS-2 SAR Data in the Gulf of Finland. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random Forest in Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications and Future Directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drǎguţ, L. Comparing Supervised and Unsupervised Multiresolution Segmentation Approaches for Extracting Buildings from Very High Resolution Imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 96, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frazier, R.J.; Coops, N.C.; Wulder, M.A.; Kennedy, R. Characterization of Aboveground Biomass in an Unmanaged Boreal Forest Using Landsat Temporal Segmentation Metrics. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlson, M.; Ostwald, M.; Reese, H.; Sanou, J.; Tankoano, B.; Mattsson, E. Mapping Tree Canopy Cover and Aboveground Biomass in Sudano-Sahelian Woodlands Using Landsat 8 and Random Forest. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10017–10041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsutsumida, N.; Comber, A.J. Measures of Spatio-Temporal Accuracy for Time Series Land Cover Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression with Random Forest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hafeez, S.; Wong, M.; Ho, H.; Nazeer, M.; Nichol, J.; Abbas, S.; Tang, D.; Lee, K.; Pun, L. Comparison of Machine Learning Algorithms for Retrieval of Water Quality Indicators in Case-II Waters: A Case Study of Hong Kong. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peterson, K.T.; Sagan, V.; Sidike, P.; Hasenmueller, E.A.; Sloan, J.J.; Knouft, J.H. Machine Learning-Based Ensemble Prediction of Water-Quality Variables Using Feature-Level and Decision-Level Fusion with Proximal Remote Sensing. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2019, 85, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jia, M.; Chen, N.; Wang, W. Long-Term Surface Water Dynamics Analysis Based on Landsat Imagery and the Google Earth Engine Platform: A Case Study in the Middle Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.; Novitski, L.N.; Qi, J.; Stevenson, R.J. Landsat TM/ETM+ and Machine-Learning Algorithms for Limnological Studies and Algal Bloom Management of Inland Lakes. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, T.M.; Perez, P.S.; Baranauskas, J.A. How Many Trees in a Random Forest? In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 7376, pp. 154–168. [Google Scholar]
- Chander, G.; Markham, B.L.; Helder, D.L. Summary of Current Radiometric Calibration Coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+, and EO-1 ALI Sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez Gómez, J.A.; Chuvieco Salinero, E.; Sastre Merlín, A. Monitoring Transparency in Inland Water Bodies Using Multispectral Images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 1567–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.M.; Watts, D.G. Nonlinear Regression Analysis and Its Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1988; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Baban, S.M.J. Detecting Water Quality Parameters in the Norfolk Broads, U.K., Using Landsat Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 1247–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipman, J.W.; Lillesand, T.M.; Schmaltz, J.E.; Leale, J.E.; Nordheim, M.J. Mapping Lake Water Clarity with Landsat Images in Wisconsin, U.S.A. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odermatt, D.; Gitelson, A.; Brando, V.E.; Schaepman, M. Review of Constituent Retrieval in Optically Deep and Complex Waters from Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duane Nellis, M.; Harrington, J.A.; Wu, J. Remote Sensing of Temporal and Spatial Variations in Pool Size, Suspended Sediment, Turbidity, and Secchi Depth in Tuttle Creek Reservoir, Kansas: 1993. Geomorphology 1998, 21, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Evaluation of Medium to Low Resolution Satellite Imagery for Regional Lake Water Quality Assessments. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hellweger, F.L.; Schlosser, P.; Lall, U.; Weissel, J.K. Use of Satellite Imagery for Water Quality Studies in New York Harbor. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 61, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, P.; Pattiaratchi, C.; Wyllie, A.; Hick, P. Water Quality Monitoring in Estuarine Waters Using the Landsat Thematic Mapper. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 46, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, G.; Nolè, A.; Urbano, V.; Amato, M.; Ferrara, A. Assessing Water Quality by Remote Sensing in Small Lakes: The Case Study of Monticchio Lakes in Southern Italy. IForest Biogeosci. For. 2009, 2, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Luo, D. Application of MODIS Satellite Data in Monitoring Water Quality Parameters of Chaohu Lake in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 148, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River Flow Forecasting through Conceptual Models Part I—A Discussion of Principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palace, M.; Herrick, C.; DelGreco, J.; Finnell, D.; Garnello, A.J.; McCalley, C.; McArthur, K.; Sullivan, F.; Varner, R.K. Determining Subarctic Peatland Vegetation Using an Unmanned Aerial System (UAS). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paliwal, M.; Kumar, U.A. Neural Networks and Statistical Techniques: A Review of Applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, J.G.; Uhler, R.S. The Demand for Automobiles. Can. J. Econ. 1970, 3, 386–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagelkerke, N. A Note on a General Definition of the Coefficient of Determination. Biometrika 1991, 78, 691–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Schielzeth, H. A General and Simple Method for Obtaining R2 from Generalized Linear Mixed-Effects Models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.S.; Dowell, M.D.; Bradt, S.; Verdu, A.R. An Optical Water Type Framework for Selecting and Blending Retrievals from Bio-Optical Algorithms in Lakes and Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, S.K. Sampling, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cornell, J.A. Factors That Influence the Value of the Coefficient of Determination in Simple Linear and Nonlinear Regression Models. Phytopathology 1987, 77, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, M.W. A Current Review of Empirical Procedures of Remote Sensing in Inland and Near-Coastal Transitional Waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 6855–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, I. Calculating the Gini Coefficient of Inequality. Northwest. Inst. BioHealth Inform. 2002. Available online: https://www.nibhi.org.uk/Training/Forms/AllItems.aspx (accessed on 6 April 2021).
- Neil, C.; Spyrakos, E.; Hunter, P.D.; Tyler, A.N. A Global Approach for Chlorophyll-a Retrieval across Optically Complex Inland Waters Based on Optical Water Types. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gons, H.J.; Auer, M.; Effler, S.W. MERIS Satellite Chlorophyll Mapping of Oligotrophic and Eutrophic Waters in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 4098–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomets, T.; Uudeberg, K.; Jakovels, D.; Zagars, M.; Reinart, A.; Brauns, A.; Kutser, T. Comparison of Lake Optical Water Types Derived from Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-3. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soomets, T.; Uudeberg, K.; Jakovels, D.; Brauns, A.; Zagars, M.; Kutser, T. Validation and Comparison of Water Quality Products in Baltic Lakes Using Sentinel-2 MSI and Sentinel-3 OLCI Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legleiter, C.J.; Roberts, D.A.; Lawrence, R.L. Spectrally Based Remote Sensing of River Bathymetry. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1039–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroumand-Jadidi, M.; Vitti, A.; Lyzenga, D.R. Multiple Optimal Depth Predictors Analysis (MODPA) for River Bathymetry: Findings from Spectroradiometry, Simulations, and Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 218, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroumand-Jadidi, M.; Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L. Novel Spectra-Derived Features for Empirical Retrieval of Water Quality Parameters: Demonstrations for OLI, MSI, and OLCI Sensors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 10285–10300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagan, V.; Peterson, K.T.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Sidike, P.; Sloan, J.; Greeling, B.A.; Maalouf, S.; Adams, C. Monitoring Inland Water Quality Using Remote Sensing: Potential and Limitations of Spectral Indices, Bio-Optical Simulations, Machine Learning, and Cloud Computing. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 205, 103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schowengerdt, R.A. Techniques for Image Processing and Classifications in Remote Sensing; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-323-13855-0. [Google Scholar]
- Gilabert, M.A.; Conese, C.; Maselli, F. An Atmospheric Correction Method for the Automatic Retrieval of Surface Reflectances from TM Images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 2065–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, P.S. An Improved Dark-Object Subtraction Technique for Atmospheric Scattering Correction of Multispectral Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 24, 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rubin, H.J.; Lutz, D.A.; Steele, B.G.; Cottingham, K.L.; Weathers, K.C.; Ducey, M.J.; Palace, M.; Johnson, K.M.; Chipman, J.W. Remote Sensing of Lake Water Clarity: Performance and Transferability of Both Historical Algorithms and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081434
Rubin HJ, Lutz DA, Steele BG, Cottingham KL, Weathers KC, Ducey MJ, Palace M, Johnson KM, Chipman JW. Remote Sensing of Lake Water Clarity: Performance and Transferability of Both Historical Algorithms and Machine Learning. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(8):1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081434
Chicago/Turabian StyleRubin, Hannah J., David A. Lutz, Bethel G. Steele, Kathryn L. Cottingham, Kathleen C. Weathers, Mark J. Ducey, Michael Palace, Kenneth M. Johnson, and Jonathan W. Chipman. 2021. "Remote Sensing of Lake Water Clarity: Performance and Transferability of Both Historical Algorithms and Machine Learning" Remote Sensing 13, no. 8: 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081434
APA StyleRubin, H. J., Lutz, D. A., Steele, B. G., Cottingham, K. L., Weathers, K. C., Ducey, M. J., Palace, M., Johnson, K. M., & Chipman, J. W. (2021). Remote Sensing of Lake Water Clarity: Performance and Transferability of Both Historical Algorithms and Machine Learning. Remote Sensing, 13(8), 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081434