Performance Analysis of BDS–5G Combined Precise Point Positioning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
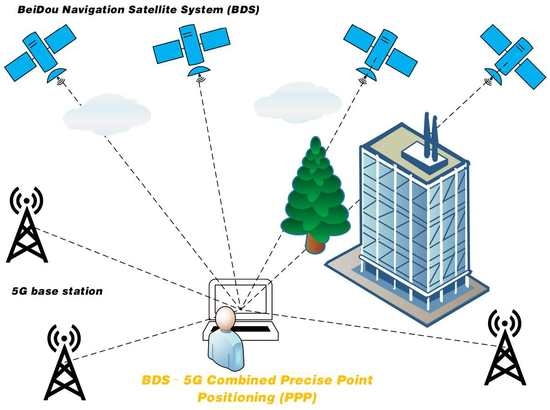
2.1. Observation Model for BDS–5G PPP
2.1.1. Observation Model for BDS PPP
2.1.2. Observation Model for 5G Millimeter Wave
2.1.3. Observation Model for BDS–5G PPP
2.2. Weight Matrix
2.3. Data Processing Strategy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Environment
3.1.1. BDS Test Environment
3.1.2. 5G Environment
3.2. Static PPP
3.2.1. Quantity
3.2.2. Geometric Configuration
3.3. Dynamic PPP
3.3.1. Quantity
3.3.2. Geometric Configuration
4. Conclusions
- As the quantity of 5G base stations participating in the positioning solution increases, the convergence time and the STD of the errors after convergence both tend to decrease. The beneficial effect brought about by the participation of 5G base stations in positioning is also evident with a smaller number of visible satellites. In particular, when a single BDS system cannot converge within 1 h or when there is a large post-convergence error in some cases, the involvement of 5G base stations can significantly speed up convergence and achieve better post-convergence positioning accuracy.
- In experiments with different geometrical configurations, there is a significant advantage for speed of convergence and STD of the errors after convergence of the various configurations in their dominant directions compared with the relatively balanced configurations. The advantage is also evident when the number of satellites is low. The dominant geometric configuration in each direction is suitable where rapid convergence is required in a particular target direction.
- The research on BDS and 5G combined precise point positioning technology is conducive to the rapid realization of indoor and outdoor seamless positioning and is of great significance to the development of the PNT community.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, S.; Su, K. PPP models and performances from single- to quad-frequency BDS observations. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, F. A method of improving ambiguity fixing rate for post-processing kinematic GNSS data. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.T. Analysis and modeling GPS NLOS effect in highly urbanized area. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; He, D.; Pei, L. BDS B1I multipath channel statistical model comparison between static and dynamic scenes in dense urban canyon environment. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, J.; Rizos, C.; El-Mowafy, A. Vulnerabilities and integrity of precise point positioning for intelligent transport systems: Overview and analysis. Satell. Navig. 2021, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, H. A Survey of Positioning Technology for 5G. J. Beijing Univ. Posts Telecommun. 2018, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, W.; Zhen, J. Fusion positioning based on WiFi and Bluetooth for the area around the corner of stairs. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 18th International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Smart Systems (MASS), Denver, CO, USA, 4–7 October 2021; pp. 162–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, X.; Guan, S.; Wang, Z. Indoor Positioning Method Based on WiFi/Bluetooth and PDR Fusion Positioning. In Proceedings of the 2021 13th International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI), Wanzhou, China, 14–16 May 2021; pp. 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanian, V.; Lowe, M. RSS-INS integration for cooperative indoor positioning. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Madrid, Spain, 4–7 October 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mamun, M.A.; Rasit Yuce, M. Map-Aided Fusion of IMU PDR and RSSI Fingerprinting for Improved Indoor Positioning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Sensors, Virtual, 31 October–3 November 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmansoori, A.; Garcia, G.E.; Destino, G.; Seco-Granados, G.; Wymeersch, H. Position and Orientation Estimation Through Millimeter-Wave MIMO in 5G Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 1822–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Simulation and Analysis of Device Positioning in 5G Ultra-Dense Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 15th International Wireless Communications; Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Tangier, Morocco, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 1529–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q. A Novel Multipath Mitigation Method for 5G Positioning. In Proceedings of the 2019 15th International Wireless Communications; Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Tangier, Morocco, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 1714–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Tu, R.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, J. Indoor location algorithm of TDOA based on 5G. Gnss World China 2021, 46, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Papp, Z.; Irvine, G.; Smith, R.; Mogyorósi, F.; Revisnyei, P.; Törős, I.; Pašić, A. TDoA based indoor positioning over small cell 5G networks. In Proceedings of the NOMS 2022–2022 IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium, Budapest, Hungary, 25–29 April 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Peral-Rosado, J.A.; Renaudin, O.; Gentner, C.; Raulefs, R.; Dominguez-Tijero, E.; Fernandez-Cabezas, A.; Blazquez-Luengo, F.; Cueto-Felgueroso, G.; Chassaigne, A.; Bartlett, D.; et al. Physical-Layer Abstraction for Hybrid GNSS and 5G Positioning Evaluations. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 90th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Fall), Honolulu, HI, USA, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Peral-Rosado, J.A.; Saloranta, J.; Destino, G.; López-Salcedo, J.A.; Seco-Granados, G. Methodology for Simulating 5G and GNSS High-Accuracy Positioning. Sensors 2018, 18, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jdel Peral-Rosado, A.; Gunnarsson, F.; Dwivedi, S.; Razavi, S.M.; Renaudin, O.; López-Salcedo, J.A.; Seco-Granados, G. Exploitation of 3D City Maps for Hybrid 5G RTT and GNSS Positioning Simulations. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 9205–9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destino, G.; Saloranta, J.; Seco-Granados, G.; Wymeersch, H. Performance Analysis of Hybrid 5G-GNSS Localization. In Proceedings of the 2018 52nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 28–31 October 2018; pp. 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, L.; Ni, Q.; Deng, Z. A GNSS/5G Integrated Positioning Methodology in D2D Communication Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2018, 36, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klus, R.; Talvitie, J.; Valkama, M. Neural Network Fingerprinting and GNSS Data Fusion for Improved Localization in 5G. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Localization and GNSS (ICL-GNSS), Tampere, Finland, 1–3 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Sun, C.; Dempster, A.G.; Zhao, H.; Cheong, J.W.; Feng, W. GNSS-5G Hybrid Positioning Based on Multi-Rate Measurements Fusion and Proactive Measurement Uncertainty Prediction. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 8501415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.X.; Tu, R.; Hong, J.; Zhang, S.X.; Zhang, P.F.; Lu, X.C. Combined positioning algorithm based on BeiDou navigation satellite system and raw 5G observations. Measurement 2022, 190, 110763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Items to Be Processed | Handling Strategy |
|---|---|
| BDS 1 observation signal type | Pseudorange and carrier phase observations: BDS B1, B3 |
| Solving mode | PPP 2-static/dynamic solving |
| Ambiguity | Float solution |
| Elevation angle | 7° |
| Sampling interval | 30 s |
| Orbital and clock difference products | IGS precise products |
| Ionospheric delay | Dual-frequency ionosphere-free combination, eliminating first-order terms and ignoring higher-order terms |
| Tropospheric Delay | The dry delay was corrected using the Saastmoinen model and the wet delay was estimated as a parameter |
| Antenna phase centers | Absolute antenna phase center model |
| Phase winding, solid tide correction, relativistic effects | Model correction |
| BDS receiver clock difference | Parameter estimation |
| Coordinate constraint method | Recursive least squares parameter estimation |
| 5G 3 observations | Eliminating outliers in measured data |
| 5G receiver clock difference | Parameter estimation |
| Number of 5G Base Stations | Scene 1 | Scene 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.8390 | 1.1422 |
| 2 | 0.8124 | 1.0386 |
| 3 | 0.7815 | 1.0216 |
| 4 | 0.7693 | 0.9602 |
| 5 | 0.7443 | 0.9418 |
| Configuration | Station 1 | Station 2 | Station 3 | Station 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | (50, 0, 0) | (20, 0, 0) | (−20, 0, 0) | (−50, 0, 0) |
| Group B | (0, 50, 0) | (0, 20, 0) | (0, −20, 0) | (0, −50, 0) |
| Group C | (0, 0, 50) | (0, 0, 20) | (0, 0, −20) | (0, 0, −50) |
| Group D | (−50, 50, 0) | (50, 50, 0) | (0, −50, 50) | (0, −50, −50) |
| Configuration | Scene 1 | Scene 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | |
| Group A | 0.353657 | 0.404852 | 0.563466 | 0.434132 | 0.438245 | 0.754619 |
| Group B | 0.494312 | 0.317482 | 0.563005 | 0.846956 | 0.339646 | 0.762221 |
| Group C | 0.499012 | 0.409185 | 0.374364 | 0.854587 | 0.451992 | 0.419991 |
| Group D | 0.444281 | 0.353196 | 0.490631 | 0.646825 | 0.376419 | 0.603754 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.; Tu, R.; Hong, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, M.; Lu, X. Performance Analysis of BDS–5G Combined Precise Point Positioning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133006
Li F, Tu R, Hong J, Zhang S, Liu M, Lu X. Performance Analysis of BDS–5G Combined Precise Point Positioning. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(13):3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133006
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Fangxin, Rui Tu, Ju Hong, Shixuan Zhang, Mingyue Liu, and Xiaochun Lu. 2022. "Performance Analysis of BDS–5G Combined Precise Point Positioning" Remote Sensing 14, no. 13: 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133006
APA StyleLi, F., Tu, R., Hong, J., Zhang, S., Liu, M., & Lu, X. (2022). Performance Analysis of BDS–5G Combined Precise Point Positioning. Remote Sensing, 14(13), 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133006