Analysis of Space-Borne GPS Data Quality and Evaluation of Precise Orbit Determination for COSMIC-2 Mission Based on Reduced Dynamic Method
Abstract
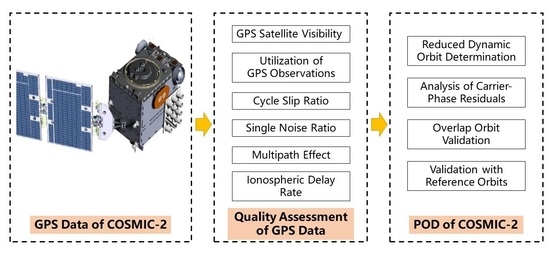
:1. Introduction
2. Quality Assessment of COSMIC-2 GPS Observations
2.1. GPS Satellite Visibility
2.2. Utilization of GPS Observations
2.3. Cycle Slip Ratio
2.4. Single Noise Ratio
2.5. Multipath Effect
2.6. Ionospheric Delay Rate
3. Reduced Dynamic Orbit Determination of COSMIC-2
3.1. Reduced Dynamic Method
3.2. Orbit Determination Strategy for COSMIC-2
3.3. Assessment of Orbit Accuracy
3.3.1. Analysis of Carrier-Phase Residuals
3.3.2. Overlap Orbit Validation
3.3.3. Validation with Reference Orbits
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiss, J.P.; Hunt, D.; Schreiner, W.; Vanhove, T.; Arnold, D.; Jaeggi, A. COSMIC-2 Precise Orbit Determination Results. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 3–8 May 2020; p. 20170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.Y. Quality Evaluation of COSMIC-2 Occultation Atmospheric Profile Inversion and Research on Boundary Layer Height Inversion Method. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Engineering, Nanjing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.; Fong, C.J.; Wenkel, M.J.; Wilczynski, P.; Yen, N.; Chang, G.S. COSMIC-2/FORMOSAT-7: The future of global weather monitoring and prediction. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Pasadena, CA, USA, 7–14 March 2015; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Guo, J.Y.; Kong, Q.L. Precise orbit determination of Jason-2 with the precision of centimeters based on space-borne GPS technique. Geo. Inform. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2014, 39, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Tsai, H.F. Electron density profiles probed by radio occultation of FORMOSAT-7/COSMIC-2 at 520 and 800 km altitude. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2015, 8, 3069–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.Y.; Huang, J.W.; Zeng, Z.B.; Chang, X.T.; Han, Y.B. Study on geometric orbit determination of COSMIC satellite based on GPS non-difference data. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2008, 1, 75–80. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=ZKJZ200801011&DbName=CJFQ2008 (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Cherniak, I.; Zakharenkova, I.; Braun, J.; Wu, Q.; Pedatella, N.; Schreiner, W.; Schreiner; Weiss, J.; Hunt, D. Accuracy assessment of the quiet-time ionospheric F2 peak parameters as derived from COSMIC-2 multi-GNSS radio occultation measurements. J. Space. Weather. Spac. 2021, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, L.; Ho, S.P.; Zhou, X. Inverting COSMIC-2 phase data to bending angle and refractivity profiles using the full spectrum inversion method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.P.; Zhou, X.; Shao, X.; Zhang, B.; Adhikari, L.; Kireev, S.; He, Y.X.; Lynch, E. Initial assessment of the COSMIC-2/FORMOSAT-7 neutral atmosphere data quality in NESDIS/STAR using in situ and satellite data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.P. Recent Precise Orbit Determination Results for the COSMIC-2 Mission. In Proceedings of the 43rd COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Online Confernece, Australia, 28 January–4 February 2021; Volume 43, p. 2337. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2021cosp...43E2337W/abstract (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Jaeggi, A.; Arnold, D.; Weiss, J.; Hunt, D. Assessment of COSMIC-2 reduced-dynamic and kinematic orbit determination. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 25–30 April 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hwang, C.; Tseng, T.; Huang, C.; Bock, H. A Near-Real-Time Automatic Orbit Determination System for COSMIC and Its Follow-On Satellite Mission: Analysis of Orbit and Clock Errors on Radio Occultation. IEEE T. Geosci. Remote. 2014, 52, 3192–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.; Tseng, T.; Lin, T.; Svehla, D.; Schreiner, B. Precise orbit determination for the FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC satellite mission using GPS. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.; Tseng, T.; Lin, T.; Fu, C.; Svehla, D. Precise Orbit Determination for FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC and Gravity Application. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 December 2006; Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2006AGUFM.A14A..04H/abstract (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Kuang, D.; Bertiger, W.; Desai, S.; Haines, B.J.; Iijima, B.A.; Meehan, T.K. Precise orbit determination for COSMIC satellites using GPS data from two on-board antennas. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium, Monterey, CA, USA, 5–8 May 2008; pp. 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, M.; Melbourne; Liu, Y.C. Radio Occultation Using Earth Satellites: A Wave Theory Approach; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Yuan, Y.B. PPP-RTK based on undifferenced and uncombined observations: Theoretical and practical aspects. J. Geo. 2018, 93, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.C.; Hou, P.; Zha, J.P.; Liu, T. Integer-estimable FDMA model as an enabler of GLONASS PPP-RTK. J. Geo. 2021, 95, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.C.; Hou, P.; Zha, J.P.; Liu, T. PPP-RTK functional models formulated with undifferenced and uncombined GNSS observations. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braasch, M.S. Isolation of GPS Multipath and Receiver Tracking Errors. Annu. Navig. 1994, 41, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Huang, J.S. GPS Surveying and Data Processing, 3rd ed.; Wuhan University Press: Wuhan, China, 2005; pp. 99–129. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.Y.; Zong, G.; Li, W. Classification Solution of Single-Epoch Ambiguity and Ionospheric Delay for Single GPS Satellite. J. Shandong Univ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 34, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.J.; Guo, J.M.; Kong, X.Y. Analyses on the systematic errors of point positioning based on TEQC. Sci. Surv. Map. 2007, 32, 27–28+34+193. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=CHKD200704012&DbName=CJFQ2007 (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Abou, G.M.; Kaloop, M.R.; Rabah, M.M.; Zeidan, Z.M. Improving Precise Point Positioning Convergence Time through TEQC Multipath Linear Combination. J. Surv. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.W.; Wang, Q.X.; Gong, Y.X. Quality analysis of new signal data of BD-3. J. Hefei Univ. Technol. 2021, 44, 1111–1117. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=HEFE202108017&DbName=CJFQ2021 (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Ge, T. Quality inspection of measured data of GNSS receiver based on TEQC. Electron. Technol. Soft. Eng. 2020, 14, 61–62. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=DZRU202014028&DbName=CJFQ2020 (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Guo, H.Y.; Song, F.C.; Qu, Q.X. Analysis of CORS data quality of single base station based on TEQC. Beijing Surv. Map. 2019, 33, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.Y.; Xiong, X. Quality Checking and Analysis on GPS Data in Northeast Asia. Geo. Inform. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2006, 31, 209–212. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=WHCH200603004&DbName=CJFQ2006 (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Zhang, H.P.; Kong, S.L.; Jiang, Y.M.; Zhou, M.S.; Gao, S.M.; Xu, Y. Efficient Application of GPS Data Preprocessing Based on TEQC. GNSS World China 2018, 43, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Lv, Z.P.; Cui, Y. Visual development of GNSS data quality analysis software based on TEQC. In Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Academic Annual Conference, Beijing, China, 13–15 May 2015; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=WXDH201505001024&DbName=IPFD2015 (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Zhang, P.F. Analysis of GNSS Data Quality of Multi System in Complex Environment. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, China, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J. Analysis of influence of surface environment on GNSS data quality. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2015. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD201601&filename=1015801737.nh (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Chen, C.X.; Chen, G.; Wang, Q.P. Data examination and Analysis for Fujian GPS observation network. Geo. Geodyn. 2014, 34, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J.; Hu, Y.K.; Beng, P. Observation quality evaluation and analysis of BDS/GPS. Beijing Surv. Map. 2017, S1, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.L.; Wang, Z.W.; Wang, Q.X.; Mao, Y. Data quality analysis of BeiDou global test satellite. Bull. Surv. Map. 2018, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estey, L.H.; Meertens, C.M. TEQC: The multi-purpose toolkit for GPS/GLONASS data. GPS Solut. 1999, 3, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.; Tseng, T.; Lin, T.; Svehla, D.; Hugentobler, U.; Chao, B.F. Quality assessment of FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC and GRACE GPS observables: Analysis of multipath, ionospheric delay and phase residual in orbit determination. GPS Solut. 2010, 14, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäggi, A.; Hugentobler, U.; Beutler, G. Pseudo-Stochastic Orbit Modeling Techniques for Low-Earth Orbiters. J. Geod. 2006, 80, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.Z.; Kong, Q.L.; Zhang, L.G. Precision orbit determination of JASON-3 satellite with on-board GPS at centimeter level. Sci. Surv. Map. 2020, 45, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.W.; Guo, J.Y.; Liu, L.; Kong, Q.L. Research on precise orbit determination of SWARM satellite based on Kinematics and Reduced Dynamics. Geo. Geodyn. 2019, 39, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dach, R.; Andritsch, F.; Arnold, D.; Vertone, S.; Thaller, D. Bernese GNSS Software Version 5.2. User manual; Astronomical Institute, University of Bern, Bern Open Publishing: Bern, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.G.; Zhao, Q.L.; Guo, J. Study on the influence of GPS antenna phase center correction on LEO satellite precise orbit determination. Acta. Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2011, 40, 34–38. Available online: http://xb.sinomaps.com/CN/Y2011/V40/ISup./34 (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Guo, J.Y. Determination of CHAMP’s Orbit and Earth Gravity Model from Onboard GPS Data. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong of Science and Technology, Taian, China, 2004. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CDFD9908&filename=2004133515.nh (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- IJssel, J.; Encarnação, J.; Doornbos, E.; Visser, P.N. Precise science orbits for the Swarm satellite constellation. Adv. Space. Res. 2015, 56, 1042–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| ≤3 (%) | 4~6 (%) | 7~10 (%) | ≥11 (%) | Mean (Number) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sat–1 | 0.10 | 18.50 | 81.17 | 0.23 | 7.56 |
| Sat–2 | 0.10 | 20.44 | 79.24 | 0.22 | 7.54 |
| Sat–3 | 0.20 | 15.57 | 83.80 | 0.42 | 7.67 |
| Sat–4 | 0.36 | 18.56 | 81.04 | 0.03 | 7.55 |
| Sat–5 | 0.30 | 12.90 | 86.12 | 0.68 | 7.71 |
| Sat–6 | 0.05 | 16.42 | 83.16 | 0.38 | 7.60 |
| DOY | Sat–1 | Sat–2 | Sat–3 | Sat–4 | Sat–5 | Sat–6 | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 138 | 27 | 33 | 28 | 28 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 139 | 26 | 35 | 30 | 27 | 30 | 28 | 29 |
| 140 | 31 | 32 | 30 | 37 | 27 | 27 | 31 |
| 141 | 43 | 30 | 34 | 38 | 33 | 28 | 34 |
| 142 | 28 | 31 | 29 | 34 | 30 | 27 | 30 |
| Mean | 31 | 32 | 30 | 33 | 29 | 28 | — |
| DOY | Sat–1 | Sat–2 | Sat–3 | Sat–4 | Sat–5 | Sat–6 | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 138 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 8 |
| 139 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 9 |
| 140 | 7 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 141 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 9 |
| 142 | 8 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 9 |
| Mean | 8 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | — |
| Models/Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Mean earth gravity | EGM2008_SMALL |
| N-body | JPL DE405 |
| Relativity | IERS2010XY |
| Ocean Tides | FES2004 |
| Solid-earth tides | TIDE2000 |
| GPS precise ephemeris | ftp://ftp.aiub.unibe.ch/CODE (accessed on 12 March 2021) |
| GPS precise clock offset | ftp://ftp.aiub.unibe.ch/CODE (accessed on 12 March 2021) |
| Antenna PCO and PCV | Igs14.atx |
| Elevation cutoff | 5° |
| Sampling interval | 10 s |
| Pseudostochastic pulses | 6 min |
| Arc length of orbit determination | 24 h |
| DOY | Sat–1 | Sat–2 | Sat–3 | Sat–4 | Sat–5 | Sat–6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 138 | 6.4 | 6.0 | 6.4 | 7.0 | 6.6 | 6.6 |
| 139 | 6.7 | 6.2 | 6.3 | 6.0 | 6.7 | 7.0 |
| 140 | — | 6.5 | 6.6 | 6.3 | 6.8 | 6.8 |
| 141 | — | 6.4 | 6.9 | 6.2 | 6.7 | 7.2 |
| 142 | 6.1 | 6.6 | 6.0 | 6.2 | 6.5 | 7.5 |
| Mean | 6.4 | 6.0 | 6.4 | 7.0 | 6.6 | 6.6 |
| R | T | N | 3D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sat–1 | 0.60 | 1.20 | 0.93 | 1.66 |
| Sat–2 | 0.92 | 1.02 | 0.53 | 1.51 |
| Sat–3 | 0.71 | 1.12 | 0.73 | 1.53 |
| Sat–4 | 0.60 | 1.07 | 1.03 | 1.64 |
| Sat–5 | 0.79 | 1.33 | 0.70 | 1.75 |
| Sat–6 | 0.65 | 0.98 | 0.62 | 1.38 |
| R | T | N | 3D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sat–1 | 5.23 | 5.98 | 2.20 | 8.26 |
| Sat–2 | 4.97 | 5.55 | 1.78 | 7.67 |
| Sat–3 | 4.23 | 5.68 | 1.93 | 7.35 |
| Sat–4 | 5.44 | 6.59 | 2.04 | 8.79 |
| Sat–5 | 5.33 | 6.44 | 2.13 | 8.64 |
| Sat–6 | 5.61 | 6.36 | 2.29 | 8.79 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Fang, W.; Wang, G.; Li, C.; Wang, T.; Bai, Q.; Han, J. Analysis of Space-Borne GPS Data Quality and Evaluation of Precise Orbit Determination for COSMIC-2 Mission Based on Reduced Dynamic Method. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153544
Kong Q, Chen Y, Fang W, Wang G, Li C, Wang T, Bai Q, Han J. Analysis of Space-Borne GPS Data Quality and Evaluation of Precise Orbit Determination for COSMIC-2 Mission Based on Reduced Dynamic Method. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153544
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Qiaoli, Yanfei Chen, Wenhao Fang, Guangzhe Wang, Changsong Li, Tianfa Wang, Qi Bai, and Jingwei Han. 2022. "Analysis of Space-Borne GPS Data Quality and Evaluation of Precise Orbit Determination for COSMIC-2 Mission Based on Reduced Dynamic Method" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153544
APA StyleKong, Q., Chen, Y., Fang, W., Wang, G., Li, C., Wang, T., Bai, Q., & Han, J. (2022). Analysis of Space-Borne GPS Data Quality and Evaluation of Precise Orbit Determination for COSMIC-2 Mission Based on Reduced Dynamic Method. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153544