VMD–WT-Based Method for Extracting On-the-Fly GNSS Tide Level and Its Realization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. OTF GNSS Tide Measurement and Solution Method
2.1.1. Instrument Placement and Coordinate Measurement
2.1.2. Reduction in Sea Surface Geodetic Height
2.1.3. Sea Surface Geodetic Height Sequence Filtering
2.1.4. Vertical Datum Conversion
2.2. OTF GNSS Tide Level Data—Extraction Method
2.2.1. Wavelet Thresholding Method
2.2.2. Normalized Cross-Correlation Coefficient (NCC)
2.2.3. The Root-Mean-Square Error (RMSE)
2.2.4. Variational Mode Decomposition
2.2.5. Energy Difference Ratio Method
2.3. The VMD–WT Filtering Method
3. Experimental Strategy and Experimental Methods
3.1. Study Area
3.2. The Tide Level of the Experimental Area
3.3. Measurement and Data Processing Flow
4. Results and Discussion
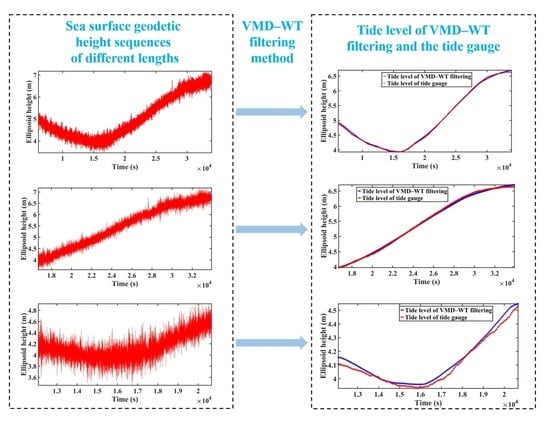
4.1. Filtering Method Combining Variational Mode Decomposition and Wavelet Transform (VMD–WT)
4.2. Comparative Analysis of the Eight Filtering Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, C.C.; Lee, H.W.; Tsui, I.F. Preliminary test of Tide-independent Bathymetric measurement Based on GPS. Geomat. Res. Australas. 2002, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, A.; Denys, P. Water level measurement and tidal datum transfer using high rate GPS buoys. N. Z. Surv. 2009, 299, 24. [Google Scholar]
- DeLoach, S.R. GPS Tides: A Project to Determine Tidal Datums with the Global Positioning System; Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering Technical Report No. 181; University of New Brunswick: Fredericton, NB, Canada, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, B.F.; Hubbard, J.R. Results from recent GPS Tides Projects. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2000 MTS/IEEE Conference and Exhibition, Providence, RI, USA, 11–14 September 2000; Conference Proceedings (Cat. No. 00CH37158). pp. 1159–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Ngagipar, S.H.M.; Yusof, O.M. RTK GPS water level measurement on dynamic sea surface. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Control and System Graduate Research Colloquium, Shah Alam, Malaysia, 27–28 June 2011; pp. 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Salleh, A.M.; Daud, M. An observation technique and GPS buoy processing strategy for ocean surface monitoring. In Advances in Civil, Architectural, Structural and Constructional Engineering; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2016; pp. 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.H.; Clarke, J.E.H.; Brucker, S.; Duffy, G. On the fly GPS tide measurement along the Saint John River. Int. Hydrogr. Rev. 2004, 5, 48–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.H.; Dong, J.; Ke, H. High Precision GPS Tide Measurement Method in a Far-Distance and Transformation Model for the Vertical Datum. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2015, 40, 761–766. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.H.; Wang, S.P.; Zhang, H.M. Long-distance and on-the-fly GPS tidal level measurement based on GPS PPK/PPP. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2008, 33, 910–913. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y. PPP-RTK based on undifferenced and uncombined observations: Theoretical and practical aspects. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, J.W.; Yu, K.G.; Zhu, Y.C.; Qian, N.J.; Chang, J. Developing and testing models for sea surface wind speed estimation with GNSS-R delay Doppler maps and delay waveforms. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3760. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.H.; Zhao, J.H.; Wang, S. Research on methods of extracting on-the-fly tidal level from GPS observation in near-shore area. 2008, 33, 1279–1282. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.L.; Zhao, J.H. Analyzing and eliminating the effect of wave in GPS tide observing. Hydroaphic Surv. Charting 2003, 23, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Yu, C.; Ren, Y.; Wang, W.; Yin, Z.; Xia, C. High Precision Attitude-Rate Measurement of Magnetically Suspended Control and Sensing Gyroscope Using Variational Mode Decomposition and Wavelet Transform. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junsheng, C.; Dejie, Y.; Yu, Y. Research on the intrinsic mode function (IMF) criterion in EMD method. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2006, 20, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lv, X. Application of the EMD method to river tides. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2018, 35, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Lv, X.; Wang, Y.; Matte, P.; Chen, H.; Jin, G. Exploration of tidal-fluvial interaction in the Columbia river estuary using S_TIDE. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 6598–6619. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, A.T.; Pan, J.; Lin, H. Multi-Timescale Analysis of Tidal Variability in the Indian Ocean Using Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2020JC016604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantin, D.; Dominique, Z. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Li, M.; Yin, H. Variational mode decomposition denoising combined the detrended fluctuation analysis. Signal Process. 2016, 125, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Pan, H.; Chen, Y.; Pan, S. Application of the Variational Mode Decomposition (VMD) method to river tides. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 261, 107570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.T.; Bian, G.; Jin, S.H. Data collection and processing of instantaneous geodetic elevation of sea level. Hydroaphic Surv. Charting 2016, 36, 50–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Bao, J.Y.; Zhou, F.N.; Feng, J.T. Heave of the positioning center in hydrographic survey. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2010, 35, 1169–1173. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.; Xiao, F.M.; Feng, Q.M. Effect of monitoring heave of transducer due to the spatial offset between montion sensor and transducer. Hydroaphic Surv. Charting 2008, 28, 4–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fund, F.; Perosanz, F.; Testut, L.; Loyer, S. An Integer Precise Point Positioning technique for sea surface observations using a GPS buoy. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Zhao, J.H. Quality control of GPS height in precise MBS measurement. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2009, 38, 22–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Varbla, S.; Liibusk, A.; Ellmann, A. Shipborne GNSS-Determined Sea Surface Heights Using Geoid Model and Realistic Dynamic Topography. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IHO. Manual on Hydrography, 1st ed.; Publication C-13; IHO: Monaco, Monaco, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.C. Mathematical models for hydrographic datum transfer. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2000, 30, 310–316. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.H.; Hughes Clarke, J.E.; Brucker, S. Establishing a Seamless Vertical Reference along the Tidal Segment of the Saint John River. Lighthouse J. Can. Hydrogr. Assoc. 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C.; Sun, Y.D. Application of a GPS-based method to tidal datum transfer. Hydrogr. J. 2004, 112, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- El-Diasty, M.; Kaloop, M.R.; Alsaaq, F. Chart Datum-to-Ellipsoid Separation Model Development for Obhur Creek Using Multibeam Hydrographic Surveying. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubechies, I. Ten Lectures on Wavelets; SIAM: Bangkok, Thailand, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Daubechies, I. Ten lectures on wavelets. In Proceedings of the CBMS-NSF Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1 November 1992; Available online: https://aip.scitation.org/doi/abs/10.1063/1.4823127 (accessed on 22 September 2022).
- Cheng, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, G. A new method for estimating the correlation of seismic waveforms based on the NTFT. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 226, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Cai, D.; Shen, W.; Su, H. Denoising method for Fiber Optic Gyro measurement signal of face slab deflection of concrete face rockfill dam based on sparrow search algorithm and variational modal decomposition. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 331, 112913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.A.; Wu, F.; Marlia, D.; Ednofri; Zhao, Y. Mitigation of Ionospheric Scintillation Effects on GNSS Signals with VMD-MFDFA. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.C.; Xu, T.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L.M.; Hu, H.P.; Bai, Y.P. MEMS hydrophone signal denoising and baseline drift removal algorithm based on parameter-optimized variational mode decomposition and correlation coefficient. Sensors 2019, 19, 4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Dong, S.; Song, T. Method for eliminating mode mixing of empirical mode decomposition based on the revised blind source separation. Signal Processing 2012, 92, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.P.; Ao, Y.; Yan, H.C.; Bai, Y.P.; Shi, N. Signal denoising based on wavelet threshold denoising and optimized variational mode decomposition. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 5599096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.N.; Chen, W.G.; Han, K.; Wang, Q. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on GA-VMD and improved WOA-LSSVM. Ieee Access 2020, 8, 166753–166767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, F.R.; Li, X.; Liu, C.C.; Tian, C.F.; Ma, T.; Yang, X. Knock detection based on the optimized variational mode decomposition. Measurement 2019, 140, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.F.; Sun, Y.L.; Chen, S.J. Analysis of observed tidal current and numerical model of tidal current in the offshore area of eastern Jiaonan. Mar. Sci. 2008, 32, 9–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.C. (Ed.) Chapter 2—Marine Geographic and Geological Environment of China. In Marine Geo-Hazards in China; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 35–75. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.G.; Turyshev, S.G.; Boggs, D.H. The past and present Earth-Moon system: The speed of light stays steady as tides evolve. Planet Sci. 2014, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronkers, J. Ocean and Shelf Tides. In Dynamics of Coastal Systems; Advanced Series on Ocean Engineering; World Scientific: Singapore, 2015; Volume 41, pp. 654–664. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Board for Marine Atlas. Surface Current Tide Tidal Current. In Marine Atlas of the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea (Hydrology); The Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1993; p. 429. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Sun, Y.L. Numerical simulation of 3D tidal current in the offshore area of jiaonan. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2005, 35, 579–582. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, J.-R.; Shieh, J.-S.; Huang, N.E. Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A novel noise enhanced data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2010, 2, 135–156. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Luo, K.; Zhang, L.; Tang, X. Data Processing and Interpretation of Antarctic Ice-Penetrating Radar Based on Variational Mode Decomposition. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

















| Length of GNSS Tide Level | Method | FFT | Second-Order Polynomial Fit | Third-Order Polynomial Fit | EMD | EEMD | CEEMD | WT | VMD–WT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.7 h | Maximum error (cm) | 82.6 | 76.2 | 23.8 | 12.2 | 14.2 | 14.1 | 11.8 | 7.2 |
| RMSE (cm) | 16.94 | 24.7 | 9.23 | 4.04 | 4.04 | 4.03 | 3.78 | 2.78 |
| Length of GNSS Tide Level | Method | FFT | Second-Order Polynomial Fit | Third-Order Polynomial Fit | EMD | EEMD | CEEMD | WT | VMD–WT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.7 h | 0–5 cm | 45.3% | 10.1% | 27.8% | 81.7% | 82.3% | 79.5% | 80.8% | 94.2% |
| 5–10 cm | 30.0% | 10.1% | 43.5% | 16.6% | 15.7% | 18.3% | 18.1% | 5.8% | |
| 10–15 cm | 10.0% | 13.0% | 22.0% | 1.7% | 2.0% | 2.2% | 1.1% | 0 | |
| 15–20 cm | 5.7% | 14.0% | 5.6% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0–90 cm | 8.2% | 52.8% | 1.1% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Length of GNSS Tide Level | Method | FFT | Second-Order Polynomial Fit | Third-Order Polynomial Fit | EMD | EEMD | CEEMD | WT | VMD–WT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.8 h | Maximum error (cm) | 141.0 | 26.5 | 8.6 | 12.3 | 14.3 | 14.3 | 13.0 | 7.2 |
| RMSE (cm) | 25.72 | 10.0 | 4.17 | 4.47 | 4.54 | 4.59 | 4.45 | 3.13 |
| Length of GNSS Tide Level | Method | FFT | Second-Order Polynomial Fit | Third-Order Polynomial Fit | EMD | EEMD | CEEMD | WT | VMD–WT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.8 h | 0–5 cm | 45.2% | 28.8% | 71.2% | 75.7% | 72.9% | 72.2% | 73.6% | 91.7% |
| 5–10 cm | 22.9% | 28.1% | 28.8% | 21.2% | 24.3% | 25.0% | 22.9% | 8.3% | |
| 10–15 cm | 9.4% | 36.1% | 0 | 3.1% | 2.8% | 2.8% | 3.5% | 0 | |
| 15–20 cm | 6.9% | 4.2% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| >20 cm | 15.6% | 2.8% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Length of GNSS Tide Level | Method | FFT | Second-Order Polynomial Fit | Third-Order Polynomial Fit | EMD | EEMD | CEEMD | WT | VMD–WT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.4 h | Maximum error (cm) | 24.5 | 12.7 | 11.5 | 8.9 | 8.6 | 9.9 | 9.6 | 6.0 |
| RMSE (cm) | 6.3 | 4.32 | 4.32 | 3.97 | 4.06 | 4.03 | 3.91 | 2.82 |
| Length of GNSS Tide Level | Method | FFT | Second-Order Polynomial Fit | Third-Order Polynomial Fit | EMD | EEMD | CEEMD | WT | VMD–WT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–5 cm | 75.0% | 80.5% | 79.9% | 78.5% | 75.7% | 80.6% | 77.1% | 94.4% | |
| 5–10 cm | 12.5% | 15.3% | 17.3% | 21.5% | 24.3% | 19.4% | 22.9% | 5.6% | |
| 2.4 h | 10–15 cm | 8.3% | 4.2% | 2.8% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 15–20 cm | 2.1% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| >20 cm | 2.1% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S. VMD–WT-Based Method for Extracting On-the-Fly GNSS Tide Level and Its Realization. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4816. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194816
Gao W, Sun Y, Wang L, Wang S. VMD–WT-Based Method for Extracting On-the-Fly GNSS Tide Level and Its Realization. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):4816. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194816
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Wenlong, Yongfu Sun, Lei Wang, and Shengli Wang. 2022. "VMD–WT-Based Method for Extracting On-the-Fly GNSS Tide Level and Its Realization" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 4816. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194816
APA StyleGao, W., Sun, Y., Wang, L., & Wang, S. (2022). VMD–WT-Based Method for Extracting On-the-Fly GNSS Tide Level and Its Realization. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 4816. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194816