Assessment of Adjacency Correction over Inland Waters Using Sentinel-2 MSI Images
Abstract
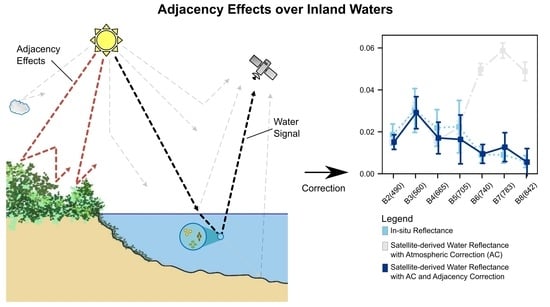
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dataset
2.2.1. MSI/Sentinel-2 Data
2.2.2. Field Data
2.3. The Selection of Water Types
2.4. Atmospheric Correction Procedure
2.5. Adjacency Effect Correction Procedure
2.5.1. SIMEC
2.5.2. AWP-Inland Water
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Inversion Model () versus MODIS Aerosol in the Atmospheric Correction
3.2. Range of the Adjacency Effect
3.3. Adjacency Effect Correction
3.4. Adjacency Effect Influence on Water Bodies
3.5. Sensitivity of Adjacency Effect at the TOA
4. Discussion
4.1. Aerosol and Atmospheric Correction
4.2. Estimation of the over Inland Waters
4.3. Influence of Adjacency Effect on Water Reflectance Data
4.4. Sensitivity and Challenges of Adjacency Effect
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
| Input Data | BIL | CON | BRA + MUT | MAM | PIR |
| Solar Zenith Angle | 48.22° | 29.52° | 29.52° | 27.78° | 27.78° |
| Solar Azimuth Angle | 33.37° | 53.65° | 53.65° | 61.70° | 61.70° |
| View Zenith Angle | 3.74° | 2.83° | 2.83° | 9.44° | 9.44° |
| View Azimuth Angle | 111.67° | 194.68° | 194.68° | 101.95° | 101.95° |
| Ozone (cm-atm) | 0.282 | 0.262 | 0.262 | 0.271 | 0.271 |
| Water Vapor (g/cm3) | 1.482 | 3.418 | 3.562 | 4.407 | 4.247 |
| Altitude (km) | 0.716 | 0.071 | 0.072 | 0.043 | 0.041 |
| Aerosol Model | Continental | ||||
| AOD at 550 nm * | 0.100 | 0.331 | 0.272 | 0.164 | 0.170 |
| AOD at 550 nm ** | 0.162 | 0.656 | 0.633 | 0.369 | 0.342 |
| Solar Zenith Angle | View Zenith Angle | Solar Azimuth Angle | View Azimuth Angle | Target Altitude | Aerosol Model | Atmospheric Profile | Band Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 33° | 6° | 53° | 141° | 0.189 (km) | * | Tropical (default) | 443–842 (nm) |
References
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Reidy Liermann, C.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boretti, A.; Rosa, L. Reassessing the projections of the World Water Development Report. Nature 2019, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO, UN-Water. United Nations World Development Report 2020: Water and Climate Change. Paris: UNESCO. 2020. Available online: https://www.unwater.org/publications/world-water-development-report-2020/ (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Pahlevan, N.; John, R.S.; Franz, B.A.; Zibordi, G.; Markham, B.; Bailey, S.; Schaaf, C.B.; Ondrusek, M.; Greb, S.; Strait, C.M. Landsat 8 remote sensing reflectance (Rrs) products: Evaluations, intercomparisons, and enhancements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Sarkar, S.; Franz, B.A.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; He, J. Sentinel-2 MultiSpectral Instrument (MSI) data processing for aquatic science applications: Demonstrations and validations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Advantages of high quality SWIR bands for ocean colour processing: Examples from Landsat-8. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 161, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Claverie, M.; Franch, B. Preliminary analysis of the performance of the Landsat 8/OLI land surface reflectance product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairo, C.; Barbosa, C.; Lobo, F.; Novo, E.; Carlos, F.; Maciel, D.; Flores Júnior, R.; Silva, E.; Curtarelli, V. Hybrid chlorophyll-a algorithm for assessing trophic states of a tropical brazilian reservoir based on MSI/Sentinel-2 data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kutser, T.; Paavel, B.; Verpoorter, C.; Ligi, M.; Soomets, T.; Toming, K.; Casal, G. Sensing of Black Lakes and Using 810 nm Reflectance Peak for Retrieving Water Quality Parameters of Optically Complex Waters. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, D.A.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Novo, E.M.L.M.; Flores Júnior, R.; Begliomini, F.N. Water Clarity in Brazilian Water Assessed Using Sentinel-2 and Machine Learning Methods. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 182, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toming, K.; Kutser, T.; Laas, A.; Sepp, M.; Paavel, B.; Nõges, T. First experiences in mapping lake water quality parameters with sentinel-2 MSI imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, V.S.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; de Carvalho, L.A.S.; Jorge, D.S.F.; Lobo, F.L.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Assessment of atmospheric correction methods for sentinel-2 MSI images applied to Amazon floodplain lakes. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otterman, J.; Fraser, R.S. Adjacency effects on imaging by surface reflection and atmospheric scattering: Cross radiance to Zenith. Appl. Opt. 1979, 197, 2852–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, R.; Bachmann, M.; Dorigo, W.; Müller, A. Influence of the Adjacency Effect on Ground Reflectance Measurements. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanré, D.; Herman, M.; Deschamps, Y. Influence of the background contribution upon space measurements of ground reflectance. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 3676–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, B.; Kiselev, V.; Zibordi, G. Simulation and analysis of adjacency effects in coastal waters: A case study. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 1523–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgarelli, B.; Zibordi, G. On the detectability of adjacency effects in ocean color remote sensing of mid- latitude coastal environments by SeaWiFS, MODIS-A, MERIS, OLCI, OLI and MSI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterckx, S.; Knaeps, E.; Ruddick, K. Detection and correction of adjacency effects in hyperspectral airborne data of coastal and inland waters: The use of the near infrared similarity spectrum. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 6479–6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.A.; Simis, S.G.H.; Selmes, N. Complementary water quality observations from high and medium resolution Sentinel sensors by aligning chlorophyll-a and turbidity algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, L.C.; Schott, J.R.; Raqueño, R. A VNIR/SWIR atmospheric correction algorithm for hyperspectral imagery with adjacency effect. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 71, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.F.; Tanré, D.; Deuzé, J.L.; Herman, M.; Morcrette, J.J. Second Simulation of the Satellite Signal in the Solar Spectrum, 6S: An Overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sei, A. Analysis of adjacency effects for two Lambertian half-spaces. Int. J. Rem. Sens. 2007, 28, 1873–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.F.; Tanré, D.; Deuzé, J.L.; Herman, M.; Morcrette, J.J. Second Simulation of the Satellite Signal in the Solar Spectrum (6S); 6S User Guide Version 3.0.; NASA-GSFC: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2006.
- Minomura, M.; Kuze, H.; Takeuchi, N. Adjacency effect in the atmospheric correction of satellite remote sensing data: Evaluation of the influence of aerosol extinction profiles. Opt. Rev. 2001, 8, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.S.; Kaleita, A.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Fassoni-Andrade, A.C.; Lobo, F.L.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Remote sensing of large reservoir in the drought years: Implications on surface water change and turbidity variability of Sobradinho reservoir (Northeast Brazil). Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2018, 13, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Du, L.; Yi, W.; Hong, J.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, J.; Li, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, D.; Fang, W.; et al. An adaptive atmospheric correction algorithm for the effective adjacency effect correction of submeter-scale spatial resolution optical satellite images: Application to a WorldView-3 panchromatic image. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 259, 112412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houborg, R.; McCabe, M.F. Adapting a regularized canopy reflectance model (REGFLEC) for the retrieval challenges of dryland agricultural systems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houborg, R.; McCabe, M.F. Impacts of dust aerosol and adjacency effects on the accuracy of Landsat 8 and RapidEye surface reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keukelaere, L.; Sterckx, S.; Adriaensen, S.; Knaep, E.; Reusen, I.; Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Hunter, P.; Neil, C.; Van der Zande, D.; et al. Atmospheric correction of Landsat-8/OLI and Sentinel-2/MSI data using iCOR algorithm: Validation for coastal and inland waters. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiselev, V.; Bulgarelli, B.; Heege, T. Sensor independent adjacency correction algorithm for coastal and inland water systems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Mangin, A.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; Smith, B.; Alikas, K.; Arai, K.; Barbosa, C.; Bélanger, S.; Binding, C.; Bresciani, M.; et al. ACIX-Aqua: A global assessment of atmospheric correction methods for Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 over lakes, rivers, and coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Sandoval, M.; Ruescas, A.; Urrego, P.; Ruiz-Verdú, A.; Delegido, J.; Tenjo, C.; Soria-Perpinyà, X.; Vicente, E.; Soria, J.; Moreno, J. Evaluation of Atmospheric Correction Algorithms over Spanish Inland Waters for Sentinel-2 Multi Spectral Imagery Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sterckx, S.; Knaeps, E.; Kratzer, S.; Ruddick, K. SIMilarity Environment Correction (SIMEC) applied to MERIS data over inland and coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, B.; Zibordi, G. Adjacency radiance around a small island: Implications for system vicarious calibrations. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.S.F.; Tucci, A.; Matarazzo, M.P.; Viana-Niero, C.; Nordi, C.S.D. Detection of Cyanotoxin-Producing Genes in a Eutrophic Reservoir (Billings Reservoir, São Paulo, Brazil). Water 2020, 12, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wengrat, S.; Bicudo, D.C. Spatial evaluation of water quality in an urban reservoir (Billings Complex, southeastern Brazil). Acta Limnol. Bras. 2011, 23, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alcantara, E.; Coimbra, K.; Ogashawara, I.; Rodrigues, T.; Mantovani, J.; Rotta, H.R.; Park, E.; Cunha, D.G.F. A satellite-based investigation into the algae bloom variability in large water supply urban reservoirs during COVID-19 lockdown. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 23, 100555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leme, E.; Silva, E.P.; Rodrigues, P.S.; Silva, I.R.; Martins, M.F.M.; Bondan, E.F.; Bernardi, M.M.; Kirsten, T.B. Billings reservoir water used for human consumption presents microbiological contaminants and induces both behavior impairments and astrogliosis in zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 151, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, F.L.; Nagel, G.W.; Maciel, D.A.; de Carvalho, L.A.S.; Martins, V.S.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Novo, E.M.L.M. AlgaeMAp: Algae Bloom Monitoring Application for Inland Waters in Latin America. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affonso, A.G.; Queiroz, H.L.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Abiotic variability among different aquatic systems of the central Amazon floodplain during drought and flood events. Braz. J. Biol. 2015, 75, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.P.; de Carvalho, L.A.S.; Novo, E.; Jorge, D.S.F.; Barbosa, C.C.F. Use of optical absorption indices to assess seasonal variability of dissolved organic matter in Amazon floodplain lakes. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 5355–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, D.S.F.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; de Carvalho, L.A.S.; Affonso, A.G.; Lobo, F.L.; Novo, E.M.L.M. SNR (signal-to-noise ratio) impact on water constituent retrieval from simulated images of optically complex Amazon lakes. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maciel, D.A.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Novo, E.M.L.M.; Cherukuru, N.; Martins, V.S.; Flores Júnior, R.; Jorge, D.S.; de Carvalho, L.A.S.; Carlos, F.M. Mapping of diffuse attenuation coefficient in optically complex waters of amazon floodplain lakes. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 170, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA, European Space Agency. Mission Search. Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Ciancia, E.; Campanelli, A.; Lacava, T.; Palombo, A.; Pascucci, S.; Pergola, N.; Pignatti, S.; Satriano, V.; Tramutoli, V. Modeling and Multi-Temporal Characterization of Total Suspended Matter by the Combined Use of Sentinel 2-MSI and Landsat 8-OLI Data: The Pertusillo Lake Case Study (Italy). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hestir, E.L.; Brando, V.E.; Bresciani, M.; Giardino, C.; Matta, E.; Villa, P.; Dekker, A.G. Measuring freshwater aquatic ecosystems: The need for a hyperspectral global mapping satellite mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ESA, European Space Agency. User Guides. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/user-guides/sentinel-2-msi/product-types/level-1c (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Barbosa, C.C.F.; Novo, E.M.L.M.; Martinez, J.M. Remote sensing of the water properties of the Amazon floodplain lakes: The time delay effects between in-situ and satellite data acquisition on model accuracy. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment: Sustaining the Millennium Development Goals, Stresa, Italy, 4–9 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Marinho, R.R.; Harmel, T.; Martinez, J.; Filizola Junior, N.P. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Suspended Sediments in the Negro River, Amazon Basin, from In Situ and Sentinel-2 Remote Sensing Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.A.; Simis, S.G.H.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Poser, K.; Bresciani, M.; Alikas, K.; Spyrakos, E.; Giardino, C.; Ansper, A. Assessment of atmospheric correction algorithms for the Sentinel-2A MultiSpectral Imager over coastal and inland waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capobianco, J.P.R.; Whately, M. Billings 2000: Ameaças e Perspectivas Para o Maior Reservatório de Água da Região Metropolitana de São Paulo. Relatório do Diagnóstico Socioambiental Participativo da Bacia Hidrográfica da Billings no Período 1989–99; Instituto Socioambiental: São Paulo, Brazil, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Affonso, A.G.; Queiroz, H.L.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Limnological characterization of floodplain lakes in Mamirauá Sustainable Development Reserve, Central Amazon (Amazonas State, Brazil). Acta Limnol. Bras. 2011, 23, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, C.C.F. Sensoriamento Remoto da Dinâmica da Circulação da Água do Sistema Planície de Curuai/Rio Amazonas. Ph.D. Thesis, National Institute for Space Research (INPE), São José dos Campos, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nagel, G.W.; Novo, E.M.L.M.; Martins, V.S.; Campos-Silva, J.V.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Bonnet, M.P. Impacts of meander migration on the Amazon riverine communities using Landsat time series and cloud computing. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D. Estimation of the Remote-Sensing Reflectance from Above-Surface Measurements. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 7442–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D. Polarized reflectance and transmittance properties of windblown sea surfaces. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 4828–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, F.L.; Costa, M.P.F.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Time-series analysis of Landsat- MSS/TM/OLI images over Amazonian waters impacted by gold mining activities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 157, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, R.; Schmechtig, C. Adjacency effects on water surfaces: Primary scattering approximation and sensitivity study. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruddick, K.G.; Cauwer, V.; Park, Y.J.; Moore, G. Seaborne measurements of near infrared water- leaving reflectance: The similarity spectrum for turbid waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Mattoo, S.; Ichoku, C.; Kahn, R.; Eck, T.F. Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10399–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermote, E.; El Saleous, N.; Justice, C.O.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Privette, J.L.; Remer, L.; Roger, C.; Tanré, D. Atmospheric correction of visible to middle-infrared EOS-MODIS data over land surfaces: Background, operational algorithm and validation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 17131–17141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Korkin, S.; Huang, D. MODIS Collection 6 MAIAC algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5741–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, V.S.; Lyapustin, A.; de Carvalho, L.A.S.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Validation of high-resolution MAIAC aerosol product over South America. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 7537–7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, F.C.; Popp, C. Critical surface albedo and its implications to aerosol remote-sensing. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2012, 4, 7725–7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Artaxo, P.; Rizzo, L.V.; Brito, J.F.; Barbosa, H.M.J.; Arana, A.; Sena, E.T.; Cirino, G.G.; Bastos, W.; Martin, S.T.; Andreae, M.O. Atmospheric aerosols in Amazonia and land use change: From natural biogenic to biomass burning conditions. Faraday Discuss. 2013, 165, 203–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Löbs, N.; Barbosa, C.G.G.; Brill, S.; Walter, D.; Ditas, F.; Sá, M.O.; Araújo, A.C.; Oliveira, L.R.; Godoi, R.H.M.; Wolf, S.; et al. Aerosol measurement methods to qualify spore emissions from fungi and cryptogamic covers in the Amazon. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrivastava, M.; Andreae, M.O.; Artaxo, P.; Barbosa, H.M.J.; Berg, L.K.; Brito, J.; Ching, J.; Easter, R.C.; Fan, J.; Fast, J.D. Urban pollution greatly enhances formation of natural aerosols over the Amazon rainforest. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Artaxo, P.; Martins, J.V.; Yamasoe, M.A.; Procópio, A.S.; Pauliquevis, T.M.; Andreae, M.O.; Guyon, P.; Gatti, L.V.; Leal, A.M.C. Physical and chemical properties of aerosols in the wet and dry seasons in Rondônia, Amazonia. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, D.R.; Giangrande, S.E.; Li, Z.; Machado, L.A.; Martin, S.T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Artaxo, P.; Barbosa, H.M.J.; et al. Substantial convection and precipitation enhancements by ultrafine aerosol particles. Science 2018, 359, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, M.; Kazadzis, S.; Amiridis, V.; Kahn, R.A. Global aerosol mixtures and their multiyear and seasonal characteristics. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 116, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores Júnior, R.; Flores Júnior, R.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Maciel, D.A.; Novo, E.M.L.M.; Martins, V.S.; Lobo, F.L.; de Carvalho, L.A.S.; Carlos, F.M. Hybrid Semi Analytical Algorithm for estimating chlrophyll-a concentration in Lower Amazon Floodplain waters. Front. Remote Sens. 2022, 3, 834576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C. Land adjacency effects on MODIS Aqua top-of-atmosphere radiance in the shortwave infrared: Statistical assessment and correction. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 4802–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R. Evolution of Ocean Color Atmospheric Correction: 1970–2005. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Joseph, J.H. Determination of surface albedos and aerosol extinction characteristics from satellite imagery. J. Geophys. Res. 1982, 87, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Kaufman, Y.J. Role of adjacency effect in the remote sensing of aerosol. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 11909–11916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, S.; Li, Z.; Gao, C.; Zhao, W.; Wu, H.; Qian, Y.; Leng, P.; Gao, M. Influence of adjacency effect on high-spatial-resolution thermal infrared imagery: Implication for radiative transfer simulation and land surface temperature retrieval. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 245, 111852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Wald, A.E.; Remer, L.A.; Gao, B.; Li, R.; Flynn, L. The MODIS 2.1-μm Channel—Correlation with Visible Reflectance for Use in Remote Sensing of Aerosol. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Rem. Sens. 1997, 35, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, M.A.G.; Lopes, V.L.R. Zero reais de funções reais. In Cálculo Numérico: Aspectos Teóricos e Computacionais, 2nd ed.; Pearson: São Paulo, Brazil, 1996; pp. 27–104. [Google Scholar]












Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paulino, R.S.; Martins, V.S.; Novo, E.M.L.M.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; de Carvalho, L.A.S.; Begliomini, F.N. Assessment of Adjacency Correction over Inland Waters Using Sentinel-2 MSI Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081829
Paulino RS, Martins VS, Novo EMLM, Barbosa CCF, de Carvalho LAS, Begliomini FN. Assessment of Adjacency Correction over Inland Waters Using Sentinel-2 MSI Images. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(8):1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081829
Chicago/Turabian StylePaulino, Rejane S., Vitor S. Martins, Evlyn M. L. M. Novo, Claudio C. F. Barbosa, Lino A. S. de Carvalho, and Felipe N. Begliomini. 2022. "Assessment of Adjacency Correction over Inland Waters Using Sentinel-2 MSI Images" Remote Sensing 14, no. 8: 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081829
APA StylePaulino, R. S., Martins, V. S., Novo, E. M. L. M., Barbosa, C. C. F., de Carvalho, L. A. S., & Begliomini, F. N. (2022). Assessment of Adjacency Correction over Inland Waters Using Sentinel-2 MSI Images. Remote Sensing, 14(8), 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081829