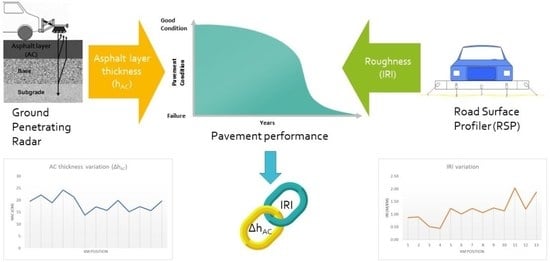
Using NDT Data to Assess the Effect of Pavement Thickness Variability on Ride Quality
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Sections
2.2. GPR Survey
2.3. RSP Survey
- The vertical displacement of the beam from the road surface.
- The vertical acceleration of the beam.
- The time and distance that the two aforementioned parameters are recorded.
- The sprung mass—ms (kg), which is the mass of the part of the vehicle that burdens the suspension and includes a percent of the weight of the suspension.
- The unsprung mass—mu (kg), which is the mass corresponding to the weight that does not burden the suspension system but is supported by the wheel or the tire and follows its displacements.
- The suspension spring with coefficient ks (kN/m).
- The suspension damping coefficient (cs) (kN s/m).
- The tire spring rate (kt) (kN/m).
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results
- 0 ≤ ΔhAC ≤ 2 cm
- 2 < ΔhAC ≤ 5 cm
- ΔhAC > 5 cm
- k = 0 Gumbel Distribution
- k > 0 Frechet Distribution
- k < 0 Weibull Distribution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plati, C.; Loizos, A.; Gkyrtis, K. Assessment of Modern Roadways Using Non-destructive Geophysical Surveying Techniques. Surv. Geophys. 2020, 41, 395–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, A.; Tosti, F.; Ortuani, B.; Giudici, M.; Mele, M. Mapping the spatial variation of soil moisture at the large scale using GPR for pavement applications. Near Surf. Geophys. 2015, 13, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, A.; Tosti, F.; Bianchini Ciampoli, L.; D’Amico, F. An overview of ground-penetrating radar signal processing techniques for road inspections. Signal Process. 2017, 132, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Meng, Z.; Han, X.; Li, H.; Tsukiji, T.; Xu, R.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, J. An automated driving systems data acquisition and analytics platform. Transp. Res. Part C 2023, 151, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Quijano, K.; Crawford, M.M. YOLOv5-Tassel: Detecting Tassels in RGB UAV Imagery with Improved YOLOv5 Based on Transfer Learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 8085–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Hashemi, E.; Xiong, L.; Khajepour, A. Autonomous Vehicle Kinematics and Dynamics Synthesis for Sideslip Angle Estimation Based on Consensus Kalman Filter. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2023, 31, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Xiong, L.; Xia, X.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Khajepour, A. Improved Vehicle Localization Using On-Board Sensors and Vehicle Lateral Velocity. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 6818–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, R.; Habib, A.; Bullock, D. Pothole Mapping and Patching Quantity Estimates using LiDAR-Based Mobile Mapping Systems. Transp. Res. Rec. 2020, 2674, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astor, Y.; Nabesima, Y.; Utami, R.; Sihombing, A.V.R.; Adli, M.; Firdaus, M.R. Unmanned aerial vehicle implementation for pavement condition survey. Transp. Eng. 2023, 12, 100168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maser, K.R. Condition Assessment of Transportation Infrastructure Using Ground Penetrating Radar. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 1996, 2, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahouar, S.; Al-Qadi, I.L.; Loulizi, A.; Clark, T.M.; Lee, D.T. Approach to Determining In Situ Dielectric Constant of Pavements: Development and Implementation at Interstate 81 in Virginia. In Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board; No. 1806; Transportation Research Board of the National Academies: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Qadi, I.L.; Lahouar, S.; Loulizi, A. Successful Application of Ground-Penetrating Radar for Quality Assurance—Quality Control of New Pavements. In Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board; No. 1861; Transportation Research Board of the National Academies: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 86–97. [Google Scholar]
- Maser, K.R.; Scullion, T. Automated Pavement Subsurface Profiling Using Radar: Case Studies of Four Experimental Field Sites. In Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board; No. 1344; Transportation Research Board of the National Academies: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; pp. 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Loken, M. Current State of the Art and Practise of Using GPR for Minnesota Roadway Applications; Minnesota Local Research Board; Office of Research Activities: St. Louis, MN, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Grote, K.; Hubbard, S.; Harvey, J.; Rubin, Y. Evaluation of Infiltration in Layered Pavements Using Surface GPR Reflection Techniques. J. Appl. Geophys. 2005, 57, 129–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, K.; Schulin, R.; Fluhler, H.; Attinger, W. Calibration of Time Domain Reflectometry for Water Content Measurements Using Composite Dielectric Approach. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 2267–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rmelie; Scullion, T. Detecting Stripping in Asphalt Concrete Layers Using Ground Penetrating Radar. In Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board; No 1568; Transportation Research Board of the National Academies: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Hammons, M.I.; Von Quintus, H.; Geary, G.M.; Wu, P.Y.; Jared, D.M. Detection of Stripping in Hot-Mix Asphalt. In Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board; No. 1949; Transportation Research Board of the National Academies: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Scullion, T.; Rmeili, E.H. Detection of Stripping in Asphalt Concrete Layers Using Ground Penetrating Radar; Research report 2964-S; Texas Transportation Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 1997.
- Saarenketo, T.; Scullion, T. Road Evaluation with Ground Penetrating Radar. J. Appl. Geophys. 2000, 43, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Lorenzl, H.; Wistuba, M.P. Crack detection in asphalt pavements—How useful is the GPR? In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Advanced Ground Penetrating Radar (IWAGPR), Aachen, Germany, 22–24 June 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tosti, F.; Bianchini Ciampoli, L.; D’Amico, F.; Alani, A.M.; Benedetto, A. An experimental-based model for the assessment of the mechanical properties of road pavements using ground-penetrating radar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elseicy, A.; Alonso-Díaz, A.; Solla, M.; Rasol, M.; Santos-Assunçao, S. Combined Use of GPR and Other NDTs for Road Pavement Assessment: An Overview. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X. Use of NDT systems to investigate pavement reconstruction needs and improve maintenance treatment decision-making. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marecos, V.; Fontul, S.; de Lurdes Antunes, M.; Solla, M. Evaluation of a highway pavement using non-destructive tests: Falling Weight Deflectometer and Ground Penetrating Radar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-H.; Bilyeu, J.; Scullion, T.; Nazarian, N.; Chiu, C.-T. Failure Investigation of a Foamed-Asphalt Highway Project. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2006, 12, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plati, C.; Georgouli, K.; Cliatt, B.; Loizos, A. Incorporation of GPR data into genetic algorithms for assessing recycled pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.H.; Scullion, T. Forensic Investigations of Roadway Pavement Failures. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2008, 22, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong-hai, L.; Zhong-xin, X.; Zhi-geng, Z.; Bing, L. Research and verification of transfer model for roughness conditions of pavement constructio. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2016, 9, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, H. Design Factors Affecting the Initial Roughness of Asphalt Pavements. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2011, 4, 268–273. [Google Scholar]
- Yero, S.A.; Hainin, M.R.; Yaacob, H. Determination of Surface Roughness Index of Various Bituminous Pavements. Int. J. Res. Rev. Appl. Sci. 2012, 13, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Elbheiry, M.; Kandil, K.; Kotb, A. Investigation of Factors Affecting Pavement Roughness. Eng. Res. J. 2011, 132, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Mei, S. Highway performance prediction model of International Roughness Index based on panel data analysis in subtropical monsoon climate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 366, 130232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Burrow, M.; Ghataora, G. Study of the Factors Affecting Road Roughness Measurement Using Smartphones. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2020, 26, 4020020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.; Luo, X.; Wang, F. Understanding the effects of structural factors and traffic loading on flexible pavement performance. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2022, 12, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkyrtis, K.; Loizos, A.; Plati, C. Integrating Pavement Sensing Data for Pavement Condition Evaluation. Sensors 2021, 21, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenovic, G.; Jiang, Y.J.; Selezneva, O.; Aref, S.; Darter, M. Comparison of As-Constructed and As-Designed Flexible Pavement Layer Thicknesses. In Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board; Transportation Research Board of the National Academies: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 1853, pp. 165–176. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Huang, X. Investigation into causes of in-place rutting in asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timm, D.H.; Newcomb, D.E.; Galambos, T.V. Incorporation of reliability into mechanistic-empirical pavement design. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2000, 1730, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureldin, A.; Sharaf, E.; Arafah, A.; Al-Sugair, F. Estimation of standard deviation of predicted performance of flexible pavements using AASHTO Model. Transp. Res. Rec. 1994, 1449, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Aguiar-Moya, J.P.; Banerjee, A.; Prozzi, J.A. Sensitivity analysis of the M-E PDG using measured probability distributions of pavement layer thickness. In Proceedings of the 88th Transportation Research Board Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 11–15 January 2009. Paper no. 09-0412. [Google Scholar]
- Geophysical Survey Sytems Inc. Model 4108 Horn Antenna. In System Settings and User Notes; Geophysical Survey Sytems Inc.: Nashua, NH, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Qadi, I.L.; Lahouar, S. Measuring Layer Thicknesses with GPR—Theory to Practice. Constr. Build. Mater. 2005, 19, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geophysical Survey Sytems Inc. Radan for Windows. User’s Manual, Geophysical Survey Systems INC (GSSI); Geophysical Survey Sytems Inc.: Nashua, NH, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Roadscanners. Road Doctor Software, User’s Guide, Version 1.1; Roadscanners: Rovaniemi, Finland, 2001.
- Dynatest. Dynatest 5051 Mark III/IV, Road Surface Profiler, Test Systems. Owner’s Manual, Version 2.3.4; Dynatest: Søborg, Denmark, 2007.
- Sayers, M.W.; Karamihas, S.M. The Little Book of Profiling: Basic Information about Measuring and Interpreting Road Profiles; Transportation Research Institute: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. E 1926–98; Standard Practice for Computing International Roughness Index of Roads from Longitudinal Profile Measurements. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Dynatest. Dynatest Data Collection (DDC); Dynatest: Søborg, Denmark, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Gu, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, W.; Wang, D. Automatic detection of asphalt pavement thickness: A method combining GPR images and improved Canny algorithm. Measurement 2022, 196, 111248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizos, A.; Plati, C. Accuracy of pavement thicknesses estimation using different ground penetrating radar analysis approaches. NDT E Int. 2007, 40, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuzzo-Scorpo, A.; Cook, A. Accuracy evaluation of traffic-speed coreless GPR techniques in pavement layer thickness estimation. In Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Advanced Ground Penetrating Radar (IWAGPR), Edinburgh, UK, 28–30 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marecos, V.; Fontul, S.; Solla, M.; de Lurdes Antunes, M. Evaluation of the feasibility of Common Mid-Point approach for air-coupled GPR applied to road pavement assessment. Measurement 2018, 128, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Z.; Al-Qadi, I.L. An innovative method for measuring pavement dielectric constant using the extended CMP method with two air-coupled GPR systems. NDTE Int. 2014, 66, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Olatubosun, O.O.; Zhang, H.; Sun, R. Automatic detection of asphalt layer thickness based on Ground Penetrating Radar. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 14–17 October 2016; pp. 2850–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, S.; Al-Qadi, I.L. Continuous real-time monitoring of flexible pavement layer density and thickness using ground penetrating radar. NDT E Int. 2018, 100, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarenketo, T. Electrical Properties of Road Materials and Subgrade Soils and the Use of Ground Penetrating Radar in Traffic Infrastructure Surveys. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Przybyla, C.P.; McDowell, D.L. Simulation-based extreme value marked correlations in fatigue of advanced engineering alloys. Procedia Eng. 2010, 2, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Highway Section | Subsection | Design Thickness (cm) |
|---|---|---|
| A | A1 | 20 |
| A2 | 22 | |
| A3 | 18 | |
| A4 | 24 | |
| A5 | 21 | |
| B | B1 | 13 |
| B2 | 17 | |
| B3 | 15 | |
| B4 | 20 | |
| B5 | 15 | |
| B6 | 17 | |
| B7 | 15 | |
| B8 | 19 |
| Highway Section | Subsection | Design Thickness (cm) | Average as Built Thickness (cm) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | A1 | 20 | 19.6 | 1.5 |
| A2 | 22 | 22.19 | 2.69 | |
| A3 | 18 | 18.89 | 1.17 | |
| A4 | 24 | 24.25 | 2.5 | |
| A5 | 21 | 21.34 | 1.94 | |
| B | B1 | 13 | 13.8 | 0.71 |
| B2 | 17 | 17.22 | 0.62 | |
| B3 | 15 | 15.7 | 0.89 | |
| B4 | 20 | 19.9 | 0.99 | |
| B5 | 15 | 15.2 | 3.33 | |
| B6 | 17 | 17.3 | 1.59 | |
| B7 | 15 | 15.67 | 1.78 | |
| B8 | 19 | 19.7 | 1.19 |
| IRIav | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 ≤ ΔhAC ≤ 2 cm | 2 < ΔhAC ≤ 5 cm | ΔhAC > 5 cm | |
| Mean | 1.01 | 1.10 | 1.22 |
| Median | 0.99 | 1.09 | 1.29 |
| Maximum | 1.91 | 1.92 | 1.62 |
| Minimum | 0.16 | 0.58 | 0.7 |
| Standard deviation | 0.37 | 0.41 | 0.27 |
| Coefficient of variance | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.22 |
| Parameters | IRIav | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 ≤ ΔhAC ≤ 2 cm | 2 < ΔhAC ≤ 5 cm | ΔhAC > 5 cm | |
| k | −0.14846 | −0.26674 | −0.68861 |
| σ | 0.33532 | 0.38739 | 0.30533 |
| μ | 0.85549 | 0.95588 | 1.1793 |
| Goodness of fit | |||
| Test statistic | 0.03256 | 0.06051 | 0.13735 |
| Significance level | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plati, C.; Georgouli, K.; Loizos, A. Using NDT Data to Assess the Effect of Pavement Thickness Variability on Ride Quality. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123011
Plati C, Georgouli K, Loizos A. Using NDT Data to Assess the Effect of Pavement Thickness Variability on Ride Quality. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(12):3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123011
Chicago/Turabian StylePlati, Christina, Konstantina Georgouli, and Andreas Loizos. 2023. "Using NDT Data to Assess the Effect of Pavement Thickness Variability on Ride Quality" Remote Sensing 15, no. 12: 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123011
APA StylePlati, C., Georgouli, K., & Loizos, A. (2023). Using NDT Data to Assess the Effect of Pavement Thickness Variability on Ride Quality. Remote Sensing, 15(12), 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123011