The Detection of Desert Aerosol Incorporating Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar and Rayleigh–Mie–Raman Lidar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Instrument
2.1. Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar
2.2. Rayleigh–Mie–Raman Lidar
3. Methodology
3.1. Retrieval Algorithm of the CDWL
3.2. Retrieval of the RMRL
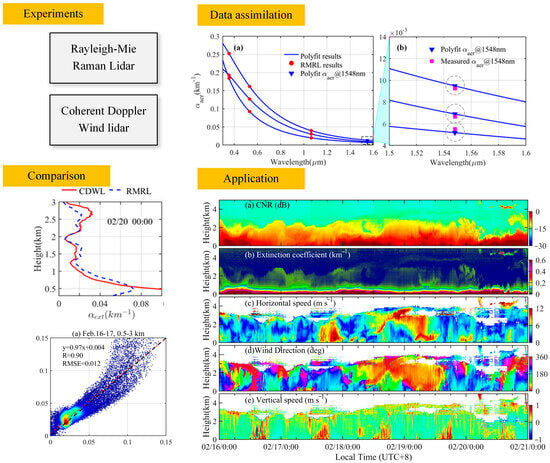
4. Experiments and Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kokhanovsky, A.A. Aerosol Optics: Light Absorption and Scattering by Particles in the Atmosphere; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stocker, T. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Caicedo, V.; Rappenglück, B.; Lefer, B.; Morris, G.; Toledo, D.; Delgado, R. Comparison of aerosol lidar retrieval methods for boundary layer height detection using ceilometer aerosol backscatter data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1609–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryazin, V.; Beresnev, S. Influence of vertical wind on stratospheric aerosol transport. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2011, 110, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wu, Y.; Shu, Z.; Su, L.; Tang, D.; Yang, Y.; Dong, J.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, H. Real-Time Synchronous 3-D Detection of Air Pollution and Wind Using a Solo Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.-E.; Favez, O.; Albinet, A.; Canonaco, F. A user-friendly tool for comprehensive evaluation of the geographical origins of atmospheric pollution: Wind and trajectory analyses. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 88, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, R.T.; Tratt, D.M. Airborne CO2 coherent lidar for measurements of atmospheric aerosol and cloud backscatter. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 5698–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.A.; Liu, Z.; Hunt, W.H.; Young, S.A. Overview of the CALIPSO mission and CALIOP data processing algorithms. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, A.; Nishizawa, T.; Jin, Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Wang, Z.; Batdorj, D.; Sugimoto, N. Evolution of a lidar network for tropospheric aerosol detection in East Asia. Opt. Eng. 2017, 56, 031219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D. A new cloud and aerosol layer detection method based on micropulse lidar measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 6788–6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, L.; Tang, D.; Dong, J.; Xia, H.; Dou, X. Stratospheric aerosol lidar with a 300 µm diameter superconducting nanowire single-photon detector at 1064 nm. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 2768–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.-M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S. A review of techniques for diagnosing the atmospheric boundary layer height (ABLH) using aerosol lidar data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, R.; Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A.; Müller, D.; Žeromskis, E.; Althausen, D.; Wehner, B. Lidar observations of the vertical aerosol flux in the planetary boundary layer. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2008, 25, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshinov, Y.F.; Bobrovnikov, S.M.; Zuev, V.E.; Mitev, V. Atmospheric temperature measurements using a pure rotational Raman lidar. Appl. Opt. 1983, 22, 2984–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, D.; Uchida, M.; Kobayashi, T. Ultraviolet high-spectral-resolution Rayleigh–Mie lidar with a dual-pass Fabry–Perot etalon for measuring atmospheric temperature profiles of the troposphere. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, H.; Dou, X.; Wu, T.; Hu, Y.; Li, M.; Shangguan, M.; Wei, T.; Zhao, L. Photon-counting distributed free-space spectroscopy. Light Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abshire, J.B.; Ramanathan, A.; Riris, H.; Mao, J.; Allan, G.R.; Hasselbrack, W.E.; Weaver, C.J.; Browell, E.V. Airborne measurements of CO2 column concentration and range using a pulsed direct-detection IPDA lidar. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 443–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Dou, X.; Sun, D.; Shu, Z.; Xue, X.; Han, Y.; Hu, D.; Han, Y.; Cheng, T. Mid-altitude wind measurements with mobile Rayleigh Doppler lidar incorporating system-level optical frequency control method. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 15286–15300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, S.C.; Senff, C.J.; Weickmann, A.M.; Brewer, W.A.; Banta, R.M.; Sandberg, S.P.; Law, D.C.; Hardesty, R.M. Doppler lidar estimation of mixing height using turbulence, shear, and aerosol profiles. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2009, 26, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiang, W.; Xia, H.; Wei, T.; Yuan, J.; Jiang, P. Robust solution for boundary layer height detections with coherent doppler wind lidar. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Xia, H.; Wei, T.; Wang, L.; Yue, B.; Wu, Y. Identifying cloud, precipitation, windshear, and turbulence by deep analysis of the power spectrum of coherent Doppler wind lidar. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 37406–37418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalikho, I.N.; Banakh, V.; Holzäpfel, F.; Rahm, S. Method of radial velocities for the estimation of aircraft wake vortex parameters from data measured by coherent Doppler lidar. Opt. Express 2015, 23, A1194–A1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Xia, H.; Hu, J.; Wang, C.; Shangguan, M.; Wang, L.; Jia, M.; Dou, X. Simultaneous wind and rainfall detection by power spectrum analysis using a VAD scanning coherent Doppler lidar. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 31235–31245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tridon, F.; Battaglia, A. Dual-frequency radar Doppler spectral retrieval of rain drop size distributions and entangled dynamics variables. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 5585–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelazim, S.; Santoro, D.; Arend, M.F.; Moshary, F.; Ahmed, S. Development and operational analysis of an all-fiber coherent Doppler lidar system for wind sensing and aerosol profiling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 6495–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, A. Analyzing the efficiency of a practical heterodyne lidar in the turbulent atmosphere: Telescope parameters. Opt. Express 2003, 11, 2041–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouza, F.; Reitebuch, O.; Groß, S.; Rahm, S.; Freudenthaler, V.; Toledano, C.; Weinzierl, B. Retrieval of aerosol backscatter and extinction from airborne coherent Doppler wind lidar measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 2909–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Wang, X.; Sun, K.; Wu, S.; Song, X.; Li, R.; Yin, J.; Wang, X. Calibration and retrieval of aerosol optical properties measured with Coherent Doppler Lidar. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2021, 38, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Preißler, J.; Wiegner, M.; von Löwis, S.; Petersen, G.N.; Parks, M.M.; Finger, D.C. Monitoring Dust Events Using Doppler Lidar and Ceilometer in Iceland. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Tan, W.; Guo, P.; Xu, Q.; Chen, S.; Lin, R.; Chen, S.; Chen, H. Two Practical Methods to Retrieve Aerosol Optical Properties from Coherent Doppler Lidar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, E.J.; Illingworth, A.J.; Hogan, R.J. A technique for autocalibration of cloud lidar. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2004, 21, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yang, Y.; O’Connor, E.J.; Lolli, S.; Haywood, J.; Osborne, M.; Cheng, J.C.; Guo, J.; Yim, S.H. Influence of a weak typhoon on the vertical distribution of air pollution in Hong Kong: A perspective from a Doppler LiDAR network. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentikäinen, P.; O’Connor, E.J.; Manninen, A.J.; Ortiz-Amezcua, P. Methodology for deriving the telescope focus function and its uncertainty for a heterodyne pulsed Doppler lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 2849–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsom, R.K.; Brewer, W.A.; Wilczak, J.M.; Wolfe, D.E.; Oncley, S.P.; Lundquist, J.K. Validating precision estimates in horizontal wind measurements from a Doppler lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.W.; Gatt, P.; Rees, D.; Huffaker, R.M. Wind lidar. In Laser Remote Sensing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 487–740. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, T.; Fukuchi, T. Laser Remote Sensing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Berkoff, T.A.; Welton, E.J.; Campbell, J.R.; Scott, V.; Spinhirne, J.D. Investigation of overlap correction techniques for the Micro-Pulse Lidar NETwork (MPLNET). In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2003, IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 4395–4397. [Google Scholar]
- Fernald, F.G. Analysis of atmospheric lidar observations: Some comments. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klett, J.D. Lidar inversion with variable backscatter/extinction ratios. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, M.; Takeuchi, N. Effects of misestimated far-end boundary values on two common lidar inversion solutions. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 6451–6456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinhuan, Q. Sensitivity of lidar equation solution to boundary values and determination of the values. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 1988, 5, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershov, A.D.; Balin, Y.S.; Samoilova, S.V. Inversion of the lidar data in investigations of the optical characteristics of weakly turbid atmosphere. In Ninth Joint International Symposium on Atmospheric and Ocean Optics/Atmospheric Physics. Part II: Laser Sensing and Atmospheric Physics; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2003; pp. 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Zhang, J.; Mao, F.; Li, J. Measurements for profiles of aerosol extinction coeffcient, backscatter coeffcient, and lidar ratio over Wuhan in China with Raman/Mie lidar. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2010, 8, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melfi, S. Remote measurements of the atmosphere using Raman scattering. Appl. Opt. 1972, 11, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, D.; Melfi, S.; Ferrare, R. Raman lidar system for the measurement of water vapor and aerosols in the Earth’s atmosphere. Appl. Opt. 1992, 31, 3068–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N. Angstrom exponent and bimodal aerosol size distributions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D07207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, N.; Eck, T.; Holben, B.; Smirnov, A.; Dubovik, O.; Royer, A. Bimodal size distribution influences on the variation of Angstrom derivatives in spectral and optical depth space. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 9787–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameter | CDWL | RMRL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser | |||
| Wavelength | 1548 nm | 355/532/1064 nm | |
| Frequency offset | 80 MHz | / | |
| Pulse energy | 110 μJ | 250/350/350 mJ | |
| Repetition rate | 10 kHz | 20 Hz | |
| Pulse width | 200 ns | 8 ns | |
| Telescope | |||
| Diameter | 100 mm | 450 mm | |
| Elevation angle | 70° | 90° | |
| Data acquisition | Detection type | BD | PMT |
| Noise bandwidth | 200 MHz | 0.3 nm | |
| Sampling rate | 250 MHz | 20 MHz | |
| Temporal resolution | 1 s | 60 s | |
| Spatial resolution | 30, 60, 150 m | 30 m |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Xia, H.; Su, L.; Han, H.; Wang, X.; Yuan, J. The Detection of Desert Aerosol Incorporating Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar and Rayleigh–Mie–Raman Lidar. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5453. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235453
Li M, Xia H, Su L, Han H, Wang X, Yuan J. The Detection of Desert Aerosol Incorporating Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar and Rayleigh–Mie–Raman Lidar. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(23):5453. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235453
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Manyi, Haiyun Xia, Lian Su, Haobin Han, Xiaofei Wang, and Jinlong Yuan. 2023. "The Detection of Desert Aerosol Incorporating Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar and Rayleigh–Mie–Raman Lidar" Remote Sensing 15, no. 23: 5453. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235453
APA StyleLi, M., Xia, H., Su, L., Han, H., Wang, X., & Yuan, J. (2023). The Detection of Desert Aerosol Incorporating Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar and Rayleigh–Mie–Raman Lidar. Remote Sensing, 15(23), 5453. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235453