Estimation and Evaluation of Zenith Tropospheric Delay from Single and Multiple GNSS Observations
Abstract
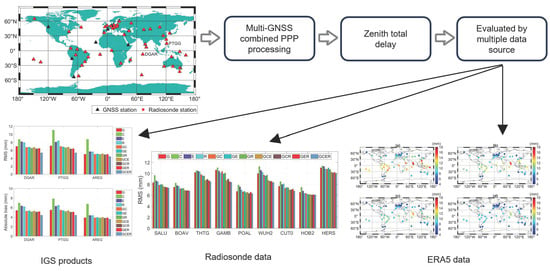
:1. Introduction
2. Observation Model and Processing Strategy
3. Data Collection
3.1. GNSS Data
3.2. Radiosonde Data
3.3. ERA5 Data
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. ZTD from Single-GNSS
4.2. ZTD from Multi-GNSS
4.3. Evaluation by IGS Final Products
4.4. Validation by Radiosonde and ERA5
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, S.; Feng, G.P.; Gleason, S. Remote sensing using GNSS signals: Current status and future directions. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Wang, Q.; Dardanelli, G. A Review on Multi-GNSS for Earth Observation and Emerging Applications. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negusini, M.; Petkov, B.H.; Sarti, P.; Tomasi, C. Ground-Based Water Vapor Retrieval in Antarctica: An Assessment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2935–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ildikó, J.; Szabolcs, R. Developing a global model for the conversion of zenith wet tropospheric delays to integrated water vapour. Acta Geod. Geophys. 2018, 53, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Herring, T.A.; Rocken, C.; Anthes, R.A.; Ware, R.H. GPS meteorology: Remote sensing of atmospheric water vapor using the global positioning system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 15787–15801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edokossi, K.; Calabia, A.; Jin, S.G.; Molina, I. GNSS-Reflectometry and Remote Sensing of Soil Moisture: A review of measurement techniques, methods and applications. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabia, A.; Molina, I.; Jin, S.G. Soil moisture content from GNSS reflectometry using dielectric permittivity from fresnel reflection coefficients. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urlichich, Y.; Subbotin, V.; Stupak, G.; Dvorkin, V.; Povalyaev, A.; Karutin, S. GLONASS modernization. In Proceedings of the 24th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2011), Portland, OR, USA, 19–23 September 2011; pp. 3125–3128. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; Yang, Y.; Cai, Z. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System and its time scales. Metrologia 2011, 48, S213–S218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Hauschild, A. Broadcast versus precise ephemerides: A multi-GNSS perspective. GPS Solut. 2014, 19, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Stürze, A.; Weber, G.; et al. The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS)–Achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, J.M.; Neilan, R.E.; Rizos, C. The International GNSS Service in a changing landscape of Global Navigation Satellite Systems. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; He, C.; Cheng, Y.; Li, X. Determination of zenith hydrostatic delay and its impact on GNSS-derived integrated water vapor. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 2807–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Li, X.; Ge, M.; Heinkelmann, R.; Nilsson, T.; Soja, B.; Dick, G.; Schuh, H. Estimation and evaluation of real-time precipitable water vapor from GLONASS and GPS. GPS Solut. 2015, 20, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbuz, G.; Akgul, V.; Gormus, K.S.; Kutoglu, S.H. Assessment of precipitable water vapor over Turkey using GLONASS and GPS. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2021, 222, 105712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Fritsche, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Precise positioning with current multi-constellation Global Navigation Satellite Systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and BeiDou. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Dai, X.; Ren, X.; Fritsche, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Accuracy and reliability of multi-GNSS real-time precise positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 607–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Xu, Z.; Ge, M.; Xu, X.; Zhu, H.; Sui, X. Estimating Zenith Tropospheric Delays from BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Observations. Sensors 2013, 13, 4514–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Li, X.; Nilsson, T.; Ning, T.; Heinkelmann, R.; Ge, M.; Glaser, S.; Schuh, H. Real-time retrieval of precipitable water vapor from GPS and BeiDou observations. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dick, G.; Lu, C.; Ge, M.; Nilsson, T.; Ning, T.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Multi-GNSS Meteorology: Real-Time Retrieving of Atmospheric Water Vapor from BeiDou, Galileo, GLONASS, and GPS Observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 6385–6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Ding, N.; Holden, L.; Wang, X.; Zheng, N. GNSS-RS Tomography: Retrieval of Tropospheric Water Vapor Fields Using GNSS and RS Observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4102313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, G.; Dick, G.; Wickert, J.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, K.; Schuh, H. Real-Time Tropospheric Delays Retrieved from Multi-GNSS Observations and IGS Real-Time Product Streams. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Li, X.; Cheng, J.; Dick, G.; Ge, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Real-Time Tropospheric Delay Retrieval from Multi-GNSS PPP Ambiguity Resolution: Validation with Final Troposphere Products and a Numerical Weather Model. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, G.; Song, S.; Ge, Y.; Su, K.; Liu, Y. Assessment of BeiDou-3 and Multi-GNSS Precise Point Positioning Performance. Sensors 2019, 19, 2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcay, S.; Turgut, M. Evaluation of the positioning performance of multi-GNSS RT-PPP method. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmohammadian, F.; Asgari, J.; Verhagen, S.; Amiri-Simkooei, A. Multi-GNSS-Weighted Interpolated Tropospheric Delay to Improve Long-Baseline RTK Positioning. Sensors 2022, 22, 5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nzelibe, I.U.; Tata, H.; Idowu, T.O. Assessment of GNSS zenith tropospheric delay responses to atmospheric variables derived from ERA5 data over Nigeria. Satell. Navig. 2023, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Li, W. An analysis of multisource tropospheric hydrostatic delays and their implications for GPS/GLONASS PPP-based zenith tropospheric delay and height estimations. J. Geod. 2021, 95, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shi, C.; Gong, J.; Zhao, Q.; Geng, J.; Wu, H.; Lou, Y.; Ge, M.; Liu, J. Recent development of PANDA software in GNSS data processing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Earth Observation Data Processing and Analysis (ICEODPA), Wuhan, China, 28–30 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Ge, M. Regional reference network augmented precise point positioning for instantaneous ambiguity resolution. J. Geod. 2010, 85, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyard, F.; Lefevre, F.; Letellier, T.; Francis, O. Modelling the global ocean tides: Modern insights from FES2004. Ocean Dyn. 2006, 56, 394–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J. A Guide to Using International GNSS Service (IGS) Products; International Gnss Service: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- van Dam, T.; Collilieux, X.; Wuite, J.; Altamimi, Z.; Ray, J. Nontidal ocean loading: Amplitudes and potential effects in GPS height time series. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the theory of atmospheric refraction. Bull. Géod. 2008, 105, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Zhang, H.; Wickert, J. A method for improving uncalibrated phase delay estimation and ambiguity-fixing in real-time precise point positioning. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niell, A.E.; Coster, A.J.; Solheim, F.S.; Mendes, V.B.; Toor, P.C.; Langley, R.B.; Upham, C.A. Comparison of Measurements of Atmospheric Wet Delay by Radiosonde, Water Vapor Radiometer, GPS, and VLBI. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2001, 18, 830–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Dai, A.; Van Hove, T.; Van Baelen, J. A near-global, 2-hourly data set of atmospheric precipitable water from ground-based GPS measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cole, H.L.; Carlson, D.J.; Miller, E.R.; Beierle, K.; Paukkunen, A.; Laine, T.K. Corrections of Humidity Measurement Errors from the Vaisala RS80 Radiosonde—Application to TOGA COARE Data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 981–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhang, B.; Guo, J. An improved global zenith tropospheric delay model GZTD2 considering diurnal variations. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2016, 23, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liang, H.; Lou, Y.; Cai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W. On the suitability of ERA5 in hourly GPS precipitable water vapor retrieval over China. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1897–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albergel, C.; Dutra, E.; Munier, S.; Calvet, J.-C.; Munoz-Sabater, J.; de Rosnay, P.; Balsamo, G. ERA-5 and ERA-Interim driven ISBA land surface model simulations: Which one performs better? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 3515–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.; Spang, R. An assessment of tropopause characteristics of the ERA5 and ERA-Interim meteorological reanalyses. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 4019–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlis, N.K.; Holmes, S.A.; Kenyon, S.C.; Factor, J.K. The development and evaluation of the Earth Gravitational Model 2008 (EGM2008). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Ye, S.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; Xia, P. Retrieving Precipitable Water Vapor Data Using GPS Zenith Delays and Global Reanalysis Data in China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, H. The Performance of Different Mapping Functions and Gradient Models in the Determination of Slant Tropospheric Delay. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobiger, T.; Ichikawa, R.; Koyama, Y.; Kondo, T. Fast and accurate ray-tracing algorithms for real-time space geodetic applications using numerical weather models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Item | Strategies |
|---|---|
| Estimator | Sequential least squares estimator |
| Observations | Raw carrier phase and pseudo-range observations; GPS + BDS + Galileo + GLONASS, about 126 satellites |
| Signal selection | GPS: L1/L2; GLONASS: L1/L2; Galileo: E1/E5a; BDS: B1/B2 |
| Sampling rate | 30s |
| Elevation cut-off | 7° |
| Weight for observations | Elevation-dependent weighting strategy |
| Receiver clock | Estimated, white noise |
| Satellite clock | Fixed |
| Satellite orbit | Fixed |
| ISB and IFB | Estimated as constant, GPS as reference |
| Phase wind-up effect | Corrected |
| Mapping function | GMF |
| Zenith Tropospheric delay | Initial modal + random walk model |
| Station displacement | Solid Earth tide, pole tide, ocean tide loading |
| Satellite antenna phase center | Corrected |
| Receiver antenna phase center | Corrected |
| Station coordinate | Fixed to coordinates of weekly solution |
| RS Station | GNSS Station | Elevation Difference (m) | Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 82281 | SALU | 16 | 2.1 |
| 82022 | BOAV | 67 | 1.6 |
| 91938 | THTG | 79 | 3.3 |
| 91948 | GAMB | 58 | 0.5 |
| 83971 | POAL | 47 | 10.0 |
| 57494 | WUH2 | −4 | 23.8 |
| 94610 | CUT0 | −7 | 9.7 |
| 94975 | HOB2 | −1 | 4.3 |
| 03882 | HERS | 26 | 3.8 |
| Solution | RMS (mm) | Bias (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| GPS | 8.7 | 5.1 |
| BDS | 9.5 | 5.6 |
| Galileo | 9.0 | 5.3 |
| GLONASS | 8.8 | 5.1 |
| GPS/BDS | 8.4 | 4.9 |
| GPS/Galileo | 8.3 | 4.8 |
| GPS/GLONASS | 8.3 | 4.9 |
| GPS/BDS/Galileo | 7.8 | 4.6 |
| GPS/BDS/GLONASS | 7.8 | 4.6 |
| GPS/Galileo/GLONASS | 7.8 | 4.5 |
| GPS/BDS/Galileo/GLONASS | 7.6 | 4.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, S.; Jin, S.; Jin, X. Estimation and Evaluation of Zenith Tropospheric Delay from Single and Multiple GNSS Observations. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5457. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235457
Xia S, Jin S, Jin X. Estimation and Evaluation of Zenith Tropospheric Delay from Single and Multiple GNSS Observations. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(23):5457. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235457
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Sai, Shuanggen Jin, and Xuzhan Jin. 2023. "Estimation and Evaluation of Zenith Tropospheric Delay from Single and Multiple GNSS Observations" Remote Sensing 15, no. 23: 5457. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235457
APA StyleXia, S., Jin, S., & Jin, X. (2023). Estimation and Evaluation of Zenith Tropospheric Delay from Single and Multiple GNSS Observations. Remote Sensing, 15(23), 5457. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235457