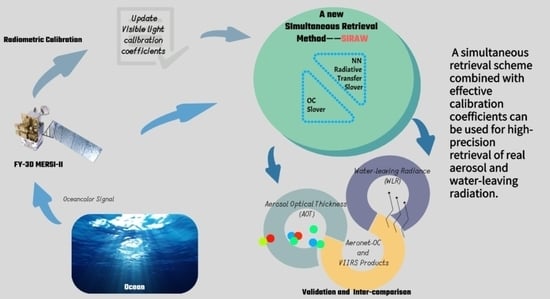
Remote Sensing of Aerosols and Water-Leaving Radiance from Chinese FY-3/MERSI Based on a Simultaneous Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data and Study Area
2.1.1. FY-3D/MERSI-II Satellite Data
2.1.2. Global/Regional Assimilation and Prediction Enhanced System (GRAPES) Data
2.1.3. AERONET-OC In Situ Measurement Data
2.1.4. Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) OC Satellite Data
2.1.5. Match-Up Procedure
2.2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Validation of NN Radiative Transfer Solver
3.2. Validation with AERONET-OC
3.3. Inter-Comparison with VIIRS Images
4. Discussion
4.1. Calibration Coefficient Correction
4.2. Inversion of Water-Leaving Radiance Based on FY-3D Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Platt, T.; Sathyendranath, S.; Forget, M.H.; White, G.N.; Caverhill, C.; Bouman, H.; Devred, E.; Son, S.H. Operational estimation of primary production at large geographical scales. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3437–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.T.O. Light and Photosynthesis in Aquatic Ecosystems, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 1–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C.; Jun, F.; Jihong, S. Influences of geometric correction on the accuracy of dark pixel atmospheric correction algorithm and water leaving irradiance retrieval:a case study of Lake Taihu. J. Lake Sci. 2011, 23, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R. Removal of atmospheric effects from satellite imagery of the oceans. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 1631–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Retrieval of water-leaving radiance and aerosol optical thickness over the oceans with SeaWiFS: A preliminary algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, Z.; Montes, M.J.; Davis, C.O.; Gao, B.-C. Atmospheric correction algorithm for hyperspectral remote sensing of ocean color from space. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, D.; Morel, A. A multiple scattering algorithm for atmospheric correction of remotely sensed ocean colour (MERIS instrument): Principle and implementation for atmospheres carrying various aerosols including absorbing ones. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1875–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, H.; Higurashi, A.; Mitomi, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Noguchi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Toratani, M. Correction of atmospheric effect on ADEOS/OCTS ocean color data: Algorithm description and evaluation of its performance. J. Oceanogr. 1998, 54, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Nakajima, T. Simultaneous determination of aerosol optical thickness and water-leaving radiance from multispectral measurements in coastal waters. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 3865–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Pan, D.; Mao, Z. Atmospheric correction of Sea WiFS imagery for turbid coastal and inland waters. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2004, 23, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Bai, Y.; Pan, D.; Tang, J.; Wang, D. Atmospheric correction of satellite ocean color imagery using the ultraviolet wavelength for highly turbid waters. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 20754–20770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W.; Esaias, W.E.; Abbott, M.R.; Barton, I.; Brown, O.B.; Campbell, J.W.; Carder, K.L.; Clark, D.K.; Evans, R.L.; et al. The NIR-SWIR combined atmospheric correction approach for MODIS ocean color data processing. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 15722–15733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Carder, K.L.; Muller-Karger, F.E. Atmospheric Correction of SeaWiFS Imagery over Turbid Coastal Waters: A Practical Method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 74, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W.; Franz, B.A.; Werdell, P.J. Estimation of near-infrared water-leaving reflectance for satellite ocean color data processing. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 7521–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.F.; Aiken, J.; Lavender, S.J. The atmospheric correction of water colour and the quantitative retrieval of suspended particulate matter in Case II waters: Application to MERIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 20, 1713–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.A.; Wang, M.; Maritorena, S.; Robinson, W. Atmospheric correction of satellite ocean color imagery: The black pixel assumption. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 3582–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomko, R.M.; Gordon, H.R. Atmospheric correction of ocean color imagery: Use of the junge power-law aerosol size distribution with variable refractive index to handle aerosol absorption. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 5560–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchinke, C.P.; Gordon, H.R.; Franz, B.A. Spectral optimization for constituent retrieval in Case 2 waters I: Implementation and performance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, P.E.; Haigh, J.D. Atmospheric correction over case 2 waters with an iterative fitting algorithm: Relative humidity effects. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 9448–9455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Nakajima, T.; Hashimoto, M. Simultaneous retrieval of aerosol optical thickness and chlorophyll concentration from multiwavelength measurement over east China sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 14,084–14,101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frouin, R.J.; Franz, B.A.; Ibrahim, A.; Knobelspiesse, K.; Ahmad, Z.; Cairns, B.; Chowdhary, J.; Dierssen, H.M.; Tan, J.; Dubovik, O.; et al. Atmospheric Correction of Satellite Ocean-Color Imagery during the PACE Era. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brajard, J.; Jamet, C.; Moulin, C.; Thiria, S. Use of a neuro-variational inversion for retrieving oceanic and atmospheric constituents from satellite ocean colour sensor: Application to absorbing aerosols. Neural Netw. 2006, 19, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamet, C.; Thiria, S.; Moulin, C.; Crepon, M. Use of a Neurovariational Inversion for Retrieving Oceanic and Atmospheric Constituents from Ocean Color Imagery: A Feasibility Study. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, T.; Behnert, I.; Schaale, M.; Fischer, J.; Doerffer, R. Atmospheric correction algorithm for MERIS above case-2 waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1469–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulquin, B.; Fablet, R.; Bourg, L.; Mercier, G.; d’Andon, O.F. MEETC2: Ocean color atmospheric corrections in coastal complex waters using a Bayesian latent class model and potential for the incoming sentinel 3—OLCI mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 172, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamnes, K.; Li, W.; Yan, B.; Eide, H.; Barnard, A.; Pegau, W.S.; Stamnes, J.J. Accurate and self-consistent ocean color algorithm: Simultaneous retrieval of aerosol optical properties and chlorophyll concentrations. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Zhai, P.W.; Franz, B.; Hu, Y.; Knobelspiesse, K.; Werdell, P.J.; Ibrahim, A.; Xu, F.; Cairns, B. Retrieval of aerosol properties and water-leaving reflectance from multi-angular polarimetric measurements over coastal waters. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 8968–8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Li, W.; Gatebe, C.K.; Jamet, C.; Zibordi, G.; Schroeder, T.; Stamnes, K. Atmospheric correction over coastal waters using multilayer neural networks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 218–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Hashimoto, M.; Shiomi, K.; Nakajima, T. Development of an Algorithm to Retrieve Aerosol Optical Properties over Water Using an Artificial Neural Network Radiative Transfer Scheme: First Result from GOSAT-2/CAI-2. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 9861–9872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, F.; Xu, N.; Zhang, X. A Novel Algorithm of Haze Identification Based on FY3D/MERSI-II Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Kang, Q.; Wei, W.; Zheng, X.B.; Zhang, Y. On-orbit Radiometric Calibration for Thermal Infrared Band of FY3D/MERSI-II Satellite Remote Sensor Based on Qinghai Lake Radiation Calibration Test-site. Guangzi Xuebao/Acta Photonica Sin. 2020, 49, 0528002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bonetti, S.; Yuan, Z.; Wei, N. Coupling a New Version of the Common Land Model (CoLM) to the Global/Regional Assimilation and Prediction System (GRAPES): Implementation, Experiment, and Preliminary Evaluation. Land 2022, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Tanr, D.; Smirnov, A.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Abuhassan, N.; Newcomb, W.W.; Schafer, J.S.; Chatenet, B.; Lavenu, F.; et al. An emerging ground-based aerosol climatology: Aerosol optical depth from AERONET. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 12067–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Mélin, F.; Berthon, J.F. Comparison of SeaWiFS, MODIS and MERIS radiometric products at a coastal site. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Holben, B.; Hooker, S.; Mélin, F.; Berthon, J.F.; Slutsker, I.; Giles, D.; Vandemark, D.; Feng, H.; Rutledge, K.; et al. A network for standardized ocean color validation measurements. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2006, 87, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straka, W.C.; Seaman, C.J.; Baugh, K.; Cole, K.; Stevens, E.; Miller, S.D. Utilization of the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (NPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) Day/Night Band for Arctic Ship Tracking and Fisheries Management. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 971–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, M.; Shi, C.; Hashimoto, M.; Nakajima, T. Analysis and validation of ocean color and aerosol properties over coastal regions from SGLI based on a simultaneous method. J. Oceanogr. 2022, 78, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaka, J.; Hirawake, T.; Toratani, M.; Frouin, R. Special section for second-generation global imager (SGLI). J. Oceanogr. 2022, 78, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, Y.; Higurashi, A.; Nakajima, T.; Yokota, T. Matrix formulations of radiative transfer including the polarization effect in a coupled atmosphere–ocean system. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2010, 111, 878–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Tsukamoto, M.; Tsushima, Y.; Numaguti, A.; Kimura, T. Modeling of the radiative process in an atmospheric general circulation model. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 4869–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Tanaka, M. Matrix formulations for the transfer of solar radiation in a plane-parallel scattering atmosphere. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1986, 35, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Tanaka, M. Algorithms for radiative intensity calculations in moderately thick atmospheres using a truncation approximation. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1988, 40, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Tanaka, M. Effect of wind-generated waves on the transfer of solar radiation in the atmosphere-ocean system. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1983, 29, 521–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, P.; Nakajima, T.; Ota, Y.; Tan, S.; Shi, G.; Shi, C.; Wang, P.; Nakajima, T.; Ota, Y.; et al. Effects of ocean particles on the upwelling radiance and polarized radiance in the atmosphere-ocean system. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 1186–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokhanovsky, A.A.; Budak, V.P.; Cornet, C.; Duan, M.; Emde, C.; Katsev, I.L.; Klyukov, D.A.; Korkin, S.V.; C-Labonnote, L.; Mayer, B.; et al. Benchmark results in vector atmospheric radiative transfer. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2010, 111, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Holben, B.; Slutsker, I.; Giles, D.; D’alimonte, D.; Mélin, F.; Berthon, J.F.; Vandemark, D.; Feng, H.; Schuster, G.; et al. AERONET-OC: A Network for the Validation of Ocean Color Primary Products. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1634–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansock, J.; Bancroft, D.; Butler, J.; Cao, C.; Datla, R.; Hansen, S.; Helder, D.; Kacker, R.; Latvakoski, H.; Mlynczak, M.; et al. NISTHB 157 Guidelines for Radiometric Calibration of Electro-Optical Instruments for Remote Sensing; U.S. Department of Commerce: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Wei, W.; Du, S.; Guo, F. Vicarious radiometric calibration of ocean color bands for fy-3d/mersi-ii at lake Qinghai, China. Sensors 2021, 21, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-M.; Hu, X.-Q.; Xu, W.-B.; Zheng, X.-B. Analysis on Response Degradation of Medium Resolution Spectral Imager on FY-3B. J. Atmos. Environ. Opt. 2014, 9, 376–383. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Guo, M.-H.; Xu, N.; Zhang, L.-J.; Liu, J.-J.; Hu, X.-Q.; Li, Y.; Rong, Z.-G.; Zhao, Z.-H. On-Orbit Response Variation Analysis of FY-3 MERSI Reflective Solar Bands Based on Dunhuang Site Calibration. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2012, 32, 1869–1877. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Hu, X.; He, Y.; Gao, K. Response Degradation Analysis of Fengyun-3A Medium-Resolution Spectral Imager Based on Intelligent Detection of Invariant Pixels. Acta Opt. Sin. 2019, 39, 0912001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wu, R.; Hu, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Sun, L. Integrated method for on-obit wide dynamic vicarious calibration of FY-3C mersi reflective solar bands. Guangxue Xuebao/Acta Opt. Sin. 2015, 35, 1228001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Purpose | Band | Central Wavelength (μm) | Spectral Bandwidth (nm) | Spatial Resolution/IFOV at S.S.P. (m) | SNR or NEΔT (K) | Maximum Reflectance ρ or Dynamic Range (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ocean watercolor, plankton, biogeochemical remote sensing | 8 | 0.412 | 20 | 1000 | 300 | 30% |
| 9 | 0.443 | 300 | ||||
| 10 | 0.490 | 300 | ||||
| 11 | 0.555 | 500 | ||||
| 12 | 0.670 | 500 | ||||
| 13 | 0.709 | 500 | ||||
| 14 | 0.746 | 500 | ||||
| 15 | 0.865 | 500 |
| Data | Dataset Name | Unit | Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| 101 layers of pressure value | plev | pa | 101 × 720 × 1440 |
| surface pressure (PRES) | psfc | pa | 720 × 1440 |
| Mean sea level pressure (PRMSL) | pmsl | pa | 720 × 1440 |
| 10 m u-component of wind (UGRD) | u-sigma | m/s | 720 × 1440 |
| 10 m v-component of wind (VGRD) | v-sigma | m/s | 720 × 1440 |
| Total column ozone | O3col | Du | 720 × 1440 |
| Relative humidity (RH) | rhlev | % | 101 × 720 × 1440 |
| Band | Wavelength (µm) | FWHM (µm) |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | 0.410 | 0.020 |
| M2 | 0.443 | 0.018 |
| M3 | 0.486 | 0.020 |
| M4 | 0.551 | 0.020 |
| M5 | 0.671 | 0.020 |
| Calibration Relative Deviation (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| March 2020 | August 2022 | |
| Band 8 | −2.35 | −19.32 |
| Band 9 | −1.86 | −11.31 |
| Wavelength (nm) | K0 | K1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 412 | −1.682800 | 0.010300 |
| 443 | −1.573260 | 0.008719 | |
| Newest | 412 | −2.230508 | 0.012328 |
| 443 | −1.755604 | 0.009795 |
| Before | After | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | MBE | RMSE | BIAS | MRB | R | MBE | RMSE | BIAS | MRB | |
| 412 nm | 0.42 | 0.0076 | 0.009 | 0.008 | 65.74% | 0.87 | 0.0016 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 23.00% |
| 443 nm | 0.37 | 0.0041 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 48.00% | 0.87 | 0.0013 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 21.70% |
| 490 nm | 0.29 | 0.0009 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 24.49% | 0.75 | 0.0006 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 13.22% |
| 555 nm | 0.75 | 0.0015 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 55.26% | 0.81 | 0.0010 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 30.32% |
| 670 nm | 0.69 | 0.0002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 153.50% | 0.74 | 0.0001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 70.38% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Shi, C.; Si, Y.; Letu, H.; Wang, L.; Tang, C.; Xu, N.; He, X.; Yin, S.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Remote Sensing of Aerosols and Water-Leaving Radiance from Chinese FY-3/MERSI Based on a Simultaneous Method. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245650
Zhang X, Shi C, Si Y, Letu H, Wang L, Tang C, Xu N, He X, Yin S, Zhang Z, et al. Remote Sensing of Aerosols and Water-Leaving Radiance from Chinese FY-3/MERSI Based on a Simultaneous Method. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(24):5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245650
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaohan, Chong Shi, Yidan Si, Husi Letu, Ling Wang, Chenqian Tang, Na Xu, Xianqiang He, Shuai Yin, Zhihua Zhang, and et al. 2023. "Remote Sensing of Aerosols and Water-Leaving Radiance from Chinese FY-3/MERSI Based on a Simultaneous Method" Remote Sensing 15, no. 24: 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245650
APA StyleZhang, X., Shi, C., Si, Y., Letu, H., Wang, L., Tang, C., Xu, N., He, X., Yin, S., Zhang, Z., & Chen, L. (2023). Remote Sensing of Aerosols and Water-Leaving Radiance from Chinese FY-3/MERSI Based on a Simultaneous Method. Remote Sensing, 15(24), 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245650