Hybrid Domain Efficient Modulation-Based Deceptive Jamming Algorithm for Nonlinear-Trajectory Synthetic Aperture Radar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
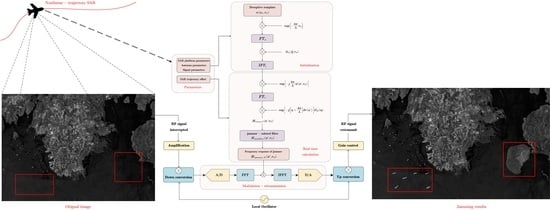
2. Nonlinear-Trajectory SAR Deception Jamming Algorithm Based on HDE
2.1. Nonlinear-Trajectory SAR System Model
2.2. Nonlinear-Trajectory SAR Deception Jamming Principle
2.3. Deceptive Jamming Based on HDE
2.3.1. Decomposition of JFR
2.3.2. Fast Algorithm of the SAR System-Related Filter Based on HDE
3. Workflow and Validity Analysis of HDE Algorithm
3.1. HDE Algorithm Workflow
- SAR platform parameters, such as SAR flight altitude H, motion velocity v;
- Antenna parameters, such as antenna elevation angle , synthetic aperture length L;
- Signal parameters, such as the carrier frequency f, bandwidth , chirp pulse duration and PRI ;
- (1)
- The first stage is jammer initialization. First, a deceptive template with complex backscatter coefficients is obtained. Then according to the SAR platform parameters and signal parameters, the jammer performs the phase compensation of the shortest slant range on the deceptive template and combines the antenna parameters to construct the azimuth frequency modulation term of the deceptive template in the SAR azimuth frequency domain. Finally, the azimuth frequency modulation term is converted to the azimuth time domain to form an initialization template for the jammer to perform trajectory deviation construction in the real-time calculation stage.
- (2)
- In the real-time calculation stage, since the trajectory deviation of nonlinear-trajectory SAR is difficult to calculate in advance, the jammer needs to obtain the SAR trajectory deviation in real time for pulse-by-pulse trajectory deviation construction. First, the SAR trajectory deviation of the current pulse time is obtained, and the trajectory deviation components and are calculated through Equation (5). Then the jammer performs the construction of the range space-variant trajectory deviation in the range time domain, and performs the construction of the space-invariant trajectory deviation and the range frequency modulation in the range frequency domain, from which the current pulse SAR system-related filter can be constructed. Finally, the jammer obtains the JFR for the current pulse time based on Equation (36).
3.2. Validity Analysis of HDE Algorithm
- A.
- Center beam approximation error
- B.
- Validity of function decomposition
- C.
- Effect of approximation on deceptive jamming Imaging
4. Simulation and Result
4.1. Fake Point Scatters Simulation
4.2. General Deceptive Scene Case
4.3. Computational Complexity Analysis
5. Discussion
- The range imaging quality of the fake point target is related to the fake target point’s slant-range length . As becomes longer, the range broadening of the target will become larger.
- The azimuth imaging quality of the fake target is related to the slant-range length and trajectory deviation of the fake target. As becomes longer, the azimuth broadening of the fake target will become larger. As the trajectory deviation becomes larger, the peak sidelobe ratio PSLR in the azimuth direction will become higher, and the sidelobes will be asymmetrical.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Digital Processing Of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data; Artech House Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 473–476. [Google Scholar]
- Condley, C. Some System Considerations for Electronic Countermeasures to Synthetic Aperture Radar. In Proceedings of the IEE Colloquium on Electronic Warfare Systems, London, UK, 14 January 1991; pp. 8/1–8/7. [Google Scholar]
- Dumper, K.; Cooper, P.; Wons, A.; Condley, C.; Tully, P. Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar and Noise Jamming. In Proceedings of the Radar 97 (Conf. Publ. No. 449), Edinburgh, UK, 14–16 October 1997; pp. 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouts, D.J.; Pace, P.E.; Karow, C.; Ekestorm, S. A Single-Chip False Target Radar Image Generator for Countering Wideband Imaging Radars. IEEE J.-Solid-State Circuits 2002, 37, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Park, J.; Shin, W.; Lee, K.; Kang, H. A Study on Jamming Performance Evaluation of Noise and Deception Jammer against SAR Satellite. In Proceedings of the 2011 3rd International Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 26–30 September 2011; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.; Ruan, H.; Zhang, S.x.; Yan, L. Study of Noise Jamming Based on Convolution Modulation to SAR. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Computer, Mechatronics, Control and Electronic Engineering, Changchun, China, 24–26 August 2010; Volume 6, pp. 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmatyuk, D.; Narayanan, R. ECCM Capabilities of an Ultrawideband Bandlimited Random Noise Imaging Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2002, 38, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wang, Y.; Jin, G.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Wang, B.; Zhou, L.; Lu, P.; Wu, Y. A Novel Jamming Method against SAR Using Nonlinear Frequency Modulation Waveform with Very High Sidelobes. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Z.; Shu, G.; Li, N. A Repeater-Type SAR Deceptive Jamming Method Based on Joint Encoding of Amplitude and Phase in the Intra-Pulse and Inter-Pulse. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.U.; Jin, N.I.; Zhang, G. A Study on the Active Deception Jamming to SAR. Acta Electron. Sin. 2003, 31, 1900–1902. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Guoqing, Z.; Yu, Z. Research on SAR Jamming Technique Based on Man-made Map. In Proceedings of the 2006 CIE International Conference on Radar, Shanghai, China, 16–19 October 2006; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Liu, P.; Xue, G. Fast Generation of SAR Deceptive Jamming Signal Based on Inverse Range Doppler Algorithm. In Proceedings of the IET International Radar Conference 2013, Xi’an, China, 14–16 April 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Du, D.; Tang, B. False Target Deceptive Jamming for Countering Missile-Borne SAR. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 17th International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering, Chengdu, China, 19–21 December 2014; pp. 1974–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zhao, B.; Tao, M.; Bai, X.; Chen, B.; Sun, G. A Large Scene Deceptive Jamming Method for Space-Borne SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4486–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Shu, T.; Zhou, S.; Tang, B.; Yu, W. A Novel Jamming Signal Generation Method for Deceptive SAR Jammer. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 19–23 May 2014; pp. 1174–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhou, F.; Bao, Z. Deception Jamming for Squint SAR Based on Multiple Receivers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3988–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Huang, L.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, J. Performance Improvement of Deception Jamming Against SAR Based on Minimum Condition Number. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 1039–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Shu, T.; Yu, K.B.; Yu, W. Efficient Deceptive Jamming Method of Static and Moving Targets Against SAR. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 3610–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, W.; Pan, X.; Dai, D.; Feng, D. A Frequency-Domain Three-Stage Algorithm for Active Deception Jamming against Synthetic Aperture Radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2014, 8, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Pan, X.; Fu, Q.; Wang, G. Inverse Omega-K Algorithm for the Electromagnetic Deception of Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 3037–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Huang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, J. Deceptive SAR Jamming Based on 1-Bit Sampling and Time-Varying Thresholds. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Ye, W.; Ma, F.; Li, G.; Tong, Q. A Large-Scene Deceptive Jamming Method for Space-Borne SAR Based on Time-Delay and Frequency-Shift with Template Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Ma, F.; Ran, D.; Ye, W.; Li, G. Fast Generation of Deceptive Jamming Signal Against Spaceborne SAR Based on Spatial Frequency Domain Interpolation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, K.W. An Integrated Raw Data Simulator for Airborne Spotlight ECCM SAR. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenghua, Z.; Dazhuan, X.; Xueming, J.; Hua, H. A Study on Active Jamming to Synthetic Aperture Radar. In Proceedings of the ICCEA 2004. 2004 3rd International Conference on Computational Electromagnetics and Its Applications, Beijing, China, 1–4 November 2004; pp. 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.h.; Wu, X.F.; Wang, X.s.; Xiao, S.p. SAR Active-Decoys Jamming Based on DRFM. In Proceedings of the 2007 IET International Conference on Radar Systems, Edinburgh, UK, 15–18 October 2007; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Jiang, X.; Xing, M.; Qiao, Z.j.; Wu, Y.; Bao, Z. Focus Improvement of Highly Squinted Data Based on Azimuth Nonlinear Scaling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2308–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; He, Z.; He, F.; Dong, Z.; Wu, M. Generalized Nonlinear Chirp Scaling Algorithm for High-Resolution Highly Squint SAR Imaging. Sensors 2017, 17, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornado, G. Trajectory Deviations in Airborne SAR: Analysis and Compensation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1999, 35, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Qu, Q.; Liu, P. Studying Atmospheric Turbulence Effects on Aircraft Motion for Airborne SAR Motion Compensation Requirements. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques Proceedings, Manchester, UK, 16–17 July 2012; pp. 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Xiang, M.; Wei, L.; Li, Y.; Hong, W. Error Analysis of SAR Motion Compensation. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques Proceedings, Manchester, UK, 16–17 July 2012; pp. 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, S.; Zamparelli, V.; Pauciullo, A.; Fornaro, G. Azimuth-to-Frequency Mapping in Airborne SAR Data Corrupted by Uncompensated Motion Errors. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1493–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschetti, G.; Iodice, A.; Perna, S.; Riccio, D. SAR Sensor Trajectory Deviations: Fourier Domain Formulation and Extended Scene Simulation of Raw Signal. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2323–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschetti, G.; Iodice, A.; Perna, S.; Riccio, D. Efficient Simulation of Airborne SAR Raw Data of Extended Scenes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2851–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proakis, J.G.; Salehi, M.; Zhou, N.; Li, X. Communication Systems Engineering; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Fornaro, G.; Franceschetti, G.; Perna, S. Motion Compensation Errors: Effects on the Accuracy of Airborne SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2005, 41, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Imagery Detail. Available online: https://www.intelligence-airbusds.com (accessed on 13 November 2022).
















| Parameter | Transmitted | Carrier | Chirp Rate | PRI | Pulse Width | Platform | Antenna |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radar Signal | Frequency | Velocity | Aperture | ||||
| Value | LFM | 10 GHz | 15 MHz/s | 5.6 ms | 10 s | 150 m/s | 2 m |
| Scatters | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | P8 | P9 | Mean | STD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | IRW(m) | RS | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.00 |
| SA | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.00 | ||
| HDE | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.00 | ||
| MLPO(m) | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | ||
| IRWB(%) | 0.28 | 0.45 | 0.66 | 0.29 | 0.47 | 0.67 | 0.28 | 0.45 | 0.66 | 0.47 | 0.16 | ||
| PSLR(dB) | RS | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | 0.00 | |
| SA | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.27 | 0.00 | ||
| HDE | −13.50 | −13.57 | −13.64 | −13.50 | −13.57 | −13.64 | −13.50 | −13.57 | −13.64 | −13.57 | 0.06 | ||
| ISLR(dB) | RS | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | 0.00 | |
| SA | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | −10.03 | 0.00 | ||
| HDE | −10.33 | −10.40 | −10.50 | −10.33 | −10.40 | −10.50 | −10.33 | −10.40 | −10.50 | −10.41 | 0.07 | ||
| Azimuth | IRW(m) | RS | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.01 |
| SA | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.01 | ||
| HDE | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.01 | ||
| MLPO(m) | 0.29 | −0.04 | 0.34 | 0.29 | −0.04 | 0.34 | 0.29 | −0.04 | 0.34 | 0.20 | 0.17 | ||
| IRWB(%) | 0.15 | 0.32 | 0.53 | 0.15 | 0.32 | 0.52 | 0.15 | 0.32 | 0.53 | 0.33 | 0.16 | ||
| PSLR(dB) | RS | −13.26 | −13.27 | −13.28 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.28 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.28 | −13.27 | 0.01 | |
| SA | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.28 | −13.27 | −13.27 | −13.28 | −13.26 | −13.27 | −13.28 | −13.27 | 0.01 | ||
| HDE | −12.28 | −13.48 | −10.91 | −12.27 | −13.48 | −10.90 | −12.27 | −13.48 | −10.90 | −12.22 | 1.05 | ||
| ISLR(dB) | RS | −11.01 | −11.02 | −11.00 | −11.01 | −11.02 | −11.00 | −11.01 | −11.02 | −11.00 | −11.01 | 0.01 | |
| SA | −11.01 | −11.02 | −11.00 | −11.01 | −11.02 | −11.00 | −11.01 | −11.02 | −11.00 | −11.01 | 0.01 | ||
| HDE | −11.18 | −11.43 | −10.37 | −11.18 | −11.43 | −10.36 | −11.18 | −11.43 | −10.36 | −10.99 | 0.45 | ||
| Algorithm | Jamming | Initialization | Real-Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Object | Stage | Stage | |
| SA | nonlinear | — | |
| trajectory SAR | |||
| HDE | nonlinear | ||
| trajectory SAR | |||
| SFI | linear | ||
| trajectory SAR | |||
| SM | linear | ||
| trajectory SAR |
| Size | Preprocessing | Real-Time | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ms) | (ms) | |||
| M | N | HDE | HDE | SA |
| 100 | 100 | 126.26 | 3.12 | 916.66 |
| 300 | 300 | 126.44 | 3.26 | 7718.07 |
| 500 | 500 | 126.98 | 3.28 | 21,907.11 |
| 1000 | 1000 | 126.78 | 3.27 | 89,696.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, J.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, W.; Cheng, W.; Liu, X. Hybrid Domain Efficient Modulation-Based Deceptive Jamming Algorithm for Nonlinear-Trajectory Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092446
Dong J, Zhang Q, Lu W, Cheng W, Liu X. Hybrid Domain Efficient Modulation-Based Deceptive Jamming Algorithm for Nonlinear-Trajectory Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(9):2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092446
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Jiaming, Qunying Zhang, Wei Lu, Wenhai Cheng, and Xiaojun Liu. 2023. "Hybrid Domain Efficient Modulation-Based Deceptive Jamming Algorithm for Nonlinear-Trajectory Synthetic Aperture Radar" Remote Sensing 15, no. 9: 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092446
APA StyleDong, J., Zhang, Q., Lu, W., Cheng, W., & Liu, X. (2023). Hybrid Domain Efficient Modulation-Based Deceptive Jamming Algorithm for Nonlinear-Trajectory Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sensing, 15(9), 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092446