Airborne Measurements of CO2 Column Concentration and Range Using a Pulsed Direct-Detection IPDA Lidar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. CO2 Line Choice and Lidar Approach
3. Airborne Lidar Description
4. CO2 Measurement Processing and Retrievals
5. 2011 Airborne Campaigns
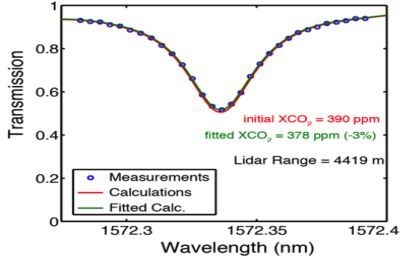
6. Airborne CO2 Measurements and Calculations
7. Range Measurements
8. Airborne Measurement Results
8. Summary
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tans, P.P; Fung, I.Y.; Takahashi, T. Observational constraints on the global atmospheric CO2 budget. Science 1990, 247, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, S.; Gloor, M.; Mahlman, J.; Pacala, S.; Sarmiento, J.; Takahashi, T.; Tans, P. A large terrestrial carbon sink in North America implied by atmospheric and oceanic carbon dioxide data and models. Science 1998, 282, 442–446. [Google Scholar]
- ESA A-SCOPE Mission Assessment Report. 2008. Available online: http://esamultimedia.esa.int/docs/SP1313-1_ASCOPE.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2013).
- NASA ASCENDS Mission Science Definition and Planning Workshop Report. 2008. Available online: http://cce.nasa.gov/ascends/12-30-08%20ASCENDS_Workshop_Report%20clean.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2013).
- Kuang, Z.; Margolis, J.; Toon, G.; Crisp, D.; Yung, Y. Spaceborne measurements of atmospheric CO2 by high-resolution NIR spectrometry of reflected sunlight: An introductory study. Geophys. Res. Lett 2002, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, D.M.; Rayner, P.J. Global observations of carbon budget 2, CO2 concentrations from differential absorption of reflected sunlight in the 1.61 um band of CO2. J. Geophys. Res 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, E.; Breon, F.M. Spaceborne estimate of atmospheric CO2 column by use of the differential absorption method: Error analysis. Appl. Opt 2003, 42, 3595–3609. [Google Scholar]
- Kuze, A.; Suto, H.; Nakajima, M.; Hamazaki, T. Thermal and near infrared sensor for carbon observation Fourier-transform spectrometer on the Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite for greenhouse gases monitoring. Appl. Opt 2009, 48, 6716–6733. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, Y.; Ota, Y.; Eguchi, N.; Kikuchi, N.; Nobuta, K.; Tran, H.; Morino, I.; Yokota, T. Retrieval algorithm for CO2 and CH4 column abundances from short-wavelength infrared spectra observations by the Greenhouse gases observing satellite. Atmos. Meas. Tech 2011, 4, 717–734. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Kawa, S.R. Sensitivity study for space-based measurement of atmospheric total column carbon dioxide by reflected sunlight. Appl. Opt 2004, 43, 914–927. [Google Scholar]
- Aben, I.; Hasekamp, O.; Hartmann, W. Uncertainties in the space-based measurements of CO2 columns due to scattering in the Earth’s atmosphere. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf 2007, 104, 450–459. [Google Scholar]
- United States National Research Council. Earth Science and Applications from Space: National Imperatives for the Next Decade and Beyond. 2007. Available online http://www.nap.edu/ (accessed on 30 August 2013).
- Durand, Y.; Caron, J.; Bensi, P.; Ingmann, P.; Bézy, J.; Meynart, R. A-SCOPE: Concepts for an ESA Mission to Measure CO2 from Space with a Lidar. Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Tropospheric Profiling, Delft, the Netherlands, 19–23 October 2009.
- Ehret, G.; Kiemle, C.; Wirth, M.; Amediek, A.; Fix, A.; Houweling, S. Space-borne remote sensing of CO2, CH4, and N2O by integrated path differential absorption lidar: A sensitivity analysis. Appl. Phys 2008, 90, 593–608. [Google Scholar]
- Caron, J.; Durand, Y. Operating wavelengths optimization for a spaceborne lidar measuring atmospheric CO2. Appl. Opt 2009, 48, 5413–5422. [Google Scholar]
- Measures, R. Laser Remote Sensing: Fundamentals and Applications; Krieger Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Weitkamp, C. Lidar: Range Resolved Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere; Springer: Berlin, Germany/Heidelberg, Germany/New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Abshire, J.B.; Riris, H.; Allan, G.R.; Weaver, C.J.; Mao, J.; Sun, X.; Hasselbrack, W.E.; Kawa, S.R.; Biraud, S. Pulsed airborne lidar measurements of atmospheric CO2 column absorption. Tellus 2010, 62, 770–783. [Google Scholar]
- Spiers, G.; Menzies, R.; Jacob, J.; Christensen, L.; Phillips, M.; Choi, Y.; Browell, E. Atmospheric CO2 measurements with a 2 um airborne laser absorption spectrometer employing coherent detection. Appl. Opt 2011, 50, 2098–2111. [Google Scholar]
- Dobler, J.; Harrison, F.; Browell, E.; Lin, B.; McGregor, D.; Kooi, S.; Choi, Y.; Ismail, S. Atmospheric CO2 column measurements with an airborne intensity-modulated continuous wave 1.57 um fiber laser lidar. Appl. Opt 2013, 52, 2874–2892. [Google Scholar]
- Riris, H.; Abshire, J.; Allan, G.; Burris, J.; Chen, J.; Kawa, S.; Mao, J.; Krainak, M.; Stephen, M.; Sun, X.; et al. A laser sounder for measuring atmospheric trace gases from space. Proc. SPIE 2007, 6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, G.R.; Riris, H.; Abshire, J.B.; Sun, X.; Wilson, E.; Burris, J.F.; Krainak, M.A. Laser Sounder for Active Remote Sensing Measurements of CO2 Concentrations. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 1–8 March 2008; pp. 1–7.
- Abshire, J.B.; Riris, H.; Allan, G.R.; Weaver, C.J.; Mao, J.; Sun, X.; Hasselbrack, W.E.; Yu, A.; Amediek, A.; Choi, Y.; et al. A lidar approach to measure CO2 concentrations from space for the ASCENDS Mission. Proc. SPIE 2010, 7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amediek, A.; Sun, X.; Abshire, J.B. Analysis of range measurements from a pulsed airborne CO2 integrated path differential absorption lidar. IEEE Trans Geosci. Remote Sens 2012, 51, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar]
- Abshire, J.B.; Riris, H.; Weaver, C.; Mao, J.; Allan, G.; Hasselbrack, W.; Browell, E. Airborne measurements of CO2 column absorption and range using a pulsed direct-detection integrated path differential absorption lidar. Appl. Opt 2013, 52, 4446–4461. [Google Scholar]
- Stephen, M.; Krainak, M.; Riris, H.; Allan, G.R. Narrowband, tunable, frequency-doubled, erbium-doped fiber-amplified transmitter. Opt. Lett 2007, 32, 2073–2075. [Google Scholar]
- Stephen, M.A.; Mao, J.; Abshire, J.B.; Kawa, S.R.; Sun, X.; Krainak, M.A. Oxygen Spectroscopy Laser Sounding Instrument for Remote Sensing of Atmospheric Pressure. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 1–8 March 2008; pp. 1–6.
- Riris, H.; Rodriguez, M.; Allan, G.; Hasselbrack, W.; Mao, J.; Stephen, M.; Abshire, J.B. Pulsed airborne lidar measurements of atmospheric optical depth using the Oxygen A-band at 765 nm. Appl. Opt 2013, 52, 6369–6382. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Kawa, S.R.; Abshire, J.B.; Riris, H. Sensitivity Studies for a Space-based CO2 Laser Sounder. AGU Fall Meet. Abst. 2007. Available online: www.agu.org/meetings/fm07/(accessed on 30 August 2013). [Google Scholar]
- Ramanathan, A.; Mao, J.; Allan, G.R.; Riris, H.; Weaver, C.J.; Hasselbrack, W.E.; Browell, E.V.; Abshire, J.B. Spectroscopic measurements of a CO2 absorption line in an open vertical path using an airborne lidar. Appl. Phys. Lett 2013, 103, 214102. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Abshire, J.B. Comparison of IPDA lidar receiver sensitivity for coherent detection and for direct detection using sine-wave and pulsed modulation. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 21291–21304. [Google Scholar]
- NASA DC-8 Aircraft Fact Sheet. Available online: http://www.nasa.gov/centers/dryden/news/FactSheets/FS-050-DFRC.html# (accessed on 30 August 2013).
- Rothman, L.S.; Gordon, I.E.; Barbe, A.; ChrisBenner, D.; Bernath, P.F.; Birk, M.; Boudon, V.; Brown, L.R.; Campargue, A.; Champion, J.P.; et al. The HITRAN 2008 molecular spectroscopic database. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf 2009, 110, 533–572. [Google Scholar]
- Lamouroux, J.; Tran, H; Laraia, A.L.; Gamache, R.R.; Rothman, L.S.; Gordon, I.E.; Hartmann, J.M. Updated database plus software for line-mixing in CO2 infrared spectra and their test using laboratory spectra in the 1.5–2.3 um region. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf 2010, 111, 2321–2331. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Vay, S.; Vadevu, K.; Soja, A.; Woo, J.; Nolf, S.; Sachse, G.; Diskin, G.S.; Blake, D.R.; Blake, N.J.; et al. Characteristics of the atmospheric CO2 signal as observed over the conterminous United States during INTEX-NA. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vay, S.; Woo, J.; Anderson, B.; Thornhill, K.L.; Blake, D.R.; Westberg, D.J.; Kiley, C.M.; Avery, M.A.; Sachse, G.W.; Streets, D.G.; et al. Influence of regional-scale anthropogenic emissions on CO2 distributions over the western North Pacific. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienecker, M.M.; Suarez, M.J.; Gelaro, R.; Todling, R.; Bacmeister, J.; Liu, E.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Shubert, S.D.; Takacs, L.; Kim, G.-K.; et al. MERRA: NASA’s modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications. J. Clim 2011, 24, 3624–3648. [Google Scholar]
Appendix
Appendix A: Lidar Wavelength Calibration and Monitoring
Appendix B: Lidar Data Processing and Screening

















| CO2 line | R16, 6,359.96 cm−1 |
| CO2 line center wavelength | 1,572.335 nm |
| Laser min & max wavelengths | 1,572.28 nm, 1,572.390 nm |
| Laser wavelength steps across line | 30 |
| Laser wavelength change/step | ∼ 3.8 pm (0.0154 cm−1) |
| Laser peak power, pulse width, energy | 25 watts, 1 μs, 25 μJ |
| Laser divergence angle | 100 μrad |
| Seed laser diode type | DFB: Fitel FOL15DCWD |
| Wavelength monitor | Burleigh WA1650 |
| Calibration heterodyne detector | New Focus 2053-FC InGaAs |
| Laser Pulse Modulator (AOM) | NEOS Model: 26035-2-155 |
| Fiber coupled CO2 cell | 80 cm path, ∼200 Torr pressure |
| Fiber Laser Amplifier (EDFA) | IPG EAR-10K-1571-LP-SF |
| Laser line scan rate | 300 Hz |
| Laser linewidth for each step | ∼15 MHz |
| Receiver Telescope type | Cassegrain, f/10 (Vixen) |
| Telescope diameter | 20 cm |
| Receiver FOV diameter | 200 μrad |
| Receiver optical bandwidth | 800 pm FWHM |
| Receiver Optics Transmission | 0.64 |
| Detector PMT type | Hamamatsu H10330A-75 |
| Detector quantum efficiency | 4% (these flights) |
| Detector dark count rate | ∼ 500 kHz |
| Receiver signal processing | Photon counting/histogramming |
| Histogram time bin width | 8 ns |
| Receiver integration time | 0.9 s per readout |
| Recording duty cycle | 90% (0.9 s every 1 s) |
| Notation: | Flight 2 | Flight 3 | Flight 5 | Flight 6 |
| Location: | Pacific Ocean | Railroad Valley, NV | Four Corners, NM | Iowa |
| Flight Dates (all 2011) | 2 August | 3 August | 9 August | 10 August |
| DC-8 Spiral Down Location (Latt, Long) | 33°02′N | 38°34′N | 36°44′N | 41°43′N |
| 122°57′W | 115°47′W | 108°13′W | 91°21′W | |
| Surface Elevation (m) | 0* | 1400 | 700 | 235 |
| Surface Pressure 1 (mbar) | 1013 | 850 | 924 | 988 |
| Approx Duration (min) | 264 | 278 | 333 | 390 |
| Primary Altitude range (km) | 3.2–12.8 | 2.9–11.2 | 4.5–12.2 | 3–12.1 |
| Altitude step size 2 (km) | 3 | 1.7 | 3 | 1.5 |
| Number of altitude steps 3 | 3–5 | 6–8 | 3–4 | 8–10 |
| Time span of data analyzed (UTC hours) | 16.25, 18.3 | 19.2, 21.9 | 17.3, 20.25 | 21.0, 23.25 |
| Location & Summary Statistics | Mean Altitude (km) | Min & Max Altitude (km) | # of Meas | Offline Single Wavel. Ave Signal (Counts) | Avocet Ref. XCO2 (ppm) | Lidar Mean XCO2 Based on MERRA atm (ppm) | Lidar SD (ppm) | Lidar Mean XCO2 Based on MERRA atm. In-situ (ppm) | Lidar Mean XCO2 Based on DC-8 atm (ppm) | Mean Lidar (DC-8) In-situ (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pacific Ocean Low Cloud Top | 3.2 | 3.1, 4.0 | 102 | 7,125 | 390.9 | 395.4 | 4.72 | 4.6 | 389.8 | −1.0 |
| Excess noise limit = 1.8 | 6.4 | 6.0, 7.0 | 117 | 5,375 | 391.3 | 392.7 | 2.68 | 1.4 | 390.0 | −1.3 |
| 60% conf. interval = 30 ppm | 7.5 | 7.0, 8.0 | 31 | 4,625 | 390.9 | 392.9 | 3.27 | 2.1 | 390.8 | −0.1 |
| # process; attempts: 559/656 | 8.5 | 8.0, 9.0 | 41 | 5,250 | 390.6 | 392.1 | 2.41 | 1.6 | 390.2 | −0.4 |
| Process success rate: 85% | 9.5 | 9.0, 10.0 | 68 | 4,875 | 390.5 | 393.5 | 2.43 | 3.0 | 391.8 | 1.3 |
| 12.7 | 12.0, 12.8 | 102 | 2,375 | 390.5 | 392.6 | 4.05 | 2.1 | 391.7 | 1.2 | |
| RRV to Ground | 4.8 | 4.5, 5.0 | 51 | 7,000 | 392.7 | 385.6 | 4.59 | −7.1 | 389.6 | −3.1 |
| Excess noise limit = 3.0 | 6.4 | 6.1, 7.0 | 179 | 7,750 | 391.9 | 388.6 | 3.09 | −3.3 | 391.3 | −0.5 |
| 60% conf. interval = 10 ppm | 8.0 | 8.0, 8.2 | 41 | 7,625 | 391.4 | 390.0 | 2.31 | −1.4 | 392.0 | 0.6 |
| # process; attempts: 514/632 | 9.6 | 9.0, 9.7 | 55 | 5250 | 391.1 | 389.1 | 2.89 | −2.1 | 390.8 | −0.4 |
| Process success rate: 81% | 11.2 | 11.1, 11.6 | 53 | 6,000 | 390.9 | 389.6 | 2.76 | −1.3 | 390.8 | −0.1 |
| 12.8 | 12.8, 12.9 | 84 | 6,125 | 390.9 | 391.4 | 2.85 | 0.5 | 391.4 | 0.4 | |
| Four Corners to Ground | 4.8 | 4.0, 4.9 | 643 | 9,500 | 391.8 | 384.9 | 4.63 | −6.9 | 390.8 | −1.0 |
| Excess noise limit = 1.8 | 6.5 | 6.4, 7.0 | 96 | 7,625 | 391.5 | 387.4 | 3.62 | −4.1 | 391.3 | −0.2 |
| 60% conf. interval = 10 ppm | 9.7 | 9.4, 10.0 | 52 | 7,000 | 391.1 | 389.3 | 3.16 | −1.8 | 391.7 | 0.6 |
| # process; attempts: 846/971 | ||||||||||
| Process success rate: 87% | ||||||||||
| Iowa to Ground | 3.2 | 3.0, 3.9 | 71 | 16,000 | 374.4 | 375.9 | 4.60 | 1.6 | 376.8 | 2.5 |
| Excess noise limit = 1.8 | 4.6 | 4.0, 5.0 | 123 | 9,000 | 378.0 | 377.9 | 3.29 | 0.0 | 376.8 | −1.1 |
| 60% conf. interval = 10 ppm | 6.3 | 6.0, 7.0 | 43 | 7,000 | 380.0 | 381.1 | 2.62 | 1.2 | 381.1 | 1.1 |
| # process; attempts: 536/704 | 7.6 | 7.0, 8.0 | 47 | 7,625 | 380.8 | 380.9 | 1.72 | 0.1 | 381.9 | 1.1 |
| Process success rate: 77% | 10.8 | 10.1, 11.0 | 72 | 6,375 | 382.7 | 381.9 | 1.78 | −0.8 | 383.2 | 0.4 |
| 12.5 | 12.1, 12.6 | 81 | 5,500 | 383.8 | 384.1 | 2.19 | 0.3 | 384.1 | 0.4 | |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Abshire, J.B.; Ramanathan, A.; Riris, H.; Mao, J.; Allan, G.R.; Hasselbrack, W.E.; Weaver, C.J.; Browell, E.V. Airborne Measurements of CO2 Column Concentration and Range Using a Pulsed Direct-Detection IPDA Lidar. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 443-469. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6010443
Abshire JB, Ramanathan A, Riris H, Mao J, Allan GR, Hasselbrack WE, Weaver CJ, Browell EV. Airborne Measurements of CO2 Column Concentration and Range Using a Pulsed Direct-Detection IPDA Lidar. Remote Sensing. 2014; 6(1):443-469. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6010443
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbshire, James B., Anand Ramanathan, Haris Riris, Jianping Mao, Graham R. Allan, William E. Hasselbrack, Clark J. Weaver, and Edward V. Browell. 2014. "Airborne Measurements of CO2 Column Concentration and Range Using a Pulsed Direct-Detection IPDA Lidar" Remote Sensing 6, no. 1: 443-469. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6010443
APA StyleAbshire, J. B., Ramanathan, A., Riris, H., Mao, J., Allan, G. R., Hasselbrack, W. E., Weaver, C. J., & Browell, E. V. (2014). Airborne Measurements of CO2 Column Concentration and Range Using a Pulsed Direct-Detection IPDA Lidar. Remote Sensing, 6(1), 443-469. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6010443