UAV Remote Sensing for Urban Vegetation Mapping Using Random Forest and Texture Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Urban Vegetation Mapping
1.2. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Remote Sensing
1.3. UAV Remote Sensing for Urban Vegetation Mapping
1.4. Aims and Objectives
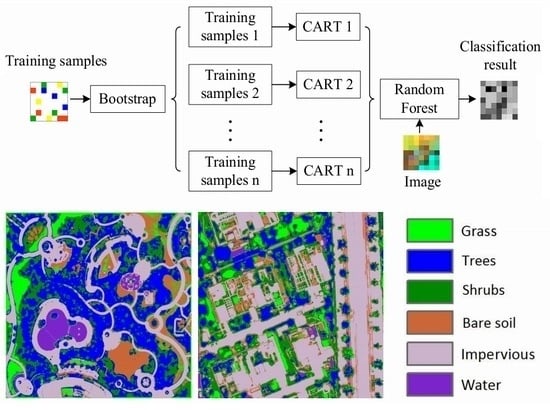
2. Method
2.1. UAV Image Processing Workflow
2.2. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing




2.3. Texture Analysis
2.4. Definition of Land Cover Classes and Sampling Procedure
2.5. Random Forest

2.6. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Parameterization of Random Forest

3.2. Classification Results


3.3. Results of Accuracy Assessment
| Image-A | Ground Truth | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classes | Grass | Trees | Shrubs | Bare soil | Impervious | Water | UA (%) |
| Grass | 461 (229) | 0 (79) | 3 (71) | 18 (26) | 12 (0) | 0 (0) | 93.3 (56.5) |
| Trees | 0 (70) | 456 (253) | 79 (142) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 85.2 (54.4) |
| Shrubs | 39 (201) | 44 (134) | 409 (281) | 25 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 79.1 (45.6) |
| Bare soil | 0 (0) | 0 (23) | 9 (6) | 457 (474) | 0 (12) | 22 (0) | 93.7 (92.0) |
| Imperious | 0 (0) | 0 (11) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 488 (488) | 30 (19) | 94.2 (94.2) |
| Water | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 448 (481) | 100 (100) |
| PA (%) | 92.2 (45.8) | 91.2 (50.6) | 81.8 (56.2) | 91.4 (94.8) | 97.6 (97.6) | 89.6 (96.2) | |
| OA (%) | 90.6 (73.5) | Kappa | 0.8876 (0.6824) | ||||
| Image-B | Ground Truth | ||||||
| Classes | Grass | Trees | Shrubs | Bare soil | Impervious | Water | UA (%) |
| Grass | 387 (268) | 44 (152) | 18 (45) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 86.2 (57.6) |
| Trees | 72 (167) | 338 (246) | 55 (96) | 10 (0) | 0 (0) | 4 (3) | 70.6 (48.1) |
| Shrubs | 39 (60) | 114 (101) | 409 (320) | 14 (13) | 1 (0) | 0 (1) | 70.9 (64.7) |
| Bare soil | 2 (5) | 4 (1) | 0 (4) | 476 (481) | 19 (12) | 0 (2) | 95.0 (95.3) |
| Imperious | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 6 (3) | 0 (6) | 480 (488) | 0 (0) | 98.8 (98.2) |
| Water | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 12 (32) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 496 (494) | 97.6 (93.9) |
| PA (%) | 77.4 (53.6) | 67.6 (49.2) | 81.8 (64.0) | 95.2 (96.2) | 96.0 (97.6) | 99.2 (98.8) | |
| OA (%) | 86.2 (76.6) | Kappa | 0.8344 (0.7188) | ||||

3.4. Variable Importance

3.5. Comparison with Maximum Likelihood

3.6. Comparison with OBIA

| Image | Method | Feature Used | OA (%) | Kappa | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image-A | OBIA | 38 | 91.8 | 0.9016 | 63.8 |
| RF + Texture | 9 | 90.6 | 0.8876 | 41.2 | |
| Image-B | OBIA | 38 | 88.1 | 0.8572 | 53.1 |
| RF + Texture | 9 | 86.2 | 0.8344 | 34.5 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nichol, J.; Lee, C.M. Urban vegetation monitoring in Hong Kong using high resolution multispectral images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 903–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C. Estimation of urban vegetation abundance by spectral mixture analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1305–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Jiang, H. Object-oriented method for urban vegetation mapping using IKONOS imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tigges, J.; Lakes, T.; Hostert, P. Urban vegetation classification: Benefits of multitemporal RapidEye satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, M.; Bookhagen, B.; Roberts, D.A. Urban tree species mapping using hyperspectral and LiDAR data fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooke, T.R.; Coops, N.C.; Goodwin, N.R.; Voogt, J.A. Extracting urban vegetation characteristics using spectral mixture analysis and decision tree classifications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shao, G. Object-based urban vegetation mapping with high-resolution aerial photography as a single data source. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 771–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, K.; Coops, N.C.; Gergel, S.E.; Stange, Y. Application of high spatial resolution satellite imagery for riparian and forest ecosystem classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfle, B.; Hollaus, M.; Hagenauer, J. Urban vegetation detection using radiometrically calibrated small-footprint full-waveform airborne LiDAR data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 67, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, R.L.; Roberts, D.A.; Dennison, P.E.; Hess, L.L. Sub-pixel mapping of urban land cover using multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis: Manaus, Brazil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, D.L.; Wiesmann, D. Land cover and impervious surface extraction using parametric and non-parametric algorithms from the open-source software R: An application to sustainable urban planning in Sicily. GISci. Remote Sens. 2013, 50, 231–250. [Google Scholar]
- Laliberte, A.S.; Rango, A. Texture and scale in object-based analysis of subdecimeter resolution Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szantoi, Z.; Escobedo, F.; Abd-Elrahman, A.; Smith, S.; Pearlstine, L. Analyzing fine-scale wetland composition using high resolution imagery and texture features. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2013, 23, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguera, F.; Aguilar, F.J.; Aguilar, M.A. Using texture analysis to improve per-pixel classification of very high resolution images for mapping plastic greenhouses. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M.; Dinstein, I.; Shanmugam, K. Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, 3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleve, C.; Kelly, M.; Kearns, M.R.; Moritz, M. Classification of the wildland–urban interface: A comparison of pixel- and object-based classifications using high-resolution aerial photography. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2008, 32, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Gong, P.; Clinton, N.; Biging, G.; Kelly, M.; Schirokauer, D. Object-based detailed vegetation classification with airborne high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laliberte, A.S.; Goforth, M.A.; Steele, C.M.; Rango, A. Multispectral remote sensing from unmanned aircraft: Image processing workflows and applications for rangeland environments. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 2529–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R. An object-based hierarchical method for change detection using unmanned aerial vehicle images. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7911–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honkavaara, E.; Saari, H.; Kaivosoja, J.; Pölönen, I.; Hakala, T.; Litkey, P.; Mäkynen, J.; Pesonen, L. Processing and assessment of spectrometric, stereoscopic imagery collected using a lightweight UAV spectral camera for precision agriculture. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5006–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, L.; Lucieer, A.; Watson, C.; Turner, D. Development of a UAV-LiDAR system with application to forest inventory. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1519–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, E.R.; Hively, W.D.; Fujikawa, S.J.; Linden, D.S.; Daughtry, C.S.T.; McCarty, G.W. Acquisition of NIR-Green-Blue digital photographs from unmanned aircraft for crop monitoring. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rango, A.; Laliberte, A.; Herrick, J.E.; Winters, C.; Havstad, K.; Steele, C.; Browning, D. Unmanned aerial vehicle-based remote sensing for rangeland assessment, monitoring, and management. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2009, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Yue, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, D.; Yu, C. Impacts of the Wenchuan Earthquake on the Chaping River upstream channel change. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 3907–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomina, I.; Molina, P. Unmanned aerial systems for photogrammetry and remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 92, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pix4D. Available online: http://pix4d.com (accessed on 31, October, 2014).
- Anys, H.; He, D.C. Evaluation of textural and multipolarization radar features for crop classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Hetrick, S.; Moran, E. Land cover classification in a complex urban-rural landscape with QuickBird imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2010, 76, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. A survey of image classification methods and techniques for improving classification performance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 823–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Stow, D. The effect of training strategies on supervised classification at different spatial resolutions. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Galiano, V.F.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Abarca-Hernandez, F.; Atkinson, P.M.; Jeganathan, C. Random forest classification of mediterranean land cover using multi-seasonal imagery and multi-seasonal texture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Sharma, R.; Joshi, P.K. Random forest classification of urban landscape using Landsat archive and ancillary data: Combining seasonal maps with decision level fusion. Appl. Geol. 2014, 48, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puissant, A.; Rougier, S.; Stumpf, A. Object-oriented mapping of urban trees using random forest classifiers. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2014, 26, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.B.; Crews, K.A. Mapping vegetation morphology types in a dry savanna ecosystem: Integrating hierarchical object-based image analysis with random forest. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 1175–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.H.; Miller, S.N.; Murphy, M.A. High-resolution land cover classification using random forest. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Galiano, V.F.; Ghimire, B.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Rigol-Sanchez, J.P. An assessment of the effectiveness of a random forest classifier for land-cover classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 67, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, J.; Brenning, A. A comparative study of different classification techniques for marine oil spill identification using RADARSAT-1 imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immitzer, M.; Atzberger, C.; Koukal, T. Tree species classification with random forest using very high spatial resolution 8-band WorldView-2 satellite data. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 2661–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paola, J.; Schowengerdt, R. A detailed comparison of backpropagation neural network and maximum-likelihood classifiers for urban land use classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 981–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, J. A method for generating floodplain maps using IKONOS images and DEMs. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 2441–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EXELIS. Available online: http://www.exelisvis.com/ProductsServices/ENVIProducts.aspx (accessed on 31 October 2014).
- Feature Extraction with Example-Based Classification Tutorial. Available online: http://www.exelisvis.com/docs/FXExampleBasedTutorial.html (accessed on 31 October 2014).
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Q.; Liu, J.; Gong, J. UAV Remote Sensing for Urban Vegetation Mapping Using Random Forest and Texture Analysis. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1074-1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70101074
Feng Q, Liu J, Gong J. UAV Remote Sensing for Urban Vegetation Mapping Using Random Forest and Texture Analysis. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(1):1074-1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70101074
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Quanlong, Jiantao Liu, and Jianhua Gong. 2015. "UAV Remote Sensing for Urban Vegetation Mapping Using Random Forest and Texture Analysis" Remote Sensing 7, no. 1: 1074-1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70101074
APA StyleFeng, Q., Liu, J., & Gong, J. (2015). UAV Remote Sensing for Urban Vegetation Mapping Using Random Forest and Texture Analysis. Remote Sensing, 7(1), 1074-1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70101074