An Effective Method for Snow-Cover Mapping of Dense Coniferous Forests in the Upper Heihe River Basin Using Landsat Operational Land Imager Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area


2.2. Data
2.2.1. Landsat OLI Images
| Band No. | Band Name | Wavelength Range (nm) | GSD (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | New Deep Blue | 433–453 | 30 |
| 2 | Blue | 450–515 | 30 |
| 3 | Green | 525–600 | 30 |
| 4 | Red | 630–680 | 30 |
| 5 | NIR | 845–885 | 30 |
| 6 | SWIR2 | 1560–1660 | 30 |
| 7 | SWIR3 | 2100–2300 | 30 |
| 8 | PAN | 500–680 | 15 |
| 9 | SWIR | 1360–1390 | 30 |
2.2.2. Ancillary Data

3. Methodology
3.1. Optical Properties of Snow
3.2. Optical Properties of Snow-Covered Forest

3.3. Differences in Optical Properties between Snow-Free and Snow-Covered Forest
3.4. The Normalized Difference Forest Snow Index

4. Experiment and Verification
4.1. Snow Extraction


4.2. Accuracy Assessment
4.2.1. Subjective Assessment
4.2.2. Objective Assessment


5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
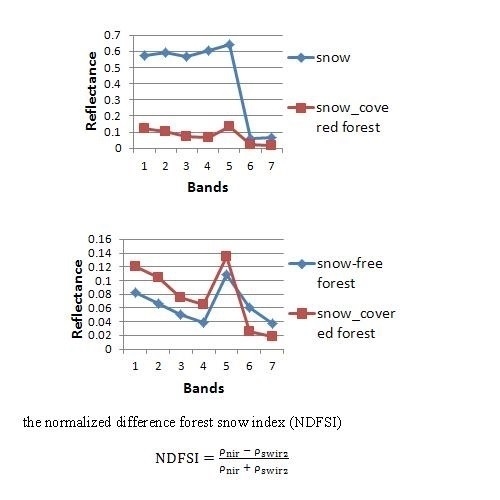
- For the effect of forest canopy, the visible reflectance of snow-covered forest is much lower than that of snow (as shown in Figure 3a). It is difficult to extract snow in forested areas using NDSI, as most snow in forest cannot be identified even if the threshold value of NDSI is decreased (as shown in Figure 8).
- (2)
- Compared with snow-free forest, snow-covered forest has a higher NIR reflectance and lower SWIR reflectance (as shown in Figure 3b), and these changes in the spectral response maybe caused by the snow underneath the forest.
- (3)
- For snow-covered forest, the NDFSI, which is defined as (ρnir − ρswir)/(ρnir + ρswir), distributes with less variance than NDSI (as shown in Figure 4a).
- (4)
- For snow-covered forest, the NDFSI value is clearly higher than that of snow-free forest (as shown in Figure 4b).
- (5)
- NDFSI is an effective index for snow-cover mapping in evergreen coniferous forests of our study site. The high accuracy of snow extraction is verified using GF-1 image.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Groisman, P.Y.; Karl, T.R.; Knight, R.W. Changes of snow cover, temperature, and radiative heat balance over the Northern Hemisphere. J. Clim. 1994, 7, 1633–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cess, R.D.; Potter, G.L.; Zhang, M.H.; Blanchet, J.P.; Chalita, S.; Colman, R.; Dazlich, D.A.; Delgenio, A.D.; Dymnikov, V.; Galin, V.; et al. Interpretation of snow-climate feedback as produced by 17 general circulation models. Science 1991, 253, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Snow and climate. Weather 1994, 49, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.Y.; Che, T. Spatiotemporal variability in snow cover from 1987 to 2011 in northern China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.X.; Hao, X.H.; Huang, X.D.; Hou, J.L.; Che, T.; Dai, L.Y.; Liang, T.G.; Huang, C.L.; Li, H.Y.; et al. Remote sensing for snow hydrology in China: challenges and perspectives. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, J.; Green, R.O.; Nolin, A.W.; Painter, T.H. Interpretation of snow properties from imaging spectrometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, s25–s37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, J. Snow reflectance from Landsat-4 thematic mapper. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1984, 22, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomonson, V.V.; Appel, I. Estimating fractional snow cover from MODIS using the normalized difference snow index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, T.H.; Rittger, K.; Mckenzie, C.; Slaughter, P.; Davis, R.E.; Dozier, J. Retrieval of subpixel snow covered area, grain size, and albedo from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikhamar, D.; Solberg, R. Subpixel mapping of snow cover in forest by optical remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 84, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, R.; Hiltbrunner, D.; Koskinen, J. Snow Algorithms and Products—Review and Recommendations for Research and Development; NR Report No. 924; Norwegian Computing Center: Oslo, Norway, 1997; Volume 111. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, M.F.; Rango, A. A microcomputer-based Alpine Snow-Cover Analysis System (ASCAS). Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1995, 61, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Painter, T.H.; Roberts, D.A.; Green, R.O.; Dozier, J. The effect of grain size on spectral mixture analysis of snow-covered area from AVIRIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 65, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V.V. Development of methods for mapping global snow cover using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 54, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Foster, J.L.; Verbyla, D.L.; Klein, A.G.; Benson, C.S. Assessment of snow-cover mapping accuracy in a variety of vegetation-cover densities in Central Alaska. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsämäki, S.; Mattila, O.P.; Pulliainen, J.; Niemi, K.; Luojus, K.; Böttcher, K. An optical reflectance model-based method for fractional snow cover mapping applicable to continental scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.C.; Woodcock, C.E.; Liu, J.C. View angle effects on MODIS snow mapping in forests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, J. Spectral signature of Alpine snow cover from the Landsat thematic mapper. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 28, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittger, K.; Painter, T.H.; Dozier, J. Assessment of methods for mapping snow cover from MODIS. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsämäki, S.; Anttila, S.; Huttunen, M. A feasible method for fractional snow cover mapping in boreal zone based on a reflectance model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.X.; Xiao, P.F.; Feng, X.Z. Retrieving snow information in typical forest zone of Tianshan mountains from multi-angle imaging spetroradiometer data. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1035–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.D.; Liu, S.M.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, M.G.; Jin, R.; Che, T.; Liu, Q.H.; Wang, W.Z.; Qi, Y.; et al. Heihe watershed allied telemetry experimental research (HiWATER): Scientific objectives and experimental design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.B.; Xie, H.J.; Huang, C.L.; Ke, C.Q. Snow cover variations and controlling factors at Upper Heihe River Basin, Northwestern China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6741–6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.Y.; Hao, X.H. Responses of snowmelt runoff to climatic change in an inland river basin, northwestern China, over the past 50 years. J. Hydrol. Earth Sys. Sci. 2010, 15, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Che, K.J.; Wang, H. Research on soil water dynamics along an elevation gradient in piceacrassifolia forestry lands in Qilian Mountains. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2009, 48, 1107–1111. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, B.; Ma, P.; Nie, A.H.; Yang, A.X.; Yao, Y.J.; Lü, W.B.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.H. Land cover mapping using time series HJ-1/CCD data. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1790–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiscombe, W.J.; Warren, S.G. A model for the spectral albedo of snow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 2712–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.H.; Wang, J.; Li, H.Y. Evaluation of the NDSI threshold value in mapping snow cover of MODIS-a case study of snow in the middle Qilian Mountains. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2008, 30, 132–138. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.-Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.-Y.; Li, H.-Y.; Hao, X.-H. An Effective Method for Snow-Cover Mapping of Dense Coniferous Forests in the Upper Heihe River Basin Using Landsat Operational Land Imager Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 17246-17257. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71215882
Wang X-Y, Wang J, Jiang Z-Y, Li H-Y, Hao X-H. An Effective Method for Snow-Cover Mapping of Dense Coniferous Forests in the Upper Heihe River Basin Using Landsat Operational Land Imager Data. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(12):17246-17257. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71215882
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiao-Yan, Jian Wang, Zhi-Yong Jiang, Hong-Yi Li, and Xiao-Hua Hao. 2015. "An Effective Method for Snow-Cover Mapping of Dense Coniferous Forests in the Upper Heihe River Basin Using Landsat Operational Land Imager Data" Remote Sensing 7, no. 12: 17246-17257. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71215882
APA StyleWang, X. -Y., Wang, J., Jiang, Z. -Y., Li, H. -Y., & Hao, X. -H. (2015). An Effective Method for Snow-Cover Mapping of Dense Coniferous Forests in the Upper Heihe River Basin Using Landsat Operational Land Imager Data. Remote Sensing, 7(12), 17246-17257. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71215882