Mapping Aquatic Vegetation in a Large, Shallow Eutrophic Lake: A Frequency-Based Approach Using Multiple Years of MODIS Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
| Type | Dominant Species |
|---|---|
| Emergent vegetation | Zizania caduciflora, Phragmites australis |
| Floating-leaved vegetation | Nymphoides peltatum, Trapa incisa var. sieb., Furctus Trapae Quadricaudatae |
| Submerged vegetation | Potamogeton maackianus, Potamogeton malaianus, Vallisneria natans, Ceratophyllum demersum, Hydrilla verticillata var. roxburghii, Elodea nuttallii, Myriophyllum verticillatum, Najas minor |
2.2. Field Data


2.3. Image Data Description and Processing
2.4. Method Description: Frequency-Based Aquatic Vegetation Mapping
| 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 10 | 8 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 8 | 3 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 62 |
| February | 3 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 8 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 43 |
| March | 6 | 6 | 10 | 9 | 11 | 8 | 4 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 78 |
| April | 7 | 12 | 13 | 4 | 9 | 7 | 12 | 4 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 97 |
| May | 4 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 14 | 14 | 7 | 6 | 10 | 11 | 101 |
| June | 5 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 54 |
| July | 7 | 13 | 4 | 8 | 7 | 12 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 10 | 12 | 86 |
| August | 9 | 11 | 6 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 11 | 2 | 7 | 8 | 89 |
| September | 9 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 5 | 11 | 8 | 13 | 8 | 3 | 91 |
| October | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 12 | 7 | 14 | 10 | 5 | 12 | 11 | 121 |
| November | 10 | 14 | 7 | 7 | 12 | 10 | 7 | 12 | 5 | 12 | 12 | 108 |
| December | 12 | 7 | 14 | 9 | 4 | 15 | 6 | 13 | 9 | 12 | 10 | 111 |
| Total | 96 | 113 | 95 | 90 | 94 | 100 | 95 | 93 | 72 | 101 | 92 | 1041 |

2.5. Classification Accuracy Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Threshold Determinations
3.1.1. FAI Threshold Determination for the Detection of Aquatic Vegetation in Lake Taihu


3.1.2. Separating the Aquatic Vegetation and Floating Algae Based on VPF
3.2. Phenological Variation in Vegetation Signal Distribution

3.3. Validation of the Method Based on Field Investigation
| Year | Measured | Predicted | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aquatic Vegetation | Open Water | User’s Accuracy | Overall Accuracy | ||
| 2008 | Aquatic vegetation | 20 | 2 | 91% | 87% |
| Open water | 4 | 21 | 84% | ||
| 2009 | Aquatic vegetation | 16 | 4 | 80% | 81% |
| Open water | 5 | 22 | 81% | ||
| 2010 | Aquatic vegetation | 8 | 4 | 67% | 77% |
| Open water | 7 | 29 | 81% | ||
| 2011 | Aquatic vegetation | 19 | 3 | 86% | 88% |
| Open water | 3 | 23 | 88% | ||
| 2012 | Aquatic vegetation | 13 | 6 | 68% | 73% |
| Open water | 7 | 22 | 76% | ||

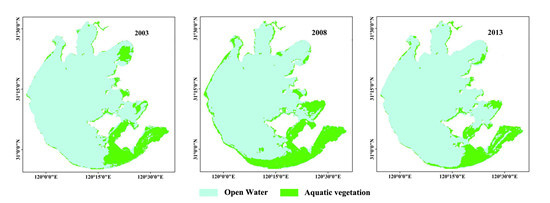
3.4. Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Aquatic Vegetation Distribution

4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages and Limitations of the Proposed Approach
4.1.1. Advantages of the Proposed Approach
4.1.2. Limitations of the Proposed Approach
4.2. Factors Affecting the Spatial and Temporal Variation of Aquatic Vegetation
4.2.1. Direct and Indirect Effects of Human Activities
4.2.2. Lake Topography and Wind Wave Disturbance

4.2.3. Implications for Aquatic Vegetation Restoration in Lake Taihu
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klemas, V. Remote sensing of emergent and submerged wetlands: An overview. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 6286–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.R.; Williams, S.L.; Duarte, C.M.; Heck, K.L., Jr.; Waycott, M. Associations of concern: Declining seagrasses and threatened dependent species. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 7, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Jiang, H.; Yang, T.; Cai, Y.; Xu, D.; An, S. Remote sensing of aquatic vegetation distribution in taihu lake using an improved classification tree with modified thresholds. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.S.; McGwire, K.C.; Fritsen, C.H. Identification and quantification of aquatic vegetation with hyperspectral remote sensing in western nevada rivers, USA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 9093–9117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, K.N.; Ffolliott, P.F.; Magner, J.A. Hydrology and the Management of Watersheds, 4th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer, M.; Nes, E.H. Shallow lakes theory revisited: Various alternative regimes driven by climate, nutrients, depth and lake size. Hydrobiologia 2007, 584, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.Q.; Yu, Q.; Zimmerman, M.J.; Flint, S.; Waldron, M.C. Differentiating aquatic plant communities in a eutrophic river using hyperspectral and multispectral remote sensing. Freshwater Biol. 2010, 55, 1658–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, L.C.; Paillisson, J.-M. A mass balance assessment of the contribution of floating-leaved macrophytes in nutrient stocks in an eutrophic macrophyte-dominated lake. Aquat. Bot. 2003, 75, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wang, M.; Qin, B. Wind and submerged aquatic vegetation influence bio-optical properties in large shallow lake taihu, china. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2013, 118, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hestir, E.L.; Khanna, S.; Andrew, M.E.; Santos, M.J.; Viers, J.H.; Greenberg, J.A.; Rajapakse, S.S.; Ustin, S.L. Identification of invasive vegetation using hyperspectral remote sensing in the california delta ecosystem. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4034–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Neill, J.D.; Costa, M. Mapping eelgrass (Zostera marina) in the gulf islands national park reserve of canada using high spatial resolution satellite and airborne imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 133, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, E.; Mutanga, O.; Rugege, D. Multispectral and hyperspectral remote sensing for identification and mapping of wetland vegetation: A review. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 18, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Quan, W. Retrieval chlorophyll-a concentration from coastal waters: Three-band semi-analytical algorithms comparison and development. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 9024–9042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, B. Lake topography and wind waves determining seasonal-spatial dynamics of total suspended matter in turbid Lake Taihu, China: Assessment using long-term high-resolution meris data. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozesmi, S.L.; Bauer, M.E. Satellite remote sensing of wetlands. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2002, 10, 381–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaç, A.; Süzen, M. Integration of environmental variables with satellite images in regional scale vegetation classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 1329–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, A.M.; Jensen, J.R. Fuzzy learning vector quantization for hyperspectral coastal vegetation classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 512–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, O.K.; Akyurek, Z.; Beklioglu, M. Identification and mapping of submerged plants in a shallow lake using quickbird satellite data. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2138–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullström, M.; Lundén, B.; Bodin, M.; Kangwe, J.; Öhman, M.C.; Mtolera, M.S.P.; Björk, M. Assessment of changes in the seagrass-dominated submerged vegetation of tropical chwaka bay (Zanzibar) using satellite remote sensing. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 67, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Wal, D.; Wielemaker-van den Dool, A.; Herman, P.M. Spatial synchrony in intertidal benthic algal biomass in temperate coastal and estuarine ecosystems. Ecosystems 2010, 13, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Wynne, T.T.; Baker, D.B.; Fahnenstiel, G.L. Interannual variability of cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Erie. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gower, J.; King, S.; Borstad, G.; Brown, L. Detection of intense plankton blooms using the 709 nm band of the meris imaging spectrometer. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C. A novel ocean color index to detect floating algae in the global oceans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Lee, Z.; Ma, R.; Yu, K.; Li, D.; Shang, S. Moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (Modis) observations of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu Lake, China. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans (1978–2012) 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Cannizzaro, J.; Carder, K.L.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Hardy, R. Remote detection of trichodesmium blooms in optically complex coastal waters: Examples with Modis full-spectral data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2048–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau-Patissier, D.; Gower, J.F.; Dekker, A.G.; Phinn, S.R.; Brando, V.E. A review of ocean color remote sensing methods and statistical techniques for the detection, mapping and analysis of phytoplankton blooms in coastal and open oceans. Prog. Oceanogr. 2014, 123, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Letelier, R.M.; Abbott, M.R. An analysis of chlorophyll fluorescence algorithms for the moderate resolution imaging spectrometer (Modis). Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Hu, W.; Zhu, J.; Huang, W.; Lin, C. A new method for modifying thresholds in the classification of tree models for mapping aquatic vegetation in Taihu Lake with satellite images. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7442–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Gu, X.; Zhang, S. Detecting aquatic vegetation changes in Taihu Lake, China using multi-temporal satellite imagery. Sensors 2008, 8, 3988–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.; Foley, J.A.; Folke, C.; Walker, B. Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature 2001, 413, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Portielje, R.; Lammens, E.H.; Noordhuis, R.; van den Berg, M.S.; Joosse, W.; Meijer, M.L. Resilience of alternative stable states during the recovery of shallow lakes from eutrophication: Lake Veluwe as a case study. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, N.; Kadono, Y.; Fukushima, M.; Nakagawa, M.; KIM, B.H.O. Effects of aquatic macrophytes on water quality and phytoplankton communities in shallow lakes. Ecol. Res. 2003, 18, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.E. Submerged aquatic vegetation correlations with depth and light attenuating materials in a shallow subtropical lake. Hydrobiologia 2003, 493, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Xu, P.; Wu, Q.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y. Earlier and warmer springs increase cyanobacterial (microcystis spp.) blooms in subtropical Lake Taihu, China. Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Lv, M.; Jiang, H.; Cai, Y.; Xu, D.; An, S. Spatio-temporal variability of aquatic vegetation in Taihu Lake over the past 30 years. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Shi, Z.; Feng, L. Temporal and spatial variations of chemical oxygen demand in Lake Taihu, China, from 2005 to 2009. Hydrobiologia 2011, 665, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Hong, Y. Algal-bloom control by allelopathy of aquatic macrophytes—A review. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2008, 2, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Paerl, H.W.; Carmichael, W.W. A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Tao, Y.; Kong, F.; Yang, Z. Relationship between temperature and cyanobacterial recruitment from sediments in laboratory and field studies. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2008, 23, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Qin, B.; Gao, G.; Cai, X. Submerged macrophyte communities and the controlling factors in large, shallow Lake Taihu (China): Sediment distribution and water depth. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Chua, H.; Li, X.; Xia, M.; Pu, P. A mosaic community of macrophytes for the ecological remediation of eutrophic shallow lakes. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.; D'Odorico, P.; McGlathery, K.; Wiberg, P. Stability and bistability of seagrass ecosystems in shallow coastal lagoons: Role of feedbacks with sediment resuspension and light attenuation. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G. Local characterization of thematic classification accuracy through spatially constrained confusion matrices. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.S.; Costa, M.P.; Melack, J.M.; Novo, E.M. Remote sensing of aquatic vegetation: Theory and applications. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 140, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Z.; Ren, J.; Qin, M.; Xia, Y.; He, L.; Chen, Y. Relationships between climate change and cyanobacterial bloom in Taihu Lake. Chin. J. Ecol. 2010, 29, 55–61. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Hu, W.; Chen, Y.; Gu, X.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ji, J. Temporal and spatial variation of aquatic macrophytes in west Taihu Lake. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2007, 27, 159–170. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Zhao, D.; Cai, Y.; An, S. A method for application of classification tree models to map aquatic vegetation using remotely sensed images from different sensors and dates. Sensors 2012, 12, 12437–12454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS Global Visualization Viewer. Available online: http://glovis.usgs.gov (accessed on 10 August 2015).
- He, J.; Zha, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, J. Aerosol indices derived from Modis data for indicating aerosol-induced air pollution. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1587–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Acharya, K.; Yu, Z. Modeling impacts of yangtze river water transfer on water ages in Lake Taihu, China. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; You, Y.; Wang, R. Influence of water diversion from yangtze river to Taihu Lake on nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in different water areas. Water Resour. Prot. 2008, 24, 53–56. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.-J.; Lu, X. Estimation of suspended sediment concentrations using terra Modis: An example from the lower Yangtze River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paillisson, J.-M.; Marion, L. Water level fluctuations for managing excessive plant biomass in shallow lakes. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geest, G.; Coops, H.; Roijackers, R.; Buijse, A.; Scheffer, M. Succession of aquatic vegetation driven by reduced water-level fluctuations in floodplain lakes. J. Appl. Ecol. 2005, 42, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Farrell, I.; Izaguirre, I.; Chaparro, G.; Unrein, F.; Sinistro, R.; Pizarro, H.; Rodríguez, P.; de Tezanos Pinto, P.; Lombardo, R.; Tell, G. Water level as the main driver of the alternation between a free-floating plant and a phytoplankton dominated state: A long-term study in a floodplain lake. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 73, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istvánovics, V.; Honti, M.; Kovács, Á.; Osztoics, A. Distribution of submerged macrophytes along environmental gradients in large, shallow lake balaton (hungary). Aquat. Bot. 2008, 88, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Jiang, H.; Cai, Y.; An, S. Artificial regulation of water level and its effect on aquatic macrophyte distribution in Taihu Lake. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y. High-frequency optical measurements in shallow Lake Taihu, China: Determining the relationships between hydrodynamic processes and inherent optical properties. Hydrobiologia 2014, 724, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleveld, M.A. Wind-induced resuspension in a shallow lake from medium resolution imaging spectrometer (MERIS) full-resolution reflectances. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ma, R.; Feng, S.; Le, C. Optically active substances and their contributions to the underwater light climate in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake in China. Fund. Appl. Limnol. 2007, 170, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokulil, M.; Chen, W.; Cai, Q. Anthropogenic impacts to large lakes in China: The Tai Hu example. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2000, 3, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Tuckett, R.; Merritt, D.; Hay, F.; Hopper, S.; Dixon, K. Dormancy, germination and seed bank storage: A study in support of ex situ conservation of macrophytes of southwest australian temporary pools. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B. Mapping Aquatic Vegetation in a Large, Shallow Eutrophic Lake: A Frequency-Based Approach Using Multiple Years of MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10295-10320. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70810295
Liu X, Zhang Y, Shi K, Zhou Y, Tang X, Zhu G, Qin B. Mapping Aquatic Vegetation in a Large, Shallow Eutrophic Lake: A Frequency-Based Approach Using Multiple Years of MODIS Data. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(8):10295-10320. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70810295
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaohan, Yunlin Zhang, Kun Shi, Yongqiang Zhou, Xiangming Tang, Guangwei Zhu, and Boqiang Qin. 2015. "Mapping Aquatic Vegetation in a Large, Shallow Eutrophic Lake: A Frequency-Based Approach Using Multiple Years of MODIS Data" Remote Sensing 7, no. 8: 10295-10320. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70810295
APA StyleLiu, X., Zhang, Y., Shi, K., Zhou, Y., Tang, X., Zhu, G., & Qin, B. (2015). Mapping Aquatic Vegetation in a Large, Shallow Eutrophic Lake: A Frequency-Based Approach Using Multiple Years of MODIS Data. Remote Sensing, 7(8), 10295-10320. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70810295