Sea-Ice Wintertime Lead Frequencies and Regional Characteristics in the Arctic, 2003–2015
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Satellite Data
2.2. Sea-Ice Lead Detection
2.3. Aggregation of Daily Maps

2.4. Cloud Artifact Filtering
3. Results
3.1. Segmentation and Filter Performance

3.2. Data Availability
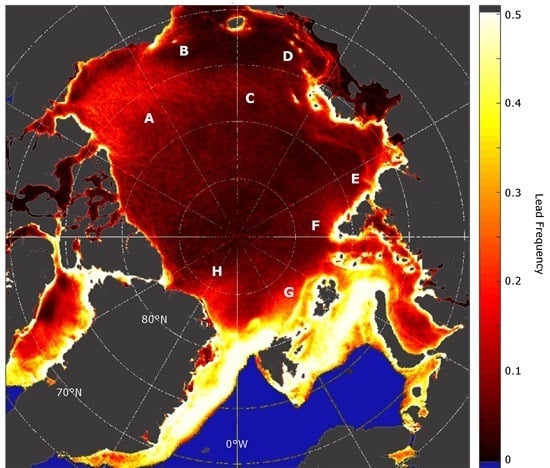
3.3. Sea-Ice Lead Frequencies and Distribution


3.4. Spatial and Temporal Lead Dynamics


4. Discussion

5. Conclusions and Outlook
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maykut, G.A. Large-scale heat exchange and ice production. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1982, 87, 7971–7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perovich, D.; Jones, K.; Light, B.; Eicken, H.; Markus, T.; Stroeve, J.; Lindsay, R. Solar partitioning in a changing Arctic sea-ice cover. Ann. Glaciol. 2011, 52, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kort, E.; Wofsy, S.; Daube, B.; Diao, M.; Elkins, J.; Gao, R.; Hintsa, E.; Hurst, D.; Jimenez, R.; Moore, F.; et al. Atmospheric observations of Arctic Ocean methane emissions up to 82° north. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Spreen, G.; Pang, S. Arctic sea ice circulation and drift speed: Decadal trends and ocean currents. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 2408–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, J.K.; Hibler, W.D. Small-scale sea ice deformation in the Beaufort Sea seasonal ice zone. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirling, I. The importance of polynyas, ice edges, and leads to marine mammals and birds. J. Mar. Syst. 1997, 10, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serreze, M.C.; Stroeve, J. Arctic sea ice trends, variability and implications for seasonal ice forecasting. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2015, 373, 20140159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihma, T. Effects of Arctic sea ice decline on weather and climate: A review. Surv. Geophys. 2014, 35, 1175–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.C.; Serreze, M.C.; Holland, M.M.; Kay, J.E.; Malanik, J.; Barrett, A.P. The Arctic’s rapidly shrinking sea ice cover: A research synthesis. Clim. ChangãĂĆ 2012, 110, 1005–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenigk, T.; Brodeau, L.; Graversen, R.G.; Karlsson, J.; Svensson, G.; Tjernström, M.; Willén, U.; Wyser, K. Arctic climate change in 21st century CMIP5 simulations with EC-Earth. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 2719–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermann, R.; Danilov, S.; Schröter, J.; Böning, C.; Sidorenko, D.; Rollenhagen, K. Ocean circulation and sea ice distribution in a finite element global sea ice–ocean model. Ocean Model. 2009, 27, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüpkes, C.; Vihma, T.; Birnbaum, G.; Wacker, U. Influence of leads in sea ice on the temperature of the atmospheric boundary layer during polar night. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcq, S.; Weiss, J. Influence of sea ice lead-width distribution on turbulent heat transfer between the ocean and the atmosphere. Cryosphere 2012, 6, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barber, D.G.; Hop, H.; Mundy, C.J.; Else, B.; Dmitrenko, I.A.; Tremblay, J.E.; Ehn, J.K.; Assmy, P.; Daase, M.; Candlish, L.M.; et al. Selected physical, biological and biogeochemical implications of a rapidly changing Arctic Marginal Ice Zone. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fily, M.; Rothrock, D. Opening and closing of sea ice leads: Digital measurements from synthetic aperture radar. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1990, 95, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, J.; Stone, R.; Maslanik, J.; Ellefsen, E. The detectability of sea-ice leads in satellite data as a function of atmospheric conditions and measurement scale. Ann. Glaciol. 1993, 17, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, R.; Rothrock, D. Arctic sea ice leads from advanced very high resolution radiometer images. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1995, 100, 4533–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drüe, C.; Heinemann, G. High-resolution maps of the sea-ice concentration from MODIS satellite data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drüe, C.; Heinemann, G. Accuracy assessment of sea-ice concentrations from MODIS using in-situ measurements. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, M.W.; Barry, R.G. A 5-year satellite climatology of winter sea ice leads in the western Arctic. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1998, 103, 21723–21734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabalka, Y.; Brucker, L.; Ivanoff, A.; Tilton, J.C. Shape-constrained segmentation approach for Arctic multiyear sea ice floe analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 4958–4961.
- Onana, V.; Kurtz, N.T.; Farrell, S.L.; Koenig, L.S.; Studinger, M.; Harbeck, J.P. A sea-ice lead detection algorithm for use with high-resolution airborne visible imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, A.; Eicken, H.; Shapiro, L.; Gens, R.; Heinrichs, T.; Meyer, F.; Gaylord, A. Mapping and Characterization of Recurring Spring Leads and Landfast Ice in the Beaufort and Chukchi Seas; Final Report; Ocs Study Boem 2012-067; University Fairbanks: Fairbanks, AK, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wernecke, A.; Kaleschke, L. Lead detection in Arctic sea ice from CryoSat-2: Quality assessment, lead area fraction and width distribution. Cryosphere 2015, 9, 1955–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, E.A.; Fleury, S.; Guerreiro, K.; Willmes, S.; Rémy, F.; Kouraev, A.V.; Heinemann, G. Sea ice leads detection using SARAL/AltiKa altimeter. Mar. Geod. 2015, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhrs, J.; Kaleschke, L. An algorithm to detect sea ice leads by using AMSR-E passive microwave imagery. Cryosphere 2012, 6, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröhan, D.; Kaleschke, L. A nine-year climatology of Arctic sea ice lead orientation and frequency from AMSR-E. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1451–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmes, S.; Heinemann, G. Pan-Arctic lead detection from MODIS thermal infrared imagery. Ann. Glaciol. 2015, 56, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreen, G.; Kwok, R.; Menemenlis, D. Trends in Arctic sea ice drift and role of wind forcing: 1992–2009. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, G.A.; Hall, D.K.; Salomonson, V.V. MODIS Sea Ice Products User Guide to Collection 5; Technical Report; National Snow and Ice Data Center, University of Colorado: Boulder, CO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.K.; Nghiem, S.V.; Rigor, I.G.; Miller, J.A. Uncertainties of temperature measurements on snow-covered land and sea ice from in situ and MODIS data during BROMEX. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2015, 54, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, R.A.; Ackerman, S.A.; Liu, Y.; Strabala, K.I.; Zhang, H.; Key, J.R.; Wang, X. Cloud detection with MODIS. Part I: Improvements in the MODIS cloud mask for collection 5. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, S.; Frey, R.; Strabala, K.; Liu, Y.; Gumley, L.; Baum, B.; Menzel, P. Discriminating Clear-Sky from Cloud with MODIS Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (MOD35); Version 6.1; Technical Report for MODIS Cloud Mask Team, Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies, University of Wisconsin: Wisconsin, WI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Key, J.R.; Frey, R.A.; Ackerman, S.A.; Menzel, W.P. Nighttime polar cloud detection with MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Key, J.R. Less winter cloud aids summer 2013 Arctic sea ice return from 2012 minimum. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Kotchenova, S.; Ray, J. MODIS Surface Reflectance Users Guide. Version 1.3; MODIS Land Surface Reflectance Science Computing Facility: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, D.; Massom, R. The role of sea ice in Arctic and Antarctic polynyas. In Polynyas, Windows to the World; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2007; Volume 74, pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, N.E.; Wilkinson, J.P.; Wadhams, P. Multi-satellite sensor analysis of fast-ice development in the Norske Øer Ice Barrier, northeast Greenland. Ann. Glaciol. 2011, 52, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janout, M.A.; Aksenov, Y.; Hölemann, J.A.; Rabe, B.; Schauer, U.; Polyakov, I.V.; Bacon, S.; Coward, A.C.; Karcher, M.; Lenn, Y.D.; et al. Kara Sea freshwater transport through Vilkitsky Strait: Variability, forcing, and further pathways toward the western Arctic Ocean from a model and observations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 4925–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinto, J.O.; Alam, A.; Maslanik, J.; Curry, J.; Stone, R.S. Surface characteristics and atmospheric footprint of springtime Arctic leads at SHEBA. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, A.; Kaleschke, L.; Lüpkes, C.; Ament, F.; Vihma, T. The impact of heterogeneous surface temperatures on the 2-m air temperature over the Arctic Ocean under clear skies in spring. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spreen, G.; Kaleschke, L.; Heygster, G. Sea ice remote sensing using AMSR-E 89-GHz channels. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113, C02S03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, M.; Brümmer, B.; Müller, G. Atmosphere—Ice forcing in the transpolar drift stream: Results from the DAMOCLES ice-buoy campaigns 2007–2009. Cryosphere 2014, 8, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksenov, Y.; Ivanov, V.; Nurser, A.; Bacon, S.; Polyakov, I.; Coward, A.; Naveira-Garabato, A.; Beszczynska-Moeller, A. The Arctic circumpolar boundary current. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luneva, M.V.; Aksenov, Y.; Harle, J.D.; Holt, J.T. The effects of tides on the water mass mixing and sea ice in the Arctic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 6669–6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Willmes, S.; Heinemann, G. Sea-Ice Wintertime Lead Frequencies and Regional Characteristics in the Arctic, 2003–2015. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010004
Willmes S, Heinemann G. Sea-Ice Wintertime Lead Frequencies and Regional Characteristics in the Arctic, 2003–2015. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleWillmes, Sascha, and Günther Heinemann. 2016. "Sea-Ice Wintertime Lead Frequencies and Regional Characteristics in the Arctic, 2003–2015" Remote Sensing 8, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010004
APA StyleWillmes, S., & Heinemann, G. (2016). Sea-Ice Wintertime Lead Frequencies and Regional Characteristics in the Arctic, 2003–2015. Remote Sensing, 8(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010004