Derivation of Sea Surface Wind Directions from TerraSAR-X Data Using the Local Gradient Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Description of the Dataset
3. Methodology
3.1. Pre-Processing Of TS-X Data
3.1.1. Radiometric Calibration of SAR Data
3.1.2. Spatial Sampling

3.2. Extraction of Sea Surface Wind Direction
3.2.1. Computation of the Local Gradient
3.2.2. Extraction of the Main Direction



4. Case Studies
4.1. General Cases
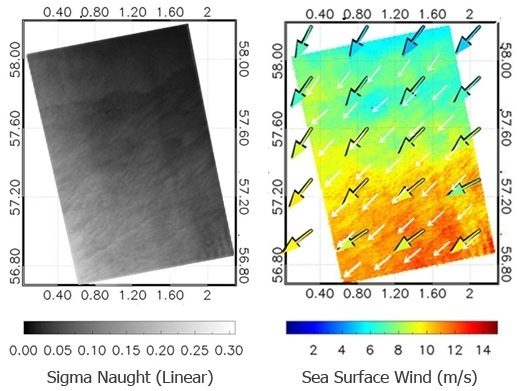
4.1.1. A Homogeneous Sea Surface Wind Case

4.1.2. An Extra-Tropical Cyclone Case

4.1.3. A Convective Cell Case

4.1.4. Verification of the TS-X Retrieved Sea Surface Wind Directions

4.2. A Tropical Cyclone Case


5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix
References
- Verspeek, J.; Stoffelen, A.; Verhoef, A.; Portabella, M. Improved ASCAT wind retrieval using NWP ocean calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2488–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentamy, A.; Fillion, D.C. Gridded sea surface wind fields from Metop/ASCAT measurements. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 1729–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lin, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, X.; Peng, H.; Zhou, W. The HY-2 satellite and its preliminary assessment. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2012, 5, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, A.K.; Prasada Rao, C.V.K. Comparison of Oceansat-2 scatterometer winds with buoy observations over the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettenhausen, M.H.; Smith, C.K.; Bevilacqua, R.M.; Wang, N.Y.; Gaiser, P.W.; Cox, S. A nonlinear optimization algorithm for WindSat wind vector retrievals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gommenginger, C.P.; Srokosz, M.A.; Challenor, P.G.; Cotton, P.D. Development and validation of altimeter wind speed algorithms using an extended collocated Buoy/Topex dataset. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Trans. 2002, 40, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourrion, J.; Vandemark, D.; Bailey, S.; Chapron, B.; Gommenginger, G.P.; Challenor, P.G.; Srokosz, M.A. A two-parameter wind speed algorithm for Ku-band altimeters. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2002, 19, 2030–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffelen, A.; Anderson, D. Scatterometer data interpretation: Estimation and validation of the transfer function CMOD4. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 5767–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Stoffelen, A.; de Haan, S. An improved C-band scatterometer ocean geophysical model function: CMOD5. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.R.; Elfouhaily, T.M.; Chapron, B. Polarization Ratio for Microwave Backscattering from the Ocean Surface at Low to Moderate Incidence Angles. In Proceedings of the 1998 Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium Proceedings, IGARSS’98, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–10 July 1998; pp. 1671–1673.
- Mouche, A.; Hauser, D.; Daloze, J.F.; Guérin, C. Dual-polarization measurements at C-band over the ocean: Results from airborne radar observations and comparison with ENVISAT ASAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaldo, F.M.; Thompson, D.R.; Pichel, W.G.; Clemente, P. A Systematic comparison of quikscat and SAR ocean surface wind speeds. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Perrie, W.; Vachon, P.W.; Li, X.; Pichel, W.G.; Guo, J.; He, Y. Ocean vector winds retrieval from C-band fully polarimetric SAR measurements. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Trans. 2012, 50, 4252–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouche, A.; Collard, F.; Chapron, B.; Dagestad, K.; Guitton, G.; Johannessen, J.A.; Kerbaol, V.; Hansen, M.W. On the use of doppler shift for sea surface wind retrieval from SAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Trans. 2012, 50, 2901–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaldo, F. The Alaska SAR demonstration and near-real-time synthetic aperture radar winds. J. Hopkins APL Tech. D 2000, 21, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Gerling, T.W. Structure of the surface wind field from the Seasat SAR. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 2308–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, P.D.; Thompson, D.R.; Vandemark, D.C. Extracting fine-scale wind fields from synthetic aperture radar images of the ocean surface. J. Hopkins APL Tech. D. 2000, 21, 108–115. [Google Scholar]
- Horstmann, J.; Thompson, D.R.; Monaldo, F.; Iris, S.; Graber, H.C. Can synthetic aperture radars be used to estimate hurricane force winds? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, S.; Horstmann, J.; Koch, W.; Rosenthal, W. Mesoscale wind measurements using recalibrated ERS SAR images. J. Geophys. Res.: Oceans 1998, 103, 7847–7856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, W. Directional analysis of SAR images aiming at wind direction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstmann, J.; Koch, W.; Lehner, S. Ocean wind fields retrieved from the advanced synthetic aperture radar aboard ENVISAT. Ocean. Dynam. 2004, 54, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstmann, J.; Koch, W. Measurement of ocean surface winds using synthetic aperture radars. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2005, 30, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; Lehner, S. Algorithm for sea surface wind retrieval from TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2928–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; Lehner, S. Sea surface wind field by TerraSAR-X in support of offshore wind farm. IEEE J.-STARS 2013, 6, 1757–1768. [Google Scholar]
- Lehner, S.; Pleskachevsky, A.; Velotto, D.; Jacobsen, S. Meteo-marine parameters and their variability observed by high resolution satellite radar. Oceanography 2013, 26, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmic, M.; Grisogono, B.; Li, X.-M.; Lehner, S. Examining deep and shallow Adriatic bora events. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.A. Longitudinal instabilities and secondary flows in the planetary boundary layer: A review. Rev. Geophys. 1980, 18, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etling, D.; Brown, R.A. Roll vortices in the planetary boundary layer: A review. Bound. Layer Meteor. 1993, 65, 215–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusch, S.; Lehner, S.; Schulz-Stellenfleth, J. Synergetic use of radar and optical satellite images to support severe storm prediction for offshore wind farming. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obeserv. Remote Sens. 2008, 1, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, G.J. An analytic model of the wind and pressure profiles in hurricanes. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1980, 108, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, D.J.; Gray, W.M. The hurricane’s inner core region. I. Symmetric and asymmetric structure. J. Atmos. Sci. 1973, 30, 1544–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-R.; Li, X.-M. Derivation of Sea Surface Wind Directions from TerraSAR-X Data Using the Local Gradient Method. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010053
Wang Y-R, Li X-M. Derivation of Sea Surface Wind Directions from TerraSAR-X Data Using the Local Gradient Method. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010053
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yi-Ran, and Xiao-Ming Li. 2016. "Derivation of Sea Surface Wind Directions from TerraSAR-X Data Using the Local Gradient Method" Remote Sensing 8, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010053
APA StyleWang, Y. -R., & Li, X. -M. (2016). Derivation of Sea Surface Wind Directions from TerraSAR-X Data Using the Local Gradient Method. Remote Sensing, 8(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010053