Quantitative Estimation of the Velocity of Urbanization in China Using Nighttime Luminosity Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nighttime Luminosity Data
2.2. The Calculation of the Velocity of Urbanization

2.3. Land Use and Socioeconomic Data
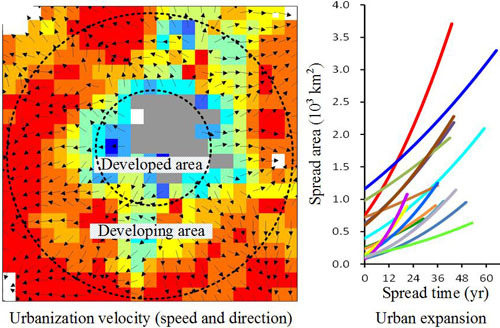
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Spatial Features of the Velocity Map of Urbanization

3.2. The Velocity of Urbanization for China’s Urban Areas

3.3. The Velocity of Urbanization in Urban Agglomerations and Cities


3.4. Land Use Changes during Urbanization


3.5. Prediction of Urban Growth

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. Tabulation on the 2000 Population Census of the People’s Republic of China by County; China Statistical Press: Beijing, China, 2003.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. Tabulation on the 2010 Population Census of the People’s Republic of China by County; China Statistical Press: Beijing, China, 2013.
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision, Highlights; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, N.B.; Foster, D.; Groffman, P.; Grove, J.M.; Hopkinsons, C.S.; Nadelhoffer, K.J.; Pataki, D.E.; Peters, D.P.C. The changing landscape: Ecosystem responses to urbanization and pollution across climatic and societal gradients. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, E.G.; Bockstael, N.E. The evolution of urban sprawl: Evidence of spatial heterogeneity and increasing land fragmentation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20672–20677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, K.C.; Güneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, B. Urbanization in developing countries: Current trends, future projections, and key challenges for sustainability. Technol. Soc. 2006, 28, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, M. The urban transformation of the developing world. Science 2008, 319, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R. Mapping city lights with nighttime data from the DMSP Operational Linescan System. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1997, 63, 727–734. [Google Scholar]
- Doll, C.N.H.; Muller, J.P.; Elvidge, C.D. Night-time imagery as a tool for global mapping of socioeconomic parameters and greenhouse gas emissions. Ambio 2000, 29, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.C. A scale-adjusted measure of “urban sprawl” using nighttime satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C.D. Spatial analysis of global urban extent from DMSP-OLS night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.; Roberts, D.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K. Census from heaven: An estimate of the global human population using night-time satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3061–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Powell, R.L.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Sutton, P.C.; Anderson, S. Shedding light on the global distribution of economic activity. Open Geogr. J. 2010, 3, 148–161. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Anderson, S.J.; Sutton, P.C.; Ghosh, T. The Night Light Development Index (NLDI): A spatially explicit measure of human development from satellite. Soc. Geogr. 2012, 7, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Elvidge, C.D. Mapping decadal change in anthropogenic night light. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 7, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Elvidge, C.D. Night on earth: Mapping decadal changes of anthropogenic night light in Asia. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 22, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Haynie, S.; Pei, T.; Xu, T. Night-time light derived estimation of spatio-temporal characteristics of urbanization dynamics using DMSPOLS satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP). Available online: http://ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/dmsp.html (accessed on 1 March 2014).
- Elvidge, C.D.; Hsu, F.C.; Baugh, K.E.; Ghosh, T. National trends in satellite observed lighting: 1992–2012. In Global Urban Monitoring and Assessment through Earth Observation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 97–120. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.E.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.W.; Erwin, E.H.; Zhizhin, M. A fifteen year record of global natural gas flaring derived from satellite data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennie, J.; Davies, T.W.; Duffy, J.P.; Inger, R.; Gaston, K.J. Contrasting trends in light pollution across Europe based on satellite observed night time lights. Sci. Rep. 2013, 4, 3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Schaaf, C.; Seto, K.C. The vegetation adjusted NTL urban index: A new approach to reduce saturation and increase variation in nighttime luminosity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S. Robust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatterplots. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loarie, S.R.; Duffy, P.B.; Hamilton, H.; Asner, G.P.; Field, C.B.; Ackerly, D.D. The velocity of climate change. Nature 2009, 462, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrough, P.A.; McDonell, R.A. Principles of Geographical Information Systems; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Yuan, Q.; Yan, C.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Li, A.; Ma, R.; Huang, J.; Cheng, J.; Chang, C.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Zeng, Y.; Bao, A. Land cover changes of China from 2000 to 2010. Quat. Sci. 2014, 34, 723–731. [Google Scholar]
- Dobson, J.E.; Bright, E.A.; Coleman, P.R.; Durfee, R.C.; Worley, B.A. LandScan: A global population database for estimating populations at risk. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 849–857. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, J.; Ban, Y. Urban growth and environmental impacts in Jing-Jin-Ji, the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 30, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.H. China’s western development program: Its rationale, implementation, and prospects. Mod. China 2002, 28, 432–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, G.; Sander, N. Quantifying global international migration flows. Science 2014, 343, 1520–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Kong, C.; Liu, G.; Wu, C.; Deng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, Q. Changes of urban wetlands in Wuhan, China, from 1987 to 2005. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2010, 34, 207–220. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Wu, X.; Ning, T.; Huang, G.; Wang, J.; Jian, S.; Lu, H. Wetland changes and mangrove restoration planning in Shenzhen Bay, Southern China. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 7, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Jiang, P.; Ding, P. Black-billed magpies (Pica pica) adjust nest characteristics to adapt to urbanization in Hangzhou. Can. J. Zool. 2008, 86, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lei, F.; Liu, S.; Li, D.; Chen, C.; Wang, P. Variation in baseline corticosterone levels of tree sparrow (Passer montanus) populations along an urban gradient in Beijing. J. Ornithol. 2011, 152, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, D.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, D.; Wang, L. Impacts of urbanization on stream habitats and macroinvertebrate communities in the tributaries of Qiangtang River. Hydrobiologia 2012, 680, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Jia, G.; Pohl, C.; Zhang, X.; Genderen, J. Assessing surface albedo change and its induced radiation budget under rapid urbanization with Landsat and GLASS data. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, T.; Yin, Z.; Li, B.; Zhou, C.; Haynie, S. Quantitative Estimation of the Velocity of Urbanization in China Using Nighttime Luminosity Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020094
Ma T, Yin Z, Li B, Zhou C, Haynie S. Quantitative Estimation of the Velocity of Urbanization in China Using Nighttime Luminosity Data. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(2):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020094
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Ting, Zhan Yin, Baolin Li, Chenghu Zhou, and Susan Haynie. 2016. "Quantitative Estimation of the Velocity of Urbanization in China Using Nighttime Luminosity Data" Remote Sensing 8, no. 2: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020094
APA StyleMa, T., Yin, Z., Li, B., Zhou, C., & Haynie, S. (2016). Quantitative Estimation of the Velocity of Urbanization in China Using Nighttime Luminosity Data. Remote Sensing, 8(2), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020094