Estimating the Exposure of Coral Reefs and Seagrass Meadows to Land-Sourced Contaminants in River Flood Plumes of the Great Barrier Reef: Validating a Simple Satellite Risk Framework with Environmental Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Great Barrier Reef as a Case Study Area
2.1. The Great Barrier Reef
2.2. Link between Contaminants and Reef and Seagrass Health
2.3. Published Ecological Thresholds for Land-Sourced Contaminants
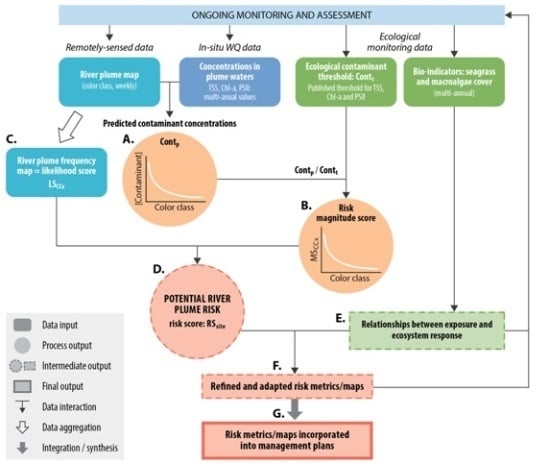
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Mapping of the GBR Plume Water Types over 10 Wet Seasons
3.2. Environmental Data: The Marine Monitoring Program (MMP)
3.2.1. Wet Season Monitoring of Water Quality
3.2.2. Seagrass Monitoring Programs
3.2.3. Coral Monitoring Programs
3.3. Testing of the Satellite Risk Framework
3.3.1. Magnitude Score
3.3.2. Likelihood Score
3.3.3. Risk Score: Magnitude × Likelihood
3.3.4. Relationships between Risk and Ecosystem Response
3.4. Spatial Distribution of Risk of Seagrasses and Coral Reefs to River Plume
4. Results
4.1. Mapping the Water Types in Flood Plumes
4.2. Contaminant Concentrations across Plume Water Types
4.3. Environmental Data: Seagrass Meadows and Proportional Macroalgae Cover in the Algal Communities
4.4. Relationships between Plume Exposure and Seagrass Response
4.5. Relationships between Plume Exposure and MAp Response
4.6. River Plume Risk Map
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tilman, D.; Fargione, J.; Wolff, B.; D’Antonio, C.; Dobson, A.; Howarth, R.; Schindler, D.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Simberloff, D.; Swackhamer, D. Forecasting Agriculturally Driven Global Environmental Change. Science 2001, 292, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, R.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabricius, K.E. Factors Determining the Resilience of Coral Reefs to Eutrophication: A Review and Conceptual Model. In Coral Reefs: An Ecosystem in Transition; Dubinsky, Z., Stambler, N., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Houten, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 493–506. [Google Scholar]
- Vitousek, P. Human Domination of Earth’s Ecosystems. Science 1997, 277, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, F.J. Towards ecologically relevant targets for river pollutant loads to the Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 65, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpern, B.S.; Walbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V.; Micheli, F.; D’Agrosa, C.; Bruno, J.F.; Casey, K.S.; Ebert, C.; Fox, H.E.; et al. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, L.J.; Yoshida, R.L.; Grech, A.; Coles, R. Queensland Seagrasses. Status 2010—Torres Strait and East. Coast; Fisheries Queensland (DEEDI): Cairns, Australia, 2010; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Brodie, J.; Waterhouse, J. A critical review of environmental management of the “not so Great” Barrier Reef. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 104–105, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, J.E.; Kroon, F.J.; Schaffelke, B.; Wolanski, E.C.; Lewis, S.E.; Devlin, M.J.; Bohnet, I.C.; Bainbridge, Z.T.; Waterhouse, J.; Davis, A.M. Terrestrial pollutant runoff to the Great Barrier Reef: An Update of Issues, Priorities and Management Responses. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 65, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grech, A.; Coles, R.; Marsh, H. A broad-scale assessment of the risk to coastal seagrasses from cumulative threats. Mar. Policy 2011, 35, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, M.; Schaffelke, B. Spatial extent of riverine flood plumes and exposure of marine ecosystems in the Tully coastal region, Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2009, 60, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Romero, J.G.; Devlin, M.; Teixeira da Silva, E.; Petus, C.; Ban, N.C.; Pressey, R.L.; Kool, J.; Roberts, J.; Cerdeira, S.; Wenger, A.; et al. Following the flow: A Combined Remote Sensing-GIS Approach To Model Exposure of Marine Ecosystems to Riverine Flood Plume. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 119, 194–207. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, M.J.; McKinna, L.W.; Álvarez-Romero, J.G.; Petus, C.; Abott, B.; Harkness, P.; Brodie, J. Mapping the pollutants in surface riverine flood plume waters in the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 65, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, M.; Harkness, P.; McKinna, L.; Waterhouse, J. Mapping the Surface Exposure of Terrestrial Pollutants in the Great Barrier Reef. Report to the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority, August 2010; Report Number 10/12; Australian Centre for Tropical Freshwater Research: Townsville, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, M.; Petus, C.; Teixeira da Silva, E.; Tracey, D.; Wolff, N.; Waterhouse, J.; Brodie, J. Water quality and river plume monitoring in the Great Barrier Reef: An Overview of Methods Based on Ocean Colour Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12909–12941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petus, C.; Teixera da Silva, E.; Devlin, M.; Álvarez-Romero, A.; Wenger, A. Using MODIS data for mapping of water types within flood plumes in the Great Barrier Reef, Australia: Towards the Production of River Plume Risk Maps for Reef and Seagrass Ecosystems. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 137, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coles, R.; McKenzie, L.; De’ath, G.; Roelofs, A.; Lee Long, W. Spatial distribution of deepwater seagrass in the inter-reef lagoon of the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 392, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, C.; Devlin, M.; Langlois, L.; Petus, C.; McKenzie, L.; Texeira da Silva, E.; McMahon, K.; Adams, M.; O”Brien, K.; Statton, J.; et al. Thresholds and Indicators of Declining Water Quality as Tools for Tropical Seagrass Management. Report to the National Environmental Research Program; Project 5.3 Final Report; Reef and Rainforest Research Centre Limited: Cairns, Australia, 2014; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Petus, C.; Collier, C.; Devlin, M.; Rasheed, M.; McKenna, S. Using MODIS data for understanding changes in seagrass meadow health: A Case Study in the Great Barrier Reef (Australia). Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 98, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, J.; Petersen, K.; Song, Y.; Ruus, A.; Grung, M.; Bakke, T.; Tollefsen, K.E. Environmental risk assessment of combined effects in aquatic ecotoxicology: A Discussion Paper. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 96, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, M.T.; Browman, H.I. Risk assessment and risk management: A Primer for Marine Scientists. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, J.; Lart, W.; de Rozarieux, N.; Kingston, A.; Caslake, R.; Le Quesne, W.; Jennings, S.; Caveen, A.; Brown, M. A development of ecological risk screening with an application to fisheries off SW England. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 72, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobday, A.J.; Smith, A.D.M.; Stobutzki, I.C.; Bulman, C.; Daley, R.; Dambacher, J.M.; Deng, R.A.; Dowdney, J.; Fuller, M.; Furlani, D.; et al. Ecological risk assessment for the effects of fishing. Fish. Res. 2011, 108, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzenmu’ller, V.; Fock, H.O.; Gimpel, A.; Rambo, H.; Diekmann, R.; Probst, W.N.; Callies, U.; Bockelmann, F.; Neumann, H.; Kröncke, I. Quantitative environmental risk assessments in the context of marine spatial management: Current Approaches and Some Perspectives. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 72, 1022–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astles, K.L. Linking risk factors to risk treatment in ecological risk assessment of marine biodiversity. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 72, 1116–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, J.; Waterhouse, J.; Maynard, J.; Bennett, J.; Furnas, M.; Devlin, M.; Lewis, S.; Collier, C.; Schaffelke, B.; Fabricius, K.; et al. Assessment of the Relative Risk of Water Quality to Ecosystems of the Great Barrier Reef. A report to the Department of the Environment and Heritage Protection, Queensland Government, Brisbane; Report Number 13/28; Australian Centre for Tropical Freshwater Research: Townsville, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Baith, K.; Lindsay, R.; Fu, G.; McClain, C.R. SeaDAS, a data analysis system for ocean color satellite sensors. Eos. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2001, 82, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Brando, V.E.; Dekker, A.G.; Blondeau-Patissier, D. Validity of SeaDAS water constituents retrieval algorithms in Australian tropical coastal waters. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L21603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOCCG. Reports of the International Ocean.-Colour Coordinating Group, No. 3, IOCCG. Remote Sensing of Ocean Colour in Coastal, and Other Optically-Complex Waters; Sathyendranath, S., Ed.; IOCCG: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Dall’Olmo, G.; Moses, W.; Rundquist, D.C.; Barrow, T.; Fisher, T.R.; Gurlin, D.; Holz, J. A simple semi-analytical model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in turbid waters: Validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3582–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odermatt, D.; Gitelson, A.; Brando, V.E.; Schaepman, M. Review of constituent retrieval in optically deep and complex waters from satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brando, V.E.; Schroeder, T.; Blondeau-Patissier, D.; Clementson, L.; Dekker, A.G. Reef Rescue Marine Monitoring Program: Using Remote Sensing for GBR Wide Water Quality; Final Report for 2010/2011 Activities; CSIRO Land & Water: Canberra, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Brando, V.E.; Schroeder, T.; Dekker, A.G.; Clementson, L. Reef Rescue Marine Monitoring Program: Using Remote Sensing for GBR Wide Water Quality. Final Report for 2011/12 Activities. Report for the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority; CSIRO Land & Water: Townsville, Australia, 2013; p. 193. [Google Scholar]
- King, E.A.; Schroeder, T.; Brando, V.E.; Suber, K. A Pre-operational System for Satellite Monitoring of Great Barrier Reef Marine Water Quality. Wealth from Oceans Flagship Report; CSIRO Land & Water: Canberra, Australia, 2014; p. 56. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, T.; Brando, V.E.; Cherukuru, N.R.C.; Clementson, L.A.; Blondeau-Patissier, D.; Dekker, A.G.; Schaale, M.; Fischer, J. Remote Sensing of Apparent and Inherent Optical Properties of Tasmanian Coastal Waters: Application to MODIS Data; Ocean. Optics XIX: Barga, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Brando, V.E.; Dekker, A.G.; Park, Y.J.; Schroeder, T. Adaptive semi-analytical inversion of ocean colour radiometery in optically complex waters. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 2808–2833. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, T.; Devlin, M.J.; Brando, V.E.; Dekker, A.G.; Brodie, J.E.; Clementson, L.A.; McKinna, L. Inter-annual variability of wet season freshwater plume extent into the Great Barrier Reef lagoon based on satellite coastal ocean colour observations. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 65, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahr, J.; Kooistra, L. Environmental risk mapping of pollutants: State of the Art and Communication Aspects. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3899–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borja, A.; Bricker, S.B.; Dauer, D.M.; Demetriades, N.T.; Ferreira, J.G.; Forbes, A.T.; Hutchings, P.; Jia, X.; Kenchington, R.; Carlos Marques, J.; et al. Overview of integrative tools and methods in assessing ecological integrity in estuarine and coastal systems worldwide. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1519–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter, G.W., II. Endpoints for regional ecological risk assessments. Environ. Manag. 1990, 14, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, J.E.; Waterhouse, J.; Lewis, S.E.; Bainbridge, Z.T.; Johnson, J. Current Loads of Priority Pollutants Discharged from Great Barrier Reef Catchments to the Great Barrier Reef; ACTFR Report 09/02; Australian Centre for Tropical Freshwater Research: Townsville, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brodie, J.; Binney, J.; Fabricius, K.; Gordon, I.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Hunter, H.; O’Reagain, P.; Pearson, R.; Quirk, M.; Thorburn, P.; et al. Scientific Consensus Statement on Water Quality in the Great Barrier Reef; The State of Queensland (Department of the Premier and Cabinet): Brisbane, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Maughan, M.; Brodie, J. Reef exposure to river-borne contaminants: A Spatial Model. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2009, 60, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De’ath, G.; Fabricius, K.E.; Sweatman, H.; Puotinen, M. The 27-year decline of coral cover on the Great Barrier Reef and its causes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 190, 17995–17999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, L.; Collier, C.; Waycott, M.; Unsworth, R.; Yoshida, R.; Smith, N. Monitoring inshore seagrasses of the Great Barrier Reef and responses to water quality. In Proceedings of the 12th International Coral Reef Symposium, Cairns, Australia, 9–13 July 2012; Mini-Symposium 15b Seagrasses and Seagrass Ecosystems. Available online: http://www.icrs2012.com/proceedings/manuscripts/ICRS2012_15B_4.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2015).
- Schaffelke, B.; Anthony, K.; Blake, J.; Brodie, J.; Collier, C.; Devlin, M.; Fabricius, K.; Martin, K.; McKenzie, L.; Negri, A.; et al. Marine and Coastal Ecosystem Impacts. In Synthesis of Evidence to Support the Reef Water Quality Scientific Consensus Statement 2013; Department of the Premier and Cabinet, Queensland Government: Brisbane, Australia, 2013; Chapter 1; p. 50. [Google Scholar]
- Collier, C.J.; Waycott, M.; Mckenzie, L.J. Light thresholds derived from seagrass loss in the coastal zone of the Great Barrier Reef. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De’ath, G.; Fabricius, K. Water quality as a regional driver of coral biodiversity and macroalgae on the Great Barrier Reef. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, T.F.; Uthicke, S.; Humphrey, C.; Fabricius, K.E. Gradients in water column nutrients, sediment parameters, irradiance and coral reef development in the Whitsunday Region, central Great Barrier Reef. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 74, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erftemeijer, P.L.A.; Reigl, B.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Todd, P.A. Environmental impacts of dredging and other sediment disturbances on corals: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1737–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udy, J.W.; Dennison, W.C. Physiological responses of seagrasses used to identify anthropogenic nutrient inputs. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1997, 48, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udy, J.W.; Dennison, W.C. Growth and physiological responses of three seagrass species to elevated sediment nutrients. J. Exp. Marine. Biol. Ecol. 1997, 217, 253–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udy, J.W.; Dennison, W.C.; Lee Long, W.J.; McKenzie, L.J. Responses of seagrass to nutrients in the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 185, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brush, M.J.; Nixon, S.W. Direct measurement of light attenuation by epiphytes on eelgrass Zostera marina. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 238, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankovich, T.A.; Fourqurean, J.W. Seagrass epiphyte loads along a nutrient availability gradient, Florida Bay, USA. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 159, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, R.K.F.; Collier, C.J.; Waycott, M.; McKenzie, L.J.; Cullen-Unsworth, L.C. A framework for the resilience of seagrass ecosystems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCook, L.J.; Jompa, J.; Diaz-Pulido, G. Competition between corals and algae on coral reefs: A Review of Evidence and Mechanisms. Coral Reefs 2001, 19, 400–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricius, K.E. Effects of terrestrial runoff on the ecology of corals and coral reefs: Review and Synthesis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, M.; Lewis, S.; Davis, A.; Smith, R.; Negri, A.; Thompson, M.; Poggio, M. Advancing Our Understanding of the Source, Management, Transport and Impacts of Pesticides on the Great Barrier Reef 2011–2015. A Report for the Queensland Department of Environment and Heritage Protection; Tropical Water & Aquatic Ecosystem Research (TropWATER) Publication, James Cook University: Cairns, Australia, 2015; p. 134. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, S.E.; Schaffelke, B.; Shaw, M.; Bainbridge, Z.T.; Rohde, K.W.; Kennedy, K.; Davis, A.M.; Masters, B.L.; Devlin, M.J.; Mueller, J.F.; et al. Assessing the additive risks of PSII herbicide exposure to the Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 65, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantin, N.E.; Negri, A.P.; Willis, B.L. Photoinhibition from chronic herbicide exposure reduces reproductive output of reef-building corals. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 344, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, A.P.; Flores, F.; Mercurio, P.; Mueller, J.F.; Collier, C.J. Lethal and sub-lethal chronic effects of the herbicide diuron on seagrass. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 165, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macinnis-Ng, C.M.O.; Ralph, P.J. Short-term response and recovery of Zostera capricorni photosynthesis after herbicide exposure. Aquat. Bot. 2003, 76, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, F.; Collier, C.J.; Mercurio, P.; Negri, A.P. Phytotoxicity of Four Photosystem II Herbicides to Tropical Seagrasses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. Water Quality Guidelines for the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park, Revised Edition 2010; Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority: Townsville, Australia, 2010; p. 100. [Google Scholar]
- Philipp, E.; Fabricius, K. Photophysiological stress in scleractinian corals in response to short-term sedimentation. J. Exp. Marine Biol. Ecol. 2003, 287, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Lott, C.; Fabricius, K. Sedimentation stress in a scleractinian coral exposed to terrestrial and marine sediments with contrasting physical, geochemical and organic properties. J. Exp. Marine. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 336, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, J.; Schroeder, T.; Rohde, K.; Faithful, J.; Masters, B.; Dekker, A.; Brando, V.; Maughan, M. Dispersal of suspended sediments and nutrients in the Great Barrier Reef lagoon during river discharge events: Conclusions from Satellite Remote Sensing and Concurrent Flood Plume Sampling. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2010, 61, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffelke, B.; Carleton, J.; Skuza, M.; Zagorskis, I.; Furnas, M.J. Water quality in the inshore great barrier reef lagoon: Implications for Long-Term Monitoring and Management. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 65, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, M.; Wenger, A.; Petus, C.; Eduardo Teixeira da Silva, E.; Debose, J.; Álvarez-Romero, J. Reef Rescue Marine Monitoring Program: Final Report of JCU Activities 2011/12—Flood Plumes and Extreme Weather Monitoring for the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority; James Cook University: Townsville, Australia, 2013; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11017/2803 (accessed on 1 March 2015).
- McKenzie, L.J.; Collier, C.J.; Langlois, L.A.; Yoshida, R.L.; Smith, N.; Takahashi, M.; Waycott, M. Marine Monitoring Program—Inshore Seagrass, Annual Report for the Sampling Period 1 June 2013–31 May 2014; Tropical Water & Aquatic Ecosystem Research (TropWATER) Publication, James Cook University: Cairns, Australia, 2015; p. 225. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A.; Schaffelke, B.; Logan, M.; Costello, P.; Davidson, J.; Doyle, J.; Furnas, M.; Gunn, K.; Liddy, M.; Skuza, M.; et al. Reef Rescue Marine Monitoring Program. Annual Report of AIMS Activities 2012 to 2013– Inshore Water Quality and Coral Reef Monitoring. Report for the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority; Australian Institute of Marine Science: Townsville, Australia, 2013; p. 182. [Google Scholar]
- Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. Reef Rescue Marine Monitoring Program: Quality Assurance/Quality Control Methods and Procedures; Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority: Townsville, Australia, 2012; p. 104. [Google Scholar]
- Bentley, C.; Devlin, M.; Paxman, C.; Chue, K.L.; Mueller, J. Pesticide Monitoring in Inshore Waters of the Great Barrier Reef Using Both Time-Integrated and Event Monitoring Techniques (2011–2012); The University of Queensland, The National Research Centre for Environmental Toxicology (Entox): Brisbane, Australia, 2012; p. 91. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, K.; Schroeder, T.; Shaw, M.; Haynes, D.; Lewis, S.; Bentley, C.; Paxman, C.; Carter, S.; Brando, V.; Bartkow, M.; et al. Long term monitoring of photosystem II herbicides–Correlation with remotely sensed freshwater extent to monitor changes in the quality of water entering the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 65, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, R.; Schreiber, U.; Escher, B.I.; Quayle, P.; Nash, S.M.B.; Mueller, J.F. Rapid exposure assessment of PSII herbicides in surface water using a novel chlorophyll a fluorescence imaging assay. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 401, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnusson, M.; Heimann, K.; Quayle, P.; Negri, A.P. Additive toxicity of herbicide mixtures and comparative sensitivity of tropical benthic microalgae. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1978–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, L.J.; Finkbeiner, M.A.; Kirkman, H. Methods for mapping seagrass distribution. In Global Seagrass Research Methods; Short, F.T., Coles, R.G., Eds.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 101–121. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, S.J.; McKenzie, L.J. Flood related loss and recovery of intertidal seagrass meadows in southern Queensland, Australia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, M.; Johns, K.; Osborne, K. Surveys of Benthic Reef Communities Using Underwater Digital Photography and Counts of Juvenile Corals. In Long-Term Monitoring of the Great Barrier Reef, Standard Operational Procedure Number 10; Australian Institute of Marine Science: Townsville, Australia, 2008; p. 75. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffelke, B.; Mellors, J.; Duke, N.C. Water quality in the Great Barrier Reef region: Responses of Mangrove, Seagrass and Macroalgal Communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, T.P.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Bellwood, D.R.; Ceccarelli, D.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; McCook, L.; Moltschaniwskyj, N.; Pratchett, M.S.; Steneck, R.S.; Willis, B. Phase Shifts, Herbivory, and the Resilience of Coral Reefs to Climate Change. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, N.L.; Box, S.J.; Mumby, P.J. Competitive effects of macroalgae on the fecundity of the reef-building coral Montastrea annularis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 367, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheal, A.J.; MacNeil, M.A.; Cripps, E.; Emslie, M.; Jonker, M.; Schaffelke, B.; Sweatman, H. Coral-macroalgal phase shifts or reef resilience: Links with Diversity and Functional Roles of Herbivorous Fishes on the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 2010, 29, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauri, C.; Fabricius, K.; Schaffelke, B.; Humphrey, C. Chemical and physical environmental conditions underneath mat- and canopy-forming macroalgae, and the effects on understory corals. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Berenbaum, M.C. The expected effect of a combination of agents: The General Solution. J. Theor. Biol. 1985, 114, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, A.D.; Collier, C.J.; Flores, F.; Negri, A.P. Acute and additive toxicity of ten photosystem-II herbicides to seagrass. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, M.; Altenburger, R.; Backhaus, T.; Blanck, H.; Boedeker, W.; Gramatica, P.; Hamer, V.; Scholze, M.; Vighi, M.; Grimme, L.H. Joint algal toxicity of 16 dissimilarly acting chemicals is predictable by the concept of independent action. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 63, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, M.J.; Teixeira da Silva, E.; Petus, C.; Wenger, A.; Zeh, D.; Tracey, D.; Álvarez-Romero, J.; Brodie, J. Combining water quality and remote sensed data across spatial and temporal scales to measure wet season chlorophyll-a variability: Great Barrier Reef lagoon (Queensland, Australia). Ecol. Process. 2013, 2, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, Z.; Wolanski, E.; Álvarez-Romero, J.G.; Lewis, S.; Brodie, J. Fine sediment and nutrient dynamics related to particle size and floc formation in a Burdekin River flood plume, Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 65, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, D.; Muller, J.; Carter, S. Pesticide and herbicide residues in sediments and seagrasses from the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area and Queensland coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 41, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, D.; Ralph, P.; Prange, J.; Dennison, B. The Impact of the Herbicide Diuron on Photosynthesis in Three Species of Tropical Seagrass. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 41, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganthy, F.; Sottolichio, A.; Verney, R. Seasonal modification of tidal flat sediment dynamics by seagrass meadows of Zostera noltii (Bassin d’Arcachon, France). J. Marine Syst. 2013, 109–110, S233–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrou, K.; Jimenez-Denness, I.; Chartrand, K.; Mccormack, C.; Rasheed, M.; Ralph, P.J. Seasonal heterogeneity in the photophysiological response to air exposure in two tropical intertidal seagrass species. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 482, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, J.; Humphrey, C.; McKinna, L.; Gourge, O.; Fabricius, K.E.; Meht, A.J.; Lewis, S.; Wolanski, E. Importance of wave-induced bed liquefaction in the fine sediment budget of Cleveland Bay, Great Barrier Reef. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 89, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffelke, B. Short-term nutrient pulses as tools to assess responses of coral reef macroalgae to enhanced nutrient availability. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 1999, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, S.A.; Done, T.J. Improved water quality can ameliorate effects of 892 climate change on corals. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carilli, J.E.; Norris, R.D.; Black, B.A.; Walsh, S.M.; McField, M. Local stressors reduce coral resilience to bleaching. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, 6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooldridge, S.A.; Brodie, J.E. Environmental triggers for primary outbreaks of crown-of-thorns starfish on the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Product | Management Outcome | Spatial and Temporal Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| A: River plume maps (Operational) | Illustrate the extent of riverine waters and plume water types, but do not provide information on the composition of the water and WQ constituents | Spatial resolution: - GBR-wide scale - NRM regions Temporal resolution: - Daily - Weekly composites - Seasonal composites: focusing on the tropical wet season (December–April). - Multi-annual composites (mean of several wet seasons) |
| B: Contaminant maps (Operational) | Plume water types are associated with different levels and combinations of pollutants and, in combination with in situ WQ information, provide a broad scale approach to reporting contaminant concentrations in the GBR marine environment. | |
| C: River plume risk maps (In progress: [16], this study) | Product aiming to evaluate the risk of GBR ecosystems from river plume exposure through the use of established risk management approaches (magnitude × likelihood) |
| CCx | Tertiary | Secondary | Primary | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC6 | CC5 | CC4 | CC3 | CC2 | CC1 | |
| TSSp (mg·L−1) | 5.66 | 6.10 | 7.33 | 10.62 | 10.52 | 33.97 |
| Chl-ap (µg·L−1) | 0.42 | 0.86 | 1.44 | 1.95 | 2.14 | 2.41 |
| PSIIp (µg·L−1) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| TSSt | 7 | |||||
| Chl-at | 0.45 | |||||
| PSIIt | 0.1 | |||||
| TSSp/TSSt | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 4.9 |
| Chl-ap/Chl-at | 0.9 | 1.9 | 3.2 | 4.3 | 4.8 | 5.4 |
| PSIIp/PSIIt | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| R | 1.8 | 2.9 | 4.4 | 6.2 | 6.6 | 10.6 |
| MS | 0 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 10 |
| Colour Class | CC1 | CC2 | CC3 | CC4 | CC5 | CC6 | Risk scores | Seagrass Cover | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnitude Score MSCCx: | 10 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | RSsite | RSNRM | |||||
| Likelihood Score: | LSCC1 | LSCC2 | LSCC3 | LSCC4 | LSCC5 | LSCC6 | Δsite | ΔNRM | Msite | MNRM | |||
| Burdekin (Bu) | JR | 0.18 | 0.31 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.47 | na | −17.53 | 6.21 | 18.40 |
| MI | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.74 | 0.01 | 0.24 | −13.80 | 24.37 | ||||
| MI2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.78 | 0.01 | 0.22 | −26.20 | 30.88 | ||||
| TSV | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.33 | 0.39 | 0.00 | 0.41 | −12.60 | 12.13 | ||||
| Burnett-Mary (BM) | RD | 0.06 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.38 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.67 | 0.59 | −32.30 | −43.20 | 14.50 | 12.42 |
| UG | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.00 | 0.52 | −54.10 | 10.34 | ||||
| Fitzroy (Fi) | GH | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.47 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.44 | −1.40 | −10.13 | 28.19 | 18.12 |
| GK | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.74 | 0.05 | 0.23 | −4.60 | 3.28 | ||||
| SWB | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.61 | 0.00 | 0.33 | −24.40 | 22.88 | ||||
| Mackay Whit. (MW) | HM | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.72 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.25 | −6.20 | −7.05 | 6.63 | 15.33 |
| MP | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.00 | 0.37 | 9.40 | 22.70 | ||||
| PI | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.65 | 0.01 | 0.16 | −10.30 | 19.64 | ||||
| SI | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.33 | −21.10 | 12.32 | ||||
| Wet Tropics (WT) | DI | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.69 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.10 | −12.10 | −7.50 | 6.83 | 14.98 |
| DI2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.65 | 0.12 | 0.17 | −5.40 | 3.44 | ||||
| GI | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 0.27 | 0.01 | −5.10 | 32.69 | ||||
| GI2 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.30 | 0.00 | −8.10 | 42.48 | ||||
| LB | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.53 | 0.01 | 0.28 | −3.20 | 2.69 | ||||
| LI | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.50 | 0.02 | −12.30 | 10.53 | ||||
| LI2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.42 | 0.00 | −12.00 | 11.01 | ||||
| YP | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.60 | 0.10 | 0.13 | −1.80 | 10.20 | ||||
| Colour Class | CC1 | CC2 | CC3 | CC4 | CC5 | CC6 | Risk Scores | MAp Cover | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnitude Score MSCCx: | 10 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | RSsite | RSNRM | |||||
| Likelihood Score: | LSCC1 | LSCC2 | LSCC3 | LSCC4 | LSCC5 | LSCC6 | Δsite | ΔNRM | Msite | MNRM | |||
| Burdekin (Bu) | GB | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.77 | 0.04 | 0.48 | 0.31 | −6.95 | −11.13 | 50.81 | 24.08 |
| HI | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.36 | 0.46 | 0.14 | −36.51 | 20.43 | ||||
| LE | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.22 | 0.62 | 0.03 | 0.58 | −32.18 | 43.20 | ||||
| MR | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.69 | 0.01 | 0.59 | 14.25 | 8.17 | ||||
| OIE | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.31 | 0.43 | 0.09 | 3.28 | 1.07 | ||||
| PAN | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.51 | 0.35 | 0.20 | −19.69 | 44.82 | ||||
| POIW | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.32 | 0.46 | 0.11 | −0.11 | 0.05 | ||||
| Fitzroy (Fi) | BI | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.42 | 0.13 | 0.58 | 5.68 | 32.73 | 2.70 | 41.00 |
| HHI | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.55 | 0.23 | 0.52 | 69.93 | 40.69 | ||||
| MI | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.71 | 0.09 | 0.49 | 59.87 | 46.21 | ||||
| NKI | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.55 | 0.24 | 0.39 | 35.36 | 51.53 | ||||
| PKI | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.63 | 0.01 | 0.92 | −10.26 | 61.59 | ||||
| PLI | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.33 | 0.53 | 0.03 | 1.00 | 35.78 | 43.24 | ||||
| Mackay Whit. (MW) | DDI | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.70 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 1.67 | 2.54 | 2.86 | 9.87 |
| DI | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.75 | 0.08 | 0.26 | −1.15 | 0.33 | ||||
| DCI | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.47 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.14 | ||||
| HI | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.06 | −0.15 | 2.03 | ||||
| PI | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.70 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 8.88 | 31.04 | ||||
| SI | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.67 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 7.03 | 31.80 | ||||
| STI | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.67 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 1.26 | 0.87 | ||||
| Wet Tropics (WT) | SIN | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.51 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 36.92 | 7.78 | 30.62 | 18.24 |
| SIS | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.45 | 0.34 | 0.21 | 0.61 | 2.66 | ||||
| FIE | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.25 | 0.37 | 0.00 | 0.66 | 0.48 | ||||
| FIW | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 0.38 | 0.08 | 1.12 | 1.39 | ||||
| FGE | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.23 | 0.43 | 0.04 | 37.13 | 17.14 | ||||
| FGW | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.39 | 0.03 | 3.06 | 11.46 | ||||
| HIE | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.40 | 0.38 | 0.15 | 7.75 | 2.27 | ||||
| HIW | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.56 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 3.91 | 7.43 | ||||
| DIN | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.66 | 0.08 | 0.45 | −5.94 | 28.55 | ||||
| DIS | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.68 | 0.08 | 0.43 | −3.85 | 37.22 | ||||
| K | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.59 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 9.33 | 61.78 | ||||
| NBG | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.58 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 2.70 | 17.83 | ||||
| Risk | I | II | III |
|---|---|---|---|
| RS | 0–0.2 | 0.2–0.4 | >0.4 |
| Δcover | +/−12 | −12/−30 | >−30 |
| number sites | 8 | 8 | 4 |
| Well classified | 7 | 5 | 2 |
| Overestimated loss | 0 | 3 (GK, MP, LB) | 2 (GH, TSW) |
| Underestimated loss | 1 (LI) | 0 | 0 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petus, C.; Devlin, M.; Thompson, A.; McKenzie, L.; Teixeira da Silva, E.; Collier, C.; Tracey, D.; Martin, K. Estimating the Exposure of Coral Reefs and Seagrass Meadows to Land-Sourced Contaminants in River Flood Plumes of the Great Barrier Reef: Validating a Simple Satellite Risk Framework with Environmental Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030210
Petus C, Devlin M, Thompson A, McKenzie L, Teixeira da Silva E, Collier C, Tracey D, Martin K. Estimating the Exposure of Coral Reefs and Seagrass Meadows to Land-Sourced Contaminants in River Flood Plumes of the Great Barrier Reef: Validating a Simple Satellite Risk Framework with Environmental Data. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(3):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030210
Chicago/Turabian StylePetus, Caroline, Michelle Devlin, Angus Thompson, Len McKenzie, Eduardo Teixeira da Silva, Catherine Collier, Dieter Tracey, and Katherine Martin. 2016. "Estimating the Exposure of Coral Reefs and Seagrass Meadows to Land-Sourced Contaminants in River Flood Plumes of the Great Barrier Reef: Validating a Simple Satellite Risk Framework with Environmental Data" Remote Sensing 8, no. 3: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030210
APA StylePetus, C., Devlin, M., Thompson, A., McKenzie, L., Teixeira da Silva, E., Collier, C., Tracey, D., & Martin, K. (2016). Estimating the Exposure of Coral Reefs and Seagrass Meadows to Land-Sourced Contaminants in River Flood Plumes of the Great Barrier Reef: Validating a Simple Satellite Risk Framework with Environmental Data. Remote Sensing, 8(3), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030210