Evaluation of PERSIANN-CDR for Meteorological Drought Monitoring over China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
2.1. Study Area
2.2. PERSIANN-CDR Satellite Precipitation Dataset
2.3. The Gridded Observation Dataset
2.4. The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI)
2.5. Statistical Evaluation Metrics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Precipitation Evaluation
3.2. Spatial Evaluation of SPI Estimates
3.2.1. Comparison of SPI Based Statistics
3.2.2. Comparison of SPI Based Drought Events
3.3. Time Series Evaluation of SPI Estimates
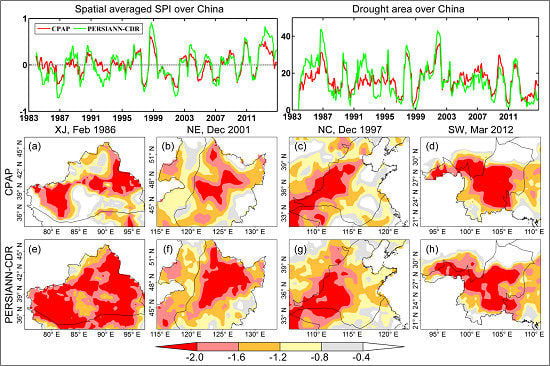
3.4. Specific Drought Events: Some Case Studies
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilhite, D.A. Drought as a natural hazard: Concepts and definitions. In Drought, A Global Assessment; Wilhite, D.A., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2000; Volume 1, pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Heim, R.R. A review of twentieth-century drought indices used in the united states. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1149–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, S.C.; Govindaraju, R.S. A copula-based joint deficit index for droughts. J. Hydrol. 2010, 380, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.G. Drought under global warming: A review. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyantash, J.; Dracup, J.A. The quantification of drought: An evaluation of drought indices. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1167–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Hoerling, M.; Eischeid, J.; Perlwitz, J.; Quan, X.; Zhang, T.; Pegion, P. On the increased frequency of mediterranean drought. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 2146–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.K.; Sheffield, J.; Pan, M.; Wood, E.F. Evaluation of the tropical rainfall measuring mission multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) for assessment of large-scale meteorological drought. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.O.; Malhi, Y.; Aragao, L.E.; Ladle, R.; Arai, E.; Barbier, N.; Phillips, O. Remote sensing detection of droughts in amazonian forest canopies. New Phytol. 2010, 187, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belayneh, A.; Adamowski, J. Standard precipitation index drought forecasting using neural networks, wavelet neural networks, and support vector regression. Appl. Comput. Intell. Soft Comput. 2012, 2012, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Lu, A.F.; Wu, J.J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, M. Drought hazard assessment and spatial characteristics analysis in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, W.C. Meteorological Drought; US Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 1965; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the Eighth Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 179–183.
- Gibbs, W.J. Rainfall Deciles as Drought Indicators; Bureau of Meteorology: Melbourne, Australia, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Bhalme, H.N.; Mooley, D.A. Large-scale droughts/floods and monsoon circulation. Mon. Weather Rev. 1980, 108, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Shafer, B.; Dezman, L. Development of a surface water supply index (SWSI) to assess the severity of drought conditions in snowpack runoff areas. In Proceedings of the 50th Annual Western Snow Conference, Reno, NV, USA, 19–23 April 1982; pp. 164–175.
- Wu, H.; Hayes, M.J.; Weiss, A.; Hu, Q. An evaluation of the standardized precipitation index, the china-z index and the statistical z-score. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, R.R. Drought indices: A review. In Drought: A Global Assessment; Wilhite, D.A., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2000; pp. 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Kallis, G. Droughts. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2008, 33, 85–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, W.M. The palmer drought severity index—limitations and assumptions. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1984, 23, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; AghaKouchak, A. A nonparametric multivariate multi-index drought monitoring framework. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.C. Characteristics of 20th Century Drought in the United States at Multiple Time Scales. Master's Thesis, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, M.; Svoboda, M.; Wall, N.; Widhalm, M. The Lincoln declaration on drought indices: Universal meteorological drought index recommended. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, R.A.; Hayes, M.; Bressan, L. Using the standardized precipitation index for flood risk monitoring. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, E. Determining the start, duration, and strength of flood and drought with daily precipitation: Rationale. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L12707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Begueria, S.; Lorenzo-Lacruz, J.; Camarero, J.J.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Revuelto, J.; Moran-Tejeda, E.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A. Performance of drought indices for ecological, agricultural, and hydrological applications. Earth Interact. 2012, 16, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Chávez, R. Dry and wet rainy seasons in the Mantaro river basin (Central Peruvian Andes). Adv. Geosci. 2008, 14, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morid, S.; Smakhtin, V.; Moghaddasi, M. Comparison of seven meteorological indices for drought monitoring in Iran. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 971–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.F.; Pulido-Calvo, I.; Portela, M.M. Spatial and temporal variability of droughts in Portugal. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W03503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordi, I.; Fraedrich, K.; Gerstengarbe, F.W.; Werner, P.C.; Sutera, A. Potential predictability of dry and wet periods: Sicily and elbe-basin (Germany). Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2004, 77, 125–138. [Google Scholar]
- Lyon, B.; Zubair, L.; Ralapanawe, V.; Yahiya, Z. Finescale evaluation of drought in a tropical setting: Case study in Sri Lanka. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2009, 48, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.Y.; Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.L.; Sorooshian, S.; Duan, Q.Y. Evaluation of the persiann-cdr daily rainfall estimates in capturing the behavior of extreme precipitation events over China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Arkin, P.; Chang, A.; Ferraro, R.; Gruber, A.; Janowiak, J.; McNab, A.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U. The global precipitation climatology project (GPCP) combined precipitation dataset. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G.J. Improving the global precipitation record: GPCP version 2.1. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L17808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.F.; Huffman, G.J.; Chang, A.; Ferraro, R.; Xie, P.-P.; Janowiak, J.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U.; Curtis, S.; Bolvin, D.; et al. The version-2 global precipitation climatology project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979–present). J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 1147–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.P.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Adler, R.; Gruber, A.; Ferraro, R.; Huffman, G.J.; Curtis, S. GPCP pentad precipitation analyses: An experimental dataset based on gauge observations and satellite estimates. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 2197–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Morrissey, M.M.; Bolvin, D.T.; Curtis, S.; Joyce, R.; McGavock, B.; Susskind, J. Global precipitation at one-degree daily resolution from multisatellite observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2001, 2, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G.J.; Nelkin, E.J.; Bowman, K.P.; Hong, Y.; Stocker, E.F.; Wolff, D.B. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P.P. Cmorph: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, T.; Sasashige, K.; Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Okamoto, K.; Aonashi, K.; Inoue, T.; Takahashi, N.; Iguchi, T.; Kachi, M.; et al. A Kalman filter approach to the global satellite mapping of precipitation (GSMaP) from combined passive microwave and infrared radiometric data. J. Meteor. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 87, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.L.; Gao, X.G.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed information using artificial neural networks. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.-L.; Gao, X.; Gupta, H.V.; Imam, B.; Braithwaite, D. Evaluation of persiann system satellite–based estimates of tropical rainfall. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, J.; Mostovoy, G.; Anantharaj, V. The NRL-blend high resolution precipitation product and its application to land surface hydrology. In Satellite Rainfall Applications for Surface Hydrology; Gebremichael, M., Hossain, F., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 85–104. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Liu, H.; You, Y.; Mullens, E.; Hu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, M.; He, L.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, X.; et al. Evaluation of high-resolution precipitation estimates from satellites during July 2012 Beijing flood event using dense rain gauge observations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, B.; Chen, B.; Gourley, J.J.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, S.; Gong, L. Intercomparison of the version-6 and version-7 TMPA precipitation products over high and low latitudes basins with independent gauge networks: Is the newer version better in both real-time and post-real-time analysis for water resources and hydrologic extremes? J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, X.; Hong, Y.; Limaye, A.S.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Khan, S.I.; Dorji, C.; Chen, S. Statistical and hydrological evaluation of TRMM-based Multi-satellite precipitation analysis over the Wangchu Basin of Bhutan: Are the latest satellite precipitation products 3B42V7 ready for use in ungauged basins? J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stisen, S.; Sandholt, I. Evaluation of remote-sensing-based rainfall products through predictive capability in hydrological runoff modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; AghaKouchak, A.; Nakhjiri, N.; Farahmand, A. Global integrated drought monitoring and prediction system. Sci. Data 2014, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katiraie-Boroujerdy, P.-S.; Nasrollahi, N.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S. Quantifying the reliability of four global datasets for drought monitoring over a semiarid region. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 123, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nana, Y.; Bingfang, W.; Sheng, C.; Xin, B. Evaluation of TRMM precipitation product for meteorological drought monitoring in Hai Basin. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 17, 012093. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.W.; Li, L.J.; Li, J.Y. The evaluation of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) in drought monitoring in the Lancang River Basin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Nijssen, B.; Huffman, G.J.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Evaluation of real-time satellite precipitation data for global drought monitoring. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burroughs, W. Climate: Into the 21st Century; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Hayes, M.J.; Wilhite, D.A.; Svoboda, M.D. The effect of the length of record on the standardized precipitation index calculation. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Samarth, A. Population dynamics and climate change: Links and issues for development. J. Public Health 2010, 32, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Shahid, S.; ElMahdi, A.; He, R.M.; Bao, Z.X.; Ali, M. Water resources management strategy for adaptation to droughts in China. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2012, 17, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Weng, B.; Zhang, P.; Li, S. Drought risk assessment in China with different spatial scales. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 10193–10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.L.; Sorooshian, S.; Braithwaite, D.K.; Knapp, K.R.; Cecil, L.D.; Nelson, B.R.; Prat, O.P. Persiann-CDR daily precipitation climate data record from multisatellite observations for hydrological and climate studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casse, C.; Gosset, M. Analysis of hydrological changes and flood increase in Niamey based on the PERSIANN-CDR satellite rainfall estimate and hydrological simulations over the 1983–2013 period. Proc. IAHS 2015, 370, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, A.M.; Hu, J.J.; Gebregiorgis, A.S.; Xue, X.W.; Zhang, X.H. Inter-comparison of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over Central Asia. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7181–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yong, B.; Hong, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X. Error analysis of multi-satellite precipitation estimates with an independent raingauge observation network over a medium-sized humid basin. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, A.; Hu, J.; Yang, B.; Stepanian, P. Comprehensive evaluation of high-resolution satellite-based precipitation products over China. Atmosphere 2015, 7, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Cao, Q.; Gourley, J.J.; Kirstetter, P.E.; Yong, B.; Tian, Y.D.; Zhang, Z.X.; Shen, Y.; Hu, J.J.; et al. Similarity and difference of the two successive v6 and v7 trmm multisatellite precipitation analysis performance over China. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 13060–13074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Zheng, C.Y.; Fang, J.Y. Biodiversity in China’s mountains. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2006, 4, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Lin, X. Regional trends in recent precipitation indices in China. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2005, 90, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bothe, O.; Fraedrich, K.; Zhu, X.H. Precipitation climate of central Asia and the large-scale atmospheric circulation. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 108, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Gong, D.; Li, J.; Li, B. Detecting and understanding the multi-decadal variability of the east Asian summer monsoon—Recent progress and state of affairs. Meteorol. Z. 2009, 18, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.D.; Wang, Y. Contrasting impacts of spring thermal conditions over Tibetan Plateau on late-spring to early-summer precipitation in southeast China. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2011, 12, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.J.; Yu, R.C.; Chen, H.M.; Dai, A.; Pan, Y. Summer precipitation frequency, intensity, and diurnal cycle over China: A comparison of satellite data with rain gauge observations. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 3997–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A.Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, P.P. Performance of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over China. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D02114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, K.R. Scientific data stewardship of International Satellite Cloud Climatology Project B1 global geostationary observations. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2008, 2, 023548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Data Record (CDR) Program Climate Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document. Available online: http://www1.ncdc.noaa.gov/pub/data/sds/cdr/CDRs/Sea_Surface_Temperature_Pathfinder/AlgorithmDescription.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2015).
- Persiann-CDR ftp Download. Available online: ftp://data.ncdc.noaa.gov/cdr/persiann/files/ (accessed on 6 April 2015).
- Hutchinson, M.F. Interpolation of rainfall data with thin plate smoothing splines. Part I: Two dimensional smoothing of data with short range correlation. J. Geogr. Inf. Decis. Anal. 1998, 2, 139–151. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, M.F. Interpolation of rainfall data with thin plate smoothing splines. Part II: Analysis of topographic dependence. J. Geogr. Inf. Decis. Anal. 1998, 2, 152–167. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xu, Y. Establishment and assessment of the grid precipitation datasets in China for recent 50 years. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2014, 34, 414–420, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, J. Assessing quality of grid daily precipitation datasets in China in recent 50 years. Plateau Meteorol. 2015, 34, 50–58, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A.; Hong, Y.; Yu, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Saharia, M. Uncertainty analysis of five satellite-based precipitation products and evaluation of three optimally merged multi-algorithm products over the Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6843–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, T.; Thomas, D.; Middleton, N. Drought dynamics on the Mongolian Steppe, 1970–2006. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordi, I.; Sutera, A. Drought monitoring and forecasting at large scale. In Methods and Tools for Drought Analysis and Management; Rossi, G., Vega, T., Bonaccorso, B., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Berlin, Germany, 2007; Volume 62, pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, K.C.; Long, L.N.; Xia, Y.L.; Yang, S.K.; Schemm, J.E.; Ek, M. Drought indices based on the Climate Forecast System Reanalysis and ensemble NLDAS. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 181–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihajlović, D. Monitoring the 2003–2004 meteorological drought over Pannonian part of Croatia. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 2213–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| SPI Value | Category |
|---|---|
| 2.0 and above | Extremely wet |
| 1.5 to 1.99 | Severely wet |
| 1.0 to 1.49 | Moderately wet |
| −0.99 to 0.99 | Near normal |
| −1.0 to −1.49 | Moderately dry |
| −1.5 to −1.99 | Severely dry |
| −2.0 and less | Extremely dry |
| Subregion | Product | Start–End | Duration (Months) | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XJ | CPAP | September 1985–August 1986 | 12 | −12.00 |
| PERSIANN-CDR | June 1985–January 1987 | 20 | −33.62 | |
| NE | CPAP | October 2001–March 2002 | 6 | −6.86 |
| PERSIANN-CDR | September 2001–March 2002 | 7 | −9.67 | |
| NC | CPAP | September 1997–March 1998 | 7 | −8.50 |
| PERSIANN-CDR | September 1997–April 1998 | 8 | −10.55 | |
| SW | CPAP | August 2011–June 2012 | 7 | −13.03 |
| PERSIANN-CDR | August 2011–June 2012 | 7 | −6.59 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, H.; Bao, A.; Liu, T.; Chen, S.; Ndayisaba, F. Evaluation of PERSIANN-CDR for Meteorological Drought Monitoring over China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8050379
Guo H, Bao A, Liu T, Chen S, Ndayisaba F. Evaluation of PERSIANN-CDR for Meteorological Drought Monitoring over China. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(5):379. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8050379
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Hao, Anming Bao, Tie Liu, Sheng Chen, and Felix Ndayisaba. 2016. "Evaluation of PERSIANN-CDR for Meteorological Drought Monitoring over China" Remote Sensing 8, no. 5: 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8050379
APA StyleGuo, H., Bao, A., Liu, T., Chen, S., & Ndayisaba, F. (2016). Evaluation of PERSIANN-CDR for Meteorological Drought Monitoring over China. Remote Sensing, 8(5), 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8050379