Multi-Temporal Evaluation of Soil Moisture and Land Surface Temperature Dynamics Using in Situ and Satellite Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. In Situ Data
2.2. Satellite Data
2.3. HidroMORE Model
3. Methodology
3.1. Analysis of SM–LST Relationship
3.2. Analysis of SM–LST Coupling/Decoupling and Critical SM
3.3. Analysis of Water/Energy-Limited ET Regimes
4. Results and Discussion
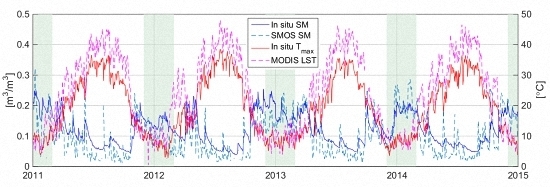
4.1. Characterization of SM and LST over the Study Area
4.2. SM–LST Relationship at the Daily Scale
4.3. SM–LST Relationship at the Seasonal Scale
4.4. SM and LST Time-Series: Coupling/Decoupling and Critical SM Estimation
4.5. Critical SM and ET Regimes during 2014
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GCOS, Global Climate Observing System. Implementation Plan for the Global Observing System for Climate in Support of the UNFCCC, 2010, GCOS-138 (GOOS-184, GTOS-76, WMO-TD/No. 1523). Available online: https://www.wmo.int/pages/prog/gcos/Publications/gcos-138.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2016).
- IPCC, International Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. In Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–151. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Long, D.G. Microwave Radar and Radiometric Remote Sensing; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2014; pp. 1–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Schmugge, T.; Gloersen, P.; Wilheit, T.; Geiger, F. Remote Sensing of Soil Moisture with Microwave Radiometers. J. Geophys. Res. 1974, 79, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmugge, T.; O’Neill, P.E.; Wang, J.R. Passive Microwave Soil Moisture Research. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, GE-24, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, R.K. Propagation phenomena affecting satellite communication systems operating in the centimeter and millimeter wavelength bands. Proc. IEEE 1971, 59, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J.; Schmugge, T. Vegetation effects on the microwave emission of soils. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 36, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.K.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Delwart, S.; Cabot, F.; Boutin, J.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Font, J.; Reul, N.; Gruhier, C.; et al. The SMOS Mission: New Tool for Monitoring Key Elements of the Global Water Cycle. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 666–687. [Google Scholar]
- Font, J.; Camps, A.; Borges, A.; Martin-Neira, M.; Boutin, J.; Reul, N.; Kerr, Y.H.; Hahne, A.; Mecklenburg, S. SMOS: The Challenging Sea Surface Salinity Measurement From Space. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMullan, K.D.; Brown, M.A.; Martin-Neira, M.; Rits, W.; Ekholm, S.; Marti, J.; Lemanczyk, J. SMOS: The Payload. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J.; et al. The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Yueh, S.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Allen, A.; Bindlish, R.; Brown, M.; Chan, S.; Colliander, A.; Crow, W.T.; et al. SMAP Handbook; JPL Publication 400-1567; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2014.
- Das, N.N.; Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G. Algorithm for merging SMAP radiometer and radar data for high resolution soil moisture retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Snyder, W. MODIS Land-Surface Temperature Algorith Theoretical Basis Document Version 3.3; Institute for Computational Earth System Science, University of California: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Aminou, D.M.A.; Jaquet, B.; Pasternak, F. Characteristics of the Meteosat Second Generation Radiometer/Imager: SEVIRI. Proc. SPIE 1997, 3221, 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, P.; Van Zyl, J.; Engman, E. Measuring soil moisture with imaging radars. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Richaume, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Mahmoodi, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Cabot, F.; Gruhier, C.; Enache Juglea, S.; et al. The SMOS Soil Moisture Retrieval Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1384–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, P.E.; Chan, S.; Njoku, E.; Jackson, T.J.; Bindlish, R. SMAP Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document: L2 & L3 Radiometer Soil Moisture (Passive) Products, Rev. B.; Technical Report; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2015.
- Er-Raki, S.; Chehbouni, A.; Hoedjes, J.; Ezzahar, J.; Duchemin, B.; Jacob, F. Improvement of FAO-56 method for olive orchards through sequential assimilation of thermal infrared-based estimates of ET. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; Kustas, W.P.; Prueger, J.H. Monitoring root-zone soil moisture through the assimilation of a thermal remote sensing-based soil moisture proxy into a water balance model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1268–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating soil moisture-climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuttleworth, W.J. Evaporation. In Handbook of Hydrology; Maidment, D.R., Ed.; McGraw-Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 41–453. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Pinker, R.T. Case study of soil moisture effect on land surface temperature retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2004, 1, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.C. The potential of remotely sensed thermal infrared data to infer surface soil moisture and evaporation. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T. An Overview of the “Triangle Method” for Estimating Surface Evapotranspiration and Soil Moisture from Satellite Imagery. Sensors 2007, 7, 1612–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.M.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Otkin, J.A.; Kustas, W.P. A climatological study of evapotranspiration and moisture stress across the continental United States based on thermal remote sensing: 1. Model formulation. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandholt, I.; Rasmussen, K.; Andersen, J. A simple interpretation of the surface temperature/vegetation index space for assessment of surface moisture status. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, G.P.; Carlson, T.N.; Wooster, M.J.; Islan, S. A review of Ts/VI remote sensing based methods for the retrieval of land surface energy fluxes and soil moisture. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 224–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.M.; Diak, G.R.; Kustas, W.P.; Mecikalski, J.R. A two-source time-integrated model for estimating surface fluxes using thermal infrared remote sensing. Remote Sens. 1997, 60, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stisen, S.; Sandholt, I.; Norgaard, A.; Fensholt, R.; Jensen, K.H. Combining the triangle method with thermal inertia to estimate regional evapotranspiration—Applied to MSG-SEVIRI data in the Senegal River basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hain, C.R.; Crow, W.T.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Anderson, M.C.; Holmes, T. An intercomparison of available soil moisture estimates from thermal infrared and passive microwave remote sensing and land surface modeling. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piles, M.; Sánchez, N.; Vall-llossera, M.; Camps, A.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Martínez, J.; González-Gambau, V. A Downscaling Approach for SMOS Land Observations: Evaluation of High-Resolution Soil Moisture Maps Over the Iberian Peninsula. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3845–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, O.; Rudiger, C.; Al Bitar, A.; Richaume, P.; Walker, J.P.; Kerr, Y.H. Disaggregation of SMOS Soil Moisture in Southeastern Australia. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1556–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piles, M.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Sánchez, N.; González-Zamora, A.; Ireland, G. Towards improved spatio-temporal resolution soil moisture retrievals from the synergy of SMOS and MSG SEVIRI spaceborne observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piles, M.; Sánchez, N. Spatial downscaling of passive microwave data with visible-to-infrared information for high-resolution soil moisture mapping. In Satellite Soil Moisture Retrieval: Techniques and Applications; Srivastava, P.K., Petropoulos, G., Kerr, Y.H., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cihlar, J.; Manak, D.; D’Iorio, M. Evaluation of compositing algorithms for AVHRR data over land. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.B.; Tu, K.P.; Baldocchi, D.D. Global estimates of the land–Atmosphere water flux based on monthly AVHRR and ISLSCP-II data, validated at 16 FLUXNET sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablos, M.; Piles, M.; Sánchez, N.; González-Gambau, V.; Vall-llossera, M.; Camps, A.; Martínez-Fernández, J. A sensitivity study of land surface temperature to soil moisture using in-situ and spaceborne observations. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 3267–3269.
- Pablos, M.; Piles, M.; Sánchez, N.; Vall-llossera, M.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Camps, A. Impact of day/night time land surface temperature in soil moisture disaggregation algorithms. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2016. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, N.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Scaini, A.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, C. Validation of the SMOS L2 soil moisture data in the REMEDHUS Network (Spain). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BEC Team. SMOS-BEC Ocean and Land Products Description; Technical Report; BEC: Barcelona, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, N.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Calera, A.; Torres, E.A.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, C. Combining remote sensing and in situ soil moisture data for the application and validation of a distributed water balance model (HidroMORE). Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, N.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, M.; Torres, E.A.; Calera, A. A simulation of soil water content based on remote sensing in a semi-arid Mediterranean agricultural landscape. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 10, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.A.; Wagner, W.; Hohensinn, R.; Hahn, S.; Paulik, C.; Xaver, A.; Gruber, A.; Drusch, M.; Mecklenburg, S.; van Oevelen, P.; et al. The International Soil Moisture Network: A data hosting facility for global in situ soil moisture measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1675–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Soil Moisture Network. Available online: https://ismn.geo.tuwien.ac.at/networks/remedhus/ (accessed on 7 July 2016).
- Bellingham, B.K. The Hydra Probe Soil Sensor: Comprehensive Stevens Hydra Probe Users Manual. Rev. IV; Stevens Water Monitoring System, Inc.: Portland, OR, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- BEC, Barcelona Expert Centre (BEC). Available online: http://cp34-bec.cmima.csic.es (accessed on 7 July 2016).
- González-Zamora, A.; Sánchez, N.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Gumuzzio, A.; Piles, M.; Olmedo, E. Long-term SMOS soil moisture products: A comprehensive evaluation across scales and methods in the Duero Basin (Spain). Phys. Chem. Earth A/B/C 2015, 83–84, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LP DACC, Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov (accessed on 7 July 2016).
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, N.; Marínez-Fernández, J.; González-Piqueras, J.; González-Dugo, M.P.; Baroncini-Turrichia, G.; Torres, E.; Calera, A.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, C. Water balance at plot scale for soil moisture estimation using vegetation parameters. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 166–167, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, R.; Hubbard, K.G. Relationship between soil moisture of near surface and multiple depths of the root zone under heterogeneous land uses and varying hydroclimatic conditions. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 3449–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SiAR, Sistema de Información Agroclimática para el Regadío (SiAR) service of the Spanish Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Environment. Available online: http://eportal.magrama.gob.es/websiar/Inicio.aspx (accessed on 7 July 2016).
- Martínez-Fernández, J.; Ceballos, A. Temporal Stability of Soil Moisture in a Large-Field Experiment in Spain. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Fernández, J.; Ceballos, A. Mean soil moisture estimation using temporal stability analysis. J. Hydrol. 2005, 312, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Trenberth, E.; Karl, T.R. Effects of clouds, soil moisture, precipitation, and water vapor on diurnal temperature range. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 2451–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durre, I.; Wallace, J.M.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Dependence of extreme daily maximum temperatures on antecedent soil moisture in the contiguos United States during summer. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 2641–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braganza, K.; Karoly, D.J.; Arblaster, J.M. Diurnal temperature range as an index of global climate change during the twentieth century. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L13217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Griend, A.A.; Camillo, P.J.; Gurney, R.J. Gurney, Discrimination of soil physical parameters, thermal inertia, and soil moisture from diurnal surface temperature fluctuations. Water Resour. Res. 1984, 21, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, D.G.; van den Berg, M.J.; Teuling, A.J.; de Jeu, R.A.M. Soil moisture-temperature coupling: A multiscale observational analysis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L21707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J.; Bindlish, R.; Cosh, M.H.; Zhao, T.; Starks, P.J.; Bosch, D.D.; Seyfried, M.; Moran, M.S.; Goodrich, D.C.; Kerr, Y.H.; et al. Validation of Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) Soil Moisture Over Watershed Networks in the U.S. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]












| In Situ Data | Satellite Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SM | SMOS SM | MODIS LST Aqua Day | ||
| (m/m) | ( °C) | (m/m) | ( °C) | |
| minimum | 0.10 | 12.4 | 0.08 | 8.4 |
| maximum | 0.16 | 22.6 | 0.22 | 32.7 |
| mean | 0.12 | 16.4 | 0.12 | 15.2 |
| std | 0.06 | 5.9 | 0.05 | 4.4 |
| Delay in SM respect to | Energy-Limited | Water-Limited | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (NDJF) | (MAMJJASO) | |||
| R | N (days) | R | N (days) | |
| Same day | 0.05 * | 120 | 0.54 | 245 |
| 1 day after | −0.07 * | 119 | 0.59 | 244 |
| 2 days after | −0.08 * | 118 | 0.61 | 243 |
| 3 days after | −0.17 * | 117 | 0.62 | 242 |
| 4 days after | −0.18 | 116 | 0.62 | 241 |
| 5 days after | −0.20 | 115 | 0.62 | 240 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pablos, M.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Piles, M.; Sánchez, N.; Vall-llossera, M.; Camps, A. Multi-Temporal Evaluation of Soil Moisture and Land Surface Temperature Dynamics Using in Situ and Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8070587
Pablos M, Martínez-Fernández J, Piles M, Sánchez N, Vall-llossera M, Camps A. Multi-Temporal Evaluation of Soil Moisture and Land Surface Temperature Dynamics Using in Situ and Satellite Observations. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(7):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8070587
Chicago/Turabian StylePablos, Miriam, José Martínez-Fernández, María Piles, Nilda Sánchez, Mercè Vall-llossera, and Adriano Camps. 2016. "Multi-Temporal Evaluation of Soil Moisture and Land Surface Temperature Dynamics Using in Situ and Satellite Observations" Remote Sensing 8, no. 7: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8070587
APA StylePablos, M., Martínez-Fernández, J., Piles, M., Sánchez, N., Vall-llossera, M., & Camps, A. (2016). Multi-Temporal Evaluation of Soil Moisture and Land Surface Temperature Dynamics Using in Situ and Satellite Observations. Remote Sensing, 8(7), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8070587