Feasibility of Acoustic Remote Sensing of Large Herring Shoals and Seafloor by Baleen Whales
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acoustic Parameters Relevant to Potential Active Acoustic Sensing in Baleen Whales and Corresponding Spatial Resolution
2.2. Detection of Scattered Returns from Herring Shoals and the Seafloor
2.3. OAWRS Experiment during Peak Herring Spawning Processes in the Gulf of Maine in Fall 2006
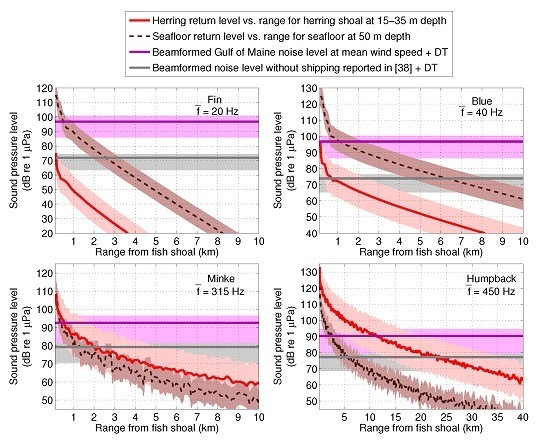
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Estimation of Expected Target Strength of a Single Herring in a Vertical Layer

References
- Wang, D.; Garcia, H.; Huang, W.; Tran, D.D.; Jain, A.D.; Yi, D.H.; Gong, Z.; Jech, J.M.; Godø, O.R.; Makris, N.C.; et al. Vast assembly of vocal marine mammals from diverse species on fish spawning ground. Nature 2016, 531, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Jain, A.D.; Tran, D.; Yi, D.H.; Wu, F.; Zorn, A.; Ratilal, P.; Makris, N.C. Ecosystem scale acoustic sensing reveals humpback whale behavior synchronous with herring spawning processes and re-evaluation finds no effect of sonar on humpback song occurrence in the Gulf of Maine in Fall 2006. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104733. [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop, R.A.; Noad, M.J.; Cato, D.H.; Stokes, D. The social vocalization repertoire of east Australian migrating humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 122, 2893–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dunlop, R.A.; Cato, D.H.; Noad, M.J. Non-song acoustic communication in migrating humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae). Mar. Mammal Sci. 2008, 24, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyack, P.; Clark, C.W. Communication and acoustic behavior of whales and dolphins. In Hearing by Whales and Dolphins, Handbook on Auditory Research; Au, W.W.L., Popper, A.N., Fay, R.R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 156–224. [Google Scholar]
- Edds-Walton, P.L. Acoustic communication signals of mysticete whales. Bioacoustics 1997, 8, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerchio, S.; Dahlheim, M. Variation in feeding vocalizations of humpback whales Megaptera novaeangliae from southeast Alaska. Bioacoustics 2001, 11, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.J.; Johnson, M.P.; Tyack, P.L. Sperm whale behaviour indicates the use of echolocation click buzzes ‘creaks’ in prey capture. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, 2239–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.; Madsen, P.; Zimmer, W.; De Soto, N.; Tyack, P. Beaked whales echolocate on prey. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, S383–S386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.; Madsen, P.T.; Zimmer, W.; De Soto, N.A.; Tyack, P. Foraging Blainville’s beaked whales (Mesoplodon densirostris) produce distinct click types matched to different phases of echolocation. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 5038–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stimpert, A.; Wiley, D.; Au, W.; Johnson, M.; Arsenault, R. ‘Megapclicks’: Acoustic click trains and buzzes produced during night-time foraging of humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae). Biol. Lett. 2007, 3, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overholtz, W.; Link, J. Consumption impacts by marine mammals, fish, and seabirds on the Gulf of Maine–Georges Bank Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus) complex during the years 1977–2002. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2007, 64, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, R.; Scott, G.; Thompson, T.; Winn, H. Estimates of prey consumption and trophic impacts of cetaceans in the USA northeast continental shelf ecosystem. J. Northwest Atl. Fish. Sci. 1997, 22, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinrich, M.; Martin, M.; Griffiths, R.; Bove, J.; Schilling, M. A shift in distribution of humpback whales, Megaptera novaeangliae, in response to prey in the southern Gulf of Maine. Fish. Bull. 1997, 95, 826–836. [Google Scholar]
- Makris, N.C.; Cato, D.H. Using singing whales to track nonsingers. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1994, 96, 3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, N.C.; Lai, Y.S.; Cato, D.H. Using broadband humpback whale vocalizations to locate nonvocal whales in shallow water. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 105, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.S. Acoustic Scattering from Stationary and Moving Targets in Shallow Water Environments—With Application of Humpback Whale Detection and Localization. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, The Department of Ocean Engineering, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Frazer, L.; Mercado, E., III. A sonar model for humpback whale song. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2000, 25, 160–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.; Frankel, A.; Helweg, D.; Cato, D. Against the humpback whale sonar hypothesis. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2001, 26, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, E., III; Frazer, L.N. Humpback whale song or humpback whale sonar? A reply to Au et al. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2001, 26, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, N.; Ratilal, P.; Symonds, D.; Jagannathan, S.; Lee, S.; Nero, R. Fish population and behavior revealed by instantaneous continental shelf-scale imaging. Science 2006, 311, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makris, N.; Ratilal, P.; Jagannathan, S.; Gong, Z.; Andrews, M.; Bertsatos, I.; Godø, O.; Nero, R.; Jech, J. Critical population density triggers rapid formation of vast oceanic fish shoals. Science 2009, 323, 1734–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagannathan, S.; Bertsatos, I.; Symonds, D.; Chen, T.; Nia, H.; Jain, A.; Andrews, M.; Gong, Z.; Nero, R.; Ngor, L.; et al. Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing (OAWRS) of marine ecosystems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 395, 137–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Andrews, M.; Jagannathan, S.; Patel, R.; Jech, J.; Makris, N.; Ratilal, P. Low-frequency target strength and abundance of shoaling Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus) in the Gulf of Maine during the Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing 2006 Experiment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 104–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.D.; Ignisca, A.; Yi, D.H.; Ratilal, P.; Makris, N.C. Feasibility of Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing (OAWRS) of Atlantic cod with seafloor scattering limitations. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 180–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, N. The effect of saturated transmission scintillation on ocean acoustic intensity measurements. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 100, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.; Swets, J. Signal Detection Theory and Psychophysics; Peninsula Publishing: Los Altos, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Au, W.; Hastings, M. Principles of Marine Bioacoustics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, B. Principles of Aperture and Array System Design: Including Random and Adaptive Arrays; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, M.; Gong, Z.; Ratilal, P. High resolution population density imaging of random scatterers with the matched filtered scattered field variance. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 126, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, R. Resonant acoustic scattering by swimbladder-bearing fish. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1978, 64, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.D. A split-step Padé solution for the parabolic equation method. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 93, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ratilal, P.; Makris, N.C. Mean and variance of the forward field propagated through three-dimensional random internal waves in a continental-shelf waveguide. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 118, 3560–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, M.; Chen, T.; Ratilal, P. Empirical dependence of acoustic transmission scintillation statistics on bandwidth, frequency, and range in New Jersey continental shelf. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.D.; Makris, N.C. Ocean acoustic hurricane classification. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, D.; Andrews, M.; Ratilal, P. Probability distribution for energy of saturated broadband ocean acoustic transmission: Results from Gulf of Maine 2006 experiment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 3659–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagannathan, S.; Küsel, E.T.; Ratilal, P.; Makris, N.C. Scattering from extended targets in range-dependent fluctuating ocean-waveguides with clutter from theory and experiments. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cato, D. Ambient sea noise in Australian waters. In Proceedings of the 5th International Congress on Sound and Vibration, Adelaide, Australia, 15–18 December 1997.
- Tyack, P. Studying how cetaceans use sound to explore their environment. In Perspectives in Ethology; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 12, pp. 251–297. [Google Scholar]
- Kenney, R.D.; Mayo, C.A.; Winn, H.E. Migration and foraging strategies at varying spatial scales in western North Atlantic right whales: A review of hypotheses. J. Cetacean Res. Manag. 2001, 2, 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Tyack, P.L. Implications for marine mammals of large-scale changes in the marine acoustic environment. J. Mammal. 2008, 89, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.H.; Scholes, P. Gas secretion and resorption in the swimbladder of the cod (Gadus morhua). J. Comp. Physiol. B 1985, 155, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLennan, D.; Simmonds, E.J. Fisheries Acoustics; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Nero, R.W.; Thompson, C.H.; Jech, J.M. In situ acoustic estimates of the swimbladder volume of Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2004, 61, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, D.E. Sound propagation in the presence of bladder fish. In Underwater Acoustics; Albers, V.M., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1967; Volume 2, pp. 55–88. [Google Scholar]





| Baleen | T | L | α | β | n | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whale Species | (dB re 1 μPa 1 m) | (s) | (Hz) | (Hz) | (dB) | (dB) | (m) | |||
| Fin | 189 ± 5.6 | 0.8 | 20 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 1.88 × 10 | 6.68 × 10 | 0.6 |
| Blue | 189 ± 5.6 | 2 | 40 | 10 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 1.19 × 10 | 2.51 × 10 | 0.4 |
| Minke | 179 ± 5.6 | 0.1 | 315 | 72.5 | 3 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 5.96 × 10 | 3.76 × 10 | 0.6 |
| Humpback | 180 ± 5.6 | 1.44 | 450 | 100 | 3 | 3.7 | 2 | 1.26 × 10 | 5.01 × 10 | 1.1 |
| Herring Shoals | H | l | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (m) | (m) | (cm) | (fish/m) | |
| Deep | 155 ± 6.5 | 50 ± 15.6 | 83 ± 31.3 | 24.2 ± 1.7 | 5.0 |
| Shallow | 25 ± 1.0 | 20 ± 6.2 | 20 ± 6.5 | 24.2 ± 1.7 | 1.0 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, D.H.; Makris, N.C. Feasibility of Acoustic Remote Sensing of Large Herring Shoals and Seafloor by Baleen Whales. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090693
Yi DH, Makris NC. Feasibility of Acoustic Remote Sensing of Large Herring Shoals and Seafloor by Baleen Whales. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(9):693. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090693
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Dong Hoon, and Nicholas C. Makris. 2016. "Feasibility of Acoustic Remote Sensing of Large Herring Shoals and Seafloor by Baleen Whales" Remote Sensing 8, no. 9: 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090693
APA StyleYi, D. H., & Makris, N. C. (2016). Feasibility of Acoustic Remote Sensing of Large Herring Shoals and Seafloor by Baleen Whales. Remote Sensing, 8(9), 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090693