Noise Localization Method for Model Tests in a Large Cavitation Tunnel Using a Hydrophone Array
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Description of Model Tests
2.2. Array Signal Processing for Source Localization
3. Results and Discussion
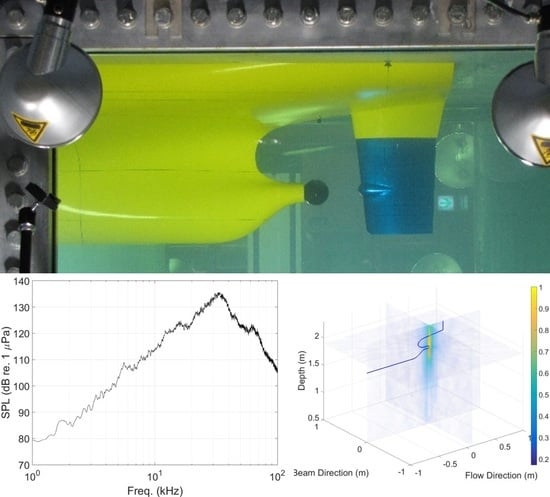
3.1. Virtual Source Experiment
3.2. Propeller Cavitation Noise Experiment
3.3. Propeller Singing Experiment
3.4. Underwater Vehicle Experiment
4. Summary and Conclusions
- (1)
- The replica field constructed using direct arrivals shows reliable localization results. When the exact simulation of the tunnel environment is difficult, it is preferable to use the direct arrivals as the replica field.
- (2)
- Both the Bartlett processor and the MV processor showed similar localization performances. However, the Bartlett processor seems to be more robust, especially when the sound pressure level is low.
- (3)
- The proposed localization method can be successfully applied to noise sources other than those of the propeller cavitation.
- (4)
- Finally, we suggest that the localization performance can be improved if the noise is measured at multiple array positions using a moving array system.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavitation ITTC Committee. Final Report and Recommendations to the 15th ITTC. In Proceedings of the 15th ITTC, Hague, The Netherlands, 15–23 September 1978.
- Bark, G.; van Berlekom, W. Experimental investigations of cavitation noise. In Proceedings of the 12th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics, Washington, DC, USA, 9–14 August 1978.
- Latorre, R. Propeller tip vortex cavitation noise inception. In Proceedings of the SNAME Propellers’81 Symposium, Virginia Beach, VA, USA, 17–18 September 1981.
- Koop, B. Test Procedures for Hydro-Acoustic Investigations in the HSVA with Some Test Results; HSVA Report No. Ac 03/77; CORDIS: Hamburg, Germany, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, D.E.; Billet, M.L. The Variation of Sheet Type surface Cavitation Noise with Cavitation Number; Applied Research Laboratory, Pennsylvania State University: Old Main, PA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Bark, G.; Johnsson, C.A. Prediction of cavitation noise from model experiments in a large cavitation tunnel. In Noise Sources in Ships 1: Propellers; Nordforsk: Stockholm, Sweden, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, W.K.; Sevik, M.M. Recent developments in cavitation noise research. In Proceedings of the ASME International Symposium on Cavitation Noise, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 14–19 November 1982.
- Cavitation ITTC Committee. Final Report and Recommendations to the 18th ITTC. In Proceedings of the 18th ITTC, Kobe, Japan, 18–24 October 1987.
- Levkovskii, Y.L. Modelling of cavitation noise. J. Sov. Phys. Acoust. 1968, 13, 337–339. [Google Scholar]
- Lovik, A. Scaling of propeller cavitation noise. Noise Sources in Ships 1: Propellers; Nordforsk: Stockholm, Sweden, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Strasberg, M. Propeller cavitation noise after 35 years of study. In Proceedings of the ASME International Symposium on Noise and Fluids Engineering, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–20 June 1977.
- Blake, W.K. Acoustic measurements in cavitation testing. In Proceedings of the DRG Seminar on Advanced Hydrodynamic Testing Facilities, Hague, The Netherlands, 11–15 March 1982.
- Cavitation ITTC Committee. Final Report and Recommendations to the 16th ITTC. In Proceedings of the 16th ITTC, St. Petersburg, Russia, 27–30 June 1981.
- Ten Wolde, T.; De Bruijn, A. A new method for the measurements of the acoustical source strength of cavitating ship propellers. Int. Shipbuild. Progress 1975, 22, 385–396. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Kooji, J.; De Bruijn, A. Acoustic measurements in the NSMB depressurized towing tank. In Proceedings of the DRG Seminar on Advanced Hydrodynamic Testing Facilities, Hague, The Netherland; 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Noordzji, L.; Van der Kooji, J. Hydro-acoustics of a cavitating screw propeller; far-field approximation. J. Ship Res. 1981, 25, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Leggat, L.J. Propeller noise investigation in a free-field environment. In Proceedings of the DRG Seminar on Advanced Hydrodynamic Testing Facilities, Hague, The Netherlands, 26–28 April 1982.
- Abbot, P.A.; Celuzza, S.A.; Etter, R.J. The acoustic characteristics of the Naval Surface Warfare Center's Large Cavitation Channel (LCC). In Proceedings of the ASME Winter Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–3 December 1993.
- Friesch, J. The new cavitation test facility of Hamburg Ship Model Basin (HYKAT). In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Hydro- and Aerodynamics in Marine Engineering, Varna, Bulgaria, 28 October–1 November 1991.
- Sato, R.; Mori, T.; Yakushiji, R.; Naganuma, K.; Nishimura, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Sasajima, T. Conceptual design of the flow noise simulator. In Proceedings of the 4th ASME_JSME Joint Fluids Engineering Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 6–10 July 2003.
- Van Trees, H.L. Part IV of detection, estimation, and modulation theory. In Optimum Array Processing; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tolstoy, A. Matched Field Processing for Underwater Acoustics; World Scientific: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Baggeroer, A.B.; Kuperman, W.A.; Mikhalevsky, P.N. An overview of matched field methods in ocean acoustics. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1993, 18, 401–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, T.J. Aeroacoustic Measurements; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.; Seol, H.; Kim, K.; Seong, W. A study on propeller noise source localization in a cavitation tunnel. Ocean Eng. 2009, 46, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.A.; Dowling, D.R. Ray-based acoustic localization of cavitation in a highly reverberant environment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 3088–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, N.A.; Ceccio, S.L. The acoustic emissions of cavitation bubbles in stretched vortices. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 130, 3209–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S. Acoustic Cavitation Localization in Reverberant Environments. Master’s Thesis, The Pennsylvania State University, State College, PA, USA, 13 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Kim, K.; Seong, W.; Lee, J. Propeller sheet cavitation noise source modeling. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 1356–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, K.; Seong, W. Non-cavitating propeller noise modeling and inversion. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 6424–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Seong, W.; Choo, Y.; Lee, J. Localization of incipient tip vortex cavitation using ray based matched field inversion method. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 354, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felli, M.; Falchi, M.; Pereira, F. Investigation of the Flow Field around a Propeller-Rudder Configuration: On-Surface Pressure Measurements and Velocity-Pressure-Phase-Locked Correlations. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors, Hamburg, Germany, 17–18 June 2011.
- Brüel & Kjær. Hydrophones—Types 8103, 8104, 8105 and 8106. Available online: http://www.lthe.fr/LTHE/IMG/pdf/DocBruelKjaerHydro.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2015).
- Park, C.; Seol, H.; Kim, G.-D.; Park, Y.-H. A study on hydrophone array design optimization for cavitation tunnel noise measurement. J. Acoust. Soc. Korea 2013, 32, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITTC. Recommended Procedures and Guidelines 7.5-02-01-05: Model Scale Noise Measurements; ITTC: Centurion, South Africa, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- International Transducer Corporation. Deep Water Omnidirectional Transducer Model ITC-1032. Available online: http://www.channeltechgroup.com/publication/model-itc-1032-deep-water-omnidirectional-transducer/ (accessed on 3 December 2015).
- Tani, G.; Viviani, M.; Armelloni, E.; Nataletti, M. Cavitation Tunnel Acoustic Characterisation and Application to Model Propeller Radiated Noise Measurements at Different Functioning Conditions. Available online: http://pim.sagepub.com/content/early/2015/01/09/1475090214563860.abstract (accessed on 15 January 2015).
- Oppenheim, A.V.; Schafer, R.W. Discrete-Time Signal Processing; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, D. Mechanics of Underwater Noise; Pergamon Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]



















| Center Frequency | Bartlett Processor | MV Processor |
|---|---|---|
| 1.6 kHz | (0.10 m, 0.0 m, 1.94 m) | (0.09 m, 0.02 m, 1.92 m) |
| 3.15 kHz | (0.11 m, 0.01 m, 1.85 m) | (0.14 m, 0.0 m, 1.86 m) |
| 6.3 kHz | (0.11 m, −0.02 m, 1.88 m) | (0.12 m, −0.03 m, 1.88 m) |
| 12.5 kHz | (0.10 m, −0.02 m, 1.92 m) | (0.11 m, −0.02 m, 1.87 m) |
| 25.0 kHz | (0.11 m, −0.02 m, 1.91 m) | (0.11 m, −0.02 m, 1.89 m) |
| 50.0 kHz | (0.11 m, −0.02 m, 1.91 m) | (0.11 m, −0.02 m, 1.91 m) |
| Mean | (0.11 m, −0.01 m, 1.90 m) | (0.11 m, −0.01 m, 1.89 m) |
| SD | (0.01 m, 0.01 m, 0.03 m) | (0.01 m, 0.01 m, 0.02 m) |
| Bartlett Processor | MV Processor | |
|---|---|---|
| Virtual Source | (0.14 m, −0.02 m, 1.93 m) | (0.14 m, −0.02 m, 1.92 m) |
| Sheet Cavitation | (0.17 m, 0.03 m, 1.99 m) | (0.17 m, 0.03 m, 1.97 m) |
| Tip Vortex Cavitation | (0.17 m, 0.02 m, 2.01 m) | (0.17 m, 0.02 m, 2.00 m) |
| Type | Low Frequency Data (5 to 10 kHz) | Tones | High Frequency Data (20 to 50 kHz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cavitation | (0.15 m, 0.22 m, 1.85 m) | (0.12 m, 0.16 m, 1.91 m) | (0.13 m, 0.23 m, 1.84 m) |
| Non-cavitation | (0.14 m, 0.19 m, 1.78 m) | (0.11 m, 0.19 m, 1.90 m) | (0.11 m, 0.16 m, 1.89 m) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, C.; Kim, G.-D.; Park, Y.-H.; Lee, K.; Seong, W. Noise Localization Method for Model Tests in a Large Cavitation Tunnel Using a Hydrophone Array. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030195
Park C, Kim G-D, Park Y-H, Lee K, Seong W. Noise Localization Method for Model Tests in a Large Cavitation Tunnel Using a Hydrophone Array. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(3):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030195
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Cheolsoo, Gun-Do Kim, Young-Ha Park, Keunhwa Lee, and Woojae Seong. 2016. "Noise Localization Method for Model Tests in a Large Cavitation Tunnel Using a Hydrophone Array" Remote Sensing 8, no. 3: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030195
APA StylePark, C., Kim, G. -D., Park, Y. -H., Lee, K., & Seong, W. (2016). Noise Localization Method for Model Tests in a Large Cavitation Tunnel Using a Hydrophone Array. Remote Sensing, 8(3), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030195