Voxel-Based Spatial Filtering Method for Canopy Height Retrieval from Airborne Single-Photon Lidar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
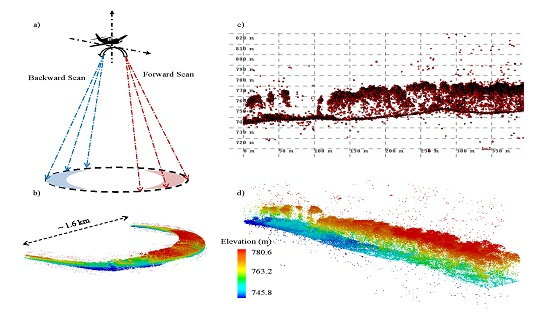
2.1. HRQLS
2.2. Reference Data
2.3. HRQLS Data Processing
2.3.1. Preprocessing
2.3.2. The Voxel-Based Spatial Filtering Method
- Calculating the maximum-noise-level threshold as the mean volume point density (points per m3) of the Level 1 SPL dataset at each 30 m × 30 m horizontal grid;
- Splitting the area of interest into 3D cells at a given size;
- Counting the number of points in each cell and its surrounding cells (a total of 27 cells);
- Labeling the points as noise if the number was less than the pre-calculated noise threshold multiplied by the volume of 27 cells.
2.3.3. The Histogram Based Method
2.4. Canopy Height Comparison
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swatantran, A.; Tang, H.; Barrett, T.; DeCola, P.; Dubayah, R. Rapid, high-resolution forest structure and terrain mapping over large areas using single photon lidar. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degnan, J.J.; Field, C.T. Moderate to high altitude, single photon sensitive, 3D imaging lidars. SPIE Proc. 2014, 9114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnan, J. Photon-counting multikilohertz microlaser altimeters for airborne and spaceborne topographic measurements. J. Geodyn. 2002, 34, 503–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi, D.; Lefsky, M.A. Prospects of photon counting lidar for savanna ecosystem structural studies. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 40, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosette, J.; Field, C.; Nelson, R.; DeCola, P.; Cook, B. A new photon-counting lidar system for vegetation analysis. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on LiDAR Applications for Assessing Forest Ecosystems (SilviLaser 2011), Hobart, Australia, 16–19 October 2011.
- Glenn, N.F.; Neuenschwander, A.; Vierling, L.A.; Spaete, L.; Li, A.; Shinneman, D.J.; Pilliod, D.S.; Arkle, R.S.; McIlroy, S.K. Landsat 8 and ICESat-2: Performance and potential synergies for quantifying dryland ecosystem vegetation cover and biomass. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadallah, M.S.; Abbott, A.L.; Thomas, V.A.; Wynne, R.H.; Nelson, R.F. Estimating forest canopy height and biophysical parameters using photon-counting laser altimetry. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on LiDAR Applications for Assessing Forest Ecosystems (SilviLaser 2013), Beijing, China, 9–11 October 2013.
- Herzfeld, U.C.; McDonald, B.W.; Wallin, B.F.; Neumann, T.A.; Markus, T.; Brenner, A.; Field, C. Algorithm for detection of ground and canopy cover in micropulse photon-counting lidar altimeter data in preparation for the ICESat-2 mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2109–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magruder, L.A.; Wharton, M.E.; Stout, K.D.; Neuenschwander, A.L. Noise filtering techniques for photon-counting ladar data. SPIE Proc. 2012, 8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussavi, M.S.; Abdalati, W.; Scambos, T.; Neuenschwander, A. Applicability of an automatic surface detection approach to micro-pulse photon-counting lidar altimetry data: Implications for canopy height retrieval from future ICESat-2 data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 5263–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesano, P.M.; Rosette, J.; Sun, G.; North, P.; Nelson, R.F.; Dubayah, R.O.; Ranson, K.J.; Kharuk, V. The uncertainty of biomass estimates from modeled ICESat-2 returns across a boreal forest gradient. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, V.; Eldridge, D.F.; Jason, A.L.; Saghy, D.L.; Steigerwald, P.R.; Stoker, J.M.; Sugarbaker, L.J.; Thunen, D.R. Status Report for the 3D Elevation Program, 2013–2014; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2015; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neil-Dunne, J.; MacFaden, S.; Royar, A. A versatile, production-oriented approach to high-resolution tree-canopy mapping in urban and suburban landscapes using geobia and data fusion. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12837–12865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, S.; Dubayah, R. Advances in remote sensing technology and implications for measuring and monitoring forest carbon stocks and change. Carbon Manag. 2011, 2, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Swatantran, A.; Johnson, K.; Duncanson, L.; Tang, H.; O’Neil Dunne, J.; Hurtt, G.; Dubayah, R. Local discrepancies in continental scale biomass maps: A case study over forested and non-forested landscapes in Maryland, USA. Carbon Balance Manag. 2015, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubayah, R.; Swatantran, A.; Huang, W.; Duncanson, L.; Johnson, K.; Tang, H.; Dunne, J.O.; Hurtt, G. CMS: LiDAR-Derived Aboveground Biomass, Canopy Height and Cover for Maryland, 2011; ORNL Distributed Active Archive Center: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, H.E.; McGaughey, R.J.; Reutebuch, S.E. Forest measurement and monitoring using high-resolution airborne lidar. In USDA Forest Service—General Technical Report PNW; USDA Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Wasser, L.; Day, R.; Chasmer, L.; Taylor, A. Influence of vegetation structure on lidar-derived canopy height and fractional cover in forested riparian buffers during leaf-off and leaf-on conditions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, S.C.; Zhao, K. A voxel-based lidar method for estimating crown base height for deciduous and pine trees. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 767–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, S.; Essery, R.; Reid, T.; Carle, J.; Baxter, R.; Rutter, N.; Huntley, B. Characterising forest gap fraction with terrestrial lidar and photography: An examination of relative limitations. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cote, J.F.; Widlowski, J.L.; Fournier, R.A.; Verstraete, M.M. The structural and radiative consistency of three-dimensional tree reconstructions from terrestrial lidar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, P. Dem generation from laser scanner data using adaptive tin models. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2000, 33, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Isenburg, M. LAStools—Efficient Lidar Processing Software (Version 140929); rapidlasso GmbH: Gilching, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, F.J. Use of windows for harmonic-analysis with discrete Fourier-transform. Proc. IEEE 1978, 66, 51–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Oliveira, M.V.N.; Reutebuch, S.E.; McGaughey, R.J.; Andersen, H.E. Estimating forest biomass and identifying low-intensity logging areas using airborne scanning lidar in Antimary State Forest, Acre State, western Brazilian Amazon. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riano, D.; Chuvieco, E.; Condes, S.; Gonzalez-Matesanz, J.; Ustin, S.L. Generation of crown bulk density for Pinus sylvestris L. from lidar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, G.W.; Wulder, M.A.; Niemann, K.O. Simulation and quantification of the fine-scale spatial pattern and heterogeneity of forest canopy structure: A lacunarity-based method designed for analysis of continuous canopy heights. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 214, 65–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskierniak, D.; Lane, P.N.J.; Robinson, A.; Lucieer, A. Extracting lidar indices to characterise multilayered forest structure using mixture distribution functions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncanson, L.I.; Niemann, K.O.; Wulder, M.A. Estimating forest canopy height and terrain relief from glas waveform metrics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ni-Meister, W.; Yang, W.Z.; Chen, Q. Physically based vertical vegetation structure retrieval from ICESat data: Validation using LVIS in white mountain national forest, New Hampshire, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2776–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.E.; Lefsky, M.; Pang, Y. Optimization of geoscience laser altimeter system waveform metrics to support vegetation measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, S.; Disney, M.; Muller, J.P.; Lewis, P.; Foster, M. A threshold insensitive method for locating the forest canopy top with waveform lidar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3286–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncanson, L.I.; Dubayah, R.O.; Cook, B.D.; Rosette, J.; Parker, G. The importance of spatial detail: Assessing the utility of individual crown information and scaling approaches for lidar-based biomass density estimation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, G.C. Airborne lidar bathymetry. In Digital Elevation Model Technologies and Applications: The DEM Users Manual, 2nd ed.; American Society for Photogrammertry and Remote Sensing: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2007; pp. 253–320. [Google Scholar]
- Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Nelson, R.F.; Næsset, E.; Ørka, H.O.; Coops, N.C.; Hilker, T.; Bater, C.W.; Gobakken, T. Lidar sampling for large-area forest characterization: A review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, Q.A. A star is born: The state of new lidar technologies. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2016, 82, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Degnan, J.; Barrett, T.; Shan, J. First evaluation on single photon-sensitive lidar data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2016, 82, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Knapp, D.E.; Martin, R.E.; Tupayachi, R.; Anderson, C.B.; Mascaro, J.; Sinca, F.; Chadwick, K.D.; Higgins, M.; Farfan, W.; et al. Targeted carbon conservation at national scales with high-resolution monitoring. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5016–E5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, B.D.; Corp, L.A.; Nelson, R.F.; Middleton, E.M.; Morton, D.C.; McCorkel, J.T.; Masek, J.G.; Ranson, K.J.; Ly, V.; Montesano, P.M. NASA Goddard’s LiDAR, Hyperspectral and Thermal (G-LiHT) airborne imager. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4045–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Spatial-Filtering | SPL—Field Height | SPL—DRL Height | ||||
| Method | r2 | Bias | RMSE | r2 | Bias | RMSE |
| p100 | 0.54 | 2.88 | 6.99 | 0.83 | 3.77 | 5.46 |
| p99 | 0.69 | 0.42 | 4.85 | 0.94 | 1.07 | 2.42 |
| p98 | 0.70 | −0.12 | 4.77 | 0.94 | 0.49 | 2.28 |
| p97 | 0.70 | −0.52 | 4.78 | 0.93 | 0.07 | 2.35 |
| p96 | 0.70 | −0.88 | 4.82 | 0.92 | −0.31 | 2.52 |
| Histogram | SPL—Field Height | SPL—DRL Height | ||||
| Method | r2 | Bias | RMSE | r2 | Bias | RMSE |
| p100 | 0.59 | 0.77 | 6.41 | 0.78 | 0.68 | 5.05 |
| p99 | 0.59 | 0.00 | 6.25 | 0.78 | −0.06 | 4.88 |
| p98 | 0.60 | −0.52 | 6.24 | 0.78 | −0.55 | 4.89 |
| p97 | 0.60 | −0.93 | 6.22 | 0.78 | −0.93 | 4.92 |
| p96 | 0.60 | −1.31 | 6.25 | 0.78 | −1.29 | 4.99 |
| z = 0.1 | z = 0.2 | z = 0.3 | z = 0.4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| xy = 1 | (11, 0.67, −1.17, 5.09) | (9, 0.74, −1.02, 4.44) | (7, 0.75, −0.67, 4.44) | (9, 0.73, 0.01, 4.50) |
| xy = 2 | (11, 0.71, −0.71, 4.65) | (8, 0.77, −0.75, 4.17) | (8, 0.76, −0.62, 4.22) | (8, 0.75, −0.48, 4.37) |
| xy = 3 | (8, 0.77, −0.83, 4.22) | (8, 0.76, −0.64, 4.22) | (9, 0.75, −0.32, 4.28) | (9, 0.75, −0.33, 4.35) |
| xy = 4 | (8, 0.76, −0.60, 4.23) | (9, 0.75, −0.30, 4.35) | (9, 0.75, −0.29, 4.30) | (9, 0.75, −0.26, 4.30) |
| xy = 5 | (9, 0.74, −0.26, 4.41) | (9, 0.74, −0.30, 4.44) | (9, 0.75, −0.29, 4.38) | (9, 0.74, −0.25, 4.39) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, H.; Swatantran, A.; Barrett, T.; DeCola, P.; Dubayah, R. Voxel-Based Spatial Filtering Method for Canopy Height Retrieval from Airborne Single-Photon Lidar. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090771
Tang H, Swatantran A, Barrett T, DeCola P, Dubayah R. Voxel-Based Spatial Filtering Method for Canopy Height Retrieval from Airborne Single-Photon Lidar. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(9):771. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090771
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Hao, Anu Swatantran, Terence Barrett, Phil DeCola, and Ralph Dubayah. 2016. "Voxel-Based Spatial Filtering Method for Canopy Height Retrieval from Airborne Single-Photon Lidar" Remote Sensing 8, no. 9: 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090771
APA StyleTang, H., Swatantran, A., Barrett, T., DeCola, P., & Dubayah, R. (2016). Voxel-Based Spatial Filtering Method for Canopy Height Retrieval from Airborne Single-Photon Lidar. Remote Sensing, 8(9), 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090771