The Sensitivity of AOD Retrieval to Aerosol Type and Vertical Distribution over Land with MODIS Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background on the MODIS Aerosol Retrieval
2.1. Basic Theory of the Aerosol Retrieval Algorithm
2.2. Aerosol Properties
2.2.1. Aerosol Type
2.2.2. Aerosol Vertical Distribution
3. Data and Method
Experiment Set up
4. Experiment Results and Discussions
4.1. Experiment 1
4.1.1. Result
4.1.2. Discussion
- Issue 1: the MODIS algorithm assumes that the can vary with the atmospheric condition in the retrieval. Obviously, this assumption is inconsistent with the fact that the surface reflectance is invariant with the atmospheric condition.
- Issue 2: to find the possible with the rearranged Equation (2), the MODIS measurement is expected to be divided into two parts: one part is the reflectance from fine-mode dominated atmosphere, and the one from coarse-mode dominated atmosphere, while the algorithm assumes the measurement to be identical to each part. By doing this, it can give a large uncertainty of the retrieval with heavy aerosol loading. Nevertheless, the uncertainty is expected to be small with low aerosol loading since the TOA reflectance is dominated by the surface contribution and little affected by the atmospheric aerosol.
4.2. Experiment 2
4.2.1. Result
4.2.2. Discussion
4.3. Experiment 3
4.3.1. Result
4.3.2. Discussion
4.4. Experiment 4
5. Conclusions & Recommendation
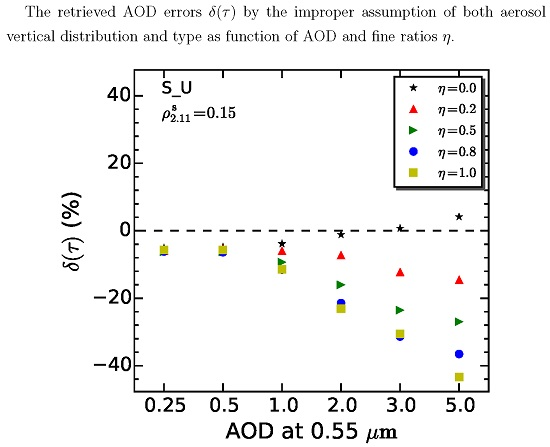
- With the simulations varied with 4 vertical distributions (ExpH2, ExpH3, Exp2L0 and Exp2L3), about 5% errors can be found in the algorithm retrieval. Even larger errors of the retrieval are shown in ExpH and Exp2L simulation series, ranging from 2% to 30% when aerosol loading of 0.5 is assumed. In the vertical distribution, the aerosol layer height is the main variable that affects the retrieval, where the errors significantly increase as increasing the aerosol layer height.
- Furthermore, the errors caused by the layer height present a strong angular dependence due to the large discrepancy of the phase function between non-dust and dust aerosols.
- Generally (), errors in aerosol type assumption can lead to uncertainty up to 8% in the AOD retrieval with the algorithm. By combining the uncertainty of the aerosol type (urbanIndustrial replaced with smoke) with its vertical profiles (ExpH2 replaced with Exp2L3), the AOD errors present a significant negative bias with the by >6%. The errors can be up to 15% when aerosol loading of 1.0 is observed.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOD | Aerosol Optical Depth |
| AERONET | Aerosol Robotic Network |
| MODIS | Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer |
| CALIPSO | Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observation |
| LUT | LookUp Table |
| DT | Dark Target |
| C6_DT | Collection 6 Dark Target |
| EE | Expected Error |
| ExpH1 | the exponential distribution with the scale height of 1, other ExpH series follow the same rule |
| Exp2L0 | the 2-layer distribution with the bottom layer at the surface (altitude: 0), other Exp2L series follow the same rule |
Appendix A. Aerosol Size Distribution
References
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Mattoo, S.; Chu, D.A.; Martins, J.V.; Li, R.R.; Ichoku, C.; Levy, R.C.; Kleidman, R.G.; et al. The MODIS aerosol algorithm, products, and validation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Vermote, E.F.; Kaufman, Y.J. Second-generation operational algorithm: Retrieval of aerosol properties over land from inversion of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer spectral reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Dubovik, O. Global aerosol optical properties and application to Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol retrieval over land. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D13210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Kahn, R.; Mishchenko, M.; Remer, L.; Lee, K.H.; Wang, M.; Laszlo, I.; Nakajima, T.; Maring, H. Uncertainties in satellite remote sensing of aerosols and impact on monitoring its long-term trend: A review and perspective. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 2755–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Reid, J.S. A decadal regional and global trend analysis of the aerosol optical depth using a data-assimilation grade over-water MODIS and Level 2 MISR aerosol products. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10949–10963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.P.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wu, Y.R.; Zhaxi, Y.; Che, H.Z.; La, B.; Wang, W.; Li, X.W. Spatio-temporal variation trends of satellite-based aerosol optical depth in China during 1980–2008. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6802–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Zibordi, G.; Chern, J.D.; Mao, J.; Li, C.; Holben, B.N. Global monitoring of air pollution over land from the Earth Observing System-Terra Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel-Cox, J.A.; Holloman, C.H.; Coutant, B.W.; Hoff, R.M. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of MODIS satellite sensor data for regional and urban scale air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2495–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, R.M.; Christopher, S.A. Remote sensing of particulate pollution from space: Have we reached the promised land? J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 645–675. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Tian, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Duan, J.; Li, X. Synergy of satellite and ground based observations in estimation of particulate matter in eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 433, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyer, E.J.; Reid, J.S.; Zhang, J. An over-land aerosol optical depth data set for data assimilation by filtering, correction, and aggregation of MODIS Collection 5 optical depth retrievals. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 379–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Lin, H.C.; Schwartz, C.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Wang, T. Three-dimensional variational assimilation of MODIS aerosol optical depth: Implementation and application to a dust storm over East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D23206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, C.S.; Liu, Z.; Lin, H.C.; Cetola, J.D. Assimilating aerosol observations with a “hybrid” variational-ensemble data assimilation system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 4043–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Chin, M.; Feingold, G.; Remer, L.A.; Anderson, T.L.; Balkanski, Y.; Bellouin, N.; Boucher, O.; Christopher, S.; et al. A review of measurement-based assessments of the aerosol direct radiative effect and forcing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 613–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellouin, N.; Jones, A.; Haywood, J.; Christopher, S.A. Updated estimate of aerosol direct radiative forcing from satellite observations and comparison against the Hadley Centre climate model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D10205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G. Consistency between satellite-derived and modeled estimates of the direct aerosol effect. Science 2009, 325, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McComiskey, A.; Schwartz, S.E.; Schmid, B.; Guan, H.; Lewis, E.R.; Ricchiazzi, P.; Ogren, J.A. Direct aerosol forcing: Calculation from observables and sensitivities to inputs. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D09202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Reid, J.S. MODIS aerosol product analysis for data assimilation: Assessment of over-ocean level 2 aerosol optical thickness retrievals. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D22207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielonen, T.; Levy, R.C.; Aaltonen, V.; Komppula, M.; de Leeuw, G.; Huttunen, J.; Lihavainen, H.; Kolmonen, P.; Lehtinen, K.E.J.; Arola, A. Evaluating the assumptions of surface reflectance and aerosol type selection within the MODIS aerosol retrieval over land: The problem of dust type selection. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; de Graaf, M.; Menenti, M. MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth retrieval over land considering surface BRDF effects. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; de Graaf, M.; Menenti, M. Improved MODIS Dark Target Aerosol Optical Depth algorithm over land: Angular effect Correction. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Jeong, M.J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.M.; Hansell, R.; Seftor, C.S.; Huang, J.; Tsay, S.C. Enhanced Deep Blue aerosol retrieval algorithm: The second generation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J. Dynamic aerosol model: Urban/industrial aerosol. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 13859–13871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Holben, B.N.; Thompson, A.M.; McNamara, D. Biomass burning aerosol size distribution and modeled optical properties. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 31879–31891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokhanovsky, A.A.; Deuzé, J.L.; Diner, D.J.; Dubovik, O.; Ducos, F.; Emde, C.; Garay, M.J.; Grainger, R.G.; Heckel, A.; Herman, M.; et al. The inter-comparison of major satellite aerosol retrieval algorithms using simulated intensity and polarization characteristics of reflected light. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 909–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.M.; Seftor, C.J.; Jeong, M.J. Retrieving the height of smoke and dust aerosols by synergistic use of VIIRS, OMPS, and CALIOP observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 2015JD023567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Mukelabai, M.M.; Piketh, S.J.; Torres, O.; Jethva, H.T.; Hyer, E.J.; Ward, D.E.; Dubovik, O.; et al. A seasonal trend of single scattering albedo in southern African biomass-burning particles: Implications for satellite products and estimates of emissions for the world’s largest biomass-burning source. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6414–6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; de Graaf, M.; Menenti, M. Unpublished work. 2006.
- Hsu, N.C.; Tsay, S.C.; King, M.D.; Herman, J.R. Aerosol properties over bright-reflecting source regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Mattoo, S.; Ichoku, C.; Kahn, R.; Eck, T.F. Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10399–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Remer, L.A.; Vermote, E.F.; Chu, A.; Holben, B.N. Operational remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol over land from EOS moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 17–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Aerosol Model | Mode | (m) | σ | (mm) | Refracitve Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ModeratelyAbsorbing/Generic | Accum | 0.1552 | 0.44205 | 0.0960 | 1.455 − 0.009i |
| Coarse | 3.2689 | 0.7782 | 0.0922 | — | |
| Absorbing/Smoke | Accum | 0.1383 | 0.4231 | 0.09423 | 1.51 − 0.02i |
| Coarse | 3.92235 | 0.76375 | 0.06499 | — | |
| NonAbsorbing/UrbanIndustrial | Accum | 0.1821 | 0.44065 | 0.097227 | 1.42 − 0.00625i |
| Coarse | 3.39575 | 0.8414 | 0.05996 | — | |
| Speriod/Dust | Accum | 0.1466 | 0.68238 | 0.04277 | 1.5017 − 0.002i |
| Coarse | 2.2 | 0.57429 | 0.32618 | — |
| Aerosol Model | , m | |
|---|---|---|
| ModeratelyAbsorbing/Generic | 0.920 | 0.261 |
| Absorbing/Smoke | 0.869 | 0.208 |
| NonAbsorbing/UrbanIndustrial | 0.947 | 0.256 |
| Speriod/Dust | 0.953 | 0.680 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; De Graaf, M.; Menenti, M. The Sensitivity of AOD Retrieval to Aerosol Type and Vertical Distribution over Land with MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090765
Wu Y, De Graaf M, Menenti M. The Sensitivity of AOD Retrieval to Aerosol Type and Vertical Distribution over Land with MODIS Data. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(9):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090765
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yerong, Martin De Graaf, and Massimo Menenti. 2016. "The Sensitivity of AOD Retrieval to Aerosol Type and Vertical Distribution over Land with MODIS Data" Remote Sensing 8, no. 9: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090765
APA StyleWu, Y., De Graaf, M., & Menenti, M. (2016). The Sensitivity of AOD Retrieval to Aerosol Type and Vertical Distribution over Land with MODIS Data. Remote Sensing, 8(9), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090765