Spatiotemporal Variability of Land Surface Phenology in China from 2001–2014
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Data Processing
2.2.1. MODIS EVI Data
2.2.2. Land Cover Data
2.2.3. Data Smoothing and Phenology Extraction
2.3. Data Analyses
2.3.1. Mann-Kendall Trend Analysis
2.3.2. Theil–Sen Median Slope Estimator
2.4. SOS and EOS Validation
3. Results
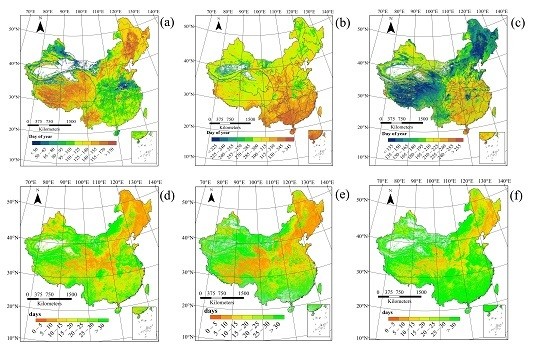
3.1. Spatial Patterns of Land Surface Phenology
3.2. Trends in Phenology
3.2.1. Spatial Patterns of Phenological Trends
3.2.2. Temporal Patterns of Phenological Trends
3.2.3. Phenological Trends for Vegetation Types
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Distribution in Phenology Parameters
4.2. Temporal Changes in Phenology at the Regional Scale
4.3. Temporal Changes in Phenology among Vegetation Types
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hmimina, G.; Dufrêne, E.; Pontailler, J.Y.; Delpierre, N.; Aubinet, M.; Caquet, B.; de Grandcourt, A.; Burban, B.; Flechard, C.; Granier, A.; et al. Evaluation of the potential of MODIS satellite data to predict vegetation phenology in different biomes: An investigation using ground-based NDVI measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.H.; Wang, H.J.; Ge, Q.S. The spatial pattern of leaf phenology and its response to climate change in China. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2014, 58, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.Y.; Running, S.W.; Lin, J.H.; Zhao, M.S.; Park, C.-R.; Loehman, R. A regional phenology model for detecting onset of greenness in temperate mixed forests, Korea: An application of MODIS leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.D.; Carbone, G.J.; Reighard, G.L.; Okie, W.R. Models to predict peach phenology from meteorological variables. HortScience 1997, 32, 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- White, M.A.; Thornton, P.E.; Running, S.W. A continental phenology model for monitoring vegetation responses to interannual climatic variability. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1997, 11, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; Jenkins, J.P.; Braswell, B.H.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Ollinger, S.V.; Smith, M.L. Use of digital webcam images to track spring green-up in a deciduous broadleaf forest. Oecologia 2007, 152, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnentag, O.; Hufkens, K.; Teshera-Sterne, C.; Young, A.M.; Friedl, M.; Braswell, B.H.; Milliman, T.; O’Keefe, J.; Richardson, A.D. Digital repeat photography for phenological research in forest ecosystems. Agric. Meteorol. 2012, 152, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henebry, G.M.; de Beurs, K.M. Remote sensing of land surface phenology: A prospectus. In Phenology: An Integrative Environmental Science; Schwartz, M.D., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 385–411. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.S.H.; Piao, S.L.; de Beeck, M.O.; Cong, N.; Zhao, H.F.; Zhang, Y.; Menzel, A.; Janssens, I.A. Recent spring phenology shifts in western Central Europe based on multiscale observations. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.S.; Wang, H.J.; Rutishauser, T.; Dai, J.H. Phenological response to climate change in China: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Galiano, V.F.; Dash, J.; Atkinson, P.M. Characterising the land surface phenology of Europe using decadal MERIS data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9390–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.C.; Liu, H.Y. Consistent shifts in spring vegetation green-up date across temperate biomes in China, 1982–2006. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.X.; Guo, X.Y.; Li, X.D.; Chen, C. Spatial and temporal changes in vegetation phenology at middle and high latitudes of the northern hemisphere over the past three decades. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10973–10995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeganathan, C.; Dash, J.; Atkinson, P.M. Characterising the spatial pattern of phenology for the tropical vegetation of India using multi-temporal MERIS chlorophyll data. Landsc. Ecol. 2010, 25, 1125–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maignan, F.; Bréon, F.M.; Vermote, E.; Ciais, P.; Viovy, N. Mild winter and spring 2007 over western Europe led to a widespread early vegetation onset. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Z.; Guo, H.D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.Y.; Qiu, Y.B.; Sun, Z.C. Assessing phenological change and climatic control of alpine grasslands in the Tibetan Plateau with MODIS time series. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2015, 59, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Kawanura, K.; Ishikawa, N.; Goto, M.; Wulan, T.; Alateng, D.; Yin, T. MODIS NDVI and vegetation phenology dynamics in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Solid Earth Discuss. 2015, 7, 2381–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suepa, T.; Qi, J.G.; Lawawirojwong, S.; Messina, P.J. Understanding spatio-temporal variation of vegetation phenology and rainfall seasonality in the monsoon Southeast Asia. Environ. Res. 2016, 147, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, N.; Wang, T.; Nan, H.J.; Ma, Y.C.; Wang, X.H.; Myneni, R.B. Changes in satellite-derived spring vegetation green-up date and its linkage to climate in China from 1982 to 2010: A multimethod analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Fu, Y.S.H.; Zeng, Z.Z.; Huang, M.T.; Li, X.R.; Piao, S.L. Temperature, precipitation, and insolation effects on autumn vegetation phenology in temperate China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, N.; Piao, S.L.; Chen, A.P.; Wang, X.H.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.P.; Han, S.J.; Zhou, G.S.; Zhang, X.P. Spring vegetation green-up date in China inferred from SPOT NDVI data: A multiple model analysis. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 165, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.C.; Wang, W.; Ma, J.S.; Yang, X. The characteristics, causes of formation and climatic impact of the 1997–1998 El Niño event. Donghai Mar. Sci. 2004, 22, 1–8, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Piao, S.L.; Cui, M.D.; Chen, A.P.; Wang, X.H.; Ciais, P.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y.H. Altitude and temperature dependence of change in the spring vegetation green-up date from 1982 to 2006 in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.S.; Dai, J.H.; Cui, H.J.; Wang, H.J. Spatiotemporal variability in start and end of growing season in China related to climate variability. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.G.; Tang, Y.H.; Chen, J.; Zhu, X.L.; Zheng, Y.H. Influences of temperature and precipitation before the growing season on spring phenology in grasslands of the central and eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.H. Climate-associated changes in spring plant phenology in China. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.W.; Zhong, M.; Tang, Z.H.; Chen, C.C. Spatiotemporal variability of vegetation phenology with reference to altitude and climate in the subtropical mountain and hill region, China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 2883–2892. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.J.; Dai, J.H.; Zheng, J.Y.; Ge, Q.S. Temperature sensitivity of plant phenology in temperate and subtropical regions of China from 1850 to 2009. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.Y.; Yin, Y.H.; Li, B.Y. A new scheme for climate regionalization in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2010, 65, 3–12, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Justice, C.O.; Vermote, E.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Defries, R.; Roy, D.P.; Hall, D.K.; Salomonson, V.V.; Privette, J.L.; Riggs, G.; Strahler, A.; et al. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS): Land remote sensing for global change research. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1228–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallimer, M.; Tang, Z.; Bibby, P.R.; Brindley, P.; Gaston, K.J.; Davies, Z.G. Temporal changes in greenspace in a highly urbanized region. Biol. Lett. 2011, 7, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Liang, L.D.; Schwartz, M.; Donnelly, A.; Wang, Z.S.; Schaal, C.B.; Liu, L.Y. Evaluating the potential of MODIS satellite data to track temporal dynamics of autumn phenology in a temperate mixed forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.Q.; Jia, G.S.; Epstein, H. Recent changes in phenology over the northern high latitudes detected from multi-satellite data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, J.; Jeganathan, C.; Atkinson, P.M. The use of MERIS Terrestrial Chlorophyll Index to study spatio-temporal variation in vegetation phenology over India. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.Q.; Tian, H.Q.; Xu, X.F.; Pan, Y.Z.; Chen, G.S.; Lin, W.P. Extension of the growing season due to delayed autumn over mid and high latitudes in North America during 1982–2006. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, P.M.; Jeganathan, C.; Dash, J.; Atzberger, C. Inter-comparison of four models for smoothing satellite sensor time-series data to estimate vegetation phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 400–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jia, L.; Menenti, M. Reconstruction of global MODIS NDVI time series: Performance of Harmonic Analysis of Time Series (HANTS). Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 163, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, P.; Eklundh, L. TIMESAT 3.0 Software Manual; Department of Earth and Ecosystem Sciences, Lund University: Lund, Sweden; Center for Technology Studies, Malmö University: Malmö, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Neeti, N.; Eastman, J.R. A contextual Mann-Kendall approach for the assessment of trend significance in image time series. Trans. GIS 2011, 15, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocic, M.; Trajkovic, S. Analysis of changes in meteorological variables using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s slope estimator statistical tests in Serbia. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 100, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.H.; Cai, W.T.; Qin, Y.; Lai, L.M.; Guan, T.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Jiang, L.H.; Du, H.; Yang, D.W.; Cong, Z.T.; et al. Alpine vegetation phenology dynamic over 16 years and its covariation with climate in a semi-arid region of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, S.L.; Fang, J.Y.; Zhou, L.M.; Ciais, P.; Zhu, B. Variation in satellite-derive phenology in China’s temperate vegetation. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 672–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.N.; Zhuang, Q.L.; He, J.S.; Luo, T.X.; Shi, Y. Phenology shift from 1989 to 2008 on the Tibetan Plateau: An analysis with a process-based soil physical model and remote sensing data. Clim. Chang. 2013, 119, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.J.; Ho, C.H.; Gim, H.J.; Brown, M.E. Phenology shifts at start vs. end of growing season in temperate vegetation over the Northern Hemisphere for the period 1982–2008. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 2385–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.T.; Guan, H.D.; Shen, M.G.; Liang, W.; Jiang, L. Changes in autumn vegetation dormancy onset date and the climate controls across temperate ecosystems in China from 1982 to 2010. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.L.; Wang, C.Z.; Guo, H.D.; Li, Q.T. Detecting winter wheat phenology with SPOT-VEGETATION data in the North China Plain. Geocarto Int. 2014, 29, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.B.; Yang, P.; Tang, H.J.; Zhou, Q.B.; Chen, Z.X.; Shibasaki, R. Characterizing spatial patterns of phenology in cropland of China based on remotely sensed data. Agric. Sci. China 2010, 9, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.P.; Qi, Y.Q.; Shen, Y.J.; Tao, F.L.; Moiwo, J.P.; Liu, J.F.; Wang, R.W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F.S. Impact of warming climate and cultivar change on maize phenology in the last three decades in North China Plain. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 124, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Schwartz, M.D.; Fei, S.L. Validating satellite phenology through intensive ground observation and landscape scaling in a mixed seasonal forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.J.; Li, L.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Sun, X.M.; Liu, L.S.; Gao, J.G.; Wang, Z.F.; Li, Y.N. Start of vegetation growing season on the Tibetan Plateau inferred from multiple methods based on GIMMS and SPOT NDVI data. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Piao, S.L.; Xu, X.T.; Ciais, P.; MacBean, N.; Myneni, R.B.; Li, L. Has the advancing onset of spring vegetation green-up slowed down or changed abruptly over the last three decades? Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guemas, V.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J.; Andreu-Buriollo, I.; Asif, M. Retrospective prediction of the global warming slowdown in the past decade. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Hu, B.; Yu, R. Spatial and temporal variation of phenological growing season and climate change impacts in temperate eastern China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badeck, F.W.; Bondeau, A.; Böttcher, K.; Doktor, D.; Lucht, W.; Schaber, J.; Sitch, S. Responses of spring phenology to climate change. New Phytol. 2004, 162, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, C.; Basler, D. Phenology under global warming. Science 2010, 327, 1461–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J.; Yi, Y.H.; Kimball, J.S.; Kim, Y.W.; Song, K.C. Climatic controls on spring onset of the Tibetan Plateau grasslands from 1982 to 2008. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16607–16622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.G.; Zhang, G.X.; Cong, N.; Wang, S.P.; Kong, W.D.; Piao, S.L. Increasing altitudinal gradient of spring vegetation phenology during the last decade on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.G. Spring phenology was not consistently related to winter warming on the Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E91–E92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.H.; Zhou, Z.Y. Increasing contamination might have delayed spring phenology on the Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Tan, B.; Yu, Y.Y. Interannual variations and trends in global land surface phenology derived from enhanced vegetation index during 1982–2010. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2014, 58, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Tarpley, D.; Sullivan, J.T. Diverse responses of vegetation phenology to a warming climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedeling, E.; Guo, L.; Dai, J.; Leslie, C.; Blanke, M.M. Differential responses of trees to temperature variation during the chilling and forcing phases. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 181, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Dai, J.H.; Wang, M.C.; Xu, J.C.; Luedeling, E. Responses of spring phenology in temperate zone trees to climate warming: A case study of apricot flowering in China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 201, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Area | Phenology Metrics | Z Test Statistic | p Value | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | SOS | −0.7664 | 0.2217 | −0.0892 |
| EOS | 2.6278 | 0.0043 | 0.2878 | |
| LOS | 2.5183 | 0.0059 | 0.3604 | |
| Northern China | SOS | −2.4088 | 0.0080 | −0.3434 |
| EOS | 1.8613 | 0.0314 | 0.1986 | |
| LOS | 2.1898 | 0.0143 | 0.4595 | |
| Tibetan Plateau | SOS | 1.5329 | 0.0627 | 0.3354 |
| EOS | 0.7664 | 0.2217 | 0.2023 | |
| LOS | −0.9854 | 0.1622 | −0.1950 | |
| Southern China | SOS | 1.6423 | 0.0503 | 0.2475 |
| EOS | 3.0657 | 0.0011 | 0.7852 | |
| LOS | 2.7372 | 0.0031 | 0.6630 |
| DBF | DNF | EBF | ENF | Farmland | Shrub | Grassland | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOS | Z | −2.1898 | −1.4234 | 1.9708 | 2.5183 | −1.4234 | 0.8759 | 0.0000 |
| p value | 0.0143 | 0.0773 | 0.0244 | 0.0059 | 0.0773 | 0.1905 | 0.5000 | |
| slope | −0.2954 | −0.4313 | 0.2662 | 0.2662 | −0.1587 | 0.1217 | 0.0159 | |
| EOS | Z | 1.6423 | −0.7664 | 2.6278 | 3.3942 | 2.9562 | 2.6278 | 1.0949 |
| p value | 0.0503 | 0.2217 | 0.0043 | 0.0003 | 0.0016 | 0.0043 | 0.1368 | |
| slope | 0.3115 | −0.1836 | 0.7194 | 0.7017 | 0.4776 | 0.7003 | 0.1839 | |
| LOS | Z | 2.6278 | 0.5474 | 2.6278 | 2.9562 | 3.1752 | 2.9562 | 0.5474 |
| p value | 0.0043 | 0.2921 | 0.0043 | 0.0016 | 0.0007 | 0.0016 | 0.2921 | |
| slope | 0.5721 | 0.1953 | 0.5887 | 0.5817 | 0.4853 | 0.4987 | 0.1503 | |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Z.; Yu, S. Spatiotemporal Variability of Land Surface Phenology in China from 2001–2014. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9010065
Luo Z, Yu S. Spatiotemporal Variability of Land Surface Phenology in China from 2001–2014. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(1):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9010065
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Zhaohui, and Shixiao Yu. 2017. "Spatiotemporal Variability of Land Surface Phenology in China from 2001–2014" Remote Sensing 9, no. 1: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9010065
APA StyleLuo, Z., & Yu, S. (2017). Spatiotemporal Variability of Land Surface Phenology in China from 2001–2014. Remote Sensing, 9(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9010065