Assessment of the Hydro-Ecological Impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on China’s Largest Freshwater Lake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Used
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition and Pre-Processing
3. Methods
4. Results
4.1. Representative Pre- and Post-TGD Year
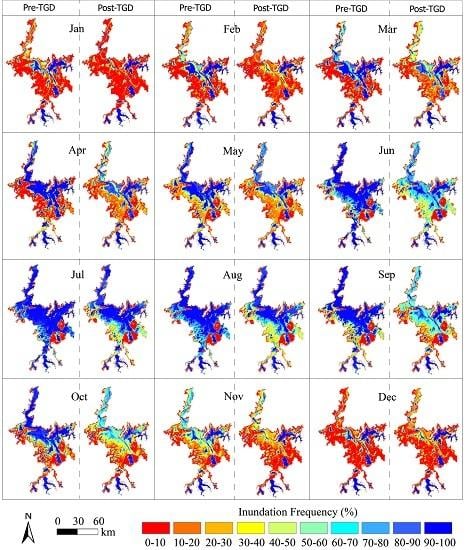
4.2. TGD-Triggered Inundation Pattern Variation
4.3. Assessment of TGD Effects on Land-Cover Change and Vegetation Distribution
4.4. Landscape Changes from the Pre- to Post-TGD Period
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arias, M.E.; Cochrane, T.A.; Kummu, M.; Lauri, H.; Holtgrieve, G.W.; Koponen, J.; Piman, T. Impacts of hydropower and climate change on drivers of ecological productivity of Southeast Asia’s most important wetland. Ecol. Model. 2014, 272, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Faber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Raskin, R.G. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.; Revenga, C.; Echeverria, J. Managing water for people and nature. Science 2001, 292, 1071–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millennium, E.A. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Wetlands and Water Synthesis; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, C.; Reidy, C.A.; Dynesius, M.; Revenga, C. Fragmentation and flow regulation of the world’s large river systems. Science 2005, 308, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poff, N.L.; Olden, J.D.; Merritt, D.M.; Pepin, D.M. Homogenization of regional river dynamics by dams and global biodiversity implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5732–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, G.; Politti, E.; Woo, H.; Cho, K.H.; Park, M.; Cho, H.; Lee, H. Dynamic vegetation model as a tool for ecological impact assessments of dam operation. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2012, 6, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorosmarty, C.J.; Sharma, K.P.; Fekete, B.M.; Copeland, A.H.; Holden, J.H.; Marble, J.; Lough, J.A. The storage and ageing of continental runoff in large reservoir systems of the world. Ambio 1997, 26, 210–219. [Google Scholar]
- Tiemann, J.S.; Gillette, D.P.; Wildhaber, M.L.; Edds, D.R. Effects of low head dams on riffle-dwelling fishes and macroinvertebrates in a midwestern river. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2004, 133, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltby, E.; Acreman, M.C. Ecosystem services of wetlands: Pathfinder for a new paradigm. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 1341–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junk, W.J.; An, S.; Finlayson, C.; Finlayson, C.M.; Gopal, B.; Květ, J.; Mitchell, S.A.; Robarts, R.D. Current state of knowledge regarding the world’s wetlands and their future under global climate change: A synthesis. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 75, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.J.; Jiang, J.H.; Huang, Q. Effects of the normal operation of the Three Gorges Reservoir on wetland inundation in Dongting Lake, China: A modelling study. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthington, A.H.; Bunn, S.E.; Poff, N.L.; Naiman, R.J. The challenge of providing environmental flow rules to sustain river ecosystems. Ecol. Appl. 2006, 16, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiman, R.J.; Latterell, J.J.; Pettit, N.E.; Olden, J.D. Flow variability and the biophysical vitality of river systems. C. R. Geosci. 2008, 340, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanch, S.J.; Walker, K.F.; Ganf, G.G. Water regimes and littoral plants in four weir pools of the River Murray, Australia. Regul. Rivers Res. Manag. 2000, 16, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiman, R.J.; Decamps, H.; McClain, M.E. Riparia: Ecology, Conservation and Management of Streamside Communities; Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Poff, N.L.; Har, D.D. How Dams Vary and Why It Matters for the Emerging Science of Dam Removal an ecological classification of dams is needed to characterize how the tremendous variation in the size, operational mode, age, and number of dams in a river basin influences the potential for restoring regulated rivers via dam removal. BioScience 2002, 52, 659–668. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, W.; Hao, F.H.; Zhao, C.; Lin, C. Vegetation response to 30years hydropower cascade exploitation in upper stream of Yellow River. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2010, 15, 1928–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsford, R.T. Ecological impacts of dams, water diversions and river management on floodplain wetlands in Australia. Austral Ecol. 2000, 25, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magilligan, F.J.; Nislow, K.H. Changes in hydrologic regime by dams. Geomorphology 2005, 71, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, M.; Harris, J.; McCartney, M.; Lew, Y.; Zhang, C. Report on Ramsar Visit to Poyang Lake Ramsar Site, PR China 12–17 April 2010; Report prepared on behalf of the Secretariat of the Ramsar Convention; The Ramsar Convention of Wetlands: Gland, Switzerland; Available online: http://archive.ramsar.org/pdf/Poyang_lake_report_v8.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2011).
- Dronova, I.; Gong, P.; Clinton, N.E.; Wang, L.; Fu, W.; Qi, S.; Liu, Y. Landscape analysis of wetland plant functional types: The effects of image segmentation scale, vegetation classes and classification methods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 127, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Feng, S.; Guo, H.; Chen, G.; Jiang, T. Interactions of the Yangtze river flow and hydrologic processes of the Poyang Lake, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 347, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wines, M. China Admits Problems with Three Gorges Dam; New York Times: New York, NY, USA, 2011; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, S. Effects of the three gorges dam on Yangtze river flow and river interaction with Poyang Lake, China: 2003–2008. J. Hydrol. 2012, 416, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Liu, J.T. Impacts of large dams on downstream fluvial sedimentation: An example of the Three Gorges Dam (TGD) on the Changjiang (Yangtze River). J. Hydrol. 2013, 480, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Wu, B.F.; Lü, Y.H.; Xu, Z.H.; Cao, J.H.; Niu, D.; Zhou, Y.M. Three Gorges Project: Efforts and challenges for the environment. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2010, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Dai, Z.; Gelder, P.; Gao, J. Linking Three Gorges Dam and downstream hydrological regimes along the Yangtze River, China. Earth Space Sci. 2015, 2, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Han, X.X.; Hu, C.M.; Chen, X.L. Four decades of wetland changes of the largest freshwater lake in China: Possible linkage to the Three Gorges Dam? Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Wu, G.P.; Guo, R.F.; Wan, R.R. Changing landscapes by damming: The Three Gorges Dam causes downstream lake shrinkage and severe droughts. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.G.; Werner, A.D.; Xin, P.; Jiang, T.; Barry, D.A. Has the Three-Gorges Dam made the Poyang Lake wetlands wetter and drier? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yang, D.; Yang, H. Impact of the Three Gorges Dam on flow regime in the middle and lower Yangtze River. Quat. Int. 2013, 304, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Guan, L.; Lu, C.; Lei, G.; Wen, L.; Liu, G. Optimising hydrological conditions to sustain wintering waterbird populations in Poyang Lake National Natural Reserve: Implications for dam operations. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 2366–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, F.; Xu, B.; Huang, H.; Yu, Q.; Gong, P. Modelling spatial-temporal change of Poyang Lake using multitemporal Landsat imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5767–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankman, D.; Keim, B.D.; Song, J. Flood frequency in China’s Poyang Lake region: Trends and teleconnections. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.M.; Chen, X.L.; Cai, X.B.; Tian, L.Q.; Gan, W.X. Assessment of inundation changes of Poyang Lake using MODIS observations between 2000 and 2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y. Capturing variations in inundation with satellite remote sensing in a morphologically complex, large lake. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R. The Legacy of the Three Gorges Dam. Science 2011, 333, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Tan, Y.; Yang, G. Environmental impact assessments of the Three Gorges Project in China: Issues and interventions. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 124, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Yu, G.; Liao, X. Effects of the dispatch modes of the three gorges reservoir on the water regimes in the Dongting Lake area in typical years. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, M.; Kambezidis, H.D.; Lykoudis, S. Generation of a “typical meteorological year” for Nicosia, Cyprus. Renew. Energy 1998, 3, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.A.; Beckman, W.A.; Duffie, J.A. A design procedure for solar heating systems. Sol. Energy 1976, 2, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.B.; Huang, Y. Research on change of coming sediment and coming water of middle-lower Yangtze River after TGP early operation. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2010, 6, 4–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Wang, G.; Liu, C.; Xu, Z. Modeling impacts of highly regulated inflow on thermal regime and water age in a shallow reservoir. J. Hydroinform. 2013, 4, 1312–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durães, M.F.; Mello, C.R. Groundwater recharge behavior based on surface runoff hydrographs in two basins of the Minas Gerais State. Rev. Ambient. Água 2013, 2, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Song, P.; Peng, J.; Ye, C. A physical explanation of the variation in threshold for delineating terrestrial water surface from multi-temporal images: Effects of radiometric correction. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 5862–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Singh, R.D.; Jain, M.K.; Lohani, A.K. Delineation of flood-prone areas using remote sensing techniques. Water Resour. Manag. 2005, 19, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.G. Application of AVHRR to monitoring a climatically sensitive playa. Case study: Chott el Djerid, southern Tunisia. Earth Surface Process. Landf. 1999, 24, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.P.; Liu, Y.B. Satellite-based detection of water surface variation in China’s largest freshwater lake in response to hydro-climatic drought. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 4511–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.X.; Chen, X.L.; Feng, L. Four decades of winter wetland changes in Poyang Lake based on Landsat observations between 1973 and 2013. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paola, J.D.; Schowengerdt, R.A. A detailed comparison of back propagation neural network and maximum-likelihood classifiers for urban land use classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 981–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Marks, B. Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical Maps: Computer Software; University of Massachusetts: Amherst, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson, E.J. Quantifying landscape spatial pattern: What is the state of the art? Ecosystem 1998, 1, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam Proposal for Poyang Lake Causes Wave of Controversy. Available online: http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/cndy/2011-08/04/content_13045840.htm (accessed on 8 April 2011).




| Satellite Imagery | Spatial Resolution (m) | Spectral Resolution (μm) | Band | Temporal Coverage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EOS-Terra | MOD02_HKM | 500 | Green: 0.54–0.57 | 4 | 2000–2015 |
| MOD02_QKM | 250 | NIR: 0.84–0.88 | 2 | ||
| Landsat | TM/ETM+/OLI | 30 | Green: 0.52–0.60 | 2 | 1980–2015 |
| NIR: 0.76–0.90 | 4 | ||||
| Pre-TGD | Inflow Discharge from Five Rivers (108 m3) | Difference (108 m3) | Post-TGD | Inflow Discharge from Five Rivers (108 m3) | Difference (108 m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1978 | 816.53 | −444.32 | 2004 | 732.73 | −402.75 |
| 1979 | 785.73 | −475.12 | 2005 | 1178.53 | 43.05 |
| 1980 | 1254.52 | −6.33 | 2006 | 1306.91 | 171.43 |
| 1981 | 1240.04 | −20.81 | 2007 | 814.64 | −320.84 |
| 1982 | 1250.02 | −10.83 | 2008 | 1015.69 | −119.79 |
| 1983 | 1630 | 369.15 | 2009 | 833.30 | −302.18 |
| 1984 | 1168.8 | −92.05 | 2010 | 1766.45 | 630.97 |
| 1985 | 1012.95 | −247.9 | 2011 | 730.15 | −405.33 |
| 1986 | 804.57 | −456.28 | 2012 | 1742.91 | 607.43 |
| 1987 | 995.10 | −265.75 | 2013 | 1135.37 | −0.11 |
| 1988 | 1220.22 | −40.63 | 2014 | 1248.50 | 113.02 |
| 1989 | 1260.40 | −0.45 | — | — | — |
| 1990 | 1108.63 | −152.22 | — | — | — |
| 1991 | 1012.6 | −248.25 | — | — | — |
| 1992 | 1551.34 | 290.49 | — | — | — |
| 1993 | 1341.91 | 81.06 | — | — | — |
| 1994 | 1494.41 | 233.56 | — | — | — |
| 1995 | 1646.75 | 385.9 | — | — | — |
| 1996 | 1071.94 | −188.91 | — | — | — |
| 1997 | 1532.99 | 272.14 | — | — | — |
| 1998 | 2076.13 | 815.28 | — | — | — |
| 1999 | 1464.89 | 204.04 | — | — | — |
| 2000 | 1122.62 | −138.23 | — | — | — |
| 2001 | 1210.68 | −50.17 | — | — | — |
| 2002 | 1615.39 | 354.54 | — | — | — |
| 2003 | 1087.97 | −172.88 | — | — | — |
| average | 1260.85 | 0 | average | 1135.48 | 0 |
| Date | Image Source | Overall Accuracy | Kappa |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1989/2/13 | Landst-5 TM | 86.78% | 0.863 |
| 1989/7/15 | Landst-5 TM | 88.82% | 0.887 |
| 2013/12/24 | Landst-8 OLI | 92.01% | 0.904 |
| 2013/7/1 | Landst-8 OLI | 93.34% | 0.911 |
| Metrics | Number of Patches (NP) | Mean Patch Area (AREA_MN) | Edge Density (ED) | Mean Fractal Dimension (FRAC_MN) | Contagion Index (CONTAG) | Shannon’s Diversity Index (SHDI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pre-TGD | low-water | 27,659 | 12.8319 | 47.1901 | 1.0126 | 46.5759 | 1.0705 |
| high-water | 14,942 | 27.7181 | 17.6297 | 1.0331 | 75.8117 | 0.5472 | |
| post-TGD | low-water | 32,144 | 10.968 | 50.7056 | 1.0524 | 42.1618 | 1.3043 |
| high-water | 18,741 | 22.09 | 23.869 | 1.0666 | 62.2445 | 0.875 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, G.; Liu, Y. Assessment of the Hydro-Ecological Impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on China’s Largest Freshwater Lake. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101069
Wu G, Liu Y. Assessment of the Hydro-Ecological Impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on China’s Largest Freshwater Lake. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(10):1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101069
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Guiping, and Yuanbo Liu. 2017. "Assessment of the Hydro-Ecological Impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on China’s Largest Freshwater Lake" Remote Sensing 9, no. 10: 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101069
APA StyleWu, G., & Liu, Y. (2017). Assessment of the Hydro-Ecological Impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on China’s Largest Freshwater Lake. Remote Sensing, 9(10), 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101069