Detecting Forest Disturbance in Northeast China from GLASS LAI Time Series Data Using a Dynamic Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Processing
3. Methods
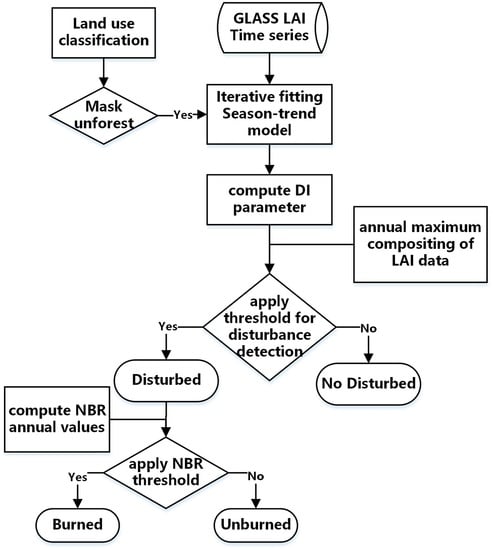
3.1. Iterative Algorithm to Detect Forest Disturbance
3.2. Distinguish the Types of Disturbances
4. Results
4.1. Comparing Results with MCD64 Products
4.2. Results of Other Disturbances
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparing Results with TM dNBR Map
5.2. Why Use GLASS LAI Data?
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonan, G.B. Forests and climate change: Forcings, feedbacks, and the climate benefits of forests. Science 2008, 320, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, R.K.; Andrasko, K.J.; Sussman, F.G.; Lavinson, M.A.; Trexler, M.C.; Vinson, T.S. Forest sector carbon offset projects: Near-term opportunities to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1993, 70, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Yang, Z.; Cohen, W.B. Detecting trends in forest disturbance and recovery using yearly landsat time series: 1. Landtrendr—Temporal segmentation algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2897–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.; Swanson, F.; Aber, J.; Burke, I.; Brokaw, N.; Tilman, D.; Knapp, A. The importance of land-use legacies to ecology and conservation. Bioscience 2003, 53, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenoff, D.J.; White, M.A.; Pastor, J.; Crow, T.R. Comparing spatial pattern in unaltered old-growth and disturbed forest landscapes. Ecol. Appl. 1993, 3, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.E.; Boyce, M.S.; Stenhouse, G.B. Grizzly bears and forestry. I. Selection of clearcuts by grizzly bears in west-central Alberta, Canada. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 199, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, J.; Franklin, S.E.; Huettmann, F.; Stenhouse, G.B. Seismic cutlines, changing landscape metrics and grizzly bear landscape use in alberta. Landsc. Ecol. 2005, 20, 811–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollins, M.G. Landfire: A nationally consistent vegetation, wildland fire, and fuel assessment. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2009, 18, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, P.; Wang, J. A sub-pixel-based calculate of fire radiative power from MODIS observations: 2. Sensitivity analysis and potential fire weather application. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 231–249. [Google Scholar]
- Wooster, M.J.; Zhang, Y.H. Boreal forest fires burn less intensely in Russia than in north America. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 183–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, C.; Tan, P.N.; Steinbach, M.; Klooster, S.; Kumar, V.; Myneni, R.; Genovese, V. Major disturbance events in terrestrial ecosystems detected using global satellite data sets. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 9, 1005–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E.; Olofsson, P. Continuous monitoring of forest disturbance using all available landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devries, B.; Verbesselt, J.; Kooistra, L.; Herold, M. Robust monitoring of small-scale forest disturbances in a tropical montane forest using landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 161, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunetta, R.S.; Knight, J.F.; Ediriwickrema, J. Land-cover characterization and change detection using multitemporal MODIS NDVI data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbesselt, J.; Hyndman, R.; Newnham, G.; Culvenor, D. Detecting trend and seasonal changes in satellite image time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbesselt, J.; Zeileis, A.; Herold, M. Near real-time disturbance detection using satellite image time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, P.; Eklundh, L. Seasonality extraction by function fitting to time-series of satellite sensor data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, P.; Eklundh, L. Timesat—A program for analyzing time-series of satellite sensor data. Comput. Geosci. 2004, 30, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.H.; Li, Z.; Cihlar, J. Hotspot and NDVI differencing synergy (hands): A new technique for burned area mapping over boreal forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 74, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, T.; Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Linke, J.; Mcdermid, G.; Masek, J.G.; Gao, F.; White, J.C. A new data fusion model for high spatial- and temporal-resolution mapping of forest disturbance based on Landsat and MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, P.M.; Grégoire, J.M.; Pereira, J.M.C. An algorithm for extracting burned areas from time series of AVHRR GAC data applied at a continental scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 69, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masek, J.G.; Cohen, W.B.; Leckie, D.; Wulder, M.A.; Vargas, R.; De Jong, B.; Healey, S.; Law, B.; Birdsey, R.; Houghton, R.A. Recent rates of forest harvest and conversion in north America. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2015, 116, 1451–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Stehman, S.V.; Potapov, P.V. Quantification of global gross forest cover loss. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8650–8655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mildrexler, D.J.; Zhao, M.; Heinsch, F.A.; Running, S.W. A new satellite-based methodology for continental-scale disturbance detection. Ecol. Appl. 2007, 17, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildrexler, D.J.; Zhao, M.S.; Running, S.W. Testing a MODIS global disturbance index across north America. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2103–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Loboda, T.; Roy, D.P.; Quayle, B.; Justice, C.O. An active-fire based burned area mapping algorithm for the MODIS sensor. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Descloitres, J.; Justice, C.O.; Kaufman, Y.J. An enhanced contextual fire detection algorithm for MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetti, L.; Roy, D.; Hoffmann, A.A. MODIS Collection 5 Burned Area Product-MCD45; Users Guide Ver 2008; University of Maryland: College Park, MD, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- George, C.; Rowland, C.; Gerard, F.; Balzter, H. Retrospective mapping of burnt areas in Central Siberia using a modification of the normalised difference water index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loboda, T.; O’Neal, K.J.; Csiszar, I. Regionally adaptable dnbr-based algorithm for burned area mapping from MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Descloitres, J.; Alleaume, S. The MODIS fire products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 244–262. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Ramo, R.; Corti, D.; Hantson, S.; Oliva, P.; Alonso-Canas, I.; Bradley, A.V.; Tansey, K.; Mota, B. Comparing the accuracies of remote sensing global burned area products using stratified random sampling and estimation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Liang, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Yin, X.; Zhang, L.; Song, J. Use of general regression neural networks for generating the glass leaf area index product from time-series MODIS surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerken, R.A. An algorithm to classify and monitor seasonal variations in vegetation phenologies and their inter-annual change. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, Y.; Sobrino, J.A. Comparison of cloud-reconstruction methods for time series of composite NDVI data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, C.H.; Benson, N.C. Landscape assessment: Ground measure of severity, the composite burn index; and remote sensing of severity, the normalized burn ratio. In FIREMON: Fire Effects Monitoring and Inventory System; Rocky Mountain Research Station, USDA Forest Service: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2006; pp. LA8–LA51. [Google Scholar]
- Cocke, A.E.; Crouse, J.E. Comparison of burn severity assessments using differenced normalized burn ratio and ground data. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2005, 14, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.K.; Lyon, L.J.; Huff, M.H.; Hooper, R.G.; Telfer, E.S.; Schreiner, D.S.; Smith, J.K. Wildland Fire in Ecosystems. Effects of Fire on Fauna; RMRS-GTR-42; USDA Forest Service: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2000.









| Data | Resolution (m) | Temporal Resolution (day) | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLASS | 1000 | 8 | 1 January 1997–31 December 2003 |
| MCD64 | 500 | Monthly | 1 January 2003–31 December 2003 |
| MOD09 | 500 | 8 | 1 January 2001–31 December 2003 |
| Classification | 30 | Year | 2003 |
| Landsat | 30 | 16 | 10 April 2003 |
| 23 April 2003 | |||
| 26 May 2003 | |||
| 13 June 2003 |
| Landsat | MODIS | Producer’s Accuracy | GLASS TSM | Producer’s Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burned | Unburned | Burned | Unburned | |||
| Jinhe (k = 0.758) | k = 0.776 | |||||
| Burned | 473 | 107 | 81.5% | 521 | 59 | 89.8% |
| Unburned | 150 | 3955 | 96.3% | 103 | 4002 | 97.5% |
| User’s accuracy | 75.9% | 97.4% | 83.5% | 98.5% | ||
| Shibazhan (k = 0.634) | k = 0.838 | |||||
| Burned | 1407 | 265 | 94.7% | 1579 | 93 | 94.4% |
| Unburned | 1115 | 17377 | 97.3% | 321 | 18171 | 98.3% |
| User’s accuracy | 80.8% | 99.3% | 83.1% | 99.5% | ||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, Z. Detecting Forest Disturbance in Northeast China from GLASS LAI Time Series Data Using a Dynamic Model. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121293
Wang J, Wang J, Zhou H, Xiao Z. Detecting Forest Disturbance in Northeast China from GLASS LAI Time Series Data Using a Dynamic Model. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(12):1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121293
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jian, Jindi Wang, Hongmin Zhou, and Zhiqiang Xiao. 2017. "Detecting Forest Disturbance in Northeast China from GLASS LAI Time Series Data Using a Dynamic Model" Remote Sensing 9, no. 12: 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121293
APA StyleWang, J., Wang, J., Zhou, H., & Xiao, Z. (2017). Detecting Forest Disturbance in Northeast China from GLASS LAI Time Series Data Using a Dynamic Model. Remote Sensing, 9(12), 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121293