Physically Based Susceptibility Assessment of Rainfall-Induced Shallow Landslides Using a Fuzzy Point Estimate Method
Abstract
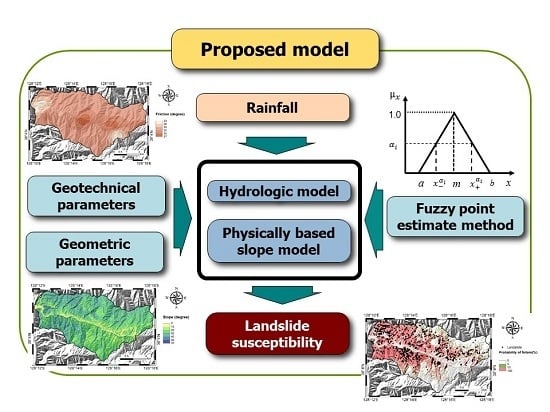
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Framework for Fuzzy-Set-Based Analysis
2.1.1. Uncertainty Modeling with Fuzzy Numbers
2.1.2. Fuzzy Point Estimate Method
2.2. Physically Based Slope Model
2.3. Study Area and Database Construction
2.3.1. The Analysis Procedure
2.3.2. Evaluation of Model Performance
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonzalez de Vallejo, L.I.; Ferrer, M. Geological Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cascini, L.; Cuomo, S.; Pastor, M.; Sorbino, G. Modeling of rainfall-induced shallow landslides of the flow-type. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2009, 136, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.C.; Lee, C.F.; Wang, S.J. Characterization of rainfall-induced landslides. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4817–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.A.; Sitar, N. Hydrologic conditions leading to debris-flow initiation. Can. Geotech. J. 1990, 27, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.; Bathurst, J.C. Physically based modelling of shallow landslide sediment yield at a catchment scale. Environ. Geol. 1998, 35, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, B.G.; Lee, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Choi, J. A method for predicting the factor of safety of an infinite slope based on the depth ratio of the wetting front induced by rainfall infiltration. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 1835–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, G.B.; Frattini, P. Distributed modelling of shallow landslides triggered by intense rainfall. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2003, 3, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruden, D.M.; Varnes, D.J. Landslides Types and Processes. In Landslides: Investigation and Mitigation; Turner, A.K., Schuster, R.L., Eds.; National Academy Press: Washington, WA, USA, 1996; pp. 36–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.; Godt, J.W. Hillslope Hydrology and Stability; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sidle, R.C.; Ochiai, H. Landslides: Processes, Prediction, and Land Use; American Geophysical Union: Washington, WA, USA, 2006; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Tofani, V.; Segoni, S.; Agostini, A.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Technical Note: Use of remote sensing for landslide studies in Europe. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghuis, A.M.; Chang, K.; Lee, H.Y. Comparison between automated and manual mapping of typhoon-triggered landslides from SPOT-5 imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1843–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debella-Gilo, M.; Kaab, A. Sub-pixel precision image matching for measuring surface displacements on mass movements using normalized cross-correlation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leprince, S.; Ayoub, F.; Klinger, Y.; Avouac, J.P. Co-registration of optically sensed images and correlation (COSI-Corr): An operational methodology for ground deformation measurements. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 1943–1946. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, P.; Stumpf, A.; Kerle, N.; Casagli, N. Object-oriented change detection for landslide rapid mapping. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelino, E.V.; Formaggio, A.R.; Maeda, E.E. Landslide inventory using image fusion techniques in Brazil. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2009, 11, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeters, R.; van Westen, C.J. Slope instability recognition, analysis, and zonation. In Landslides: Investigation and Mitigation; Turner, A.K., Schuster, R.L., Eds.; National Academy Press: Washington, WA, USA, 1996; pp. 129–177. [Google Scholar]
- Stumpf, A.; Kerle, N. Object-oriented mapping of landslides using Random Forests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2564–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.; Hwang, J.H.; Chen, L.C.; Lin, T.H. Post-disaster assessment of landslides in southern Taiwan after 2009 Typhoon Morakot using remote sensing and spatial analysis. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weirich, F.; Blesius, L. Comparison of satellite and air photo based landslide susceptibility maps. Geomorphology 2007, 87, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, K.E.; Belliss, S.E.; Samsonov, S.V.; McNeill, S.J.; Glassey, P.J. A review of the status of satellite remote sensing and image processing techniques for mapping natural hazards and disasters. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, N.S.; Seijmonsbergen, A.C.; Bouten, W. Multi-scale and object-oriented image analysis of high-res LiDAR data for geomorphological mapping in Alpine mountains. Proceedings of Geomorphometry 2009, Zurich, Switzerland, 31 August–2 September 2009; pp. 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Barlow, J.; Franklin, S.; Martin, Y. High spatial resolution satellite imagery, DEM derivatives, and image segmentation for the detection of mass wasting processes. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, N.; Fanti, R.; Nocentini, M.; Righini, G. Assessing the capabilities of VHR satellite data for debris flow mapping in the Machu Picchu area. In Landslides, Risk Analysis and Sustainable Disaster Management; Sassa, K., Fukuoka, H., Wang, F., Wang, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Catani, F.; Casagli, N.; Ermini, L.; Righini, G.; Menduni, G. Landslide hazard and risk mapping at catchment scale in the Arno River basin. Landslides 2005, 2, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.S.; Wei, C.; Chang, S.C. Locating landslides using multi-temporal satellite images. Adv. Space Res. 2004, 33, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebby, S.; Naden, J.; Cunningham, D.; Tansey, K. Integrating airborne multispectral imagery and airborne LiDAR data for enhanced lithological mapping in vegetated terrain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Kanungo, D.P. An integrated approach for landslide susceptibility mapping using remote sensing and GIS. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2004, 70, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzone, F.; Cardinali, M.; Galli, M.; Guzzetti, F.; Reichenbach, P. Identification and mapping of recent rainfall-induced landslides using elevation data collected by airborne Lidar. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 7, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini, A.; Cervi, F.; Daehne, A.; Ronchetti, F.; Borgatti, L. Coupling geomorphic field observation and LIDAR derivatives to map complex landslides. In Landslides Processes-from Geomorphologic Mapping to Dynamic Modelling, Proceedings of the Landslide Processes Conference, Strasbourg, France, 6–7 February 2009; Malet, J.P., Remaître, A., Bogaard, T., Eds.; CERG Editions: Strasbourg, France, 2009; pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Dunning, S.A.; Massey, C.I.; Rosser, N.J. Structural and geomorphological features of landslides in the Bhutan Himalaya derived from terrestrial laser scanning. Geomorphology 2009, 103, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaboyedoff, M.; Pedrazzini, A.; Horton, P.; Loye, A.; Surace, I. Preliminary slope mass movements susceptibility mapping using LIDAR DEM. In Proceedings of the 61th Canadian Geotechnical Conference, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 21–24 September 2008; pp. 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Jaboyedoff, M.; Oppikofer, T.; Minoia, R.; Locat, J.; Turmel, D. Terrestrial LIDAR investigation of the 2004 rockslide along Petit Champlain street, Quebec City (Quebec, Canada). In Proceedings of the 4th Canadian Conference on Geohazards: From Causes to Management, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2008; Locat, J., Perret, D., Turmel, D., Demers, D., Leroueil, S., Eds.; Canadian Geotechnical Society, Engineering Geology Division: Richmond, BC, Canada, 20–24 May 2008; pp. 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Longoni, L.; Papini, M.; Brambilla, D.; Barazzetti, L.; Roncoroni, F.; Scaioni, M.; Ivanov, V.I. Monitoring riverbank erosion in mountain catchments using terrestrial laser scanning. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlands, K.A.; Jones, L.D.; Whitworth, M. Landslide laser scanning: A new look at an old problem. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2003, 36, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhroy, V.; Molch, K. Characterizing and monitoring rockslides from SAR techniques. Adv. Space Res. 2004, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuti, P.; Casagli, N.; Catani, F.; Falorni, G.; Farina, P. Integration of remote sensing techniques in different stages of landslide response. In Progress in Landslide Science; Sassa, K., Fukuoka, H., Wang, F., Wang, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 251–259. [Google Scholar]
- Cascini, L.; Fornaro, G.; Peduto, D. Analysis at medium scale of low-resolution DInSAR data in slow-moving landslide-affected areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colesanti, C.; Wasowski, J. Investigating landslides with space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) interferometry. Eng. Geol. 2006, 88, 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilley, G.E.; Burgmann, R.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Rocca, F. Dynamics of slow-moving landslides from permanent scatterer analysis. Science 2004, 304, 1952–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Casagli, N.; Catani, F.; Tofani, V. Persistent Scatterers Interferometry Hotspot and Cluster Analysis (PSI-HCA) for detection of extremely slow-moving landslides. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 466–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righini, G.; Pancioli, V.; Casagli, N. Updating landslide inventory maps using Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 2068–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casson, B.; Delacourt, C.; Allemand, P. Contribution of multi-temporal remote sensing images to characterize landslide slip surface? Application to the La Clapiere landslide (France). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 5, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacourt, C.; Allemand, P.; Casson, B.; Vadon, H. Velocity field of the “La Clapiere” landslide measured by the correlation of aerial and QuickBird satellite images. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L15619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacourt, C.; Allemand, P.; Berthier, E.; Raucoules, D.; Casson, B.; Grandjean, P.; Pambrun, C.; Varel, E. Remote-sensing techniques for analysing landslide kinematics: A review. Bull. Soc. Geol. Fr. 2007, 178, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervas, J.; Barredo, J.I.; Rosin, P.L.; Pasuto, A.; Mantovani, F.; Silvano, S. Monitoring landslides from optical remotely sensed imagery: The case history of Tessina landslide, Italy. Geomorphology 2003, 54, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kääb, A. Photogrammetry for early recognition of high mountain hazards: New techniques and applications. Phys. Chem. Earth B Hydrol. Oceans Atmos. 2000, 25, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.; Hurni, L.; Gogu, R. Remote sensing of landslides: An analysis of the potential contribution to geo-spatial systems for hazard assessment in mountainous environments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 284–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Costantini, M.; Franceschetti, G.; Iodice, A.; Pietranera, L.; Rizzo, V. Use of differential SAR interferometry in monitoring and modelling large slope instability at Maratea (Basilicata, Italy). Eng. Geol. 2003, 68, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, G.; Pauciullo, A.; Serafino, F. Deformation monitoring over large areas with multipass differential SAR interferometry: A new approach based on the use of spatial differences. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 1455–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisina, C.; Zucca, F.; Conconi, F.; Verri, F.; Fossati, D.; Ceriani, M.; Allievi, J. Use of Permanent Scatterers technique for large-scale mass movement investigation. Quat. Int. 2007, 171, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, C.; Ferretti, A.; Perissin, D. Recent advances on surface ground deformation measurement by means of repeated space-borne SAR observations. J. Geodyn. 2010, 49, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, H. Requirements and applications of satellite techniques for monitoring slope instability in Alpine areas. In Workshop on Risk Mitigation of Slope Instability; JRC-Institute for the Protection and Security of the Citizen: Ispra, Italy, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Strozzi, T.; Farina, P.; Corsini, A.; Ambrosi, C.; Thüring, M.; Zilger, J.; Wiesmann, A.; Wegmuller, U.; Werner, C. Survey and monitoring of landslide displacements by means of L-band satellite SAR interferometry. Landslides 2005, 2, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strozzi, T.; Delaloye, R.; Kaab, A.; Ambrosi, C.; Perruchoud, E.; Wegmüller, U. Combined Observations of Rock Mass Movements Using Satellite SAR Interferometry, Differential GPS, Airborne Digital Photogrammetry, and Airborne Photography Interpretation. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, F1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.F.; Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Curtis, S.; Nelkin, E.J. Tropical rainfall distributions determined using TRMM combined with other satellite and rain gauge information. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 2007–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, R.L.; Godt, J.W. Early warning of rainfall-induced shallow landslides and debris flows in the USA. Landslides 2010, 7, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Adler, R.; Huffman, G. Evaluation of the potential of NASA multi-satellite precipitation analysis in global landslide hazard assessment. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L22402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Catani, F.; Leoni, L.; Segoni, S.; Tofani, V. HIRESSS: A physically based slope stability simulator for HPC applications. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segoni, S.; Leoni, L.; Benedetti, A.I.; Catani, F.; Righini, G.; Falorni, G.; Gabellani, S.; Rudari, R.; Silvestro, F.; Rebora, N. Towards a definition of a real-time forecasting network for rainfall induced shallow landslides. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 2119–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Westen, C.J.; Seijmonsbergen, A.C.; Mantovani, F. Comparing landslide hazard maps. Nat. Hazards 1999, 20, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Esaki, T.; Zhou, G. GIS based probabilistic mapping of landslide hazard using a three dimensional deterministic model. Nat. Hazards 2004, 33, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloetti, P.; Chowdhury, R. Landslide hazard assessment: Summary review and new perspectives. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 1999, 58, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Westen, C.J. The modeling of landslide hazard using GIS. Surv. Geophys. 2000, 21, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frattini, P.; Crosta, G.B.; Fusi, N.; Negro, P.D. Shallow landslides in pyroclastic soils: A distributed modeling approach for hazard assessment. Eng. Geol. 2004, 73, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godt, J.W.; Baum, R.L.; Savage, W.Z.; Salciarini, D.; Schulz, W.H.; Harp, E.L. Transient deterministic shallow landslide modeling: Requirements for susceptibility and hazard assessments in a GIS framework. Eng. Geol. 2008, 102, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokceoglu, C.; Sonmez, H.; Ercanoglu, M. Discontinuity controlled probabilistic slope failure risk maps of the Altindag (settlement) region in Turkey. Eng. Geol. 2000, 55, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsevski, P.V. Landslide Hazard Modeling Using GIS. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Idaho, Moscow, ID, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Guimaraes, R.F.; Montgomery, D.R.; Greenberg, H.M.; Fernandes, N.F.; Gomes, R.A.T.; Carvalho, O.A., Jr. Parameterization of soil properties for a model of topographic controls on shallow landsliding: Application to Rio de Janeiro. Eng. Geol. 2003, 69, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.Y.; Lee, K.T.; Chang, T.C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Liao, Y.H. Influence of spatial distribution of soil thickness on shallow landslide prediction. Eng. Geol. 2012, 124, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Chi, Y.Y. Rainfall induced landslide risk at Lushan, Taiwan. Eng. Geol. 2011, 123, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Wu, C. Mapping susceptibility of rainfall-triggered shallow landslides using a probabilistic approach. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzi, I.; Pergalani, F. Application of statistical and GIS techniques to slope instability zonation. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 1996, 15, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.R.; Dietrich, W.E. A physically based model for the topographic control on shallow landsliding. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 1153–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Sidle, R.C. A distributed slope stability model for steep forested basins. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 2097–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Esaki, T.; Mitani, Y.; Xie, M.; Mori, J. Spatial probabilistic modeling of slope failure using an integrated GIS Monte Carlo simulation approach. Eng. Geol. 2003, 68, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corominas, J.; van Westen, C.; Frattini, P.; Cascini, L.; Malet, J.P.; Fotopoulou, S.; Catani, F.; Van Den Eeckhaut, M.; Mavrouli, O.; Agliardi, F.; et al. Recommendations for the quantitative analysis of landslide risk. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2014, 73, 209–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.; Arkell, T.J.; Bathurst, J.C. Field variability of landslide model parameters. Environ. Geol. 1998, 35, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostyn, G.R.; Li, K.S. Probabilistic slope analysis—State of play. In Proceeding of the Conference on Probabilistic Method in Geotechnical Engineering, Canberra, Australia, 10–12 February 1993; AA Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 89–109. [Google Scholar]
- Mostyn, G.R.; Small, J.C. Methods of stability analysis. In Soil Slope Instability and Stabilization; Walker, B.F., Fell, R., Eds.; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 71–120. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen, B. New trend in rock slope stability analysis. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2000, 58, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; West, T.R. Development of a probabilistic approach for rock wedge failure. Eng. Geol. 2001, 59, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Woo, I. Assessment of rainfall-induced shallow landslide susceptibility using a GIS-based probabilistic approach. Eng. Geol. 2013, 161, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Um, J.G. Assessment of rock slope stability using GIS-based probabilistic kinematic analysis. Eng. Geol. 2016, 203, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, S.; Nilsen, B. Probabilistic rock slope stability analysis for Himalayan condition. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2004, 63, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raia, S.; Alvioli, M.; Rossi, M.; Baum, R.M.; Godt, J.W.; Guzzetti, F. Improving predictive power of physically based rainfall-induced shallow landslide models: A probabilistic approach. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 495–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, K.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Liu, H. Hazard analysis of Li-Shan landslide in Taiwan. Geomorphology 2009, 103, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, A.; Mahadevan, S. Probability, Reliability and Statistical Methods in Engineering Design; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Giasi, C.I.; Masi, P.; Cherubini, C. Probabilistic and fuzzy reliability analysis of a sample slope near Aliano. Eng. Geol. 2003, 67, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, C.H.; Jhi, Y.Y.; Lee, D.H. Stability analysis of existing slopes considering uncertainty. Eng. Geol. 1998, 49, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, H.J. Fuzzy Set Theory and Its Applications; Kluwer Academic: Boston, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dodagoudar, G.R.; Venkatachalam, G. Reliability analysis of slope using fuzzy sets theory. Comput. Geotech. 2000, 27, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, M.; Zhang, Y.; Quek, S.T.; Phoon, K.K. Reliability analysis with scare information: Comparing alternative approaches in a geotechnical engineering context. Struct. Saf. 2013, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Juang, C.H. Evaluation of failure potential in mudstone slopes using fuzzy sets. In Stability and Performance of Slopes and Embankments II; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 1992; pp. 1137–1151. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, T.J.; Keller, C.P. Modeling uncertainty in natural resource analysis using fuzzy sets and Monte Carlo simulation: Slope stability prediction. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 1997, 11, 409–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Mei, S.H. Fuzzy system method for the design of a jointed rock slope. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2004, 41, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Um, J.G.; Woo, I.; Kim, J.W. Application of fuzzy set theory to evaluate the probability of failure in rock slopes. Eng. Geol. 2012, 125, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Tien, Y.M.; Chen, J.M.; Juang, C.H. Robust design of rock slopes with multiple failure modes: Modeling uncertainty of estimated parameters statistics with fuzzy number. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 2957–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Wang, L.; Khoshnevisan, S.; Juang, C.H.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J. Robust geotechnical Design of earth slope using Fuzzy sets. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2015, 141, 0401484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.P.; Hudson, J.A. Incorporating parameter variability in rock mechanics analysis: Fuzzy mathematics applied to underground rock spalling. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2010, 43, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, C.H.; Lee, D.H. Mapping slope failure potential using fuzzy sets. J. Geotech. Eng. 1992, 118, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, C.H.; Elton, D.J. A practical approach to uncertainty modelling in geotechnical engineering. In Uncertainty in the Geologic Environment: From Theory to Practice; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 1996; pp. 1269–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Atamturktur, S.; Juang, C.H.; Huang, H.; Lin, P.S. Probability of serviceability failure in a braced excavation in a spatially random field: Fuzzy finite element approach. Comput. Geotech. 2011, 38, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. In Information and Control; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1965; pp. 338–353. [Google Scholar]
- Regmi, N.; Giardino, J.R.; Vitek, J.D. Assessing susceptibility to landslides: Using models to understand observed changes in slopes. Geomorphology 2010, 122, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J. Factor of safety and reliability in geotechnical engineering. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2000, 126, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baecher, G.B.; Christian, J.T. Reliability and Statistics in Geotechnical Engineering; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Harr, M.E. Reliability Based on Design in Civil Engineering; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.J.; West, T.R.; Woo, I. Probabilistic analysis of rock slope stability and random properties of discontinuity parameters, Interstate Highway 40. Eng. Geol. 2005, 79, 230–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoon, K.K.; Retief, J.V. Reliability of Geotechnical Structures in ISO2394; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.M.; Wong, F.S. Fuzzy weighted averages and implementation of the extension principle. Fuzzy Set Syst. 1987, 21, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblueth, E. Point estimates for probability moments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 3812–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvioli, M.; Guzzetti, F.; Rossi, M. Scaling properties of rainfall induced landslides predicted by a physically based model. Geomorphology 2014, 213, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, B.G.; Park, K.B.; Park, H.J.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, M.I. Analysis of slope stability considering the saturation depth ratio by rainfall infiltration in unsaturated soil. J. Eng. Geol. 2012, 22, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIDP (National Institute for Disaster Prevention). Fundamental Issues for Landslide Hazard Avoidance or Mitigation Plans; Research Report; National Institute for Disaster Prevention: Seoul, Korea, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, A.M.S.; Kim, Y.T. Application and comparison of shallow landslide susceptibility models in weathered granite soil under extreme rainfall events. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 5761–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, R.L.; Savage, W.Z.; Godt, J.W. TRIGRS—A Fortran Program for Transient Rainfall Infiltration and Grid Based Regional Slope Stability Analysis; U.S. Geological Survey Open File Report 02-424; USGS: Durango, CO, USA, 2002.
- Baum, R.L.; Savage, W.Z.; Godt, J.W. TRIGRS—A Fortran Program for Transient Rainfall Infiltration and Grid-Based Regional Slope-Stability Analysis, Version 2.0; U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2008-1159; USGS: Durango, CO, USA, 2008.
- Iverson, R.M. Landslide triggering by rain infiltration. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 1897–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salciarini, D.; Godt, J.W.; Savage, W.Z.; Conversini, P.; Baum, R.L.; Michael, J.A. Modeling regional initiation of rainfall-induced shallow landslides in the eastern Umbria Region of central Italy. Landslides 2006, 3, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yoo, N. A study on debris flow landslide disasters and restoration at Inje in Kangwon Province, Korea. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2009, 9, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- NIDP (National Institute for Disaster Prevention). A Study on the Steep Slope Information Compilation and Establishment of an Analysis System; Research Report; National Institute for Disaster Prevention: Seoul, Korea, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cardinali, M.; Reichenbach, P.; Guzzetti, F.; Ardizzone, F.; Antonini, G.; Galli, M.; Cacciano, M.; Castellani, M.; Salvati, P. A geomorphological approach to the estimation of landslide hazards and risks in Umbria, Central Italy. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 2, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D.V.; Huang, J.S.; Fenton, G.A. Probabilistic infinite slope analysis. Comput. Geotech. 2011, 38, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.C.; Kao, S.J.; Hsu, M.L.; Lin, J.C. Stochastic procedure to extract and to integrate landslide susceptibility maps: An example of mountainous watershed in Taiwan. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 6, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, K.J.; Chen, Y.L. Spatial risk analysis of Li-shan landslide in Taiwan. Eng. Geol. 2005, 80, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, A.; Heath, A.C. A GIS application for assessing landslide hazard over a large area. Comput. Geotech. 2008, 35, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, M.J.; Uzielli, M.; Lacasse, S. Probability risk assessment of landslides: A case study at Finneidfjord. Can. Geotech. J. 2008, 45, 1250–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Au, S. Efficient Monte Carlo Simulation of parameter sensitivity in probabilistic slope stability analysis. Comput. Geotech. 2010, 37, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulnier, G.M.; Beven, K.J.; Obled, C. Including spatially variable effective soil depths in TOPMODEL. J. Hydrol. 1997, 202, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Jung, S.J.; Choi, E.K.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, K.H.; Oh, J.L.; Park, D.G. Time status of slope collapse for 1999–2011, in Korea. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2013, 49, 669–681. [Google Scholar]
- Begueria, S. Validation and evaluation of predictive models in hazard assessment and risk management. Nat. Hazards 2006, 37, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swets, J. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science 1988, 240, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, F.; Lambe, T.W.; Marr, W.A. Probability and risk of slope failure. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2008, 134, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AGS. Landslide risk management concepts and guidelines. Aust. Geomech. 2000, 35, 49–92. [Google Scholar]
- Fell, R.; Corominas, J.; Bonnard, C.; Cascini, L.; Leroi, E.; Savage, W.Z. Guidelines for landslide susceptibility, hazard and risk zoning for land use planning. Eng. Geol. 2008, 102, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priest, S.D.; Brown, E.T. Probabilistic stability analysis of variable rock slopes. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. 1983, 92, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Melchiorre, C.; Frattini, P. Modeling probability of rainfall-induced shallow landslides in a changing climate, Otta, Central Norway. Clim. Chang. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchioore, C.; Carellanos Abella, E.A.; Van Westen, C.J.; Matteucci, M. Evaluation of prediction capability, robustness, and sensitivity in non-linear landslide susceptibility models, Guantanamo, Cuba. Comput. Geosci. 2011, 37, 410–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Model | True Positive Rate (TPR) | False Positive Rate (FPR) | Area Under the Curve (AUC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzzy PEM | 0.852 | 0.383 | 0.734 |
| Probabilistic analysis | 0.885 | 0.413 | 0.736 |
| Deterministic analysis with the transient model | 0.471 | 0.163 | 0.654 |
| Fuzzy PEM with reduced COV | 0.772 | 0.328 | 0.722 |
| Probabilistic analysis with reduced COV | 0.594 | 0.219 | 0.688 |
| Fuzzy PEM with | 0.708 | 0.281 | 0.714 |
| Fuzzy PEM with | 0.930 | 0.509 | 0.711 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.-J.; Jang, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-H. Physically Based Susceptibility Assessment of Rainfall-Induced Shallow Landslides Using a Fuzzy Point Estimate Method. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050487
Park H-J, Jang J-Y, Lee J-H. Physically Based Susceptibility Assessment of Rainfall-Induced Shallow Landslides Using a Fuzzy Point Estimate Method. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(5):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050487
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hyuck-Jin, Jung-Yoon Jang, and Jung-Hyun Lee. 2017. "Physically Based Susceptibility Assessment of Rainfall-Induced Shallow Landslides Using a Fuzzy Point Estimate Method" Remote Sensing 9, no. 5: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050487
APA StylePark, H. -J., Jang, J. -Y., & Lee, J. -H. (2017). Physically Based Susceptibility Assessment of Rainfall-Induced Shallow Landslides Using a Fuzzy Point Estimate Method. Remote Sensing, 9(5), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050487